Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Electrochemistry) (Answers)
Uploaded by
Shreyash KolekarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Electrochemistry) (Answers)
Uploaded by
Shreyash KolekarCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE TEST PAPER-04
CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Electrochemistry)
[ANSWERS]
Topic: -Kohlrausch Law & Electrolysis
1. An electrolyte that ionises completely in solution is a strong electrolyte eg. NaCl , CaCl2
etc and an electrolyte that ionizes partially in solution is weak electrolyte eg CH3
COOH , NH4OH etc.
2. Kohlrausch Law of independent migration states that limiting molar conductivity of an
electrolyte can be represented as the sum of the individual contributions of the anion
and cation of the electrolyte.
3. Relation between limiting molar conductance and degree of dissociation –
Ωm
α= where α = degree of dissociation
Ω om
λ m = molar conductance
λ m0 Limiting molar conductance
Relation between dissociation constant and limiting molar conductance –
C λ m2
Ka = where c = concentration
λ m0 (λ m 0 - λ m)
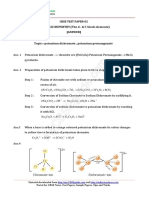
4. A = strong Electrolyte
B = weak Electrolyte
In case of B , it is not possible to get an exact value of limiting molar conductance.
5. λm 0 (NH 4 OH) = λm o (Na 4 Cl) + λm o (NaOH)-λm o (NaCl)
= 129.8 +217.4 – 108.9 = 237.3 5 cm2 /mol
λm 9.33 5 cm 2 / mol
Degree of dissociation , α = =
λ m0 237.3 5 cm 2 / mol
= 0.039 or 3.9 %.
6. Faraday’s Laws of electrolysis
First Law: The amount of chemical reaction which occurs at any electrode during
electrolysis by a current is proportional to the quantity of electricity
passed through the electrolyte.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Second Law: The amount of different substances liberated by the same quantity of
electricity passing through the electrolytic solution is proportional to
their chemical equivalent weights.
7. Faraday’s constant is the quantity of electricity carried by one mole of electrons.
1 F = 96500 C/mol
8. Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu
Two faradays are needed to reduce 1g mole Cu2+ ∴ 6 Faradays will be needed to
reduce 3g mole of Cu2+.
9. Q = It = 1× 15 × 60 = 900C
The reaction is 2Cl- → Cl2 + 2e-
2mol 1mol 2mol
∴ 2F . produces 1 mol of Cl2
1mol of Cl2 = 71g
∴ 2 × 96500 C produces 71g of Cl 2
71 900
900 C will produce × g = 0.331 g of Cl2.
2 96500
10. Q = It = 5X 193 = 965 C
96500C = 1 mol of electrons = 6.022X1023 mol-1
× 965
965 C = 6.022 X 1023
96500
21
= 6.022 × 10 electrons.
11. Zn2+ has higher reduction potential (-0.76v) Than H2O (- 0.83v) and therefore Zn2+ is
reduced to Zn preferentially at cathode.
