Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Insulation Resistance Portfolio
Insulation Resistance Portfolio
Uploaded by
Paul Bugeja0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Insulation Resistance portfolio.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesInsulation Resistance Portfolio
Insulation Resistance Portfolio
Uploaded by
Paul BugejaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
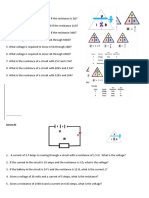
Insultation Resistance
What is insulation resistance?
Insulation resistance is defined as the resistance to current
leakage through and over the surface of the insulation
material surrounding a conductor. It is measured in Ohm`s
and its value represents a very important factor to
electricians working within the electrical industry.
What is insulation resistance testing?
The insulation resistance test is an electrical test which uses
a certain type and level of voltage (500V d.c. for low voltage
installations i.e.: 230V) to measure insulation resistance in
Ohm`s.
The measured resistance indicates the condition of the
insulation between two conductive parts. An infinite
resistance would be the perfect result, but no insulator is
perfect, so the higher the reading the better.
The table below shows the required test voltage and the
minimum required resistance in accordance with BS 7671.
Nominal Circuit Voltage Test Voltage Minimum Resistance
Between 0 V and 50 V a.c. 250 V d.c. 0.5 M ohm
Between 50 v and 500 V a.c. 500 V d.c. 1M ohm
Between 500 V and 1000 V a.c. 1000 V d.c. 1 M ohm
Insulation Resistance sequence
Step 1: Switch OFF Power supply
Step 2: By using an Insulation Resistor Tester Connect one lead to the
Earth conductor and the other to the Neutral conductor.
Step 3: Set the test required voltage (generally 250V) and check the
installation. Repeat the test with the Live conductor to earth
conductor, and between the Live and Neutral conductors. An
acceptable result should be not less than 1MΩ
Step 4: If result is below 1MΩ then one must repeat the tests on
every individual circuit by disconnecting the live and the neutral
conductors of each individual circuit. (By this way one can find which
is the faulty circuit)
Step 5: Fix the faulty circuit. Repeat the test on the individual circuit
and if the result is more then 1MΩ connect again all circuits and
repeat the test on the whole installation
You might also like
- Breakdown Characteristics of Air GapsDocument9 pagesBreakdown Characteristics of Air GapsSupun Amarasinghe100% (6)
- Megger Test Procedure Explained With Transformer ExampleDocument4 pagesMegger Test Procedure Explained With Transformer ExamplesamsungloverNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance (IR) Values - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument29 pagesInsulation Resistance (IR) Values - Electrical Notes & ArticlesNikhil Chakravarthy Vatsavayi100% (1)
- Principle of Tan Delta TestDocument12 pagesPrinciple of Tan Delta TestDeal Achmad FadealNo ratings yet
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- A Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsFrom EverandA Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- 21 Golden Safety Rules. PortfolioDocument2 pages21 Golden Safety Rules. PortfolioPaul Bugeja100% (2)
- Reference Material I 24-08-2021 Exp 3 Insulation ResistanceDocument10 pagesReference Material I 24-08-2021 Exp 3 Insulation Resistancerishika chhibberNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance (IR) Values - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument28 pagesInsulation Resistance (IR) Values - Electrical Notes & ArticlesjengandxbNo ratings yet
- Comment Insulation Resistance (IR) Values - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument41 pagesComment Insulation Resistance (IR) Values - Electrical Notes & ArticlesMunazar HussainNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance (IR) Values - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument29 pagesInsulation Resistance (IR) Values - Electrical Notes & ArticlesSunny SinghNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance (IR) Values: Voltage Level IR TesterDocument13 pagesInsulation Resistance (IR) Values: Voltage Level IR Testerandrenoel1123 suazoNo ratings yet
- Measurement of FLUKE Insulation Resistance MeggerDocument22 pagesMeasurement of FLUKE Insulation Resistance MeggerEmmanuel S SombilonNo ratings yet
- Insulation ResistanceDocument41 pagesInsulation Resistancekhozema_goodluck75% (4)
