Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Load Flow Study in Buet
Uploaded by
হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Load Flow Study in Buet
Uploaded by
হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যCopyright:
Available Formats
EEE 306 Power System I Laboratory
Experiment 2
Load flow Study of a Power System
Objectives
In this experiment, load flow study for a 7-bus system will be performed. CYMEPSAF software will
be used for this purpose.
Introduction
The performance of a power system in steady state condition is of primary importance for utility
agencies. Given a specified load condition, the basic question to be answered are:
- What are the line and transformer loads throughout the system?
- What are the voltages throughout the system?
We are particularly interested in answering these questions as we evaluate proposed changes in an
existing system such as:
- New generation sites
- Projected load growth
- New transmission line
Load flow solution of a system provides these essential information.
Application of the software CYMEPSAF
Follow the steps described below:
1. Create a new folder in any drive of your PC.
2. Open the software PSAF 2.81. From ‘Database’ menu, select ‘New Blank Database
Directory’ to show the path of the folder created in step 1.
3. From ‘File’ menu, select ‘Preferences’ to open ‘Preference settings’ window. Under
‘Directory’ tab, select ‘DATABASE’ under ‘Item’ and click ‘Browse’ to show the ‘Path’ of
the folder created in step 1. Do the same for ‘NETWORK’ under ‘Item’.
4. From ‘File’ menu, select ‘New Study’. In ‘Loading Network Data’ window, select ‘Use
tabular format’ for network data presentation and click ‘OK’. Next select ‘creating a new
network’ in ‘New Study Dialog’ window and ‘Default 1 bus’ in ‘New Network Dialog’
window.
5. Create the network by using tabular format.
Dept. of EEE, BUET P age |1
EEE 306 Power System I Laboratory
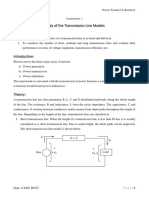
Fig. 1: One-line diagram of the 7-bus system in study
Power Flow Analysis
1. Using the information given in the following tables, create the network shown in Fig. 1.
Bus
ID Base kV Operating kV
B1 11 11
B2 132 132
B3 11 11
B4 132 132
B5 11 11
B6 132 132
B7 132 132
Fixed-tap transformer
From To Primary Secondary Rating Z1 X1/R1 Standard Loading
Bus Bus kV kV (MVA) (p.u.) Limit (MVA)
B1 B2 11 132 400 0.015 12.5 400
B3 B4 11 132 500 0.012 12.0 500
B5 B6 11 132 250 0.024 12.0 250
Dept. of EEE, BUET P age |2
EEE 306 Power System I Laboratory
Generator
Bus Type Voltage Rating Active generation Max. Min.
ID (kV) (MVA) (MW) (MVAR) (MVAR)
B1 Swing 11 650 - - -
B3 Voltage 11 750 500 400 -300
Controlled
B5 Voltage 11 400 200 140 -100
Controlled
Line
From To kV Loading limit R1 X1 B1 Length
Bus Bus level (Amps) (Ohms/km) (Ohms/km) (μ.S./km) (km)
2 6 132 800 0.4 2.4 155.5 10
4 7 132 800 0.4 2.4 155.5 10
2 4 132 800 0.4 2.4 155.5 6.52
6 7 132 800 0.4 2.4 155.5 6.52
Load
Bus ID P (MW) Q (MVAR)
B2 200 30
B3 60 8
B4 200 20
B5 50 5
B6 100 30
B7 200 50
2. From ‘Analysis’ menu, click ‘Select Solver’. Select ‘Power Flow Analysis’ in ‘Engine
Selection Dialog’ window.
3. From ‘Analysis’ menu, select ‘Study’. In ‘Load Flow Study Dialog’ window under the
‘Monitoring’ tab, click ‘Select’. A window showing the message ’23 components selected!’
(the number will vary depending on the number of components in the network) will appear.
Click ‘Ok’. Then click ‘Ok’ again to close ‘Load Flow Study Dialog’ window.
4. From ‘Analysis’ menu, select ‘Solve’. In ‘Load Flow Solver Dialog’ window, select
‘Newton-Raphson’ under ‘Method’, select ‘Flat start’ and deselect ‘Apply constraints’ under
‘Options’. Then click ‘Solve!’.
Dept. of EEE, BUET P age |3
EEE 306 Power System I Laboratory
5. From ‘Report’ menu, select ‘Show Text Report’. Report will appear on the bottom part of the
window.
