Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIO-MEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION SYLLABUS
Uploaded by
dhoni0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views2 pagesOriginal Title
EEE1008_BIO-MEDICAL-INSTRUMENTATION_ETH_2.0_39_EEE1008
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views2 pagesBIO-MEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION SYLLABUS
Uploaded by
dhoniCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
EEE1008 BIO-MEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION L T P J C
3 0 0 4 4
Pre-requisite NIL Syllabus version
Anti-requisite v. 2.0
Course Objectives:
1. To give an understanding of the biological signals and signal acquisition
2. To provide the design concepts of bioelectric amplifiers
3. To learn the principle and operation of various biomedical systems
Expected Course Outcomes:
On the completion of this course the student will be able to:
1. Evaluate and analyse the different physiological signals
2. Relate the knowledge to select appropriate medical instruments
3. Design and maintain the bio electric devices used for diagnostic equipment
4. Develop and analyse the therapeutic devices.
5. Create and understand the procedure in analysis of Blood used in medical laboratory
6. Evaluate the process involved in blood cell counters and sensors
7. Use the knowledge to differentiate the advanced diagnostic techniques.
8. Design a component or a product applying all the relevant standards with realistic
constraints
Student Learning Outcomes (SLO): 5,9,10
5. Having design thinking capability
9. Having problem solving ability- solving social issues and engineering problems
10. Having a clear understanding of professional and ethical responsibility
Module:1 Introduction to Biomedical Instrumentation and Measurement 8 Hours
Sources of bioelectric potentials, cardiovascular system, Central nervous system, Muscular System,
linear/nonlinear analysis of different physiological signals (ECG, EEG, EMG), Electrode theory-
mathematical analysis including Nernst equation, Goldman equation, Electrical conductivity of
electrode, Electrodes for ECG, EEG &EMG.
Module:2 General Considerations of Medical Instruments 8 Hours
Operational Amplifiers, Bioelectric Amplifiers, Selection of biomedical amplifiers – Isolation
amplifiers, Charge amplifiers and Chopper amplifier. Characteristics of biomedical recorder
amplifiers, Physiological effects of electric currents, Electric shock hazards and leakage currents,
Methods of accident prevention.
Module:3 Diagnostic Equipment 7 Hour
ECG Lead Configuration, Vector cardiograph, Phono-cardiograph, EEG and EMG Electrode system,
Recorders, Measurement of various volumes/capacity of lungs, Spirometer. Measurement of cardiac
output, blood flow and blood pressure.
Module:4 Therapeutic Equipment 6 Hours
Cardiac pacemakers, cardiac defibrillators, nerve & muscle stimulators, diathermy-types, ventilators,
Dialyzer.
Module:5 Medical Laboratory Instrumentation 5 Hours
Analysis of Blood-Measurement of pH, pO2 and pCO2 value of blood using pH/gas analyzers
Module:6 Medical Laboratory Measurement 4 Hours
Photometers, Hematology, Blood cell counters, Electrophoresis- Serum detection and classification,
Blood Glucose Sensors, GSR measurements.
Module:7 Advanced Diagnostic Techniques 5 Hours
2D, 3D Analysis and Visualization (X-Ray, MRI, CT), Biomedical Spectroscopy, Optical coherence
tomography, Fluorescence based Bio-detection & Bio-imaging- Case study: Telemedicine based
health care monitoring system.
Module:8 Contemporary issues: 2 hours
Text Book(s)
Leslie Cromwell, Fred J, Weibell & Erich A and P Feiffer, ‘Biomedical Instrumentation and
1.
Measurements’, 2nd Edition, PHI, 2011.
J.J. Carr & J.M. Brown, ‘Introduction to biomedical Equipment Technology’, Prentice Hall,
2.
4th Edition, 2011.
Reference Books
R. S. Khandpur, ‘Handbook of Biomedical Instrumentation’, Tata Mc-Graw Hill, 2nd
1.
edition, 2014.
John.E. Hall, Guyton and Hall, Textbook of Medical Physiology, Saunders; 13th Edition,
2.
2015.
Rangaraj M. Rangayyan, ‘Biomedical Signal Analysis’, A Case-Study Approach, Wiley, 2nd
3.
Edition, 2015.
