0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views4 pagesMachining Surface Finish Chart
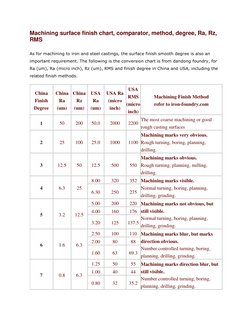
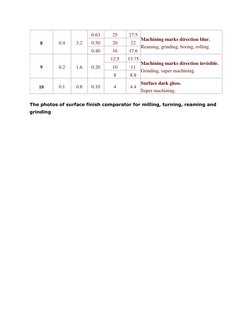
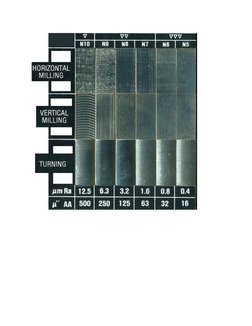
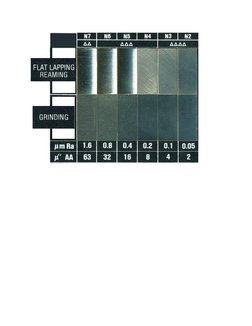
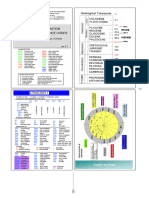
1. The document provides a conversion chart comparing surface finish measurements and degrees between China and the USA for machined iron and steel castings.
2. The surface finish is measured using parameters like Ra, Rz, and RMS roughness and is classified into 10 degrees ranging from very coarse to super fine.
3. The chart lists the numerical values of each parameter corresponding to each degree of finish and examples of machining methods that can achieve each level of surface smoothness.
Uploaded by
sunilCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views4 pagesMachining Surface Finish Chart
1. The document provides a conversion chart comparing surface finish measurements and degrees between China and the USA for machined iron and steel castings.
2. The surface finish is measured using parameters like Ra, Rz, and RMS roughness and is classified into 10 degrees ranging from very coarse to super fine.
3. The chart lists the numerical values of each parameter corresponding to each degree of finish and examples of machining methods that can achieve each level of surface smoothness.
Uploaded by
sunilCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd