Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 2
Uploaded by
John HopkinsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 2
Uploaded by
John HopkinsCopyright:
Available Formats
ME 321 - MECHANICS OF DEFORMABLE BODIES
ASSIGNMENT 2 - DUE SEP 5, 2019
Practice Problems: From Prescribed Text - 2.5, 2.6, 2.15, 2.27, 2.31, 2.32, 2.33.
Problems - (To be turned in):
(1) The state of stress in an infinitesimal cube is given (in MPa) by:
√ √
σxx = 3, σyy = 0, σzz = −1, σxy = − 2, σyz = − 2, σzx = 1
Determine the principal stresses and their direction. [10 pts]
(2) Check if the given stress field is a possible stress field description. [5 pts]
σxx = ayz, σyy = bxz, σzz = cxy, σxy = dz 2 , σyz = f x2 , σzx = ey 2
(3) The stress tensor at a point is given by: [10 pts]
σxx = σ, σyy = σ, σzz = σ, σxy = aσ, σyz = cσ, σzx = bσ
where a, b, c are constants and σ is some stress value. Determine the constants a, b, c so that the
stress vector vanishes on the octahedral plane.
(4) The stresses acting at a point in a piece of material are: [10 pts]
σxx = 4, σyy = 7, σzz = −9, σxy = 4, σyz = 5, σzx = 0
Calculate:
(a) The normal stress, resultant stress and the shear stress on a plane whose normal makes angles
of 50◦ with the positive x-axis and 60◦ with the positive y-axis.
(b) The direction cosines of the shear stress with respect to the x, y and z-axes.
(c) The principal stresses and the direction cosines of the normals to the principal planes with
respect to x, y and z.
(d) The maximum shear stress at the point in the material.
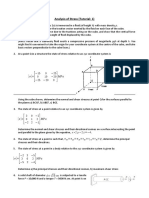
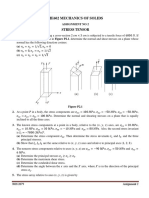
(5) The planar stress description associated with a wedge is given
by: σxx = −90, σyy = −150, σxy = −75. Find the traction
vector, normal and shear stresses on the inclined plane of the
wedge shown in the Figure. [10 pt]
Note: Do not use any ”shortcuts” and show all the steps of your work.
You might also like
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- X.0.hooke's LawDocument32 pagesX.0.hooke's LawSuresh SjNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mechanics of Solids - Question SetDocument3 pagesAdvanced Mechanics of Solids - Question SetAshish ZachariahNo ratings yet
- ts5 TorsionDocument5 pagests5 TorsionOmkar VanjariNo ratings yet
- 710901N Me Winter 2015Document2 pages710901N Me Winter 2015chandsixNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Stress Tut 1Document2 pagesAnalysis of Stress Tut 1Himanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Stress Tut 1Document2 pagesAnalysis of Stress Tut 1Himanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Theories of Stress and Strain-2011Document3 pagesTutorial 1 - Theories of Stress and Strain-2011Kiat HauNo ratings yet
- EN380 Naval Materials Science and Engineering Course Notes, U.S. Naval AcademyDocument7 pagesEN380 Naval Materials Science and Engineering Course Notes, U.S. Naval Academysrinivas pavan kumar ANo ratings yet
- Mohr S CircleDocument8 pagesMohr S Circlelalala uNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Meem 4150 Oct. 4Th, 2011Document2 pagesExam 1 Meem 4150 Oct. 4Th, 2011Rayleight SilversNo ratings yet
- CE: 2051: Advanced Mechanics of Materials: SLIIT/Curtin: Civil Engineering: Year 2 Semester 2 Tutorial 9Document2 pagesCE: 2051: Advanced Mechanics of Materials: SLIIT/Curtin: Civil Engineering: Year 2 Semester 2 Tutorial 9Sayan KirinathanNo ratings yet
- 2017 - MSY 310 - Semester Test 1Document8 pages2017 - MSY 310 - Semester Test 1Zibusiso NcubeNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering, Architecture and Technology:: Course Title: Course Number: Course DescriptionDocument13 pagesCollege of Engineering, Architecture and Technology:: Course Title: Course Number: Course DescriptionEdmil Jhon AriquesNo ratings yet
- ENA Lect. Notes Unit 5 - 5.6 Problems On Mohrs Circle NewDocument16 pagesENA Lect. Notes Unit 5 - 5.6 Problems On Mohrs Circle Newsaadan.tarun10No ratings yet
- Homework4 Revised Solutions 2005 PDFDocument11 pagesHomework4 Revised Solutions 2005 PDFFaridehNo ratings yet
- Practise Problems Set02Document5 pagesPractise Problems Set02rohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Teknik Kekuatan BahanDocument29 pagesTeknik Kekuatan BahanfayuangNo ratings yet
- MATH1050A1Document2 pagesMATH1050A1songpengyuan123No ratings yet
- MEC 3611: Structural Mechanics: Lecture 3: REVIEWDocument22 pagesMEC 3611: Structural Mechanics: Lecture 3: REVIEWhellolover0% (1)
- Tutorial 2 PDFDocument3 pagesTutorial 2 PDFafif bukhoriNo ratings yet
- Exam 04032021Document2 pagesExam 04032021Giannis MamalakisNo ratings yet