Mode of Evaluation: CAT I & II – 30%, DA I & II – 20%, Quiz – 10%, FAT – 40%
Mode of assessment:
Recommended by Board of Studies 30/11/2015
Approved by Academic Council 39th AC Date 17/12/2015
You might also like
- Principles of Measurement and Transduction of Biomedical VariablesFrom EverandPrinciples of Measurement and Transduction of Biomedical VariablesNo ratings yet
- EEE1008 BIO-MEDICAL INSTRUMENTATIONDocument3 pagesEEE1008 BIO-MEDICAL INSTRUMENTATIONNathan ShankarNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide for Biomedical Signals Analysis Using Machine Learning Techniques: A MATLAB Based ApproachFrom EverandPractical Guide for Biomedical Signals Analysis Using Machine Learning Techniques: A MATLAB Based ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- KTU BISyllabus1Document2 pagesKTU BISyllabus1Arun JerardNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Biosensors: Applications in Diagnostics, Therapeutics, Environment, and Food ManagementFrom EverandElectrochemical Biosensors: Applications in Diagnostics, Therapeutics, Environment, and Food ManagementNo ratings yet
- EE372 Biomedical InstrumentationDocument2 pagesEE372 Biomedical InstrumentationASHIK PRASADNo ratings yet
- Phye222 13Document3 pagesPhye222 13praveenNo ratings yet
- EE372 Biomedical InstrumentationDocument2 pagesEE372 Biomedical InstrumentationDeepu V SNo ratings yet
- EC8073 SYLLABUSDocument1 pageEC8073 SYLLABUSb.obsr.o.bbins.67.8No ratings yet
- Microfluidic BiosensorsFrom EverandMicrofluidic BiosensorsWing Cheung MakNo ratings yet
- AE403BIOMEDICALINSTRUMENTATIONDocument2 pagesAE403BIOMEDICALINSTRUMENTATIONalwin sozaNo ratings yet
- BMI403.3 Biomedical InstrumentationDocument2 pagesBMI403.3 Biomedical InstrumentationDarpan Specchio PudasainiNo ratings yet
- Department of Biomedical Engineering Jimma University, Jimma Institute of TechnologyDocument5 pagesDepartment of Biomedical Engineering Jimma University, Jimma Institute of Technologymisgana etichaNo ratings yet
- BM 603 Biomedical Instrumentation Course OverviewDocument3 pagesBM 603 Biomedical Instrumentation Course OverviewA.V.R. Krishna RaoNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument1 pageSyllabusRubini RavichandranNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument1 pageSyllabusRubini RavichandranNo ratings yet
- AE403BIOMEDICALINSTRUMENTATION (Careeryuga)Document2 pagesAE403BIOMEDICALINSTRUMENTATION (Careeryuga)Akhil A BNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Instrumentation EE473 EE573 SylDocument1 pageBiomedical Instrumentation EE473 EE573 SylRahmi ArslanNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Instrumentation EE473 EE573 Syl PDFDocument1 pageBiomedical Instrumentation EE473 EE573 Syl PDFRahmi ArslanNo ratings yet
- Medical Electronics SyllabusDocument1 pageMedical Electronics SyllabusJanani MunisamyNo ratings yet
- 0 Biomedical EngineeringDocument3 pages0 Biomedical EngineeringChristy PollyNo ratings yet
- Bio-Medical Engineering Open ElectiveDocument1 pageBio-Medical Engineering Open ElectiveArun Kumar DhupamNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Instrumentation - Department Elective - IDocument2 pagesBiomedical Instrumentation - Department Elective - IKapasi TejasNo ratings yet
- 2161712Document4 pages2161712RaviNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document4 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Jigneshkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Equipment-I: Course Code: BM 19. Total Lectures: 40Document1 pageBiomedical Equipment-I: Course Code: BM 19. Total Lectures: 40Sachin Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Essential biomedical equipment and clinical monitoring systemsDocument1 pageEssential biomedical equipment and clinical monitoring systemsSachin Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- For More Visit WWW - Ktunotes.inDocument3 pagesFor More Visit WWW - Ktunotes.inVishnuNo ratings yet
- EC482 Biomedical Engineering (Ktustudents - In)Document3 pagesEC482 Biomedical Engineering (Ktustudents - In)Sachin SukumaranNo ratings yet
- EC482 Biomedical Engineering (Careeryuga)Document3 pagesEC482 Biomedical Engineering (Careeryuga)neenakaNo ratings yet
- EC482 Biomedical EngineeringDocument3 pagesEC482 Biomedical EngineeringAlex VincentNo ratings yet
- B Tech ECE Syllabus 2008-09 Non-UnitizedDocument1 pageB Tech ECE Syllabus 2008-09 Non-UnitizedAnirudh MaheshwaramNo ratings yet
- Notice For Publication of Syllabus For Paramedical PostsDocument7 pagesNotice For Publication of Syllabus For Paramedical Postsom vermaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Biomedical Systems & DevicesDocument8 pagesPrinciples of Biomedical Systems & DevicesR3B3LYOU5No ratings yet
- IC407 Biomedical InstrumentationDocument2 pagesIC407 Biomedical InstrumentationVaishnav PsNo ratings yet
- EE-473/EE-573 Biomedical InstrumentationDocument1 pageEE-473/EE-573 Biomedical InstrumentationmakislaskosNo ratings yet
- BMEDocument2 pagesBMEsansureNo ratings yet
- EC365 Biomedical EngineeringDocument3 pagesEC365 Biomedical Engineeringgodwinraj123No ratings yet
- 5th Sem B.tech BME SyllabusDocument11 pages5th Sem B.tech BME SyllabusSouvik DasNo ratings yet
- BioinstrumentationDocument394 pagesBioinstrumentationapi-370230280% (5)
- Lecture 1Document6 pagesLecture 1غيث باسم محمد عباسNo ratings yet
- PHDY 303 Biomedical Instrumentation L T PC 3 0 0 3: M. Sc. Physics Regulations 2019Document2 pagesPHDY 303 Biomedical Instrumentation L T PC 3 0 0 3: M. Sc. Physics Regulations 2019Amiruddin RafiudeenNo ratings yet
- Ei 6704Document2 pagesEi 6704kotteeswaranNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Biophysics (PHR 177) COURSEDocument29 pagesAn Introduction To Biophysics (PHR 177) COURSENermeinKhattabNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University Biomedical EngineeringDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University Biomedical EngineeringPriyank ShahNo ratings yet
- ECE 309 Biomedical Signal ProcessingDocument2 pagesECE 309 Biomedical Signal Processing;(No ratings yet
- FYVAC Medical Gadgets For Healthcare SyllabusDocument1 pageFYVAC Medical Gadgets For Healthcare SyllabusGennyNo ratings yet
- Legends: L-Lecture T - Tutorial/Teacher Guided Theory Practice P - Practical C - Credit ESE - End Semester Examination PADocument7 pagesLegends: L-Lecture T - Tutorial/Teacher Guided Theory Practice P - Practical C - Credit ESE - End Semester Examination PADr JNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Instrumentation EC704C Contacts: 3L Credits: 3 Module - 1 (Fundamentals)Document2 pagesBiomedical Instrumentation EC704C Contacts: 3L Credits: 3 Module - 1 (Fundamentals)Vigneshwaran SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Webster BioinstrumentationDocument394 pagesWebster BioinstrumentationMaria Jose GardeaNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Instrumentation (BTEE 341) Course Content: Joseph Asamoah-Asare STUDocument6 pagesBiomedical Instrumentation (BTEE 341) Course Content: Joseph Asamoah-Asare STUAbugba EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Dasar ElektronikaDocument6 pagesDasar ElektronikaAngga Putra MargaNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation & Control Engineering Electives and CoursesDocument21 pagesInstrumentation & Control Engineering Electives and CoursesNeha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Biomedical InstrumentationDocument1 pageBasics of Biomedical InstrumentationFrancy Irudaya Rani E67% (3)
- Biophysics Medical PhysicsDocument6 pagesBiophysics Medical PhysicsCpopNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction in Biomedical SensorsDocument15 pagesChapter 1 Introduction in Biomedical Sensorssadeq ali al-srabiNo ratings yet
- EE4904 Biomedical Instrumentation - OBTLDocument6 pagesEE4904 Biomedical Instrumentation - OBTLAaron TanNo ratings yet
- Double Field Revolving Theory ExplainedDocument5 pagesDouble Field Revolving Theory ExplaineddhoniNo ratings yet
- Circle Diagram Performance AnalysisDocument26 pagesCircle Diagram Performance AnalysisdhoniNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 19-Feb-2020 Frequency TransformationDocument4 pagesWINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 19-Feb-2020 Frequency TransformationdhoniNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - DC - MotorDocument39 pagesUnit 3 - DC - MotordhoniNo ratings yet
- Circle Diagram Performance AnalysisDocument26 pagesCircle Diagram Performance AnalysisdhoniNo ratings yet
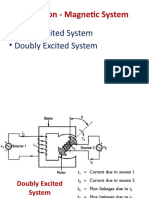
- Excitation - Magnetic System: - Singly Excited System - Doubly Excited SystemDocument12 pagesExcitation - Magnetic System: - Singly Excited System - Doubly Excited SystemdhoniNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 10-Feb-2020 IIR - Bilinear Transformation ExamplesDocument9 pagesWINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 10-Feb-2020 IIR - Bilinear Transformation ExamplesdhoniNo ratings yet