12. 2.417 g of silver.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
You might also like
- New Yellow Book 01-07-2014Document115 pagesNew Yellow Book 01-07-2014scegts100% (2)
- CFA Level 2 Formula Sheets SampleDocument5 pagesCFA Level 2 Formula Sheets SampleBernard Bortey0% (1)
- Org Chem Lab ReportDocument5 pagesOrg Chem Lab ReportAyshee CapuchinoNo ratings yet
- LMS Solutions ElectrochemistryDocument200 pagesLMS Solutions ElectrochemistrySai Rithvik Kanakamedala80% (10)
- Chapter Three Kinetics of Electrochemical CellsDocument22 pagesChapter Three Kinetics of Electrochemical CellsBayan O. Abu SaadaNo ratings yet
- 12th Unit 9 ElectrochemistryDocument6 pages12th Unit 9 ElectrochemistryThahseen AfzalNo ratings yet
- Kohlrausch Law Chemistry Questions With SolutionsDocument7 pagesKohlrausch Law Chemistry Questions With SolutionsAdugnaw BiksNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Key Concepts: RT C D E E NF A BDocument6 pagesElectrochemistry Key Concepts: RT C D E E NF A BRohit ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Salt AnalysisDocument42 pagesChemistry Salt AnalysisVATSAL KHANDALNo ratings yet
- Chem Quiz 8Document10 pagesChem Quiz 8Gaurav ShekharNo ratings yet
- E.G. Ferrous - Ferric Electrode: Fe, Fe - PT(S) : A B A BDocument4 pagesE.G. Ferrous - Ferric Electrode: Fe, Fe - PT(S) : A B A BSudhanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: 2 303 G - RtlogkDocument7 pagesElectrochemistry: 2 303 G - RtlogkSnehashis BoseNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry PDFDocument10 pagesElectrochemistry PDFSulaiman KhanNo ratings yet
- 10 FullDocument4 pages10 FullroobanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ElectrochemistryDocument5 pagesChapter 3 ElectrochemistryPranshu VermaNo ratings yet
- Ck&e 1Document33 pagesCk&e 1Zekarias LibenaNo ratings yet
- Che 323 Problem Set 6: Electrochemistry March 12, 2014 Engr. May V. Tampus ConceptsDocument1 pageChe 323 Problem Set 6: Electrochemistry March 12, 2014 Engr. May V. Tampus ConceptsLouie G NavaltaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ElectrochemistryDocument23 pagesChapter 3 ElectrochemistryAnmay BalaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 Class 12 Chemistry (Electrochemistry)Document8 pagesCbse Test Paper-03 Class 12 Chemistry (Electrochemistry)raghupredator2No ratings yet
- Online Test On Electrochemistry PDFDocument2 pagesOnline Test On Electrochemistry PDFrvignesh2809No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - Workbook SolutionDocument41 pagesElectrochemistry - Workbook SolutionSamNo ratings yet
- 0BwSxA9Cnz5kvaVNNZzZpSENmdzg PDFDocument54 pages0BwSxA9Cnz5kvaVNNZzZpSENmdzg PDFThakur Aryan Singh100% (2)
- Revision Note Ajc-1Document8 pagesRevision Note Ajc-1Madhavilatha LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Problems in ElectrochemistryDocument9 pagesProblems in Electrochemistryrohit kohliNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 3Document22 pages12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 3Deepak PradhanNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis/ Electrochemistry: Shall We Begin A New Age of KnowledgeDocument21 pagesElectrolysis/ Electrochemistry: Shall We Begin A New Age of Knowledgeguru beesmartNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis/ Electrochemistry: Shall We Begin A New Age of KnowledgeDocument21 pagesElectrolysis/ Electrochemistry: Shall We Begin A New Age of Knowledgeguru beesmartNo ratings yet
- XIIElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesXIIElectrochemistryAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument8 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYlatestdaaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Notes 2Document6 pagesElectrochemistry Notes 2Riya JoseNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry PPT NotesDocument23 pagesElectrochemistry PPT NotesHemanshi KocharNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic ConductanceDocument8 pagesElectrolytic Conductancevijaye36100% (1)
- NEET UG Chemistry Redox Reactions and ElectrochemistryDocument24 pagesNEET UG Chemistry Redox Reactions and ElectrochemistryAmanNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument176 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYgsvssumaNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY Worksheet With AnswersDocument5 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRY Worksheet With AnswersG.D. Pranav.LaskhminarasimhanNo ratings yet
- 2.electrochemistry QB (2023-24)Document6 pages2.electrochemistry QB (2023-24)Shana Chandran 18083No ratings yet
- Hello ChemDocument14 pagesHello ChemAndreiFoxNo ratings yet
- Polar Iz AbilityDocument5 pagesPolar Iz AbilityManaviNo ratings yet
- 6) 2020 ElectrochemistryDocument14 pages6) 2020 ElectrochemistryFaizan AnsariNo ratings yet