- BFC20903 - Chapter2 - Strain Transformation 1aDocument28 pagesBFC20903 - Chapter2 - Strain Transformation 1aFoo Chee HengNo ratings yet
- Two Dimensional Stress TransformationDocument3 pagesTwo Dimensional Stress TransformationKishan MadhooNo ratings yet
- CP4 June 2016Document6 pagesCP4 June 2016Sifei ZhangNo ratings yet
- Principal StressesDocument13 pagesPrincipal StressesSathish SelvaNo ratings yet
- 4-M-NumericalMethodsinChemicalEngg 20171122083203.479 X PDFDocument3 pages4-M-NumericalMethodsinChemicalEngg 20171122083203.479 X PDFMani SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1SijuKalladaNo ratings yet
- Principal Stresses (Civil Engg. For AUST EEE 1/1)Document25 pagesPrincipal Stresses (Civil Engg. For AUST EEE 1/1)Fazlay ElahiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 02Document2 pagesAssignment 02Sailesh BastolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Stress and Strain - A4Document15 pagesChapter 6 - Stress and Strain - A4steven_gog0% (1)
- Tutorial 1 1 PDFDocument22 pagesTutorial 1 1 PDFSuresh g.s.No ratings yet
- + + 2 I+ 3 x+4 y J+ 2 X + 4 Z K: Analysis of Strain (Tutorial: 2)Document2 pages+ + 2 I+ 3 x+4 y J+ 2 X + 4 Z K: Analysis of Strain (Tutorial: 2)Himanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- MECH3310 Mechanics of Solids 2: The University of SydneyDocument8 pagesMECH3310 Mechanics of Solids 2: The University of SydneyJim LettermanNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics 1 Problem Solution Set 1Document5 pagesStructural Mechanics 1 Problem Solution Set 1saeedsoftNo ratings yet
- HD EXP STRESS ANALYSIS Chapter 2 Stress Rev September 2013+assignmentDocument24 pagesHD EXP STRESS ANALYSIS Chapter 2 Stress Rev September 2013+assignmenttengyanNo ratings yet
- Curve Tracing: Monotonic Function, Concavity and Point of InflectionDocument9 pagesCurve Tracing: Monotonic Function, Concavity and Point of InflectionpreetiNo ratings yet
- Mem503: Mechanics of Solids - Ii Syllabus: Analysis of Stress and StrainDocument11 pagesMem503: Mechanics of Solids - Ii Syllabus: Analysis of Stress and StrainShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aero 2 ExerciseDocument5 pagesAero 2 ExerciseHavner Scherrer CruzNo ratings yet
- HW1Document3 pagesHW1Naveen RajNo ratings yet
- MIET1071-2021-Task 1 Milestone 1Document2 pagesMIET1071-2021-Task 1 Milestone 1Usama AdeelNo ratings yet
- Deber 3Document2 pagesDeber 3Jose PinedaNo ratings yet
- Mohr CircleDocument5 pagesMohr CircleSteeve JohnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 ExerciseDocument6 pagesChapter 11 ExerciseThe Mindset MessengerNo ratings yet
- Stress TransformationDocument22 pagesStress TransformationTran Manh HuyNo ratings yet
- AE 321 - Homework #3 Due: Monday February 25, 2019 Chapter 2: Traction and StressDocument1 pageAE 321 - Homework #3 Due: Monday February 25, 2019 Chapter 2: Traction and Stressbob toodleNo ratings yet
- Model Questions ElasticityDocument3 pagesModel Questions Elasticityrameshbabu_1979No ratings yet
- 5 StressDocument1 page5 StressR S PappuNo ratings yet
- Asssignment 02, Parviz Hosseini SarjouDocument10 pagesAsssignment 02, Parviz Hosseini Sarjouamin hNo ratings yet
- Min 05037 Geo Technical EngineeringDocument15 pagesMin 05037 Geo Technical EngineeringBhaskar ReddyNo ratings yet
- TS 5Document2 pagesTS 5KayulaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity Ass Final-1Document26 pagesElasticity Ass Final-1Mesfin FikreaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 2023Document1 pageAssignment 1 2023shivam ojhaNo ratings yet
- σ σ xxσ σ σ σ σ τ τ τ σ σ σ σ σ τ σ τ σ τ τ τ σ xx+σ σ σ: xx yy zz xy yz zxDocument4 pagesσ σ xxσ σ σ σ σ τ τ τ σ σ σ σ σ τ σ τ σ τ τ τ σ xx+σ σ σ: xx yy zz xy yz zxIrfan HaiderNo ratings yet
- Math Dse4Document4 pagesMath Dse4facto GamerNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 PGDocument1 pageTutorial 2 PGHarryNo ratings yet
- A Rectangular Steel Bar Having A CrossDocument2 pagesA Rectangular Steel Bar Having A CrossHitesh PrajapatNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 PDFJohn HopkinsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Btech Lab Manual-CH 202Document17 pagesChemistry Btech Lab Manual-CH 202John HopkinsNo ratings yet
- If Men-Homogeneo-: Equations Plmy HomogeneousDocument15 pagesIf Men-Homogeneo-: Equations Plmy HomogeneousJohn HopkinsNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Gandhi's SpeechDocument1 pageInterpretation of Gandhi's SpeechJohn HopkinsNo ratings yet
- This Definition Is Given by - We Will Touch Upon Main Points of Other Definitions in Tutorial SessionsDocument3 pagesThis Definition Is Given by - We Will Touch Upon Main Points of Other Definitions in Tutorial SessionsJohn HopkinsNo ratings yet