Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transational Model - Burnlund's Model: Meaning
Uploaded by
Manika AggarwalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transational Model - Burnlund's Model: Meaning
Uploaded by
Manika AggarwalCopyright:
Available Formats
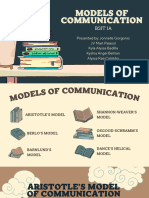
Transational model – Burnlund’s model
Meaning:
In 1970 Dean Barnlund developed a transactional communication
model, consisting of a multi layered feedback system. Feedback is
continues throughout the exchange. Feedback for the sender is the
reply from the receiver.
The Transactional Model of Communication proposed by
Barnlund states that giving and receiving messages is reciprocal..
Here, both sender and receiver are known as communicators and
their role reverses each time in the communication process as both
processes of sending and receiving occurs at the same time.
For example – talking/listening to friends. While your friend is
talking you are constantly giving them feedback on what you think
through your facial expression verbal feedback without necessarily
stopping your friend from talking.
Components of Burnlund’s model:
Cues: Cues refers to the signs for doing something. As per
Barnlund there are: public cues, private cues and behavioral cues.
Public cues (Cpu) are physical, environmental or artificial
and natural or man-made.
Private objects of orientation (Cpr) are a second set of cues.
They go beyond public inspection or awareness. Examples
include the cues gained from sunglasses, earphones, or the
sensory cues of taste and touch. Both public and private cues
may be verbal or nonverbal in nature.
Behavioral cues can be verbal (Cbehv) as well as non-verbal
(Cbehnv)
Arrows: The arrows and their directions show that the message is
intentionally sent and actively taken where the receiver plays a key
role of giving feedback. Arrows also show the process of
production of technical encoding, interpretation and decoding.
Jagged lines: It show that the availability of cues can be unlimited
and are denoted as VVVV.
valence signs (+, 0, or -): They have been attached to public,
private, and behavioral cues. They indicate the potency or degree
of attractiveness associated with the cues. Presumably, each cue
can differ in degree of strength as well as in kind.
Filters: They are the realities of people engaged in communication.
Here the senders’ and receivers’ personal filters might differ
according to cultures, traditions, content of the message, etc.
Noise: This is the problem that arises in communication flow and
disturbs the message flow.
Barnlund’s Transactional Model is a multi-layered feedback system. This is a
continuous process where sender and receiver interchanges their places and both
are equally important. The message passing takes place with a constant
feedback being provided from both parties. A feedback for one is the message
for the other
Advantages of Barnlund’s Transactional Model of
Communication
The model shows shared field experience of the sender and receiver.
Transactional model talks about simultaneous message sending, noise and
feedback.
Barnlund’s model is taken by critics as the most systematic model of
communication.
Disadvantages of Barnlund’s Transactional Model
of Communication
Barnlund’s model is very complex.
Both the sender and receiver must understand the codes sent
by the other. So they must each possess a similar “code
book”. (The concept of code book is not mentioned in the
model but understood.
Helical Model
Meaning
In 1967, Frank Dance proposed the communication model called Dance’s
Helix Model for a better communication process. The name helical
comes from “Helix” which means an object having a three-dimensional
shape like that of a wire wound uniformly around a cylinder or cone.
The helix represents the way communication evolves in an individual
from his birth to the existing moment.
Communication is affected by the curve from which it emerges which
denotes past behavior and experiences. Slowly, the helix leaves its lower
levels of behavior and grows upward in a new way. It always depends on
the lowest level to form the message. Thus, the communicative
relationship reaches to the next level in which people share more
information.
Advantages:
The model assumes sender and receiver to be interchangeable and makes
communication process to be two way.
The model takes the communication process speculative and
intellectual.
Disadvantages:
The model is taken as more simple than it should be.
Some critics don’t take it to be a model as it has very few variables.
It is not testable because it is abstract.
It is not represent in a systematic and orderly way.
Variables cannot be differentiated in this model.
Continuity may not always be true for communication. There might be
breaks in situations as well as events can be meaningless, forced or
unproductive.
The purpose of communication is not always growth.
You might also like
- Book ReportDocument5 pagesBook ReportLiberry ChrômãzNo ratings yet
- ABM - AOM11 Ia B 1Document3 pagesABM - AOM11 Ia B 1Jarven Saguin50% (6)
- Nature and Elements of Communication ExplainedDocument13 pagesNature and Elements of Communication ExplainedPhilip Jayson L. Lestojas100% (12)
- Images of Tibet in The 19th and 20th Centuries ExcerptsDocument564 pagesImages of Tibet in The 19th and 20th Centuries ExcerptsBLhundrup100% (15)
- Barlunds Transactional ModelDocument6 pagesBarlunds Transactional ModelephraimNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument5 pagesModels of CommunicationJoel PagkalinawaNo ratings yet
- Bank and NBFCDocument21 pagesBank and NBFCManika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Nidhi CompaniesDocument14 pagesNidhi CompaniesManika Aggarwal50% (2)
- Lesson Plan of Producers Consumers DecomposersDocument7 pagesLesson Plan of Producers Consumers Decomposersapi-315857509No ratings yet
- Differences Between High-Touch and High-Tech Product Positioning StrategiesDocument15 pagesDifferences Between High-Touch and High-Tech Product Positioning StrategiesKevin Us-LazPreces Timetoshine100% (4)
- The Rape of The Nile Tomb Robbers, Tourists, and Archaeologists in Egypt. Brian M. FaganDocument2 pagesThe Rape of The Nile Tomb Robbers, Tourists, and Archaeologists in Egypt. Brian M. Fagansychev_dmitryNo ratings yet
- ESSENTIAL ATTRIBUTES OF GOOD RESEARCHDocument1 pageESSENTIAL ATTRIBUTES OF GOOD RESEARCHRijurahul Agarwal Singh67% (6)
- Barnlund's Transactional Model of Communication ExplainedDocument3 pagesBarnlund's Transactional Model of Communication ExplainedMiss ANo ratings yet
- Dean BarnlundDocument2 pagesDean BarnlundJulie Dampo Dicdican100% (2)
- CGMartin OCModule2Document9 pagesCGMartin OCModule2Cloie Irish MartinNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication ResearchhhhhhhDocument8 pagesOral Communication ResearchhhhhhhRonie PadlanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 3Document6 pagesModule 1 Lesson 3Mikayah g.No ratings yet
- Nature and Elements of CommunicationDocument56 pagesNature and Elements of CommunicationJohn Zandro TanquinticNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelsDocument3 pagesCommunication ModelsMary Yvonne AresNo ratings yet
- Models-Of-communicationDocument13 pagesModels-Of-communicationleonwaypNo ratings yet
- Oralcom Module 2 Week 2 Models of CommunicationDocument9 pagesOralcom Module 2 Week 2 Models of CommunicationCesarNo ratings yet
- Nature and Elements of CommunicationDocument28 pagesNature and Elements of CommunicationJerwin LualhatiNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Task 1 DIOQUINODocument5 pagesAsynchronous Task 1 DIOQUINORm DioquinoNo ratings yet
- Points to Remember in Oral CommunicationDocument5 pagesPoints to Remember in Oral CommunicationMarco Antonio MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- -NOES2Document5 pages-NOES2HighsNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Mod2 Week 2Document5 pagesOral Communication Mod2 Week 2Josie EscalaNo ratings yet
- Communication TheoryDocument5 pagesCommunication TheoryJulie Ann GernaNo ratings yet
- The Communication Model ShaiDocument9 pagesThe Communication Model ShaiShainna PanopioNo ratings yet
- Nature and Elements of CommunicationDocument56 pagesNature and Elements of CommunicationJohn Zandro TanquinticNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument20 pagesModels of CommunicationNiro MadlusNo ratings yet
- Understanding Human Communication 1Document16 pagesUnderstanding Human Communication 1ilantamizh RNo ratings yet
- 1Document4 pages1Samantha ClaireNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument38 pagesModels of CommunicationSia JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Model of Communications: Linear ModelsDocument13 pagesLesson 3: Model of Communications: Linear ModelsScarlett YuNo ratings yet