- Revision - Electrochemistry (Cbse 2023)Document2 pagesRevision - Electrochemistry (Cbse 2023)Sahana BanuNo ratings yet
- (Chapter 3) (Electrochemistry) : Intext QuestionsDocument8 pages(Chapter 3) (Electrochemistry) : Intext QuestionsVeerNo ratings yet
- NOtes ElectroChm CalculationDocument12 pagesNOtes ElectroChm CalculationmohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- 03 04 Faradays Laws of Electrolysis and ApplicationsDocument12 pages03 04 Faradays Laws of Electrolysis and ApplicationsPavan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Ncertt SolutionDocument28 pagesElectrochemistry Ncertt SolutionREJA MUKIB KHANNo ratings yet
- PolarizabilityDocument9 pagesPolarizabilityFabioNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument2 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYShivaanee SKNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument9 pagesElectrochemistryrandom idNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument47 pagesElectrochemistryUtshav paudelNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Class XIDocument17 pagesElectrolysis Class XIPrashantNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ElectrochemistryDocument8 pagesUnit 3 ElectrochemistryYashvee GuptaNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistyDocument21 pagesElectrochemistyAagash PranavNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction: Grade Xi Chiran Dhakal MSC Chemistry CDC KirtipurDocument36 pagesOxidation and Reduction: Grade Xi Chiran Dhakal MSC Chemistry CDC KirtipurDipesh KhatriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - ElectrochemistryDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - ElectrochemistryMADHAVNo ratings yet
- Sr-Chem QB 23-24 - UjcDocument42 pagesSr-Chem QB 23-24 - Ujcunitedrj.hgpNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 04 PDFDocument1 page12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 04 PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH03 Electro Chemistry 02 PDFDocument9 pages12 Chemistry Impq CH03 Electro Chemistry 02 PDFamanNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH03 Electro Chemistry 02 PDFDocument9 pages12 Chemistry Impq CH03 Electro Chemistry 02 PDFamanNo ratings yet
- DG QDN NHJo L7 JWDW 0 NAdcDocument7 pagesDG QDN NHJo L7 JWDW 0 NAdcarindamNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - Revision Session-HandbookDocument5 pagesElectrochemistry - Revision Session-HandbookDamsNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - UNIT 2Document38 pagesElectrochemistry - UNIT 2shrijNo ratings yet
- PART-2 ElectrochemistryDocument32 pagesPART-2 ElectrochemistrySangeetha RajaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsFrom EverandElectrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsAndrzej LewenstamNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes) (Answers)Document3 pagesCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes) (Answers)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements) (Answers)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements) (Answers)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes) (Answer)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes) (Answer)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements) (Answers)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements) (Answers)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements) (Answers)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements) (Answers)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Test 05 Answer s2l6 PDFDocument2 pages12 Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Test 05 Answer s2l6 PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- CHCHCHBR X Y Z: Cbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes)Document1 pageCHCHCHBR X Y Z: Cbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds Test 03 PDFDocument1 page12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds Test 03 PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds)Document3 pagesCbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds) (Answer)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds) (Answer)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds) (Answer)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds) (Answer)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements) (Answers)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements) (Answers)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements) (Answer)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements) (Answer)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-04 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements) (Answer)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements) (Answer)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-05 