- IR Insulation Resistance ValuesDocument11 pagesIR Insulation Resistance ValuesBenabidNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance (IR) Values - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument13 pagesInsulation Resistance (IR) Values - Electrical Notes & ArticlesSharath Teja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance TestDocument5 pagesInsulation Resistance TestS.DharanipathyNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance (IR) Values - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument37 pagesInsulation Resistance (IR) Values - Electrical Notes & Articlesnyong dro100% (1)
- Insulation Test Report of Liberty Knit Ware Ltd-11570Document28 pagesInsulation Test Report of Liberty Knit Ware Ltd-11570roniNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance IR Values PDFDocument14 pagesInsulation Resistance IR Values PDFRodel D DosanoNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance (IR) ValuesDocument14 pagesInsulation Resistance (IR) ValuesHimdad Tahir100% (3)
- Insulation Resistance Test - Open Electrical PDFDocument4 pagesInsulation Resistance Test - Open Electrical PDFHeri SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance NotesDocument27 pagesInsulation Resistance NotessdvijayNo ratings yet
- Megger TestsDocument14 pagesMegger TestsJoao Silva100% (1)
- MeggerDocument10 pagesMeggershahanbashaNo ratings yet
- Minimum Ir ResultDocument22 pagesMinimum Ir ResultRaymond Gan100% (1)
- Measurement of Insulation Resistance IR Part 1Document5 pagesMeasurement of Insulation Resistance IR Part 1hafizg100% (1)
- Insulation Resistance (IR) Values - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument31 pagesInsulation Resistance (IR) Values - Electrical Notes & ArticlesKush SharmaNo ratings yet
- I.R Test of TransformerDocument1 pageI.R Test of TransformerVedant .Chavan50% (2)
- Insulation Resistance Value Insulation Level: Ohmmeter. This Is How The Test Works: DC Voltage of 500Document4 pagesInsulation Resistance Value Insulation Level: Ohmmeter. This Is How The Test Works: DC Voltage of 500Anonymous XXyhgBhDy3100% (1)
- Testing of TransformerDocument4 pagesTesting of Transformerdownload4sumitNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 5Document25 pagesChapter2 5alemaklil21No ratings yet
- LESSON NOTES HeszronDocument7 pagesLESSON NOTES HeszronHezron gibronNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance Test of Circuit BreakerDocument2 pagesInsulation Resistance Test of Circuit BreakerVedant .ChavanNo ratings yet
- A19 (F) Segregation and Insulation Resistance TestsDocument1 pageA19 (F) Segregation and Insulation Resistance TestsLilet P. DalisayNo ratings yet
- Ohm LawsDocument3 pagesOhm LawsimanuelsukarnoNo ratings yet
- Testing ProcedureDocument6 pagesTesting ProcedureNaing Win TunNo ratings yet
- Asefa - LV Test Procedure (MDB)Document4 pagesAsefa - LV Test Procedure (MDB)Magicneering PredictNo ratings yet
- His Insulation Megger TestingDocument1 pageHis Insulation Megger TestingthiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Megger TesterDocument2 pagesChoosing A Megger Testersawtheingitun13No ratings yet
- Testing of Transformers: T.R.Sathyanarayana RaoDocument24 pagesTesting of Transformers: T.R.Sathyanarayana RaoBasudev Patra100% (1)
- Insulation Resistance Test - Factors Affecting Test ResultsDocument2 pagesInsulation Resistance Test - Factors Affecting Test Resultstenk_manNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Transmission 4Document7 pagesElectrical Power Transmission 4FaisalSoNo ratings yet
- The Art of Transformer Maintenance, Inspection and Repair (Recommended Practices)Document5 pagesThe Art of Transformer Maintenance, Inspection and Repair (Recommended Practices)Abdul Mohid SheikhNo ratings yet
- What Happens To Insulation When Temperature Rises?Document2 pagesWhat Happens To Insulation When Temperature Rises?Aayush AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Department Electrical Installations and Drawings (ENEE323) Lecture Notes Instruments, Inspection, and Testing A) InstrumentsDocument13 pagesElectrical Engineering Department Electrical Installations and Drawings (ENEE323) Lecture Notes Instruments, Inspection, and Testing A) InstrumentsHamza KefayahNo ratings yet
- Cable Fault Location in Power Cables: Fault Classification: Insulation and Resistance MeasurementDocument5 pagesCable Fault Location in Power Cables: Fault Classification: Insulation and Resistance Measurementmherold2No ratings yet
- Voltech Notes: Laminate Transformer TestingDocument12 pagesVoltech Notes: Laminate Transformer Testingebersworld_2011No ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance Test - Open ElectricalDocument4 pagesInsulation Resistance Test - Open ElectricalDelmar FerrerNo ratings yet
- Breakdown Characteristics of Air PageDocument9 pagesBreakdown Characteristics of Air PageNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Insulation Resistance (IR) - Part 1 - EEP PDFDocument7 pagesMeasurement of Insulation Resistance (IR) - Part 1 - EEP PDFmahmoud fawzyNo ratings yet
