0% found this document useful (0 votes)
152 views2 pagesDesign of Frame
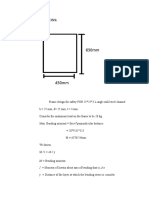
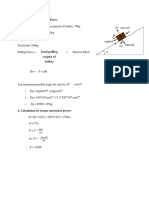
The document summarizes the design of a frame including its dimensions and materials. It then calculates the mass, total weight, stress on the frame, and verifies that the design is safe based on the material yield stress. It also provides calculations for a DC motor including its speed, current, torque, and verification that a 9mm diameter shaft made of mild steel can withstand the torque.
Uploaded by
pramo_dassCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
152 views2 pagesDesign of Frame
The document summarizes the design of a frame including its dimensions and materials. It then calculates the mass, total weight, stress on the frame, and verifies that the design is safe based on the material yield stress. It also provides calculations for a DC motor including its speed, current, torque, and verification that a 9mm diameter shaft made of mild steel can withstand the torque.
Uploaded by
pramo_dassCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd