Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NSTP Chapter 6 - Drug Education
Uploaded by
神様Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NSTP Chapter 6 - Drug Education
Uploaded by
神様Copyright:
Available Formats
DRUG EDUCATION
Section 1: Substance abuse
DRUGS - A medicine or other substance which has a physiological effect when
ingested or otherwise introduced to the body.
DRUG ABUSE - The excess consumption of drugs or taking in combinations of
drugs without listening to the advice or following the prescription given by
competent authorities.
DRUG ADDICTON - The state of chronic intoxication caused by repeated and
improper consumption of drugs.
Characterized by
An overpowering desire to take the substance
A tendency to increase the dosage.
A psychological and physical dependence on the substance.
DRUG DEPENDENCE - The state of having an unruly drive to use drugs in
order to achieve physical and mental stability following a cycle but improper
use of the substance.
DRUG TOLERANCE - A condition in which the body builds up resistance to the
effects of a drug, so that larger quantities are needed to obtain the same effect.
Withdrawal syndrome - The condition in which the user becomes uncomfortable
and very irritable as an after effect of the drug taken.
Classifications of Dangerous Substances
Prohibited Drugs - Drugs that are considered illegal and only drug manufacturers
and institutions engaged in the study of scientific and medicinal importance are
authorized to use and have it.
Regulated Drugs - Drugs that have great medicinal value given or administered
only with proper authorization from doctors or other competent authorities.
Common signs of substance abuse
- IRRITABLE, DISCOURTEOUS, DEFIANT AND AGGRESSIVE
BEHAVIOR
- UNTRUSTWORTHY AND LACKS SELF-CONFIDENCE
- HAS LOW FRUSTRATION TOLERANCE
- SUDDEN CHANGE OF HABITS
- UNHEALTHY AND DISINTERESTED ABOUT HIS GROOMING AND
APPEARANCE
- INAPPROPRIATE EYE PUPIL DILATION AND CONTRACTION
- PREFERS TO BE IN THE COMPANY OF BAD ELEMENTS
- LOSES INTERESTS IN STUDIES OR WORK
- INAPPROPRIATE WEARING OF SUNGLASSES
- REDUCED OR IMPAIRED PHYSICAL CAPABILITIES
Common reasons why people turn to drugs
- LACKS OF PARENTAL GUIDANCE
- TO ESCAPE FROM PROBLEMS
- CURIOSITY ABOUT ITS EFFECTS
- TO BE ACCEPTED IN A GROUP OR PEER PRESSURE
- IGNORANCE ON THE EFFECTS OF THE SUBSTANCE
- TO EMULATE A NEGATIVE ROLE MODEL
- LACK OF OUTLETS FOR OTHER INTERESTS
- LACK OF SELF-CONFIDENCE
- DEPRESSIONS AND FRUSTRATIONS
- TO STAY AWAKE, ALERT AND FULL OF VIGOR
Section 2: Basic classification of addictive substances
Narcotics - a drug or other substance affecting mood or behavior and sold for
nonmedical purposes, especially an illegal one.
Examples: Opium, Morphine, Codeine and heroin
Depressants or Sedatives - a drug taken for its calming or sleep-inducing effect.
Commonly referred to as downers.
Examples Barbiturates, alcohol
Stimulants - a substance that raises levels of physiological or nervous activity in
the body.
Examples: Amphetamine, Cocaine, Shabu, Caffeine and nicotine.
Hallucinogens - a drug that causes hallucinations. Changes perception, thoughts
and feelings.
Examples: LSD, Marijuana, Ecstasy
Inhalants - a solvent or other material producing vapor that is inhaled by users for
its intoxicating effect which contains mind or mood altering chemical.
Examples – Solvent Cement, Contact Cement, Acetone
Effects of drug abuse to an individual
Malnutrition – They miss their regular meals because they lose appetite.
Panic Reaction – the loss of thought processes can cause panic reaction or feelings
of invulnerability, both of these states can lead to injury or death.
Physical Damages - In addition to those diseases which accompany the use of
unsterile syringes and contaminated drugs, drug abuse may cause certain medical
problems.
Section 3: Drug prevention measures.
Government responsibilities
1. There must be clear cut anti-drug policies and make sure that these policies are
being observed and laws strictly enforced.
2. Government must provide adequate programs and facilities for the total
development especially of young individuals.
3. Implement or encourage programs that will help strengthen the moral fiber of the
society
Parental Responsibilities
1. Have time for the children.
2. Help young individuals gain self-confidence.
3. Encourage the children to participate socially, emotionally, morally, physically,
mentally and spiritually enriching activities in school or in the community.
4. Encourage the children to plan for a sound future.
5. Help them to appreciate the value of good health and healthy lifestyle.
Individuals Responsibility
1. Learn to say no even when the one offering is your close friend or relative.
2. Learn how to deal with negative feelings and emotions.
3. Talk to someone who can be trusted if you need advice for your problems.
4. Learn to socialize.
5. Enhance your special talents and explore for new interests and hobbies.
The four pillars of actions against illegal drugs
- Supply reduction
- Demand reduction
- Alternative development
- Civic awareness
Comprehensive Dangerous Drugs Act of 2002 - or Republic Act No.
9165 is a consolidation of Senate Bill No. 1858 and House Bill No. 4433.
It was enacted and passed by the Senate of the Philippines and House of
Representatives of the Philippines on May 30, 2002 and May 29, 2002,
respectively. It was signed into law by President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo
on June 7, 2002.
This Act repealed the Republic Act No. 6425, otherwise known as the
Dangerous Drugs Act of 1972, as amended, and providing funds for its
implementation. Under this Act, the Dangerous Drugs Board (DDB)
remains as the policy-making and strategy-formulating body in planning
and formulation of policies and program on drug prevention and control.
It also created the Philippine Drug Enforcement Agency (PDEA) under
the Office of the President, which serves as the implementing arm of the
DDB, shall be responsible for the efficient and effective ambt ... law
enforcement of all the provisions on any dangerous drugs, controlled
precursors and essential chemicals as provided in this Act.
Article II Unlawful Acts and Penalties
• Section 4 –Importation of Dangerous Drugs –Penalty Life Imprisonment
to death with fine of P500,000 to P10,000,000.
• Section 5 –Sale Trading, Admin Station, Dispensation, Delivery,
Distribution
PURPOSES OF RANDOM DRUG TESTING
1. To determine the prevalence of drug users among the students
2. To assess the effectivity of school-based and community based
prevention programs
3. To deter the use of illegal drugs
4. To facilitate the rehabilitation of drug users and dependents
5. To strengthen the collaboration efforts of identified agencies against the
use of illegal drugs and in the rehabilitation of drug users and dependents..
“Drug Counselor” shall mean a person trained in the techniques of
guidance counseling particularly dealing with cases of drug dependency.
The Drug Testing Coordinator shall designate such person.
“Drug Testing Coordinator ” shall be the point person in the school
tasked with handling random drug testing which shall be the principal of a
secondary school, the administrator of a technical vocational education
and training institution or the administrator appointed by the
president/chief executive officer in tertiary institutions.
You might also like
- Activity 7, NSTPDocument3 pagesActivity 7, NSTPZam-zamNo ratings yet
- Drug Education: Understanding the Effects of Substance AbuseDocument32 pagesDrug Education: Understanding the Effects of Substance AbuseGianne Ina Castillo0% (3)
- Module 2Document11 pagesModule 2R-jay RiveraNo ratings yet
- Module 7 NSTP 1Document55 pagesModule 7 NSTP 1PanJan BalNo ratings yet
- The Paulinian Story 2Document17 pagesThe Paulinian Story 2Theother OneNo ratings yet
- What Is Drug Abuse and AddictionDocument5 pagesWhat Is Drug Abuse and AddictionSiddarth NyatiNo ratings yet
- NSTP Module 5 Drug EducationDocument12 pagesNSTP Module 5 Drug EducationMarco Estebat100% (4)
- R A-6425Document76 pagesR A-6425Lovely Ann Ayapana100% (1)
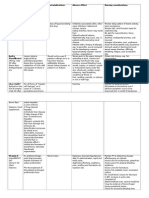
- Drug Classification, Action, Nursing ConsiderationsDocument14 pagesDrug Classification, Action, Nursing ConsiderationsLovely Saad TubañaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1introduction To The Study of GlobalizationDocument32 pagesLesson 1introduction To The Study of GlobalizationNorman LingahanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 NSTP 1-1Document28 pagesModule 3 NSTP 1-1PanJan BalNo ratings yet
- The Generics ActDocument19 pagesThe Generics ActCJ Halasan100% (1)
- Understanding the Physical and Sexual SelfDocument27 pagesUnderstanding the Physical and Sexual SelfEthan VercoloNo ratings yet
- PHILPOPCULTURE3Document24 pagesPHILPOPCULTURE3He PulalonNo ratings yet
- Rediscovery Of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesRediscovery Of The PhilippinesMikashi Lang50% (4)
- Classification of DrugsDocument58 pagesClassification of DrugsLerma Manalac100% (1)
- Drug Education: Classifying Commonly Abused SubstancesDocument8 pagesDrug Education: Classifying Commonly Abused SubstancesArhann Anthony Almachar Adriatico100% (1)
- Drug Awareness Seminar: Police Community Relations LectureDocument93 pagesDrug Awareness Seminar: Police Community Relations LectureQuelly100% (3)
- Drug and Substance Abuse Prevention and ControlDocument28 pagesDrug and Substance Abuse Prevention and ControlKarlyn RamosNo ratings yet
- A. Food-Based Dietary Guidelines-Philippines: Daily Nutritional Guide (DNG) PyramidDocument2 pagesA. Food-Based Dietary Guidelines-Philippines: Daily Nutritional Guide (DNG) PyramidAndrea MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Selection and ProclamationDocument3 pagesSelection and ProclamationBebe NopsNo ratings yet
- Filipino PsychologyDocument3 pagesFilipino PsychologyJohn Russell MoralesNo ratings yet
- Cause of Drug AddictionDocument2 pagesCause of Drug AddictionLaatha Wani100% (1)
- Our Culture Is Our DestinyDocument4 pagesOur Culture Is Our DestinyPrincess Niña PasuengosNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document18 pagesModule 6Neil Paul Baquiran100% (1)
- NSTP CWTS Chapter 3 Filipino Social ValuesDocument6 pagesNSTP CWTS Chapter 3 Filipino Social ValuesRaging PotatoNo ratings yet
- National Service Training Program I Lesson I Citizenship TrainingDocument9 pagesNational Service Training Program I Lesson I Citizenship TrainingRonald AlmagroNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument18 pagesArt AppreciationLeigh Rence Alababa100% (1)
- HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS EXPLAINEDDocument15 pagesHIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS EXPLAINEDJoseph Enoch ElisanNo ratings yet
- Scholarship Form (Iskolar Ni Gob)Document1 pageScholarship Form (Iskolar Ni Gob)cedricXXXNo ratings yet
- General Orientation On RA 9165Document1 pageGeneral Orientation On RA 9165potaot100% (4)
- Propaganda MovementDocument13 pagesPropaganda MovementSamuel Castro0% (1)
- Critique Paper About SpoliariumDocument2 pagesCritique Paper About SpoliariumLourdes AmorNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System and Immunity - Seeleys - NotesDocument9 pagesLymphatic System and Immunity - Seeleys - NotesLol lol100% (2)
- Kartilya NG Katipunan by Emilio JacintoDocument7 pagesKartilya NG Katipunan by Emilio JacintoJvc CawiliNo ratings yet
- Report HistoryDocument6 pagesReport HistoryLysss EpssssNo ratings yet
- The Golden Rules of Emergency CareDocument8 pagesThe Golden Rules of Emergency CareRaven AvoNo ratings yet
- Definers of Rules Constricting Rules Positive Effects Negative Effects SchoolDocument1 pageDefiners of Rules Constricting Rules Positive Effects Negative Effects SchoolDanna Barredo0% (1)
- De-development and Zero Growth for a Sustainable FutureDocument1 pageDe-development and Zero Growth for a Sustainable FutureMillenieNo ratings yet
- Phcl111+Week+3+ +Pharmaceutical+MeasurementDocument38 pagesPhcl111+Week+3+ +Pharmaceutical+MeasurementRain Alyanna CuarterosNo ratings yet
- Drug EducationDocument48 pagesDrug EducationEdelyne MarzanNo ratings yet
- Trait Theories and Biological Factors in CriminologyDocument8 pagesTrait Theories and Biological Factors in CriminologyMuhammad HassanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Prohibited Drug Prevention and Drug EducationDocument16 pagesModule 4 Prohibited Drug Prevention and Drug EducationDannyelle SorredaNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Self Through Society and CultureDocument3 pagesUnderstanding the Self Through Society and CultureRenalyne Andres BannitNo ratings yet
- What Is Drug Education and TreatmentDocument6 pagesWhat Is Drug Education and TreatmentAdrian BagayanNo ratings yet
- Constitution of The PhilippinesDocument37 pagesConstitution of The PhilippinesJana Bautista-TeNo ratings yet
- CFA - Module - 7 - M7W13 - P1 DoneDocument2 pagesCFA - Module - 7 - M7W13 - P1 DoneAngelo ValdezNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument1 pageNSTPbwijjayNo ratings yet
- Act 3 EthicsDocument2 pagesAct 3 EthicsLopez Marc JaysonNo ratings yet
- Human Flourishing and The Pursuit of The Good LifeDocument19 pagesHuman Flourishing and The Pursuit of The Good Liferaprap camarinesNo ratings yet
- Philippine - American Special RelationsDocument2 pagesPhilippine - American Special RelationsPatNo ratings yet
- SybilDocument3 pagesSybilPatch Andres0% (1)
- Module 2 Drug EducationDocument33 pagesModule 2 Drug Educationlouie jay aguadoNo ratings yet
- UTS - The Sexual SelfDocument15 pagesUTS - The Sexual SelfHanz Christian PadiosNo ratings yet
- Drug AbuseDocument5 pagesDrug Abusenimra turkNo ratings yet
- Q: Is Looking After The Benefit of Your Own Family Overall Other Aspects Considered As Another Form of Egoism?Document1 pageQ: Is Looking After The Benefit of Your Own Family Overall Other Aspects Considered As Another Form of Egoism?Tat MadzNo ratings yet
- NE 8 - Marc Lou G. Apdian - Positive Filipino Trait ReflectionDocument1 pageNE 8 - Marc Lou G. Apdian - Positive Filipino Trait ReflectionmarcNo ratings yet
- Drug Education in The PhilippinesDocument32 pagesDrug Education in The PhilippinesTrixie Ann MenesesNo ratings yet
- Drug EducationDocument43 pagesDrug EducationFritzie Gaile C. BaniquedNo ratings yet
- Inbound 8079528717247421315Document45 pagesInbound 8079528717247421315EnahyahNo ratings yet
- The University of QueenslandDocument2 pagesThe University of Queenslandimmanuel nauk elokpereNo ratings yet
- 7306 31980 1 PBDocument10 pages7306 31980 1 PBRaihan Aditiya JuniorNo ratings yet
- KA B200 - B200C POH (BB-734 Thru BB-1443Document1,309 pagesKA B200 - B200C POH (BB-734 Thru BB-1443JULIAN OCAMPO100% (2)
- Rubber Conveyor Belt Wear ResistanceDocument5 pagesRubber Conveyor Belt Wear ResistanceBelt Power LLCNo ratings yet
