Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Xanthoproteic Test
Uploaded by
Lou Andrae G. SantosCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Xanthoproteic Test
Uploaded by
Lou Andrae G. SantosCopyright:
Available Formats
3.
Xanthoproteic Test
This test used to determine aromatic amino acids containing in a protein solution that
which gives a yellow color solution. By heating the solution with concentrated Nitric acid, the
aromatic benzene ring will undergo nitration process in which produces yellow colored product.
On adding an alkali in these nitro derivative salts, the color change from yellow to orange.
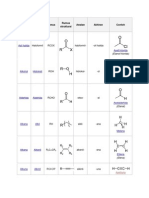
Table 3. Xanthoproteic test results:
Sample Figure Observation
Tryptophan (+) Yellow solution, became
orange upon addition of NaOH
Fig. 3.1 reaction with NaOH
Tyrosine (+) Light yellow solution,
became yellow upon addition
of NaOH
Fig. 3.2 reaction with NaOH
Glycine (-) Clear solution remains
colorless upon addition of
NaOH
Fig. 3.3 reaction with NaOH
Alanine (-) Clear solution remains
colorless upon addition of
NaOH
Fig. 3.4 reaction with NaOH
Phenylalanine (-) Clear solution remains
colorless upon addition of
NaOH
Fig. 3.5 reaction with NaOH
Results and Discussion
As shown in table 3, both figure 3.1 (tryptophan) and 3.2 (tyrosine) yields a positive result
that turned into yellow solution, which means the sample protein solution contains amino acids.
The intensity of the yellow color deepens when the reaction occurs by adding the basic solution
and the nitric acid gives a color yellow when heated with proteins, thus the color is due to nitration.
Figure 3.6 Chemical reaction of tyrosine and tryptophan
Nitration takes place on the benzene rings and the reaction is therefore specific for
aromatic nuclei (Gortner, 1929). Thus, this test is for proteins depending on the presence of amino
acids. Phenylalanine gives negative or weakly positive reaction though this amino acid contains
aromatic nucleus because it is difficult to nitrate under normal condition and benzene ring is not
activated which is colorless solution. (figure 3.5 shown) while figure 3.3 (glycine) and figure 3.4
(alanine) did not yield a positive result because there is an absence of phenol in their structure
that is needed in the chemical reaction of the sample.
You might also like
- Protein Solubility pH EffectDocument3 pagesProtein Solubility pH EffectDan Floyd FernandezNo ratings yet
- 03 NormalityDocument49 pages03 NormalityEdna Lip AnerNo ratings yet
- Formal Biochem Lab Report - Isolation and Hydrolysis of GlutenDocument1 pageFormal Biochem Lab Report - Isolation and Hydrolysis of GlutenIke BravoNo ratings yet
- Module Anachem Acid-Base 2Document9 pagesModule Anachem Acid-Base 2arejay castroNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Lab ReportDocument10 pagesCarbohydrates Lab ReportMarice Abigail MarquezNo ratings yet
- Detecting Proteins Using Biuret ReagentDocument5 pagesDetecting Proteins Using Biuret ReagentSHAFIKANOR3661No ratings yet
- Lab Activity 4 - CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesLab Activity 4 - Carbohydratesdjarylkate22No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document9 pagesChapter 7alibel caballeroNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Carbohydrates ExperimentDocument12 pagesQualitative Analysis of Carbohydrates Experimentasdf653652547No ratings yet
- Formal Report-Proteins and Amino AcidsDocument10 pagesFormal Report-Proteins and Amino AcidsQuenieMarielIlar100% (1)
- Reactions of CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesReactions of Carbohydratespaulocarpio100% (6)
- Activity 12 Group 69Document4 pagesActivity 12 Group 69Abdulrahman Amlih0% (1)
- Qualitative Tests for Elements in Organic Compounds (QTEOCDocument10 pagesQualitative Tests for Elements in Organic Compounds (QTEOCRovic MelladoNo ratings yet