- Essential Nature of Communication in Engineering ProjectsDocument5 pagesEssential Nature of Communication in Engineering ProjectsCarlo Jhan LolongNo ratings yet
- Interactive English Exam ReviewDocument14 pagesInteractive English Exam Reviewgeorgia mae lacsonNo ratings yet
- Modelsofcommunicationhandout 160711061345 PDFDocument39 pagesModelsofcommunicationhandout 160711061345 PDFRicaNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument21 pagesOral Communicationrowena.enorpeNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument39 pagesModels of Communicationqwertyuiop100% (12)
- Models of CommunicationDocument7 pagesModels of CommunicationВіка СобчукNo ratings yet
- Business Communication ModelsDocument29 pagesBusiness Communication ModelsBharatNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Mass Communication ModelsDocument23 pagesIntroduction to Mass Communication ModelsRimshaNo ratings yet
- Models of Communication ExplainedDocument8 pagesModels of Communication ExplainedMarcus Henry Acoymo HabanaNo ratings yet
- Eng111 Unit IDocument19 pagesEng111 Unit ILumactod EarthanNo ratings yet
- Communication Models (1)Document26 pagesCommunication Models (1)Wu XianNo ratings yet
- Oral 2 1Document13 pagesOral 2 1Dobby The elfNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument26 pagesModels of CommunicationAjay PadhiNo ratings yet
- 8 Communication ModelsDocument2 pages8 Communication ModelsJenelou PareraNo ratings yet
- ModelsDocument34 pagesModelsClaire SingsonNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument23 pagesModels of Communicationalissaray69No ratings yet
- Models of Communication ExplainedDocument5 pagesModels of Communication ExplainedEnzo PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 PURCOMDocument8 pagesChap 1 PURCOMJimz A-dreyll SaldonNo ratings yet
- (N) Lesson 1 - Nature and Elements of CommunicationDocument4 pages(N) Lesson 1 - Nature and Elements of Communicationnicey wayNo ratings yet
- Transactional and Linear Models of Communication ComparedDocument5 pagesTransactional and Linear Models of Communication ComparedSudarsan SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Oral Com Week 2Document29 pagesOral Com Week 2JanzyNo ratings yet
- 5 Models of CommunicationDocument2 pages5 Models of CommunicationAnonymous HBcjucZnNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument34 pagesModels of CommunicationSepida, Ma. Elliane V.No ratings yet
- 1 2 MergedDocument8 pages1 2 MergedAira CorderoNo ratings yet
- Oral Week5Document2 pagesOral Week5Anika RomeroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Models of CommunicationDocument52 pagesLesson 2 Models of CommunicationMarvic ReyesNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICATIONDocument4 pagesCOMMUNICATIONRoisa JoyNo ratings yet
- Nature of CommunicationDocument4 pagesNature of CommunicationStephanie Joyce TejadaNo ratings yet
- 1-Model of CommunicationDocument4 pages1-Model of CommunicationÂdriân ViloriâNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm. HandoutDocument4 pagesOral Comm. HandoutshannenkrishagwapaNo ratings yet
- Process of CommunicationDocument42 pagesProcess of CommunicationNelson Gail DagaasNo ratings yet
- Purp ComDocument8 pagesPurp ComMark Christian MaghinangNo ratings yet
- Chapter I Communication ModelsDocument8 pagesChapter I Communication ModelsodysonNo ratings yet
- Models CommunicationDocument6 pagesModels CommunicationJames Robert CanlasNo ratings yet
