Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wound Types PDF
Wound Types PDF
Uploaded by
ChrisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wound Types PDF
Wound Types PDF
Uploaded by
ChrisCopyright:
Available Formats
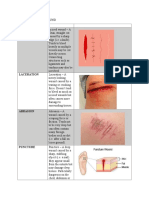
Different Types of Wounds & Bleeding
Bruise (Contusion) Abrasion Cut (Incision) Laceration Puncture Tear (Avulsion)
Kind of wound Closed Open Open Open Open Open
Blow from something Skin being scraped Something sharp (e.g. Machinery, barbed wire, Blunt or pointed
Caused by blunt across a hard surface knife or glass) teeth or claws instruments
Severe force
Skin and other soft tissues to
Vessels under skin to Outer layer of skin and Skin, soft tissue or Skin and underlying Skin and underlying
Injury causes bleed into surrounding tiny underlying blood tissue damage and
be partially or completely
muscles to be severed tissue damage torn away
tissues vessels to be exposed possible infection
RICE 1. Clean wound 1. Clean wound 1. Clean wound 1. Clean wound 1. Return skin to
Rest the patient and 2. Apply non- thoroughly with thoroughly with thoroughly with original position is
the injured part adherent sterile gauze sterile gauze sterile gauze possible
dressing soaked in saline soaked in saline soaked in saline 2. Apply pressure to
Icepacks (cold
(if available) or in (if available), or (if available), or wound using a pad,
compress) in a wet
cooled, boiled in cooled boiled in cooled boiled with hand pressure
cloth may be applied to
water water water of a dressing to
the injury – for 15 mins
2. Apply non- 2. Apply non- 2. Apply non- control any bleeding
every 2 hrs for 24 hrs,
Management adherent adherent adherent 3. Bandage
then 15 mins every 4
dressing dressing dressing
hrs for 24 hrs
Compression
Bandages, such as
elastic bandages,
should be firmly
applied to extend well
beyond the injury
Elevate the injured part
St John Ambulance Australia (VIC) ABN: 69 061 844 380 in partnership with St John Ambulance Australia Inc. (RTO 88041)
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan Sample (Student Made)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan Sample (Student Made)tegoshi0870% (10)
- Advanced French Vocabulary: Embedded in SentencesFrom EverandAdvanced French Vocabulary: Embedded in SentencesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- WOUNDDocument6 pagesWOUNDLouie ParillaNo ratings yet
- Work Permit: Jazz Residences Condominium CorporationDocument1 pageWork Permit: Jazz Residences Condominium CorporationminaNo ratings yet
- AGC Round 3 Question Paper Class 2Document1 pageAGC Round 3 Question Paper Class 2Debi Ghosh80% (5)
- Edexcel GCSE Music Student WorkbookDocument147 pagesEdexcel GCSE Music Student WorkbookMary Lin100% (2)
- First Aid HandoutDocument3 pagesFirst Aid HandoutMaria Alyssa NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Open Fractures in Ortho PatientsDocument23 pagesOpen Fractures in Ortho PatientsCharisse Ann GasatayaNo ratings yet
- First Aid Guide (11.7 × 8.3in)Document1 pageFirst Aid Guide (11.7 × 8.3in)Styx XieNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument13 pagesFirst AidArnel AbestanoNo ratings yet
- Wounds and BleedingDocument3 pagesWounds and BleedingJames Peter FernandezNo ratings yet
- First Aid GuideDocument1 pageFirst Aid GuideStyx XieNo ratings yet
- Tanishk Injuries PDF Flex 1Document1 pageTanishk Injuries PDF Flex 1tanishk malviyaNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic WoundDocument69 pagesAcute and Chronic Woundaufar isytaharNo ratings yet
- Bleeding: First AidDocument11 pagesBleeding: First AidAnonymous 9edNAsrNo ratings yet
- Tan. Injuries PDFDocument1 pageTan. Injuries PDFtanishk malviyaNo ratings yet
- First Aid GuideDocument1 pageFirst Aid GuideStyx XieNo ratings yet
- First Aid GuideDocument1 pageFirst Aid GuideStyx XieNo ratings yet
- Bleeding & WoundsDocument28 pagesBleeding & WoundsMalakaiNo ratings yet
- Endo AcuteDocument1 pageEndo AcutebouglaglastellaNo ratings yet
- Demo Wound DressingDocument21 pagesDemo Wound Dressingaarti sahuNo ratings yet
- First Aid For Common Unintentional InjuriesDocument13 pagesFirst Aid For Common Unintentional InjuriesORENJI ORENJI ORENJINo ratings yet
- Poster (Healable)Document1 pagePoster (Healable)ppnidpk rsumNo ratings yet
- DressingDocument11 pagesDressingShini SimonNo ratings yet
- Safe Debridment The Conceps of Future Wound Management and Legality Safe Debridment The Conceps of Future Wound Management and LegalityDocument16 pagesSafe Debridment The Conceps of Future Wound Management and Legality Safe Debridment The Conceps of Future Wound Management and LegalitySiti NurazlinaNo ratings yet
- FirstaidDocument16 pagesFirstaidSamSamNo ratings yet
- Muscuskeletal DisordersDocument4 pagesMuscuskeletal DisordersGhadeer AbedNo ratings yet
- Pressure Ulcer Staging CardDocument2 pagesPressure Ulcer Staging CardMary RiveroNo ratings yet
- Latihan Amali: Wja 102:balutan Ringkas 9 NOVEMBER 2020Document19 pagesLatihan Amali: Wja 102:balutan Ringkas 9 NOVEMBER 2020pei yeu tehNo ratings yet
- Splinting and Bandaging: Kinds of Wounds/Bruises ContusionDocument4 pagesSplinting and Bandaging: Kinds of Wounds/Bruises ContusionErnst BacallaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Jovel E. Cortez 2 Year Olfu Val 11BDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan: Jovel E. Cortez 2 Year Olfu Val 11BJovel CortezNo ratings yet
- Bandages: General Types of Bandages Triagular and Cravat BandagesDocument3 pagesBandages: General Types of Bandages Triagular and Cravat BandagesHannah DuyagNo ratings yet
- Wound Care, Suture Materials & Suturing TechniquesDocument80 pagesWound Care, Suture Materials & Suturing TechniquesAlwin PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Basic TraumaDocument152 pagesBasic Traumasanpedro.diorelNo ratings yet
- 13 - Fracture in ChildrenDocument34 pages13 - Fracture in ChildrenManow ChawisaNo ratings yet
- NCP NeuroDocument2 pagesNCP NeuroMarie Frances Lalican-RingelNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument7 pagesFirst AidjuliaNo ratings yet
- 1.03. Physical InjuriesDocument4 pages1.03. Physical InjuriesAllandale NacinoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanIsabelle Madrid100% (1)
- Emergency Survival KitDocument2 pagesEmergency Survival Kitsammyyy alberichNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 WoundDocument54 pagesLecture 4 WoundVet IrfanNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 5Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 5JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin Integrity Related To Trauma or Infection: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesImpaired Skin Integrity Related To Trauma or Infection: Objectivesmhean azneitaNo ratings yet
- Cebu Institute of Technology - University College of NursingDocument2 pagesCebu Institute of Technology - University College of NursingSergi Lee OrateNo ratings yet
- Sim Deftac 113 Ulo BDocument10 pagesSim Deftac 113 Ulo BLieca BalolongNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument7 pagesImpaired Skin Integrityprickybiik100% (8)
- 1.1 Musculoskeletal Care Modalities PDFDocument20 pages1.1 Musculoskeletal Care Modalities PDFDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- BANDAGESDocument26 pagesBANDAGESGienette RamirezNo ratings yet
- ST ND RD THDocument8 pagesST ND RD THLuvleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Bandaging: Saint Paul University ofDocument7 pagesBandaging: Saint Paul University ofjohannah reine buenaflorNo ratings yet
- Wound: Types of Wound Healing Healing Process Factors Affecting Healing ComplicationsDocument59 pagesWound: Types of Wound Healing Healing Process Factors Affecting Healing Complicationsjaveria choudharyNo ratings yet
- SFATDocument9 pagesSFATKateNo ratings yet
- ks3 BleedingDocument29 pagesks3 BleedingAlan AzadNo ratings yet
- Assisting in Application of CastDocument9 pagesAssisting in Application of CastJames PanesNo ratings yet
- Rabies PJ NCPDocument3 pagesRabies PJ NCPFredrick PaderangaNo ratings yet
- FirstaidtipsDocument8 pagesFirstaidtipsdemos70No ratings yet
- CD Additional LessonsDocument13 pagesCD Additional LessonsAlma Janella TOSINONo ratings yet
- Pressure UlcerDocument4 pagesPressure Ulcerjds6z4sgfwNo ratings yet
- First Aid Treatment For Injuries 20240324 175218 0000Document2 pagesFirst Aid Treatment For Injuries 20240324 175218 0000beabalela07No ratings yet
- Wot and Nott's Race Against Time: Part Two - the Realm of the Black CrystalsFrom EverandWot and Nott's Race Against Time: Part Two - the Realm of the Black CrystalsNo ratings yet
- 2012A For InvestorsDocument1 page2012A For InvestorsDebi GhoshNo ratings yet
- (F) Vacancy in Pvt. Facilities Other Than Requisitioned COVID Hospital, As On 22 .06 .20Document1 page(F) Vacancy in Pvt. Facilities Other Than Requisitioned COVID Hospital, As On 22 .06 .20Debi GhoshNo ratings yet
- (F) Vacancy in Pvt. Facilities Other Than Requisitioned COVID Hospital, As On 22 .06 .20Document1 page(F) Vacancy in Pvt. Facilities Other Than Requisitioned COVID Hospital, As On 22 .06 .20Debi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Favipiravir - Wikipedia PDFDocument39 pagesFavipiravir - Wikipedia PDFDebi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Notice of Postal Ballot Form PDFDocument14 pagesNotice of Postal Ballot Form PDFDebi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Advance Planning and Optimization: Sail - IspDocument55 pagesAdvance Planning and Optimization: Sail - IspDebi GhoshNo ratings yet
- TSP Ship No OneDocument37 pagesTSP Ship No OneDebi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Myenglish Terms and Conditions: Myenglish Participation Communication SkillsDocument4 pagesMyenglish Terms and Conditions: Myenglish Participation Communication SkillsDebi GhoshNo ratings yet
- AGC Round2 Question Paper Class 2Document1 pageAGC Round2 Question Paper Class 2Debi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited: ST STDocument5 pagesReliance Jio Infocomm Limited: ST STDebi GhoshNo ratings yet
- What Is Research PDFDocument246 pagesWhat Is Research PDFDebi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Where Is My BusinessDocument7 pagesWhere Is My BusinessDebi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Rule 200 BookDocument3 pagesRule 200 BookDebi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Rules and Guidelines (Revision 1A.) : Apr-Association of Top/Achiever' Scouts (Apr-Atas)Document2 pagesRules and Guidelines (Revision 1A.) : Apr-Association of Top/Achiever' Scouts (Apr-Atas)Debi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Hands On Activities Integration Architecture PDFDocument26 pagesHands On Activities Integration Architecture PDFDebi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Python 3.3.7 PDFDocument157 pagesPython 3.3.7 PDFAchraf KmoutNo ratings yet
- Hamilton vs. Jefferson NotesDocument6 pagesHamilton vs. Jefferson NotesJess ReynoldsNo ratings yet
- A Conference Interpreters View - Udo JorgDocument14 pagesA Conference Interpreters View - Udo JorgElnur HuseynovNo ratings yet
- Example Road Pavement DesignDocument2 pagesExample Road Pavement Designnuraina aqilahNo ratings yet
- How To Get IPs On SteamDocument9 pagesHow To Get IPs On SteamKo Ko OoNo ratings yet
- Book of PriestcraftDocument130 pagesBook of PriestcraftEduardo Luiz Pinto100% (1)
- Subject:: Social Science (For Mid-Term Exams.)Document2 pagesSubject:: Social Science (For Mid-Term Exams.)SKULL XT GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Corporate Sustainability, Social Responsibility and Environmental ManagementDocument377 pagesCorporate Sustainability, Social Responsibility and Environmental ManagementNoli CorralNo ratings yet
- Survey On Fashion Brand of BangladeshDocument9 pagesSurvey On Fashion Brand of BangladeshMd ShakibNo ratings yet
- (PC) Weaver v. California Correctional Institution Confinement Shu - Document No. 3Document2 pages(PC) Weaver v. California Correctional Institution Confinement Shu - Document No. 3Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Lawer, L., Brusilovskiy, E., Salzer, M. S., & Mandell, D. S. (2009) - Use of Vocational Rehabilitative Services Among Adults With AutismDocument8 pagesLawer, L., Brusilovskiy, E., Salzer, M. S., & Mandell, D. S. (2009) - Use of Vocational Rehabilitative Services Among Adults With AutismTomislav CvrtnjakNo ratings yet
- Design Methodology of A UAV Propeller Implemented in Monitoring ActivitiesDocument17 pagesDesign Methodology of A UAV Propeller Implemented in Monitoring ActivitiesEdgar Cando NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Edited Thesis Group 6Document46 pagesEdited Thesis Group 6Nhel Denton Cabusas88% (88)
- Bài Tập Chapter 3Document7 pagesBài Tập Chapter 3Huỳnh Ngọc Bảo TrânNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Plan Blended Learning November 21-24, 2022Document1 pageWeekly Learning Plan Blended Learning November 21-24, 2022Estefany LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Bar Charts: Exam Information - Describing A Bar ChartDocument8 pagesBar Charts: Exam Information - Describing A Bar ChartBùi Trí DũngNo ratings yet
- Class-7: DPP # 01 Topic: Motion & Time PhysicsDocument2 pagesClass-7: DPP # 01 Topic: Motion & Time PhysicsRiya PatelNo ratings yet
- Article 05 MehboobDocument20 pagesArticle 05 MehboobMUHAMMAD HASHAAMNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical Exam in English 9: Johnson National High SchoolDocument4 pagesSecond Periodical Exam in English 9: Johnson National High SchoolZaldy Osico TejadoNo ratings yet
- Non-Destructive Tests On Eco-Friendly Anti-Corrosion Paint: September 2017Document10 pagesNon-Destructive Tests On Eco-Friendly Anti-Corrosion Paint: September 2017nanoNo ratings yet
- Terminal Con Copa 3M Cold Shrink QT-III 769X-S-4 KitsDocument20 pagesTerminal Con Copa 3M Cold Shrink QT-III 769X-S-4 KitsEnrique G.No ratings yet
- Understanding Shared Memory and Semaphores - Oracle FAQDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Shared Memory and Semaphores - Oracle FAQHari SuryakanthNo ratings yet
- Heat Conduction Equation: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & ApplicationsDocument75 pagesHeat Conduction Equation: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & Applicationssalim ekizNo ratings yet
- Telephone ConversationDocument2 pagesTelephone ConversationMJNo ratings yet
- Vsphere Esxi 703 Installation Setup GuideDocument238 pagesVsphere Esxi 703 Installation Setup GuideErdem EnustNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 - Information LiteracyDocument10 pagesLESSON 3 - Information LiteracyAngel Trisha MariNo ratings yet
- AsemblerDocument115 pagesAsemblerBaskar Arumugam50% (2)
- The Cask of Amontillado (Summary)Document5 pagesThe Cask of Amontillado (Summary)Ria LopezNo ratings yet