- HZVDocument6 pagesHZVnurrozaqNo ratings yet
- Organization-and-Management Q1 LAS Wk1Document5 pagesOrganization-and-Management Q1 LAS Wk1Joyce CelineNo ratings yet
- Use of Passive VoiceDocument13 pagesUse of Passive VoiceLuciana DicieroNo ratings yet
- DesignMind Data WarehouseDocument31 pagesDesignMind Data WarehouseMark GinnebaughNo ratings yet
- G25M R TransmissionDocument29 pagesG25M R TransmissionMaksym VovkNo ratings yet
- MS6711 Data Mining Homework 1: 1.1 Implement K-Means Manually (8 PTS)Document6 pagesMS6711 Data Mining Homework 1: 1.1 Implement K-Means Manually (8 PTS)Yihan WangNo ratings yet
- Cargo Security Awareness - Etextbook - 2nd - Ed - 2016 - TCGP-79Document185 pagesCargo Security Awareness - Etextbook - 2nd - Ed - 2016 - TCGP-79kien Duy Phan80% (5)
- Environmental, Health and Safety Guidelines For Textiles ManufacturingDocument20 pagesEnvironmental, Health and Safety Guidelines For Textiles ManufacturingHitesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Excerpts From The Way of The Samurai (Shīdo) : Primary Source Document With Questions (DBQS)Document2 pagesExcerpts From The Way of The Samurai (Shīdo) : Primary Source Document With Questions (DBQS)Valeria MontalvaNo ratings yet
- Lect 1 Transforming EER Diagrams Into Relations (Part III)Document13 pagesLect 1 Transforming EER Diagrams Into Relations (Part III)KIM OFFNo ratings yet
- Biotensegrity and Myofascial Chains A Global Approach To An Integrated Kinetic ChainDocument8 pagesBiotensegrity and Myofascial Chains A Global Approach To An Integrated Kinetic ChainMohamed ElMeligieNo ratings yet
- An Engineer's Guide To Designing With Precision Amplifiers: E-BookDocument60 pagesAn Engineer's Guide To Designing With Precision Amplifiers: E-BookIan ChegeNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Lesson: Module 4 - Acids and BasesDocument3 pagesGrade 7 Lesson: Module 4 - Acids and BasesJoedelyn Wagas100% (4)
- PreceptronDocument17 pagesPreceptroneng_kmmNo ratings yet
- The Right Help at The Right Time: MatterDocument24 pagesThe Right Help at The Right Time: MattermariustudoracheNo ratings yet
- Spelling Bee Word ListDocument26 pagesSpelling Bee Word Listsan_6303No ratings yet
- CV of Dr. Mohammad TahirDocument12 pagesCV of Dr. Mohammad TahirMuhammad FayyazNo ratings yet
- Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti Language UniversityDocument30 pagesKhwaja Moinuddin Chishti Language UniversityShivam ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Types of DC Motors Notes Electric DrivesDocument77 pagesTypes of DC Motors Notes Electric DrivesJyothish VijayNo ratings yet
- SEO-Optimized Title for Document on English Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesSEO-Optimized Title for Document on English Exam Questionsminh buiNo ratings yet
- Legal Documents Evidence in Safety Related Proceedings 1663086621Document9 pagesLegal Documents Evidence in Safety Related Proceedings 1663086621richardNo ratings yet
- Impact of Sugarcane Molasses in Concrete As Time Retarding and Water Reducing AdmixtureDocument131 pagesImpact of Sugarcane Molasses in Concrete As Time Retarding and Water Reducing AdmixtureMohamed MoralesNo ratings yet
- Case3: What's in A Car 1. What Kind of Research Study Should Shridhar Undertake? Define TheDocument2 pagesCase3: What's in A Car 1. What Kind of Research Study Should Shridhar Undertake? Define TheRoshan kumar Rauniyar0% (3)
- Revised Bsy Elementary Siatonwest 2 and Pio-Macahig - 2014-15 As of June 6 2014Document31 pagesRevised Bsy Elementary Siatonwest 2 and Pio-Macahig - 2014-15 As of June 6 2014api-273918959No ratings yet
- Probability Concepts and Random Variable - SMTA1402: Unit - IDocument105 pagesProbability Concepts and Random Variable - SMTA1402: Unit - IVigneshwar SNo ratings yet