- What Is " " Insulation?Document8 pagesWhat Is " " Insulation?Vimala KannanNo ratings yet
- Fluke - Appnotes - Basic Electrical Install Testing PDFDocument4 pagesFluke - Appnotes - Basic Electrical Install Testing PDFNguyen Thanh TrungNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Insulation Resistance Withstand of Cables: Experiment 6Document15 pagesMeasurement of Insulation Resistance Withstand of Cables: Experiment 6shalini nimsNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 - High Voltage Testing of EquipmentDocument16 pagesChap 6 - High Voltage Testing of Equipmenthadrien100% (1)
- Insulation ResistanceDocument2 pagesInsulation ResistanceDEADMAN0% (1)
- Electrical Engineering Portal Com Measurement of Insulation Resistance 2Document20 pagesElectrical Engineering Portal Com Measurement of Insulation Resistance 2Ratheesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 4.various Tests Part 1Document69 pages4.various Tests Part 1Rohit JoshiNo ratings yet
- 4.various Tests Part 1Document53 pages4.various Tests Part 1Rohit JoshiNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Diet BDocument11 pagesDiet BPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Diet ODocument4 pagesDiet OPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Work 11 JanuaryDocument6 pagesWorksheet Work 11 JanuaryPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- #11 - Unclog A Sink by Using A PlungerDocument2 pages#11 - Unclog A Sink by Using A PlungerPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- TASK3 MentoringDocument1 pageTASK3 MentoringPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- TASK Teaching, Learning and Assessment in VET 2Document2 pagesTASK Teaching, Learning and Assessment in VET 2Paul BugejaNo ratings yet
- #12 - CirclesDocument1 page#12 - CirclesPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- RCD Testing: What Is An RCD?Document3 pagesRCD Testing: What Is An RCD?Paul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Task 3 - Reflections - DeborahDocument1 pageTask 3 - Reflections - DeborahPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Pitch Sizes For Small Sided Games - FootballDocument1 pagePitch Sizes For Small Sided Games - FootballPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- 3v3 +3 Neutrals Pass To Target SessionDocument1 page3v3 +3 Neutrals Pass To Target SessionPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Drill Name: Setup: Instructions: Coaching PointsDocument1 pageDrill Name: Setup: Instructions: Coaching PointsPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- School Development Action Plan: Key AreaDocument2 pagesSchool Development Action Plan: Key AreaPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- GALVODocument3 pagesGALVOPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Before The Start of Every Examination: Attention All ReservesDocument2 pagesBefore The Start of Every Examination: Attention All ReservesPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Primary Pe CurriculumDocument19 pagesPrimary Pe CurriculumPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- 11 Feb 2017 - Combining & Improve Passing For Penetration - Sampling Stage Session by Paul Bugeja - UEFA Elite Youth A Diploma Course PDFDocument2 pages11 Feb 2017 - Combining & Improve Passing For Penetration - Sampling Stage Session by Paul Bugeja - UEFA Elite Youth A Diploma Course PDFPaul Bugeja100% (1)
- Drill Name: Setup: Instructions: Coaching PointsDocument1 pageDrill Name: Setup: Instructions: Coaching PointsPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Drill Name: Setup: Instructions: Coaching PointsDocument1 pageDrill Name: Setup: Instructions: Coaching PointsPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Drill Name: Setup: Instructions: Coaching PointsDocument1 pageDrill Name: Setup: Instructions: Coaching PointsPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Drill Name: Setup: Instructions: Coaching PointsDocument1 pageDrill Name: Setup: Instructions: Coaching PointsPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Multilateral Development ProgrammeDocument17 pagesMultilateral Development ProgrammePaul Bugeja100% (2)
- 3 Exercises On 5 Co-Ordinative CapacitiesDocument8 pages3 Exercises On 5 Co-Ordinative CapacitiesPaul Bugeja100% (1)
- Drill Name: Setup: Instructions: Coaching PointsDocument1 pageDrill Name: Setup: Instructions: Coaching PointsPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Gacon TestDocument2 pagesGacon TestPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Drill Name: Setup: Instructions: Coaching PointsDocument1 pageDrill Name: Setup: Instructions: Coaching PointsPaul BugejaNo ratings yet
- Defending in Midfield - Paul BugejaDocument2 pagesDefending in Midfield - Paul BugejaPaul BugejaNo ratings yet