- YB2 - EXPT2 - Apostol and Santos PDFDocument12 pagesYB2 - EXPT2 - Apostol and Santos PDFCaryll ApostolNo ratings yet
- Chem2 Laboratory TermsManual MLS - LA1 7Document47 pagesChem2 Laboratory TermsManual MLS - LA1 7BETHEL GRACE P. MARTINEZ0% (3)
- LipidsDocument10 pagesLipidsLuna DanNo ratings yet
- Expt 6Document10 pagesExpt 6beatriz balingit0% (1)
- Salivary Digestion and Enzyme ActionDocument29 pagesSalivary Digestion and Enzyme Actionkelvin91% (23)
- 7 Activity Protein PrecipitationDocument7 pages7 Activity Protein PrecipitationNicole Dane100% (1)
- Want Chemistry Games, Drills, Tests and More? You Need To Become An !Document18 pagesWant Chemistry Games, Drills, Tests and More? You Need To Become An !Liezl ValienteNo ratings yet
- Xanthoproteic TestDocument2 pagesXanthoproteic TestLovely Gay PascualNo ratings yet
- Pettenkofer's TestDocument13 pagesPettenkofer's TestPrincess Lie Rizo AquinoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Urine Lab ReportDocument7 pagesChemistry of Urine Lab ReportMark Ryan TripoleNo ratings yet
- Biochem Laboratory MidtermDocument15 pagesBiochem Laboratory MidtermNica DonioNo ratings yet
- Formal Report On Enzymes: Effect of PH and Temperature On Invertase ActivityDocument4 pagesFormal Report On Enzymes: Effect of PH and Temperature On Invertase ActivityYoreeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 General Reactions of Carbohydrates: NH OHDocument16 pagesExperiment 3 General Reactions of Carbohydrates: NH OHAl Cris BarroNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of Casein from MilkDocument4 pagesIsolation and Characterization of Casein from MilkValent TambunanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report 11sapitula SaysonDocument9 pagesLaboratory Report 11sapitula SaysonAlih KathlyannNo ratings yet
- CONCLUSIONDocument1 pageCONCLUSIONXyrelle Navarro100% (1)
- Analyzing Deer Death Causes With Analytical ChemistryDocument11 pagesAnalyzing Deer Death Causes With Analytical ChemistryLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- BL NurBio Activity 7 - Proteins Precipitation (REVISED 6.25.20)Document8 pagesBL NurBio Activity 7 - Proteins Precipitation (REVISED 6.25.20)Niño PadacaNo ratings yet
- Identify Unknown Carbs with Qualitative TestsDocument10 pagesIdentify Unknown Carbs with Qualitative TestsIsabel Joice EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Tests Reveal Amino Acid PropertiesDocument38 pagesQualitative Tests Reveal Amino Acid PropertiesYousra ZeidanNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesIsolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesEvans DionNo ratings yet
- Experiment #5 Analysis of Acetic Acid: September 8, 2016 Prof. Jeanne Grace AberionDocument33 pagesExperiment #5 Analysis of Acetic Acid: September 8, 2016 Prof. Jeanne Grace AberionShiennah Joy Linguete EupeñaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6 Alkalimetric AnalysisDocument16 pagesMODULE 6 Alkalimetric AnalysisMrl AshiaNo ratings yet
- Moisture DeterminationDocument3 pagesMoisture DeterminationSamuel PelayoNo ratings yet
- Colloids Experiment No. 2Document5 pagesColloids Experiment No. 2Chris K. Ramirez100% (1)
- Discussion Part 3Document6 pagesDiscussion Part 3limNo ratings yet
- Final Lab Report 2Document5 pagesFinal Lab Report 2api-340388320No ratings yet
- Formal Report Synthesis of AspirinDocument4 pagesFormal Report Synthesis of AspirinEdrick Ramoran0% (1)
- Expt. 4 Protein DenaturationDocument10 pagesExpt. 4 Protein DenaturationMary Ella Mae Pila100% (1)
- Fehling's Test: Adlawan - Cainoy - Lawagon - Pascua - Rodriguez - Tarnate - UdalbeDocument16 pagesFehling's Test: Adlawan - Cainoy - Lawagon - Pascua - Rodriguez - Tarnate - UdalbeRocen Azleen TarnateNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Laboratory Activity Chemical Tests For The Components of Nucleic AcidDocument4 pagesExperiment 3 - Laboratory Activity Chemical Tests For The Components of Nucleic AcidDelosreyes ChildrenNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Tests For ProteinsDocument1 pageQualitative Tests For ProteinsMuhammad Aslam100% (4)
- Activity 1 - Biochemical ProcessesDocument4 pagesActivity 1 - Biochemical ProcessesMy Roses Are RosèNo ratings yet
- Conclusions and Recommendations4Document1 pageConclusions and Recommendations4Lara Melissa Orense50% (2)
- Isolation, Hydrolysis, and Characterization of GlycogenDocument4 pagesIsolation, Hydrolysis, and Characterization of GlycogenRyan Enriquez100% (1)
- Protein TestsDocument13 pagesProtein TestsMa. Loucel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Objective: The Objective of This Laboratory Is: - To Standardise of A Hydrochloric Acid (HCL) SolutionDocument12 pagesObjective: The Objective of This Laboratory Is: - To Standardise of A Hydrochloric Acid (HCL) SolutionShaker HusienNo ratings yet
- Antacid Analysisrty4Document4 pagesAntacid Analysisrty4Melced BenasasNo ratings yet
- Fleur Isabelle Cansino (Lab Act 6)Document4 pagesFleur Isabelle Cansino (Lab Act 6)Fleur Astrid CansinoNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Hydrolysis of Polysaccharides Group 3BDocument8 pagesIsolation and Hydrolysis of Polysaccharides Group 3BArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Non Enzymatic BrowningDocument10 pagesNon Enzymatic Browninghurm350% (2)
- Experiment 2 Enzyme Assays and Factors Affectingenzyme ActivityDocument15 pagesExperiment 2 Enzyme Assays and Factors Affectingenzyme Activitymohamad ashaziq100% (4)
- ISOLATION AND TESTING OF GLYCOGEN FROM CHICKEN LIVERDocument4 pagesISOLATION AND TESTING OF GLYCOGEN FROM CHICKEN LIVERJuliefer May Fanilag Pleños100% (1)
- Experiment 5: Analysis of Carbohydrates (Post-Lab Report)Document9 pagesExperiment 5: Analysis of Carbohydrates (Post-Lab Report)Jemina SacayNo ratings yet
- Dye Solubility TestDocument5 pagesDye Solubility TestAsif Rahman100% (1)
- Carboxylic Acids: Properties, Derivatives & ExperimentsDocument7 pagesCarboxylic Acids: Properties, Derivatives & ExperimentsSteffi Grace NotaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 130.1 NOR-AINADocument19 pagesChemistry 130.1 NOR-AINACriszia Mae FloresNo ratings yet
- Productivity Software Description and Use Review: Twitter Is ADocument3 pagesProductivity Software Description and Use Review: Twitter Is ALou Andrae G. SantosNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 Vaccine:: A Multibillionaire Dollar RaceDocument2 pagesCOVID 19 Vaccine:: A Multibillionaire Dollar RaceLou Andrae G. SantosNo ratings yet
- Productivity Software Description and Use Review Photoshop Is Adobe's PhotoDocument2 pagesProductivity Software Description and Use Review Photoshop Is Adobe's PhotoLou Andrae G. SantosNo ratings yet
- SANTOS - LOU ANDRAE PHILIPP - Graded Assessment 2Document1 pageSANTOS - LOU ANDRAE PHILIPP - Graded Assessment 2Lou Andrae G. SantosNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment 1.1 Benefits and Limitations of MARDocument1 pageFormative Assessment 1.1 Benefits and Limitations of MARLou Andrae G. SantosNo ratings yet
- I Wonder As I WanderDocument6 pagesI Wonder As I WanderLou Andrae G. SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7A The Cardiovascular System BLOOD PDFDocument126 pagesChapter 7A The Cardiovascular System BLOOD PDFLou Andrae G. SantosNo ratings yet
- Ama Namin by Barbie Dumlao SatbDocument8 pagesAma Namin by Barbie Dumlao SatbLou Andrae G. SantosNo ratings yet
- Gcworld JapanDocument3 pagesGcworld JapanLou Andrae G. SantosNo ratings yet
- Concept Map OrgDocument1 pageConcept Map OrgLou Andrae G. SantosNo ratings yet
