Professional Documents
Culture Documents
System of CoPlanar Forces Notes Engineering Mechanics
Uploaded by
Kiran BeldarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
System of CoPlanar Forces Notes Engineering Mechanics
Uploaded by
Kiran BeldarCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering Mechanics Unit No.
2.1 Problems on Beam Reaction
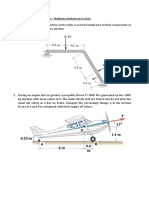
1] Find the reactions at the supports of the beam applying conditions of equilibrium. (May
2010) [Ans: Ra=10.16kN,θ= 56.15o, Rb= 7.216kN upward]
2] Find the support reaction at B and the load P, for the beam shown in fig. If the reaction at
support A is zero. (May 2014) [Ans: P=176kN Downward, Rb=252kN upward]
Fig: 1 Fig:2
3] Find the reactions at the supports of the beam as shown in fig. [Ans: Ha=116.86N
Rightside,Va= 82.77N upward, Rb= 173.72N]
4] Determine the intensity of distributed load W at the end C of the beam ABC for which the
reaction at C is zero. Also calculate the reaction at B. (May 2008) [Ans: W=3 kN/m,
Rb=21.6kN upward]
Fig: 3 Fig: 4
5] Fig. Shows two beams AC and DF. The end D of the beam DF rests on a roller which in turn
rests on the end C of the beam AC. For the loads determine support reactions. [Ans: Hf= 0,
Vf=90kN upward, Ha=125kN left side, Va= 45.62kN upward, Ma=75.62kN-m
anticlockwise]
6] Find reactions at supports of the beam AB loaded as shown in figure below. (May 2011)
[Ans: Rb= 8.88kN, θ= 76.18o, Ra= 7.5kN upward]
Fig: 5 Fig: 6
7] Find the reactions at the supports of the beam loaded as shown in fig. (Dec. 2009) [Ans:
Rb=60kN upward, Va= 50kN upward, Ha= 0]
8] Find the reactions at the supports of the beam, applying conditions of equilibrium. [Ans: Ha=
22.08kN rightside, Va= 36.7kN upward, Rb= 44.16kN ]
Fig: 7 Fig: 8
For Div. D ……….Prepared by Mr. Kiran Beldar
Engineering Mechanics Unit No. 2
9] Calculate the reactions of the beam loaded as shown in fig. [Ans: Rb= 11.7kN upward,
Va= 7.3kN upward, Ha= 0]
10] Find the reactions at A and B for a bent beam ABC loaded is as shown in figure. [Ans: Ha=
18kN, Va= 13.15kN, Rb= 4.85kN]
Fig: 9 Fig: 10
11] Find analytically the support reaction at B and the load P, for the beam shown in figure, if
reaction at support A is Zero. (Dec. 2008, Dec. 2011) [Ans: P=26kN downward, Rb= 72kN
upward]
12] Find the support reaction at A and B for the beam shown in figure. (Dec. 2013) (Dec. 2017)
[Ans: Rb= 314.08kN, Ha= 157.04kN rightside, Va= 108kN upward]
Fig: 11 Fig: 12
13] Find support reactions at A and B for the beam loaded as shown in fig. A is hinged and B is
roller. (Dec. 2015) [Ans: Rb= 86.16N, Ha= 0, Va= 22.84N upward]
14] Find the reactions at supports A and E for the beam loaded as shown in the figure below.
(May 2016) [Ans: Re= 49.03N, Ra= 59.75N, θ= 65.27o]
Fig: 13 Fig: 14
15] A uniform beam AB hinged at A is kept horizontal by supporting and setting a 100N weight
by using a string tied at B and passing over a smooth pulley at C. The beam also loaded as
shown in fig. Below. Find the reactions at A and C. (May 2016)[Ans: Ra= 67.25N, θ= 48.45o,
Rc= 84.89N, α= 58.23o]
16] Find the support reaction at point A and B on given beam (May 2018)
Fig: 15
Fig: 15 Fig: 16
For Div. D ……….Prepared by Mr. Kiran Beldar
Engineering Mechanics Unit No. 2
2.2 Problems on Equilibrium system of coplanar forces
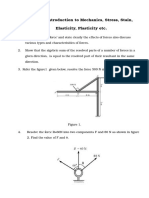
1] A 30kg pipe is supported at ‘A’ by a system of Five chords. Determine the force in each
chord for equilibrium. (May 2009) [Ans: TBC= 562.29N, TBD= 490.48N,TAE= 169.19N,TAB=
339.82N ]
2] Find force transmitted by cable ‘BC’ shown. E is a friction less pulley , where B and D are
weightless rings.[Ans: FBC= 565.69N]
Fig:1 Fig: 2
3] A cylinder with 1500N weight is resting in a unsymmetrical smooth groove as shown in fig.
