Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Material
Uploaded by
Aakshi JairathCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Material
Uploaded by
Aakshi JairathCopyright:
Available Formats
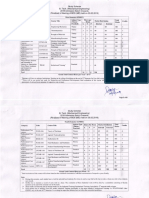
# Course Title : Basic Material Sciences Weightage
1 Course Objectives: The aim of the present course is to acquaint the students with various
methods of material fabrications, their characterization and applications.
2 Prerequisites: Graduate level chemistry and thermal physics
Annexure ‘AAB-
3 Student Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to demonstrate the knowledge of CD-01a’
modern materials, their synthesis and characterization techniques alongwith technical L T P/ SW/F TOTAL
aaplications. S W CREDIT
Course Contents / Syllabus: UNITS Course
4 Module I Introduction to materials 25
3 3 Title:
Basic
Classification of technical materials, Non crystalline solids, Metals and alloys, Single
crystals, Poly crystalline materials, Ceramics and Glasses. Liquid crystals and quasi Material Sciences
crystals. Polymers and composites: Structure and characteristics. Thick and thin films of
materials, Nanomaterials: nano clusters, nano particles and nano tubes. Course Code: to be decided later
5 Module II Synthesis techniques 25 Credit Units: 3
Level: Undergraduate
Phase diagram, Gibbs phase Rule, Two component system, Nucleation, Grain Growth,
crystal growth techniques, Czochralski technique, Solid state reaction, Ceramic Forming
processes, Glass forming methods, Thick film processing, Thin film synthesis techniques
6 Module III Characterization techniques 25 Please give your valuable feedback ratings (on the
Microstructure: Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Atomic force microscopy (AFM) scale of 6 points) for following course curriculum
Structural analysis: Powder X-ray diffractometery (XRD), Dilatometry technique for with respect to relevance to Industry / Profession:
thermal expansion, Photoluminescence spectroscopy, Impedance measurement
techniques, measurement of dielectric constant and loss.
7 Module IV Properties and applications of materials 25
Stress – strain behaviour, Elastic, anelastic and viscoeleastic behaviour, Heat capacity,
density and thermal expansion of crystals and glasses, thermal conductivity, Band theory
of solids, Indirect and direct band gap semiconductors, dc and ac electrical conductivities,
electrical polarization mechanisms, complex impedance, admittance and dielectric
constant, Dia, para and ferromagnetic materials, hard and soft magnetic materials.
Refraction and absorption of light in materials, complex refractive index. Applications of Text:
engineering materials.
1. Material Science and Engineering: An
8 Pedagogy for Course Delivery: Marker-Board introduction, W D Callister Jr, Wiley India, 2010.
2. Materials Science, M S Vijaya and G Rangrajan,
Tata McGrawhill, 2011.
9
Assessment/ Examination Scheme:
Theory L/T (%) Lab/Practical/Studio (%) total
3. Physics of Semiconductor Devices, S M Sze, Wiley (2007).
4. Ceramic Materials for Electronics, R C Buchanan (Ed), Marcel Dekker Inc, (1991).
5. Nano: The Essentials, T Pradeep, Tata McGraw Hill, (2007).
6. Thin Film Phenomena, K L Chopra, Mc Graw Hill (1969).
Remarks and Suggestions:
Suggested Book: MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING :A FIRST COURSE, V. Raghavan, PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd.
Dr. O.P. Thakur, Scientist ‘F’, Solid state Physics Laboratory, DRDO, Delhi
_______________________________
Date: 30th May, 2014 Name, Designation, Organisation
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Free Veg Nutrition Plan YSF PDFDocument8 pagesFree Veg Nutrition Plan YSF PDFBhuvanNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Poster ScheduleDocument16 pagesPoster ScheduleAakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Pg. 200 PDFDocument1 pagePg. 200 PDFAakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Pearl InternationalAuthorisationDocument1 pagePearl InternationalAuthorisationAakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Bus 125Document14 pagesBus 125Aakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Fastandfurious PDFDocument1 pageFastandfurious PDFAakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Davisco PDFDocument1 pageDavisco PDFAakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- Upper Lower4day PDFDocument1 pageUpper Lower4day PDFJsn Pl Cabg-sNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- OBESE 60 WORKOUT PLAN by Guru Mann PDFDocument4 pagesOBESE 60 WORKOUT PLAN by Guru Mann PDFAkul ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 5 Day Push Pull Leg SplitDocument4 pages5 Day Push Pull Leg SplitSudeep NNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- DR Physique Lean Bulking Plan 2017Document64 pagesDR Physique Lean Bulking Plan 2017Andreea Mocian100% (1)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- ELEctronicDocument3 pagesELEctronicAakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Preparation of Buffer: Experiment No: 1 DateDocument5 pagesPreparation of Buffer: Experiment No: 1 DatePraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- USN GAIN MASSIVE MUSCLE Training Plan PDFDocument2 pagesUSN GAIN MASSIVE MUSCLE Training Plan PDFOsbaldo SalazarNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Legal Steroids PDF (V2) PDFDocument22 pagesLegal Steroids PDF (V2) PDFAakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Zhang Presentation NanoCampDocument30 pagesZhang Presentation NanoCampAakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- X RayDocument5 pagesX RayAakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Which Is A Better RelationshipDocument16 pagesWhich Is A Better RelationshipAakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- 2 - Dairy Management - Animal Breeds, Animal Feed, Dairy Products - ImpDocument6 pages2 - Dairy Management - Animal Breeds, Animal Feed, Dairy Products - ImpAakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document1 pagePresentation 2Aakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument11 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Presentation 1Document3 pagesPresentation 1Aakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- The Trade of Bear Gall Bladders and Bear Bile Is A Serious Threat To The Conservation of Asian Bear SpeciesDocument1 pageThe Trade of Bear Gall Bladders and Bear Bile Is A Serious Threat To The Conservation of Asian Bear SpeciesAakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- Pearl InternationalAuthorisationDocument1 pagePearl InternationalAuthorisationAakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- Shopping List For Muscle Building by FoodspringDocument5 pagesShopping List For Muscle Building by FoodspringMostafa SennaNo ratings yet
- MI40-X - Supplement GuideDocument22 pagesMI40-X - Supplement GuideBhimsen Budhathoki95% (20)
- Infographic Poultry Processing LineDocument1 pageInfographic Poultry Processing LineDANIAL FITRI BIN MUSTAPANo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- PollutionDocument5 pagesPollutionAakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- DaviscoDocument1 pageDaviscoAakshi JairathNo ratings yet
- Rao Gunti, Asokan - 2012 - Thermodynamic, Raman and Electrical Switching Studies On Si15Te85-xAgx (4 X 20) Glasses (3) - AnnotatedDocument6 pagesRao Gunti, Asokan - 2012 - Thermodynamic, Raman and Electrical Switching Studies On Si15Te85-xAgx (4 X 20) Glasses (3) - AnnotatedJagan KbNo ratings yet
- Biochemical TestsDocument2 pagesBiochemical TestsJacqueline DavisNo ratings yet
- Reactor Design ReportDocument12 pagesReactor Design Reportعلی محمد قادر خضرNo ratings yet
- ThermoFlex Service ManualDocument90 pagesThermoFlex Service ManualDavide RadaelliNo ratings yet
- Subatomic Particles Models of An AtomDocument36 pagesSubatomic Particles Models of An AtomrayNo ratings yet
- Unit V EvaporationDocument23 pagesUnit V EvaporationpavijayaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy Storage - Exercises 2022-2023Document32 pagesThermal Energy Storage - Exercises 2022-2023Michiel WalNo ratings yet
- Wright (Heat) (1893)Document374 pagesWright (Heat) (1893)Marcelo Silvano de CamargoNo ratings yet
- Case Study Karthik - SansDocument16 pagesCase Study Karthik - SansKarthik B KamathNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals On HVAC Systems PresentationDocument52 pagesFundamentals On HVAC Systems PresentationJane NixonNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Study On The Temperature Variation Inside The Biodigester of Modified 2 m3 GGC 2047 Biogas PlantDocument5 pagesStudy On The Temperature Variation Inside The Biodigester of Modified 2 m3 GGC 2047 Biogas PlantEr Shankar Singh DhamiNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction 24898Document20 pagesReflection and Refraction 24898Yay SandovalNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Slides - CHE304 - Chapter 26Document51 pagesMass Transfer Slides - CHE304 - Chapter 26RehabNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment Grade 11Document9 pagesSummative Assessment Grade 11Tamerlan KudaibergenNo ratings yet
- Partial Molar Free EnergyDocument15 pagesPartial Molar Free EnergyArshit Dobriya0% (1)
- PMC National MDCAT Syllabus 2020 19-10-2020Document46 pagesPMC National MDCAT Syllabus 2020 19-10-2020Mughees AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mohd Zafri Bin Mazri - 12694 - Chemical Engineering - Cold Energy Utilization From LNG Regasification PDFDocument75 pagesMohd Zafri Bin Mazri - 12694 - Chemical Engineering - Cold Energy Utilization From LNG Regasification PDFThanh Phong NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Btech Syllabus For Gndec LudhianaDocument38 pagesBtech Syllabus For Gndec Ludhianaਅਰ ਜੋਤNo ratings yet
- A Energetics Notes Chem Unit 1 - (New)Document8 pagesA Energetics Notes Chem Unit 1 - (New)Khaila SimmondNo ratings yet
- Lec 8 NeutralizationDocument32 pagesLec 8 Neutralizationhaseeb tahirNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Boyle's LawDocument1 pageActivity 2 - Boyle's LawEderwil Labora75% (4)
- D FaseDocument34 pagesD FaseDien BachtiarNo ratings yet
- POSTLAB 9 - Heat of Formation of NaClDocument7 pagesPOSTLAB 9 - Heat of Formation of NaClRaniel Miranda100% (1)
- Chapter 3 MixturesDocument14 pagesChapter 3 MixturesHazel Penix Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 541 TitrimetryDocument5 pages541 TitrimetryCristian GomezNo ratings yet
- Cyclone Design - Stairmand MethodDocument4 pagesCyclone Design - Stairmand MethodFaizan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Answers Kinetics 2Document12 pagesAnswers Kinetics 2migdalr2100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Buffer SolutionDocument20 pagesLesson Plan Buffer SolutionNurmlia100% (1)
- Form of Corrosion and Their Example in Real Life - MUHAMMADHAMZA FAROOQDocument11 pagesForm of Corrosion and Their Example in Real Life - MUHAMMADHAMZA FAROOQSyed Hassan.911No ratings yet
- WaterDocument8 pagesWaterMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet