Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Algebra II Reference: Completing The Square and Quadratics Polynomials
Uploaded by
Tim_C0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
122 views2 pagesAlgebra 2 guide
Original Title
algebra 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAlgebra 2 guide
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
122 views2 pagesAlgebra II Reference: Completing The Square and Quadratics Polynomials
Uploaded by
Tim_CAlgebra 2 guide
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
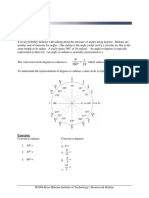
Algebra II Reference
Polynomials Completing the Square and Quadratics
Definitions Completing the 2
Square 2 Quadratic −b ± b2 − 4ac
b b Formula x =
Monomial: a variable, a real number or the product of a real number and ( ax ) + abx + = ax +
2
2a
variables raised to a whole and positive power 2 2 2
Polynomial: an expression which is the sum of one or more monomials b − 4ac > 0 → two real roots
Quadratic Equation b2 − 4ac = 0 → a real, repeated root
Root: the value of the variable when the polynomial function is zero; also
ax 2 + bx + c = 0 b2 − 4ac < 0 → two complex roots
considered the solution to the polynomial function
Degree: the highest exponent of a polynomial function Relations and Functions
Fundamental Theorem of Algebra: every polynomial equation with a degree Definitions Examples
greater than zero has at least one root in the set of complex numbers Relation: any set of ordered pairs For the examples below,
Dividing Polynomials Function: a relation which pairs each f(x)=h and g(x)=k
( 3 2
)
Divide x − 3x − 5x − 25 by ( x − 5 ) . Long Division
Divide the first term dividend by the first
element of the domain with exactly one
element of the range
Composite
f
Functions
( ( )) = f ( k )
g x
Synthetic Division term divisor and distribute the result.
2 Adding Functions
Find the root of the divisor. x Types of Functions
( )
x − 5 = 0 → x = 5
x − 5 x 3 −3x 2 −5 x −25 Algebraic Function: a function for which x f ( x ) + g ( x) = h + k
List all coefficents of the polynomial. is constant Subtracting Functions
5 1 −3 −5 −25 x 3 −5x 2 f ( x ) − g ( x )=h −k
Bring down the first coefficient. Rational Functions: a function in which a
5 1 −3 −5 −25 Subtract the result from the dividend. polynomial function is divided by another Multiplying Functions
x2 polynomial function not equal to zero f ( x ) ⋅ g ( x ) = hk
↓
Piecewise Functions: a function that is Dividing Functions
1 x − 5 x 3 −3x 2 −5x −25 Where k is not equal to zero
Multiply the first coefficient by the root. defined by different equations for
5 1 −3 −5 −25 x 3 −5x 2 f (x ) h
2 different portions of the domain =
↓ 5 0 2x
Composite Functions: a function in which g (x ) k
Bring down the next term from the dividend.
1
x2 the variable is another function
Add the product to the second coefficient.
5 1 −3 −5 −25 x − 5 x 3 −3x 2 −5x −25 Logarithms, Exponents, Radicals
↓ 5 x 3 −5x 2 ↓
1 2
Definitions
2
0 2x −5x Natural Base: the irrational number, e, that is approximately
Repeat previous two steps for all. Repeat the previous 3 steps for each term.
5 1 −3 −5 −25 x 2
+ 2x + 5
2.71828…
↓ 5 10 25 Logarithm: the inverse of an exponential function
3 2
1 2 5 0 x −5 x −3x − 5x −25 Equivalent Exponent and Logarithmic Forms: For any positive
The final integer is the remainder. ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ base b, where b is greater than 0 and not equal to 1:
Insert variables starting with one less 5x −25 bx = y if and only if x = logb (y).