- FiiDocument5 pagesFiiManika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Metaphysics of MoralsDocument9 pagesMetaphysics of MoralsManika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Plato - The Republic - Internet Encyclopedia of PhilosophyDocument19 pagesPlato - The Republic - Internet Encyclopedia of PhilosophyManika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Marketing Channels and Supply Chain ManagementDocument70 pagesMarketing Channels and Supply Chain ManagementManika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- 1 - Mutual Funds and BenefitsDocument19 pages1 - Mutual Funds and BenefitsManika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Marketing Management 1Document53 pagesWelcome To Marketing Management 1Manika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Amity Business School: Organisation BehaviourDocument21 pagesAmity Business School: Organisation BehaviourManika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Amity Business School: MBA, Semester 1 Mpob Ms. Anshu YadavDocument23 pagesAmity Business School: MBA, Semester 1 Mpob Ms. Anshu YadavManika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Amity Business School: MBA, Semester 1Document32 pagesAmity Business School: MBA, Semester 1Manika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Net Present ValueDocument2 pagesCalculation of Net Present ValueManika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- PerceptionDocument26 pagesPerceptionManika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Feasibility AnalysisDocument5 pagesFeasibility AnalysisManika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Feasibility StudyDocument3 pagesFeasibility StudyManika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Clasa A 9-ADocument4 pagesClasa A 9-APODINA ANCUTANo ratings yet
- Ahmad Shawqi: The Pioneer of Dramatic Poetry in the Arabic LiteratureDocument17 pagesAhmad Shawqi: The Pioneer of Dramatic Poetry in the Arabic Literatureشذرات للتسوق الالكترونيNo ratings yet
- Religion in British and America-Introduce To America British Culture-Debora Rahmawati-21210006-2021 (Revision)Document46 pagesReligion in British and America-Introduce To America British Culture-Debora Rahmawati-21210006-2021 (Revision)Debora RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Urban Growth and Social Change in MarrakechDocument19 pagesUrban Growth and Social Change in MarrakechYongliang LiuNo ratings yet
- Kalidasa, Sakuntala - Tr. Monier W.Document350 pagesKalidasa, Sakuntala - Tr. Monier W.Anonymous IogovJW0% (1)
- Clothing and Age - A Critical Review PDFDocument21 pagesClothing and Age - A Critical Review PDFIoan-ovidiu CordisNo ratings yet
- Memoire D2Document117 pagesMemoire D2hamida douidaNo ratings yet
- Karen Edoff's Presentation Makeover Magic Over View - RedoDocument9 pagesKaren Edoff's Presentation Makeover Magic Over View - Redokme1011No ratings yet
- Emile DurkheimDocument34 pagesEmile DurkheimLouraineNo ratings yet
- Botong Francisco (Contemporary Arts)Document2 pagesBotong Francisco (Contemporary Arts)Sophia LantinNo ratings yet
- Classroom Management Strategies for Disciplinary IssuesDocument6 pagesClassroom Management Strategies for Disciplinary IssuesSyafiq AddinNo ratings yet
- Metaphorical Constructions of Manifest Destiny PaperDocument10 pagesMetaphorical Constructions of Manifest Destiny PaperHassen ZribaNo ratings yet
- 1jik-Gennext TranskirpDocument2 pages1jik-Gennext TranskirpMawi KarimNo ratings yet
- Art Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesArt Lesson Planapi-334880340No ratings yet
- Pi 01Document13 pagesPi 01Emon EspejoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Companion To Natural Law JurisprudenceDocument4 pagesCambridge Companion To Natural Law JurisprudenceAlonso Ramiro Begazo CaceresNo ratings yet
- Inclusive Assessment 1Document10 pagesInclusive Assessment 1api-483696979No ratings yet
- Introduction - Quran Translation (George Sale)Document11 pagesIntroduction - Quran Translation (George Sale)Gulzar AliNo ratings yet
- Five Models For Thinking About Disabilty ImplicatiDocument12 pagesFive Models For Thinking About Disabilty ImplicatiAnaMariaCastroNo ratings yet
- Book Review - Duane Elmer - Cross-Cultural ServanthoodDocument10 pagesBook Review - Duane Elmer - Cross-Cultural Servanthoodspeliopoulos50% (2)
- 建构文化研究书评1Document3 pages建构文化研究书评1weareyoung5833No ratings yet
- Module 3Document5 pagesModule 3Empress Cris TVNo ratings yet
- Letter of IntentDocument1 pageLetter of IntentDarren RuelanNo ratings yet