Determine the reactions at the points of contacts. (May 2014) [Ans: R1= 1344.86N, R2=
1098.08N]
4] A roller of weight W= 1000N rest on a smooth incline plane . It is kept from rolling down
the plane by a string AC. Find the tension in the string and reaction at the point of contact
D.(Dec. 2008) [Ans: T= 732.04N, Rd= 896.57N]
Fig: 3 Fig: 4
5] Two spheres A and B of weight 1000N and 750N respectively are kept as shown in the figure.
Determine the reactions at all contact points 1,2,3,4. radius of A = 400mm and radius of B=
300mm.(May 2011) [Ans: R1= 496.6N, R2= 1463.2N, R3= 869.1N, R4= 573.5N]
6] Three cylinders are piled up in a rectangular channel as shown in figure. Determine the
reactions at point 6 between the cylinder A and the vertical wall of the channel.(Cylinder A:
radius= 4cm, m= 15kg),(Cylinder B: radius =6cm, m= 40kg), (Cylinder C: radius = 5cm,
m=20kg). (May 2010, Dec. 2015) [Ans: R6= 785N]
Fig: 5 Fig: 14
7] Two spheres A and B are kept in a horizontal channel. Determine the reactions coming from
all the contact surfaces. Consider the radius of A and B are 40 mm and 30mm respectively.
Take Wa= 500N and Wb= 200N. (May 2016) [Ans: R1= 204.09N, R2= 285.75N, R3= 204.09N,
R4= 700N]
For Div. D ……….Prepared by Mr. Kiran Beldar
Engineering Mechanics Unit No. 2
8] Three identical spheres P,Q, R of weight ‘W’ are arranged on smooth inclined surface as
shown in the figure. Determine the angle ‘α’ which will prevent the arrangement from
collapsing. [Ans: θ= 10.94o]
Fig: 7 Fig: 8
9] Two cylinders are kept in a channel as shown in figure. Determine the reactions at all the
contact points A, B,C and D. Assume all surfaces are smooth.(May 2014) [Ans: RA=
48.96kN, RB= 118.52kN, RC= 37.5kN, RD= 62.5kN]
10] Determine the reactions at points of contact 1,2 and 3. Assume smooth surfaces. Take Wa=
1Kg, Ra= 1cm, Wb= 4kG, Rb= 4cm. (Dec. 11, Dec. 2017) [Ans: R1= 19.73N, R2= 11.6N, R3=
32.22N]
Fig: 9 Fig: 10
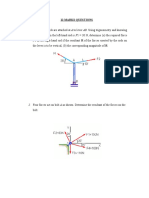
11] The lever AB is hinged at C and attached to a cable at A. If the lever is subjected as B to a
400 N horizontal force, determine: I) the tension in the cable ii) The reaction at C.[Ans: TAD=
300N, HC= 250N Rightside, VC= 259.8N upward]
12] The roller shown in fig. Is of weight 1500 N. What force ‘T’ is necessary to start the roller
over the block A, if θ= 25o. Also find the minimum force ‘T’ required to start the roller over the
block A. [Ans: T= 1759.34N, Tmin= 1355.23N]
Fig: 11 Fig: 12
13] Two cylinders , having weights Wa= 2000N and Wb= 1000N, are resting on smooth
inclined planes having inclinations 60o and 45o with the horizontal respectively as shown in
figure . They are connected by a weightless bar AB with hinge connections. The bar AB makes
15o angle with the horizontal. Find the magnitude of the force ‘P’ required to hold the system in
equilibrium. (May 2017) [Ans: P= 535.88N]
14] Find the support reactions at A, B, C for the rigid link DEF supported by the cylinders at D
and F. the link is loaded by a single force of 20kN as shown in the figure. Neglect friction and
For Div. D ……….Prepared by Mr. Kiran Beldar
Engineering Mechanics Unit No. 2
self weight of link and cylinders. Take diameters of cylinders as 200mm and DE=EF= 300mm
[Ans: RA= 12.14kN rightside, RB= 15.18kN upward, RC= 3.03kN ]
Fig: 5 Fig: 6
Fig: 13 Fig: 14
15] A cylinder weighing 1000N and 1.5 m diameter is supported by a beam AB of length 6m
and weight 400N as shown in fig. Neglecting friction at the surfaces of contacts, determine i)
Wall reaction at D, ii) Tension in the cable BC and iii) Hinged reaction at support A. (Dec.
2013,May 2018) [Ans: RD= 1000N rightside, RP= 1414.21N, T= 588.08N, HA= 490.71
leftside, VA= 1105.96N upward]
16] A bar of 3m length and negligible weight rests in horizontal position on two smooth
inclined planes. Determine the distance x at which the load Q= 150N should be placed from
point B to keep the bar horizontal. (May 2015) [Ans: x= 1.22m]
Fig: 15 Fig: 16
17] A man raises a 12 kg joist of length 4m by pulling on a rope. Find the tension in the rope and
the reaction at A. (Dec. 2010) [Ans: T= 98.48N, RA= 177.44N at θ= 58.56o]
18] A boom is supported as shown in figure by a cable runs from ‘C’ over a small smooth
pulley at D. Compute the tension T in cable and reaction at A. Neglect the weight of boom and
size of the pulley. (May 2017)
Fig: 17 Fig: 18
For Div. D ……….Prepared by Mr. Kiran Beldar
Engineering Mechanics Unit No. 2
2.3 Analysis of Plane Trusses
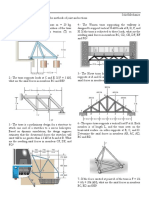
1] A truss is loaded as shown in the figure in the diagram given below. Determine: i) Support
reactions ii) Forces on BC,BD by Method of section. iii) Forces on AB,AE and BE by
method of joints ( Dec. 2014) [Ans: RD= 475N, RA= 152.069N, FBC= 212.132N (T),FBD=
225.347N (C), FBE= 200N(T), FAB= 45.068N(C), FAE= FDE= 187.5N (T)]
2] Find the forces in members BD,BE and CE by method of section only for the truss shown in
the figure. Also find the forces in other members by method of joints (Dec. 2013) [Ans: FCE=
0kN , FBD= 2.79kN(T),FBE= 1.12kN (C), FAB= 1.677kN(T), FAC= 0, FBC= 0,FEF= 1.414kN
(C), FDF= 2.5kN(T), FDE= 2.248kN(C)]
Fig: 1 Fig: 2
3] Referring to the truss shown in figure, find: i) Reactions ii) Zero force members iii) forces in
members FB, FC, FE and DE by method of sections tabulate the results of the analysis. (Dec.
2012, Dec. 2017) [Ans: VD= 15kN, HD= 0kN, VC= 85kN, FFB= FFC= 0kN,FEF= 50kN, FDE=
50kN]
4] A simply supported pin jointed truss is loaded and supported as shown in the following
figure. Identify the members carrying zero force and find forces in members by method of
joints. (May 2010) [Ans: FAB= 21.21kN, FCD= 18 kN, FBE= 21.21 kN, FAF= 25 kN, FBF= 30
kN, FFE= 25 kN, FED= 10 kN, FCE= 15 kN,FBC= 0 kN]
Fig: 3 Fig: 4
5] For the truss loaded as shown in figure find the foprce in members CE and CF by method of
sections only (Dec. 2009, Dec. 2015) [Ans: FCE= 12.5kN(T), FCF= 25kN(T)]
6] Find forces in members CE,CD and BD by method of sections and remaining forces in
members by method of joints. Tabulate the results properly. (May 2008, Dec. 2011) [Ans:
FCE= 4.5kN(C), FCD= 2.5kN(C), FBD= 6.5kN(T)]
Fig: 5 Fig: 6
7] Determine the forces in members BC, CE and DE by method of sections and all other
members by method of joints. Give the result in a table. (May 2014) [Ans: FBC= 34.5kN(C),
For Div. D ……….Prepared by Mr. Kiran Beldar
Engineering Mechanics Unit No. 2
FCE= 40 kN(T), FDE= 19.9 kN(T), FAB= 34.56 kN(C), FAE= 59.9 kN(T), FBE= 40 kN(C),
FCD= 40 kN(C)]
8] Find the forces in CF and CD by method of section and the remaining by method of joints.
(May 2016) [Ans: FCD= 15.79 kN, FCF= 17.24 kN, FDE= 15.75 kN, FAB= 12.67 kN]
Fig: 7 Fig: 8
9] A simply supported pin jointed truss is loaded and supported as shown in fig. i) Identify the
members carrying zero forces ii) Find support reactions iii) Find forces in members CD, CG,
FG and CF using method of section. (May 2018)
10] In the truss shown compute the forces in each member. (May 2017)
Fig: 9 Fig: 10
11] A truss is loaded and supported as shown. Determine the following: i) Identify the zero
force members if any. ii) Find the forces in members EF,ED and FC by method of joints. iii)
Find the forces in members GF, GC and BC by method of sections. (Dec. 2016)
Fig: 11
For Div. D ……….Prepared by Mr. Kiran Beldar
You might also like
- Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies: Problems Worked Out in ClassDocument5 pagesEquilibrium of Rigid Bodies: Problems Worked Out in ClassAman GuptaNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument11 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodiesdonald escalanteNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1mohityaav0% (1)
- BT RRM 16 схемаDocument17 pagesBT RRM 16 схеманикNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Solutions of Right Triangles: Math 12 Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDocument12 pagesLesson 3: Solutions of Right Triangles: Math 12 Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDan CasuraoNo ratings yet
- EE592 Lab Manual Power Sytem LabDocument48 pagesEE592 Lab Manual Power Sytem LabCiczmockingbird TsvkAdmNo ratings yet
- 300+ TOP D.C. GENERATORS Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument32 pages300+ TOP D.C. GENERATORS Multiple Choice Questions and Answershem singhNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document8 pagesModule 3VenkatNo ratings yet
- All (GT) Nitin SirDocument708 pagesAll (GT) Nitin SirARP100% (1)
- Quiz #3 - Eng'g MechanicsDocument4 pagesQuiz #3 - Eng'g MechanicsAnthony Jay PoraqueNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Rigid Bodies and FBD PDFDocument7 pagesTutorial 1 Rigid Bodies and FBD PDFBharat SaiNo ratings yet
- File 1582710448 PDFDocument5 pagesFile 1582710448 PDFNatasha Marie MallareNo ratings yet
- Structural AnalysisDocument14 pagesStructural AnalysisPrincess Gupo Tañas100% (1)
- 01 - OMICRON PD Seminar - Introduction of Partial Discharge MeasurementDocument7 pages01 - OMICRON PD Seminar - Introduction of Partial Discharge Measurementtranhieu123100% (1)
- Assignment 1 MOSDocument47 pagesAssignment 1 MOSGaurav RajNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Analysis of Electric Power SystemsDocument181 pagesModelling and Analysis of Electric Power SystemsPasztNo ratings yet
- Tut Applied-I PDFDocument34 pagesTut Applied-I PDFMadan PanditNo ratings yet
- 12 MarksDocument23 pages12 Markslakshmigsr6610No ratings yet
- PDFDocument543 pagesPDFAon HemmatadNo ratings yet
- CMXC 007 Service Manual 003038-9Document9 pagesCMXC 007 Service Manual 003038-9Siding BarroNo ratings yet
- PSAD 4 May 5 2023Document19 pagesPSAD 4 May 5 2023Renne Jude Rollorata100% (1)
- Engineering Mechanics Unit 1 QuestionsDocument4 pagesEngineering Mechanics Unit 1 QuestionsShrey SanwariaNo ratings yet
- E.Mech Tutorials Mod 1Document8 pagesE.Mech Tutorials Mod 1rajee101No ratings yet
- Applied Mechanics I Tutorials and Assignment - RemovedDocument20 pagesApplied Mechanics I Tutorials and Assignment - RemovedYoukesh GautamNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument7 pagesDynamics of Rigid BodiesRichelle Valerie BastroNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document2 pagesQuiz 2JonathanNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Rigid BodiesDocument15 pagesMechanics of Rigid BodiessoulcivicNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Engineering LectureDocument12 pagesEarthquake Engineering LectureMeverlyn RoqueroNo ratings yet
- Civil Iii Year 2017-2018Document109 pagesCivil Iii Year 2017-2018Frank JohnNo ratings yet
- Question Bank & Bit BankDocument20 pagesQuestion Bank & Bit BankKomma HemaNo ratings yet
- November 2023 - PSAD 1Document2 pagesNovember 2023 - PSAD 1Viele Antonette NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No 1Document3 pagesProblem Set No 1Fatima Therese ManaloNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Set - ADocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Set - AJeana Rick GallanoNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument11 pagesStrength of Materialsjerold_arandiaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems - Strema Part 1Document4 pagesPractice Problems - Strema Part 1Meverlyn RoqueroNo ratings yet
- GEOTECH 1 Module 8Document12 pagesGEOTECH 1 Module 8Earl averzosaNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET in Hydraulics-1Document4 pagesPROBLEM SET in Hydraulics-1Earl averzosaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Fluid Mechanics - Drill 6: MM 200 E A E A Gpa 105 MM 500 E ADocument4 pagesStrength of Materials and Fluid Mechanics - Drill 6: MM 200 E A E A Gpa 105 MM 500 E ANicole RodilNo ratings yet
- TrussDocument5 pagesTrussChaubey AjayNo ratings yet
- Pretest, RC Part 2 PDFDocument1 pagePretest, RC Part 2 PDFleanne DespaNo ratings yet
- ENGR207 - Assignment#1Document5 pagesENGR207 - Assignment#1GendyNo ratings yet
- BrasdaDocument3 pagesBrasdaJayson Brylle MojaresNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials 6 (May 2022)Document4 pagesStrength of Materials 6 (May 2022)Kristelle V. TorrealbaNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 1Document2 pagesQuiz No 1Tris ZackNo ratings yet
- Newest CompreDocument5 pagesNewest CompreJohn Dominic B. EugenioNo ratings yet
- Review Module 23 Geotechnical Engineering 4 Part 1Document2 pagesReview Module 23 Geotechnical Engineering 4 Part 1Mark Daren Patrona RamonNo ratings yet
- Sec - PS1Document2 pagesSec - PS1Monica Amor AbengozaNo ratings yet
- A Circular Prestressed Concrete Pile Having A Diameter of 40 CM Is To Be Driven in A Layer of Loose SandDocument2 pagesA Circular Prestressed Concrete Pile Having A Diameter of 40 CM Is To Be Driven in A Layer of Loose SandJay Saberdo CayaNo ratings yet
- MS TowerDocument2 pagesMS TowerSamuelNo ratings yet
- Problems FluidmechanicsDocument5 pagesProblems Fluidmechanicsanon_182348362No ratings yet
- School of Mechanical Engineering, Kiit University Assignment 1 Subject: Engineering Mechanics DueonDocument3 pagesSchool of Mechanical Engineering, Kiit University Assignment 1 Subject: Engineering Mechanics Dueonmantra20100% (3)
- Electronics and Communications Engineering: Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesDocument8 pagesElectronics and Communications Engineering: Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesdeevoncNo ratings yet
- Final BookDocument98 pagesFinal BookgautamNo ratings yet
- Exercise WorkshopDocument2 pagesExercise WorkshopNicolas CorreaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Trigonometry of Right Triangles: Math 12 Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDocument13 pagesLesson 2: Trigonometry of Right Triangles: Math 12 Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDan CasuraoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy: Choose The Letter of The Best Answer in Each Questions - Avoid ERASURESDocument131 pagesEngineering Economy: Choose The Letter of The Best Answer in Each Questions - Avoid ERASURESStephanie ParkNo ratings yet
- Math Terms 1 RefresherDocument4 pagesMath Terms 1 Refreshercat buenafeNo ratings yet
- Ce60 Theory of StructuresDocument2 pagesCe60 Theory of StructuresKhryzzia Maye FelicildaNo ratings yet
- MSTE Module 6Document2 pagesMSTE Module 6jovar jumao-asNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Part 1Document1 pageAssignment 3 Part 1Student555No ratings yet
- Mechanics sTREngth of MaterialsDocument1 pageMechanics sTREngth of MaterialsDenaiya Watton Leeh100% (1)
- 3-Dimensional Drawings, or Photographic or Pictorial Drawings. Isometric DrawingDocument12 pages3-Dimensional Drawings, or Photographic or Pictorial Drawings. Isometric DrawingHarshit SolankiNo ratings yet
- Practice ProblemsFluidsDocument4 pagesPractice ProblemsFluidsRitsu TainakaNo ratings yet
- Timber Design ReviewDocument4 pagesTimber Design ReviewalfredoNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 Engineering Mechanics Set 1Document3 pagesCE Board Nov 2020 Engineering Mechanics Set 1Eugenio Genesis AbadNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 EquilibriumDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 EquilibriumNirmit PatilNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Statically Determinate StructureDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 Statically Determinate Structurerajiv sharmaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Course Assignment-I Question Paper 12-05-2023Document4 pagesEngineering Mechanics Course Assignment-I Question Paper 12-05-2023Sruthi ChallapalliNo ratings yet
- 4 Lecture Junction Box and Insulation TapeDocument4 pages4 Lecture Junction Box and Insulation TapeKiran BeldarNo ratings yet
- 4 Lecture Cable Lugs - Part 1Document6 pages4 Lecture Cable Lugs - Part 1Kiran Beldar100% (1)
- 3 Lecture Cable Glands - Part 1Document5 pages3 Lecture Cable Glands - Part 1Kiran BeldarNo ratings yet
- 1 Lecture MC4 Connectors - Part 1Document8 pages1 Lecture MC4 Connectors - Part 1Kiran BeldarNo ratings yet
- 1 Lecture ACDC COMBINER BOX - Part 1Document7 pages1 Lecture ACDC COMBINER BOX - Part 1Kiran BeldarNo ratings yet
- Force Physics (F Ma)Document3 pagesForce Physics (F Ma)Golden TrioNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment 4Document4 pagesLab Experiment 4Saad AliKhanNo ratings yet
- WCS1800 PDFDocument5 pagesWCS1800 PDFAbhii BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Water Rocket PhysicsDocument8 pagesWater Rocket PhysicsFranciscoNo ratings yet
- chp5 1Document6 pageschp5 1Harshith GowdaNo ratings yet
- PRW Series: Cylindrical Proximity Sensor With Cable Outgoing ConnectorDocument6 pagesPRW Series: Cylindrical Proximity Sensor With Cable Outgoing ConnectorMin ZayarNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of A Wireless Power Transfer System With An Intermediate Coil For High EfficiencyDocument10 pagesAnalysis and Design of A Wireless Power Transfer System With An Intermediate Coil For High Efficiencywalidghoneim1970No ratings yet
- Electric Current and Emf: PHYS 2 LSD 2020Document16 pagesElectric Current and Emf: PHYS 2 LSD 2020wonuNo ratings yet
- DC 06 Series Parallel Cks Rev02Document42 pagesDC 06 Series Parallel Cks Rev02kennypennyNo ratings yet
- The Damped Harmonic Oscillator: 1. Mass-Spring SystemDocument10 pagesThe Damped Harmonic Oscillator: 1. Mass-Spring SystemI AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Appendix B: Magnetic Core DataDocument16 pagesAppendix B: Magnetic Core Datadorin serbanNo ratings yet
- Ial Maths Mech 1 RE1 PDFDocument16 pagesIal Maths Mech 1 RE1 PDFWandaNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Computational Approach For Frictional Analysis in ABAQUSDocument12 pagesAn Efficient Computational Approach For Frictional Analysis in ABAQUSMallikarjunachari GNo ratings yet
- Guidelines and Fundamental Considerations For Axle BalancingDocument40 pagesGuidelines and Fundamental Considerations For Axle BalancingAnonymous PVXBGg9TNo ratings yet
- Formulas For The Skin EffectDocument13 pagesFormulas For The Skin Effectsergi67No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Engineering Mechanics Basic Concepts, Methods and ProblemsDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Engineering Mechanics Basic Concepts, Methods and ProblemsWendell FloresNo ratings yet
- Gandhinagar Institute of Technology: Mechanical DepartmentDocument17 pagesGandhinagar Institute of Technology: Mechanical DepartmentPAL PARTHIVNo ratings yet
- Single-Phase Motors - Troubleshooting FlukeDocument4 pagesSingle-Phase Motors - Troubleshooting FlukeTo Duc Hung100% (1)
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Kaushal KumarNo ratings yet
- Ee 151 - Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesEe 151 - Electrical EngineeringsubhazNo ratings yet
- Common Units in Electrical and Electrical EngineeringDocument2 pagesCommon Units in Electrical and Electrical Engineeringegaupc2123No ratings yet