degree for each coefficient. 5x −25 Common Log: the function f(x)=log10x; can be shortened to
x 2 + 2x + 5 R= 0 ( x − 5 ) 0
f(x)=logx
Finding Roots Natural Log: the function f(x)=logex in which the base, e, is the
Factoring Polynomial Functions: a process where a polynomial is written as special number 2.71828…; function is also written as f(x)=lnx
the multiplication of two or more different polynomials or monomials Formulas and Properties
Complex Conjugates Theorem: If a+bi is a root of a polynomial function with
Product of Quotient of Quotient of Negative Inverse
real coefficients, then a-bi is also a root of the function
Exponents Exponents Radicals Exponents Properties
Rational Root Theorem: Let f(x)=a polynomial function in standard form with m n
integer coefficients; If p is all factors of the constant term and q is all factors bm ⋅ bn = bm +n a = a m −n n a = a x −a = 1 logb b = x
x
n n a
of the leading coefficient, then (p/q) is all possible roots of y=f(x) Exponent of a a b b x b logb x = x
Formulas for Factoring Product Fractional Changing Bases
( ) m
= m m Exponents log x
Greatest Common Factor Sum of Two Cubes ab a b logb x = a
(
a 3 b + a 2 b2 + ab2 = ab a 2 + ab + b ) (
a 3 + b3 = ( a + b ) a 2 − ab + b2 )
an Exponent
a
Exponent of x b = b x a = b x ( )
a
Product of
loga b
Logarithms
Grouping Difference of Two Cubes Exponent of a logb ( mn ) = logb m + logb n
( )( )
n
ax + cx + ay + cy = ( a + c )( x + y ) a 3 − b3 = ( a − b ) a 2 + ab + b2 a m = a m ⋅n Quotient Quotient of Logarithms
m
General Trinomial Perfect Squares Product of a am m
acx 2 + adx + bcx + bd = ( ax + b )( cx + d ) b = m logb = logb m − logb n
Radicals b n
a 2 + 2ab + b2 = ( a + b )
2
−n n n
Difference of Two Squares n ab = n a ⋅ n b a = b = b Powers of Logarithms
a 2 − 2ab + b2 = ( a − b ) ( )
2
a 2 − b2 = ( a + b )( a − b ) b a n logb m p = p ⋅ logb m
a
Rose-Hulman Homework Hotline 1 Algebra II Study Guide
Imaginary and Complex Numbers Series and Sequences
Definitions Definitions
Imaginary Number: the number i that squared yields a result of -1. Sequence: an ordered list of numbers or terms
i = −1 i 2 = −1 Explicit Formula: a formula that defines all the terms of a sequence
Complex Number: a number that can be written in the form a+bi Recursive Formula: a formula that uses one or more previous terms to
where the a term is real and the bi term is imaginary generate the next term
Powers of i Series: an expression that indicates the sum of terms of a sequence
To find in , divide n by 4 and match the remainder to one of the Arithmetic Sequence: a sequence whose successive terms differ by the
powers of i to the right. i = −1 i 2 = −1 i 3 = −i i4 =1 same common difference, d
Arithmetic Series: the indicated sum of the terms of an arithmetic sequence
Conic Sections Geometric Sequence: a Formulas
Definitions sequence in which the Arithmetic Sequence Geometric Sequence
Circle: the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a ratio of successive terms is
an = a1 + (n − 1)d an = a1 r n −1
given point, the center in the plane. the same common ratio, r
Ellipse: the set of all points in a plane such that the sum of the Geometric Series: the Arithmetic Series Geometric Series
distances from two fixed points, the foci, is constant
Parabolas: the set of all points in a plane that are the same
indicated sum of the terms
of a geometric sequence
n
Sn = ( a1 + an )
2 Sn =
a1 1 − r n ( )
distance from a given point, the focus, and a given line, the Binomial Theorem: a 1−r
directrix formula for finding the Binomial Theorem
Hyperbola: the set of all points in a plane such that the absolute expansion of the powers of n n n n!
a binomial expression ( a + b ) = ∑ a n −k bk ; =
n
value of the difference of the distances from two fixed points, the
foci, is constant
k
k =0 k
( n − k )! k !
Standard Equations Probability
(h,k) = center or vertex r =radius of circle Definitions
Circle
( x − h )2 + ( y − k )2 = r 2 Fundamental Counting Principle: if event can occur in m ways and another
Ellipse Horizontal Major Axis Vertical Major Axis event that can occur in n ways, then the first event followed by the second
event can occur in m·n ways
For a>b (x − h) (y − k )
2 2
(y − k ) (x − h)
2 2
+ =1 + =1 Independent Events: events that do not affect the outcomes of each other
a2 b2 a2 b2 Dependent Events: events that affect the outcomes of each other
Parabola Opens up if a>0, down if a<0 Opens right if a>0, left if a<0 Mutually Exclusive Events: two events that cannot occur at the same time
y = a(x − h) + k
2
x = a(y − k ) + h
2 Inclusive Events: two events whose outcomes may be the same
Combination: an arrangement of objects in which order is not important
Hyperbola Horizontal Transverse Axis Vertical Transverse Axis
Permutation: an arrangement of objects in which order is important
(x − h) (y − k )
2 2
(y − k ) (x − h)
2 2
Formulas
− =1 − =1
a2 b2 a2 b2 Probability with Two Probability with Two Combination
Independent Events Dependent Events n!
P ( A ∩ B ) = P ( A) ⋅ P (B ) P ( A ∩ B ) = P ( A) ⋅ P (B A) ( ) ( n − r ) ! r !
Other Notes C n,r =
Probability of Success Probability of Mutually Permutation
Exclusive Events n!
P (s ) =
s P ( n,r ) =
s +f P ( A ∪ B ) = P ( A) + P (B ) (n − r )!
Probability of Inclusive Events Permutation w/ Repetitions
n!
P ( A ∪ B ) = P ( A) + P (B ) − P ( A ∩ B ) P (n) =
p! q!
Matrices and Determinates
Definitions Formulas
Matrix: A rectangular array of variables or constants in horizontal
rows and vertical columns, usually enclosed in brackets. Addition and Subtraction of Matrices 2nd Order Determinate
Adding/Subtracting Matrices: addition or subtraction of matrices a b c j k l a ± j b±k c ±l a b
may only occur if the matrices are the same dimensions; d e f ± m n o = d ± m e ± n f ± o = ad − bc
c d
corresponding entries are added or subtracted to form the
g h i p q r g ± p h±q i ±r
result
Multiplying Matrices by a Constant: each entry of the matrix is Multiplying Matrices 3rd Order Determinate
By a constant, k
multiplied by the indicated constant a b ka kb a b c
Multiplying Matrices by another Matrix: the number of columns k = kd d e f =
c d kc
in the first matrix must be the same as the number of rows in g h i
the second matrix; multiply each By another matrix
e f d f d e
Determinate: a square array of numbers or variables enclosed a b e f ae + bg af + bh a −b +c
between two parallel lines. c d ⋅ g h = ce + dg cf + dh h i g i g h
Rose-Hulman Homework Hotline 2 Algebra II Study Guide
You might also like
- Algebra 2Document200 pagesAlgebra 2Yomisis Academy94% (17)
- Homework Practice WorkbookDocument184 pagesHomework Practice Workbookjugumuikals100% (10)
- Pre-Algebra Homework BookDocument218 pagesPre-Algebra Homework BookRuben Pulumbarit III100% (12)
- Review basic calculus concepts for business, biology & psychologyDocument4 pagesReview basic calculus concepts for business, biology & psychologySammar Ellahi100% (6)
- Prealgebra OPDocument1,146 pagesPrealgebra OPHoa Dinh Nguyen100% (4)
- Study Guide and Intervention WorkbookDocument184 pagesStudy Guide and Intervention WorkbookIshneet Dhillon100% (14)
- Algebra WorkbookDocument299 pagesAlgebra Workbookmakomdd100% (3)
- Algebra 2 Practice WorkbookDocument92 pagesAlgebra 2 Practice WorkbookIgor Vasić100% (1)
- Workbook For Algebra 1Document96 pagesWorkbook For Algebra 1Michael Depurba67% (3)
- Algebra WorkbookDocument260 pagesAlgebra Workbookbannerpercussion100% (6)
- Pre-Algebra and AlgebraDocument66 pagesPre-Algebra and Algebramiccass100% (20)
- Honors Geometry Solutions ManualDocument586 pagesHonors Geometry Solutions Manualdevi100% (1)
- AP Calculus BC Study GuideDocument16 pagesAP Calculus BC Study GuideBrimwoodboy100% (3)
- ACT Test Prep MathDocument58 pagesACT Test Prep Mathvaishnavi100% (1)
- Study NBDocument256 pagesStudy NBsosoho100% (5)
- College Algebra Quick Reference Sheet GuideDocument2 pagesCollege Algebra Quick Reference Sheet Guidetxungo100% (1)
- Glencoe Algebra-I-Solutions-Manual PDFDocument789 pagesGlencoe Algebra-I-Solutions-Manual PDFginotrucheli86% (7)
- (SAT Math Mastery (Book 1) ) Christian Heath - SAT Math Mastery - Essential Algebra 1 & Algebra 2. 1-Love The SAT Academic Press (2020) PDFDocument481 pages(SAT Math Mastery (Book 1) ) Christian Heath - SAT Math Mastery - Essential Algebra 1 & Algebra 2. 1-Love The SAT Academic Press (2020) PDFIlir Hoxha100% (1)
- Introductory AlgebraDocument214 pagesIntroductory AlgebraUgonna Ugo100% (2)
- Algebra 2 Answer Key PDFDocument411 pagesAlgebra 2 Answer Key PDFDino Jajcanin60% (5)
- Algebra 2 PDFDocument600 pagesAlgebra 2 PDFAndré Camargo Llano100% (16)
- Algebra 2 - Study NotebookDocument256 pagesAlgebra 2 - Study NotebookIshneet Dhillon100% (7)
- Precalculus Student Solution ManualDocument305 pagesPrecalculus Student Solution Manualfire&gas100% (2)
- Glenco Algebra 1 Chapter 1Document119 pagesGlenco Algebra 1 Chapter 1shraddha78% (18)
- AlgebraHandbook PDFDocument178 pagesAlgebraHandbook PDFTim_CNo ratings yet
- Express Review Guide - Algebra 1Document176 pagesExpress Review Guide - Algebra 1Margaret100% (4)
- Holt McDougal Florida Larson Algebra 1 PDFDocument431 pagesHolt McDougal Florida Larson Algebra 1 PDFArthur Braga90% (10)
- Algebra 8-1studyguideDocument110 pagesAlgebra 8-1studyguideßarbiє Castillo71% (7)
- Alg 1 SnbseDocument240 pagesAlg 1 SnbseAbelia Allcca80% (5)
- ACT Math GauntletDocument37 pagesACT Math GauntletYash AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Prentice Hall Algebra 1 Cumulative Review Chapters 1-8Document16 pagesPrentice Hall Algebra 1 Cumulative Review Chapters 1-8Rocket Fire50% (8)
- Hon Alg 2 Ans KeyDocument411 pagesHon Alg 2 Ans Keypn11x2100% (2)
- Math Handbook of Formulas, Processes and Tricks: TrigonometryDocument109 pagesMath Handbook of Formulas, Processes and Tricks: TrigonometryShri Arjun100% (1)
- Algebra 1Document32 pagesAlgebra 1Sam Lanka100% (1)
- Pre-Algebra Concepts 2nd Edition, Mastering Essential Math Skills: 20 minutes a day to successFrom EverandPre-Algebra Concepts 2nd Edition, Mastering Essential Math Skills: 20 minutes a day to successRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Tenn Algebra 2 EOC Practice WorkbookDocument128 pagesTenn Algebra 2 EOC Practice WorkbookBubba1963No ratings yet
- A 2 C 1 RMDocument92 pagesA 2 C 1 RMDevilmite100% (4)
- Golden Ratio ReportDocument30 pagesGolden Ratio ReportRoselynOrbigoso100% (1)
- Geometry HandbookDocument82 pagesGeometry HandbookCarmen ResmeritaNo ratings yet
- Benchmark Algebra I PracticeDocument40 pagesBenchmark Algebra I PracticeJunaid K Jumani100% (2)
- Psat 8 9 and Psat NMQST PresentationDocument35 pagesPsat 8 9 and Psat NMQST Presentationapi-296918325No ratings yet
- Algebra 2 PracticeDocument101 pagesAlgebra 2 PracticeStanley Song67% (3)
- Saxon Algebra 2 SmallDocument601 pagesSaxon Algebra 2 SmallDamaru Mallaiah100% (2)
- 2014 Calculus AB Free Response Questions (Answers and Explanations)Document7 pages2014 Calculus AB Free Response Questions (Answers and Explanations)eric100% (1)
- Study Guide and Intervention Workbook Course 2 EditionDocument92 pagesStudy Guide and Intervention Workbook Course 2 Editionapi-261894355100% (1)
- Algebra I EOC Test Prep PacketDocument45 pagesAlgebra I EOC Test Prep Packetbesp63100% (1)
- Let's Practice GeometryDocument553 pagesLet's Practice GeometryEthan Dyer94% (18)
- Geometry Eoc Review PacketDocument41 pagesGeometry Eoc Review PacketCeline Loh100% (1)
- Vector Game Math Processors PDFDocument530 pagesVector Game Math Processors PDFTim_CNo ratings yet
- Principles of Math 12 - Transformations Lesson 2Document9 pagesPrinciples of Math 12 - Transformations Lesson 2Tim_CNo ratings yet
- Geometric ProofsDocument20 pagesGeometric Proofsshanna_heena100% (1)
- CalculusHandbook PDFDocument235 pagesCalculusHandbook PDFTim_C100% (1)
- Principles of Math 12 - Transformations Lesson 1Document11 pagesPrinciples of Math 12 - Transformations Lesson 1Tim_CNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1. (Electronic Resource) Concepts and SkillsDocument244 pagesAlgebra 1. (Electronic Resource) Concepts and SkillsginotrucheliNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1 Placement Exam Study Guide 2011 PDFDocument15 pagesAlgebra 1 Placement Exam Study Guide 2011 PDFCher Jay-ar Doronio100% (1)
- Unit 3 TrigfunctionsDocument92 pagesUnit 3 Trigfunctionskae ayako100% (1)
- Saxon - Algebra - 0.5 022218 SampleDocument6 pagesSaxon - Algebra - 0.5 022218 Samplenitikanehi0% (1)
- v2 - Algebra II (Common Core) Regents Review Sheet - Facts You Must Know ColdDocument19 pagesv2 - Algebra II (Common Core) Regents Review Sheet - Facts You Must Know ColdIkhri574No ratings yet
- Algebra 1Document61 pagesAlgebra 1Erik Gomez40% (5)
- Deep Learning Tutorial Release 0.1Document173 pagesDeep Learning Tutorial Release 0.1lerhlerhNo ratings yet
- Class VI I.I.T. Foundation, N.T.S.E.& Mathematics Olympiad Curriculum & Chapter NotesDocument65 pagesClass VI I.I.T. Foundation, N.T.S.E.& Mathematics Olympiad Curriculum & Chapter Notesspatel1972No ratings yet
- IJSO Stage-I & II - Expert - IX - Mahtemaitcs PDFDocument175 pagesIJSO Stage-I & II - Expert - IX - Mahtemaitcs PDFSanvi Gadhvi 18100% (2)
- Factoring Polynomial PresentationDocument59 pagesFactoring Polynomial PresentationJackie Salvador100% (3)
- Distribution of Prime NumbersDocument81 pagesDistribution of Prime NumbersAlfredoNo ratings yet
- 2015 RSM Olympiad QA G6-7Document4 pages2015 RSM Olympiad QA G6-7VikasNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry SGDocument35 pagesTrigonometry SGTim_CNo ratings yet
- NewtonProgrammerRef20 PDFDocument1,390 pagesNewtonProgrammerRef20 PDFTim_CNo ratings yet
- Cyclic Redundancy Check: Mathematical and Hardware OverviewDocument26 pagesCyclic Redundancy Check: Mathematical and Hardware OverviewMohammed Publications100% (3)
- Pemulihan Teacher's ModuleDocument173 pagesPemulihan Teacher's ModuleABU_JALEN100% (1)
- 124 Fractions Multdiv AllDocument20 pages124 Fractions Multdiv AllSathish NarayanNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2Document4 pagesAlgebra 2Kim OrtuosteNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Enrichment Packet - Answer KeyDocument36 pagesAlgebra 2 Enrichment Packet - Answer KeyMarylene Montoya100% (1)
- How To Modify Old Qbasic Programs To Run in Visual Basic: Bergmann@rowan - Edu Chandrupatla@rowan - Edu Osler@rowan - EduDocument7 pagesHow To Modify Old Qbasic Programs To Run in Visual Basic: Bergmann@rowan - Edu Chandrupatla@rowan - Edu Osler@rowan - EduJohn K.E. EdumadzeNo ratings yet
- Topic 4.4.3 Project Management Pert and Gantt Charts 9608Document16 pagesTopic 4.4.3 Project Management Pert and Gantt Charts 9608ABHISHEK KUMARNo ratings yet
- Useful SummationsDocument1 pageUseful Summationsosama_gmaNo ratings yet
- CH 14 Applications of Geometry and Trig PDFDocument21 pagesCH 14 Applications of Geometry and Trig PDFTim_CNo ratings yet
- 2100 Ug PDFDocument292 pages2100 Ug PDFTim_CNo ratings yet
- Technology Close-Up: Choosing the Right PhotodetectorDocument4 pagesTechnology Close-Up: Choosing the Right PhotodetectorTim_CNo ratings yet
- Tim's LB CalcDocument6 pagesTim's LB CalcTim_CNo ratings yet
- Principles of Math 12 - Transformations Lesson 4Document16 pagesPrinciples of Math 12 - Transformations Lesson 4Tim_CNo ratings yet
- Tips Labview DevelopmentDocument39 pagesTips Labview DevelopmentTim_CNo ratings yet
- Principles of Math 12 - Transformations Practice Exam PDFDocument23 pagesPrinciples of Math 12 - Transformations Practice Exam PDFTim_CNo ratings yet
- Principles of Math 12 - Transformations Practice Exam Answers PDFDocument13 pagesPrinciples of Math 12 - Transformations Practice Exam Answers PDFTim_C100% (1)
- Principles of Math 12 - Transformations Lesson 3Document9 pagesPrinciples of Math 12 - Transformations Lesson 3Tim_CNo ratings yet
- Tips Labview DevelopmentDocument39 pagesTips Labview DevelopmentTim_CNo ratings yet
- HILTI Seismic - Manual - W4365 - EN PDFDocument104 pagesHILTI Seismic - Manual - W4365 - EN PDFTim_CNo ratings yet
- Ufc 3-555-01n 400 Hertz Medium Voltage Conversion - Distribution and Low Voltage Utilization Systems (16 January 2004)Document115 pagesUfc 3-555-01n 400 Hertz Medium Voltage Conversion - Distribution and Low Voltage Utilization Systems (16 January 2004)Bob VinesNo ratings yet
- Tips Labview DevelopmentDocument39 pagesTips Labview DevelopmentTim_CNo ratings yet
- Temporary Structures: Slab Form DesignDocument9 pagesTemporary Structures: Slab Form Designapi-19878202No ratings yet
- Chapter Five Falsework and FormsDocument26 pagesChapter Five Falsework and FormsTim_CNo ratings yet
- Excavations and Excavations SupportDocument15 pagesExcavations and Excavations SupportAndrei LeuNo ratings yet
- Bbe 105 - Business Calculations Methods PDFDocument175 pagesBbe 105 - Business Calculations Methods PDFThato MofarasiNo ratings yet
- SET THEORY BASICSDocument10 pagesSET THEORY BASICSreeta ramNo ratings yet
- v13 n4Document4 pagesv13 n4sharad dsouzaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods: Solution of Nonlinear Equations Lectures 5-11Document97 pagesNumerical Methods: Solution of Nonlinear Equations Lectures 5-11eyassadailehNo ratings yet
- 2nd Periodical TestDocument4 pages2nd Periodical TestRubyrose NievesNo ratings yet
- CantorDocument5 pagesCantorPlop DianaNo ratings yet
- Compare and Operation DecimalDocument32 pagesCompare and Operation DecimalFarrahheda MohamadNo ratings yet
- MA203 Real Analysis: MA103 Revision Material: Lecture NotesDocument39 pagesMA203 Real Analysis: MA103 Revision Material: Lecture NotesTOM DAVISNo ratings yet
- Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument4 pagesDerivative of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsKristan Glen PulidoNo ratings yet
- Factorisation PDFDocument3 pagesFactorisation PDFRaj Kumar0% (1)
- ASSIGNMENT Teacherapptemproot280 20230821123852Document7 pagesASSIGNMENT Teacherapptemproot280 20230821123852syaNo ratings yet
- OBE Assignment (BITS 1123) 2012 - 2013 FTMK BITI S1G1 - Topic 2 Subtopic 4 - Karnaugh MapDocument6 pagesOBE Assignment (BITS 1123) 2012 - 2013 FTMK BITI S1G1 - Topic 2 Subtopic 4 - Karnaugh MaptechspaceofatulNo ratings yet
- DsdsDocument46 pagesDsdspNo ratings yet
- Admath Properties 1Document6 pagesAdmath Properties 1Missy ForlajeNo ratings yet
- Stat HandoutDocument7 pagesStat HandoutJenrick DimayugaNo ratings yet
- REGENT SECONDARY SCHOOL END OF YEAR EXAMINATION (SA2) 2017Document29 pagesREGENT SECONDARY SCHOOL END OF YEAR EXAMINATION (SA2) 2017Eugene ChanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 AnswersDocument5 pagesTutorial 5 AnswersFrantz ClermontNo ratings yet
- GMAT Arithmetic Formula ListDocument4 pagesGMAT Arithmetic Formula ListCynthia J. HendershotNo ratings yet
- Grade 5Document25 pagesGrade 5Lenie Boo100% (1)
- Maths Form 1 End TermDocument6 pagesMaths Form 1 End Termparmeet singh100% (1)
- Interesting Facts About Bitwise Operators in C - GeeksforGeeksDocument6 pagesInteresting Facts About Bitwise Operators in C - GeeksforGeeksGokul ChinnathuraiNo ratings yet
- Aomplementary NumbersDocument22 pagesAomplementary NumbersDraganNo ratings yet