Study:
From the report of CYMEPSAF, voltage magnitude and voltage angle of the buses, power flow
through the lines, power losses etc. will be known. You have to identify different abnormal
conditions (overloaded and underloaded lines and transformers, buses outside voltage limit etc.) from
the results. You have to determine what to do in order to ameliorate these conditions. For example,
you can add capacitor bank (static VAR compensator) at the buses to improve the bus voltages. You
can also add additional lines to improve overloaded line conditions. Additional lines might also
improve the bus voltages.
Report:
Add a new generator having capacity of 200 MW connected through a transformer of appropriate
rating to bus 7 of the system in Fig. 1. Perform load flow analysis for the changed network
configuration.
1. Mention the abnormal conditions prevailing at different parts of the system.
2. Propose necessary modifications to remove the abnormal conditions. Perform power flow
analysis for your proposed network and demonstrate the improvement you achieved.
3. What is the role of ‘swing generator’ in load flow analysis? How is the real and reactive
power of the swing generator calculated?
4. Write short note on ‘static VAR compensator’.
Reference:
1. Power System Analysis – John J. Grainger and William D. Stevenson, Jr.
Dept. of EEE, BUET P age |4
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Brac Bank ACCountDocument1 pageBrac Bank ACCountহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Annexure 1Document3 pagesAnnexure 1হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- E-GP Registration and Tendering Process enDocument3 pagesE-GP Registration and Tendering Process enহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Circular 16172Document2 pagesCircular 16172হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- 2019 04 11 17 21 44 PPA 2006, PPR 2008 With All Amendments Up To January, 2019 PDFDocument274 pages2019 04 11 17 21 44 PPA 2006, PPR 2008 With All Amendments Up To January, 2019 PDFMd Shamim HasanNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Annexure 1Document4 pagesAnnexure 1হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- Ar (t"Lc'4: Qr3reDocument3 pagesAr (t"Lc'4: Qr3reহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Constructs Ex-OR Gate Using Basic Gates and Verify Its/ Constructs Ex-NOR Gate Using Basic Gates and Verify Its.Document4 pagesConstructs Ex-OR Gate Using Basic Gates and Verify Its/ Constructs Ex-NOR Gate Using Basic Gates and Verify Its.হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Tft0'lb (Ql-Cn. - : FrffiDocument1 pageTft0'lb (Ql-Cn. - : Frffiহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Transmission Network Map MainDocument1 pageTransmission Network Map Mainহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Construction of All Basic Gates Using Universal (NAND/NOR) Gates and Verify Its.Document4 pagesConstruction of All Basic Gates Using Universal (NAND/NOR) Gates and Verify Its.হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Verify The Truth Table For Basic Gates and Others Logic Gates.Document2 pagesVerify The Truth Table For Basic Gates and Others Logic Gates.হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- Construction of All Basic Gates Using Universal (NAND/NOR) Gates and Verify Its.Document4 pagesConstruction of All Basic Gates Using Universal (NAND/NOR) Gates and Verify Its.হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Chemistry Class9 Part1Document5 pagesChemistry Class9 Part1হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Uncertainty of ElectronDocument1 pageUncertainty of Electronহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- Generic Wind by PSSEDocument31 pagesGeneric Wind by PSSEহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Differentiation Test: Marks:100 Time:1.30 HoursDocument2 pagesDifferentiation Test: Marks:100 Time:1.30 Hoursহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- Word Collection by MEDocument2 pagesWord Collection by MEহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Higher K Value or Lower PK Valu Indicates Strong AcidDocument3 pagesHigher K Value or Lower PK Valu Indicates Strong Acidহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Equation Editor The Word 2007/2010 Equation Editor Shortcut CommandsDocument11 pagesEquation Editor The Word 2007/2010 Equation Editor Shortcut CommandspanchopanzaNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Equation Editor The Word 2007/2010 Equation Editor Shortcut CommandsDocument11 pagesEquation Editor The Word 2007/2010 Equation Editor Shortcut CommandspanchopanzaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 PDFDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 PDFJarin TasnimNo ratings yet
- Some Information About PointerDocument1 pageSome Information About Pointerহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- PSP Lab 1Document5 pagesPSP Lab 1হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্য0% (1)