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-05 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Coordination Compounds)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 02 PDFDocument2 pages12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 02 PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 01 Answer 8b9m PDFDocument2 pages12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 01 Answer 8b9m PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Electrochemistry) (Answers)Document3 pagesCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Electrochemistry) (Answers)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements) (Answer) Topic: - F-Block Elements: Lanthanoids and ActinoidsDocument1 pageCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (The D - & F-Block Elements) (Answer) Topic: - F-Block Elements: Lanthanoids and ActinoidsShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Electrochemistry) (Answers)Document2 pagesCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Electrochemistry) (Answers)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 03 PDFDocument1 page12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 03 PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 05 PDFDocument1 page12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 05 PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 04 PDFDocument1 page12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 04 PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Project Report GodrejDocument92 pagesProject Report Godrejshubham SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Thermax Power BrochureDocument32 pagesThermax Power BrochurerovilbhaiNo ratings yet
- Apostila Ansys TrainingDocument586 pagesApostila Ansys TrainingJorge Mauricio de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods in Rock MechanicsDocument24 pagesNumerical Methods in Rock Mechanicsali100% (2)
- 4.1 Thick Walled CylindersDocument27 pages4.1 Thick Walled CylindersDASitchNo ratings yet
- Summary and Future WorkDocument10 pagesSummary and Future WorkofilipNo ratings yet
- Testing and Modeling of Soil-Structure InterfaceDocument10 pagesTesting and Modeling of Soil-Structure InterfaceANKIT KUMARNo ratings yet
- Solve For X If 8Document3 pagesSolve For X If 8Gellie BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- en Centrifuge 12 DG SpinDocument50 pagesen Centrifuge 12 DG SpinDodik E. PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Guía de Usuario Hisense HLTE 223EDocument10 pagesGuía de Usuario Hisense HLTE 223ERaúl RivasNo ratings yet
- CRB03 CRB05 For Boric Acid Removal 2005-09 Rev 01 2000-02Document13 pagesCRB03 CRB05 For Boric Acid Removal 2005-09 Rev 01 2000-02MildoggNo ratings yet
- Module 2 (Answered)Document33 pagesModule 2 (Answered)Roland Paul PrincipeNo ratings yet
- LG Chem TDS SP988 EnglishDocument1 pageLG Chem TDS SP988 EnglishSérgio BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Imploding Strong Shock Wave in Uniform Real Dusty GasDocument10 pagesCylindrical Imploding Strong Shock Wave in Uniform Real Dusty GasIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Modulare Systems For Conveyor PlantsDocument36 pagesModulare Systems For Conveyor Plantsado31No ratings yet
- Laserframe Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesLaserframe Brochure PDFsdewssNo ratings yet
- C196e059a Catalogo Hic SP e NPDocument8 pagesC196e059a Catalogo Hic SP e NPcamilavignaNo ratings yet
- Periodic TrendsDocument30 pagesPeriodic TrendsMaureen GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Gen NotesDocument1 pageGen NotesGian OrillosaNo ratings yet
- s-20ph10 - Electromagnetic Induction Motional and Induced Emf Faraday's LawDocument26 pagess-20ph10 - Electromagnetic Induction Motional and Induced Emf Faraday's LawsetsunaNo ratings yet
- Air CoolersDocument18 pagesAir CoolersPRATIK P. BHOIRNo ratings yet
- Tables of Properties of HC Copper ConductorsDocument7 pagesTables of Properties of HC Copper ConductorsSaid WahdanNo ratings yet
- Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer: Contents Lists Available atDocument67 pagesJournal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer: Contents Lists Available atKamal Singh ThapaNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document40 pagesChap 2squishyapply100% (1)
- Solar System PV Calculation and DesignDocument3 pagesSolar System PV Calculation and DesignMustafa Tasci100% (1)
- AM FShpEmbreak2168 enDocument1 pageAM FShpEmbreak2168 enRamirez FrancisNo ratings yet
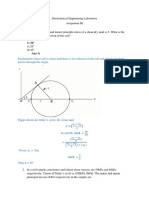
- Geotechnical Engineering Laboratory (Noc19 - Ce36) - Week 3, Assignment 3 - SolutionDocument4 pagesGeotechnical Engineering Laboratory (Noc19 - Ce36) - Week 3, Assignment 3 - SolutionAKASH MAURYANo ratings yet