- Org Chem Lab 2Document7 pagesOrg Chem Lab 2Lou Andrae G. SantosNo ratings yet
- GC-MS analysis identifies 24 compounds in Citrus hystrix essential oilDocument34 pagesGC-MS analysis identifies 24 compounds in Citrus hystrix essential oilchrisNo ratings yet
- Herbs& SpicesDocument50 pagesHerbs& SpicesAbdul Salam BabjiNo ratings yet
- Registered Pesticide Sept2016Document16 pagesRegistered Pesticide Sept2016Jehy100% (2)
- Lipid Chemistry Experiment ReportDocument6 pagesLipid Chemistry Experiment ReportSJ MananquilNo ratings yet
- Port-said University Faculty of Science Metabolism Final ExamDocument4 pagesPort-said University Faculty of Science Metabolism Final ExamMohsen HaleemNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Electrophilic ReactionsDocument124 pagesAromatic Electrophilic ReactionsAllan DNo ratings yet
- 3 NomenclatureDocument45 pages3 Nomenclaturerusnah chungNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 LipidsDocument13 pagesExperiment 5 LipidsClemence Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Lipid Oxidation and Improving The Oxidative Stability: Fereidoon Shahidi and Ying ZhongDocument13 pagesLipid Oxidation and Improving The Oxidative Stability: Fereidoon Shahidi and Ying ZhongGabriella C VicenteNo ratings yet
- List Obat Kronis BpjsDocument6 pagesList Obat Kronis BpjsHelmi AgustianNo ratings yet
- Rates of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution ExperimentDocument3 pagesRates of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution ExperimentJoone Xyron CreenciaNo ratings yet
- Am in ADocument7 pagesAm in ARega LinzaNo ratings yet
- IVMS General Principles of Toxicology FormativeDocument2 pagesIVMS General Principles of Toxicology FormativeMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- LasaDocument13 pagesLasaAfif MaharajaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid DegradationDocument57 pagesAmino Acid DegradationUjjwal YadavNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ChemicalsDocument52 pagesLaboratory ChemicalsSwissHuge HugeNo ratings yet
- Esterification Salicylic AcidDocument3 pagesEsterification Salicylic AcidBobbyGunarsoNo ratings yet
- Iupac Nomenclature Rules 1Document1 pageIupac Nomenclature Rules 1CjES EvaristoNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Key BiomoleculesDocument15 pagesIntroduction to Key BiomoleculesManish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Polyestirene Packing Material Treatmen PDFDocument3 pagesPolyestirene Packing Material Treatmen PDFANDRES FELIPE PALACIOS PESCADORNo ratings yet
- Intro Lab Report Biology 091Document2 pagesIntro Lab Report Biology 091Danish Fitri RoslanNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Zumdahl Chapter 22Document21 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Zumdahl Chapter 22Nurul AzizahNo ratings yet
- Trna Model PDFDocument3 pagesTrna Model PDFYoga NovalNo ratings yet
- LIDINews 2013Document40 pagesLIDINews 2013Alemu RegasaNo ratings yet
- Master ObatDocument46 pagesMaster Obatbelahan jiwaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology - Part 1Document40 pagesEndocrine Physiology - Part 1Terrence Beniasi CharumbiraNo ratings yet
- Board Question Paper: March 2015Document10 pagesBoard Question Paper: March 2015Tashvi KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Many Organic Solvents, Making Polymers and Its Beginning MaterialsDocument2 pagesMany Organic Solvents, Making Polymers and Its Beginning MaterialsCarmina DinerosNo ratings yet
- Activity-Rna Protein Synthesis h2Document17 pagesActivity-Rna Protein Synthesis h2api-534200298No ratings yet
- Informasi Nilai Gizi Satuan: Bifidobacterium Lactis NCC 2818 1 × 10 CFU/100gDocument1 pageInformasi Nilai Gizi Satuan: Bifidobacterium Lactis NCC 2818 1 × 10 CFU/100gTheresia Stephani SihiteNo ratings yet