- Prepared by Hasin Mussayab Ahmed, Lecturer, Dept of EEE, UU: Power Plant Engineering Lecture On Nuclear Power PlantDocument26 pagesPrepared by Hasin Mussayab Ahmed, Lecturer, Dept of EEE, UU: Power Plant Engineering Lecture On Nuclear Power Plantহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- AP Electron Config U ExceptionsDocument8 pagesAP Electron Config U Exceptionsহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- Editable - Application For Learner's Driving LicenseDocument2 pagesEditable - Application For Learner's Driving LicenseFoisul AlamNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Fault AnalysisDocument5 pagesFault Analysisহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্য100% (1)
- Short Circuit Study For A Test NetworkDocument32 pagesShort Circuit Study For A Test Networkহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Writing Baby First TermDocument12 pagesScheme of Work Writing Baby First TermEmmy Senior Lucky100% (1)
- WSDL Versioning Best PracticesDocument6 pagesWSDL Versioning Best Practiceshithamg6152No ratings yet
- Academics: Qualification Institute Board/University Year %/CGPADocument1 pageAcademics: Qualification Institute Board/University Year %/CGPARajesh KandhwayNo ratings yet
- Hostel Survey Analysis ReportDocument10 pagesHostel Survey Analysis ReportMoosa NaseerNo ratings yet
- Sequential Circuit Description: Unit 5Document76 pagesSequential Circuit Description: Unit 5ramjidr100% (1)
- Comparative Analysis of Oyo & Ginger Grp-9 PDFDocument31 pagesComparative Analysis of Oyo & Ginger Grp-9 PDFadityakr2410100% (1)
- Chapter 4Document21 pagesChapter 4Ahmad KhooryNo ratings yet
- Case Study Sustainable ConstructionDocument5 pagesCase Study Sustainable ConstructionpraisethenordNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Mid Term Syllabus 202324Document4 pagesClass 10 Mid Term Syllabus 202324Riya AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Conductivity On Animal SpermDocument8 pagesConductivity On Animal SpermAndrew AdamsNo ratings yet
- Five TemperamentDocument5 pagesFive TemperamentDhaivatPatelNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Jillin ExplosionDocument10 pagesJillin ExplosionArjun ManojNo ratings yet
- Second Form Mathematics Module 5Document48 pagesSecond Form Mathematics Module 5Chet AckNo ratings yet
- Sap 47n WF TablesDocument56 pagesSap 47n WF TablesjkfunmaityNo ratings yet
- El Otro Lado PDFDocument21 pagesEl Otro Lado PDFRichard OssandónNo ratings yet
- Project Management GUIDE 2020: Revision 1Document27 pagesProject Management GUIDE 2020: Revision 1lorranaNo ratings yet
- 12.22.08 Dr. King Quotes BookletDocument16 pages12.22.08 Dr. King Quotes BookletlamchunyienNo ratings yet
- Guide Specification - SDP 200: GeneralDocument10 pagesGuide Specification - SDP 200: GeneralhbookNo ratings yet
- Attachment 4A Security Classification GuideDocument42 pagesAttachment 4A Security Classification GuidepingNo ratings yet
- Psionic Bestiary - Phrenic HegemonyDocument12 pagesPsionic Bestiary - Phrenic HegemonyEduardo Ferreira SuzartNo ratings yet
- Function, Roles, and Skills of A Manager: Lesson 3Document12 pagesFunction, Roles, and Skills of A Manager: Lesson 3Christine Joy ResponteNo ratings yet
- Qualifications Recruitment Promotions Scheme - University AcademicsDocument10 pagesQualifications Recruitment Promotions Scheme - University Academicsuteachers_slNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document13 pagesChapter 6Melissa Nagy100% (1)
- Learning StylesDocument10 pagesLearning Stylesrose marie RegalaNo ratings yet
- A CEO Job Description: by Stever RobbinsDocument7 pagesA CEO Job Description: by Stever RobbinsSameer YadavNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire of Measuring Employee Satisfaction at Bengal Group of IndustriesDocument2 pagesQuestionnaire of Measuring Employee Satisfaction at Bengal Group of IndustriesMuktadirhasanNo ratings yet
- GVP CmdsDocument3 pagesGVP CmdsShashank MistryNo ratings yet
- NOLS 2014 Fall Catalog PDFDocument60 pagesNOLS 2014 Fall Catalog PDFcoldflame81No ratings yet
- Black-Scholes Excel Formulas and How To Create A Simple Option Pricing Spreadsheet - MacroptionDocument8 pagesBlack-Scholes Excel Formulas and How To Create A Simple Option Pricing Spreadsheet - MacroptionDickson phiriNo ratings yet
- Data MiningDocument14 pagesData MiningRavi VermaNo ratings yet
- Crossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetFrom EverandCrossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- The Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeFrom EverandThe Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (59)
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansFrom EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansNo ratings yet
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignFrom EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (137)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataFrom EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Summary of Neil Postman's Amusing Ourselves to DeathFrom EverandSummary of Neil Postman's Amusing Ourselves to DeathRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- The Finite Element Method: Linear Static and Dynamic Finite Element AnalysisFrom EverandThe Finite Element Method: Linear Static and Dynamic Finite Element AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)