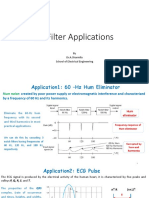
- WINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 17-Feb-2020 IIR Filter ApplicationsDocument7 pagesWINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 17-Feb-2020 IIR Filter ApplicationsdhoniNo ratings yet
- InTech-Principles of External Defibrillators PDFDocument24 pagesInTech-Principles of External Defibrillators PDFdhoniNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2019-20 EEE1008 ETH VL2019205002298 Reference Material I 21-Feb-2020 PacemakersDocument31 pagesWINSEM2019-20 EEE1008 ETH VL2019205002298 Reference Material I 21-Feb-2020 PacemakersdhoniNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2018-19 - CSE1002 - LO - SJT120 - VL2018195003969 - Reference Material II - Practice Problems On Pointers and DMADocument3 pagesWINSEM2018-19 - CSE1002 - LO - SJT120 - VL2018195003969 - Reference Material II - Practice Problems On Pointers and DMAdhoniNo ratings yet
- BIO-MEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION SYLLABUSDocument2 pagesBIO-MEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION SYLLABUSdhoniNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 27-Jan-2020 Analog FiltersDocument8 pagesWINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 27-Jan-2020 Analog FiltersdhoniNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 10-Feb-2020 IIR - Bilinear Transformation ExamplesDocument9 pagesWINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 10-Feb-2020 IIR - Bilinear Transformation ExamplesdhoniNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2018-19 - CSE1002 - LO - SJT120 - VL2018195003969 - Reference Material I - Solution - Print All Permutations of A Given String Using PointersDocument2 pagesWINSEM2018-19 - CSE1002 - LO - SJT120 - VL2018195003969 - Reference Material I - Solution - Print All Permutations of A Given String Using PointersdhoniNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 03-Feb-2020 DESIGN OF IIR FILTER PDFDocument53 pagesWINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 03-Feb-2020 DESIGN OF IIR FILTER PDFdhoniNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2018-19 - CSE1002 - LO - SJT120 - VL2018195003969 - Reference Material II - Practice Problems in CDocument1 pageWINSEM2018-19 - CSE1002 - LO - SJT120 - VL2018195003969 - Reference Material II - Practice Problems in CdhoniNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2019-20 CSE2003 EPJ VL2019205001834 Review I Schedule Lab 1 Study Materials For ArrayDocument9 pagesWINSEM2019-20 CSE2003 EPJ VL2019205001834 Review I Schedule Lab 1 Study Materials For ArraydhoniNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 04-Dec-2019 Int-Dsp-1 PDFDocument51 pagesWINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 04-Dec-2019 Int-Dsp-1 PDFAlfredNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2018-19 - CSE1002 - LO - SJT120 - VL2018195003969 - Reference Material II - Practice Problems On Pointers and DMADocument3 pagesWINSEM2018-19 - CSE1002 - LO - SJT120 - VL2018195003969 - Reference Material II - Practice Problems On Pointers and DMAdhoniNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifiers and Linear Integra 59adfcda1723ddc0c501612bDocument2 pagesOperational Amplifiers and Linear Integra 59adfcda1723ddc0c501612bpoornaNo ratings yet
- Answers To Review QuestionsDocument17 pagesAnswers To Review Questionsdhoni0% (1)
- TermsDocument1 pageTermsdhoniNo ratings yet
- Power Systems Guides Book by CL Wadhwa PDFDocument3 pagesPower Systems Guides Book by CL Wadhwa PDFAnkit Kumar0% (4)
- Medical Image Forgery Detection For Smart Healthcare: IEEE Communications Magazine April 2018Document6 pagesMedical Image Forgery Detection For Smart Healthcare: IEEE Communications Magazine April 2018dhoniNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 17-Feb-2020 IIR Filter ApplicationsDocument7 pagesWINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 17-Feb-2020 IIR Filter ApplicationsdhoniNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2019-20 STS2102 SS VL2019205000241 Reference Material I 20-Dec-2019 B.Tech II Yr 4th Sem Writing SkillsDocument5 pagesWINSEM2019-20 STS2102 SS VL2019205000241 Reference Material I 20-Dec-2019 B.Tech II Yr 4th Sem Writing SkillsdhoniNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 19-Feb-2020 Frequency TransformationDocument4 pagesWINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 19-Feb-2020 Frequency TransformationdhoniNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 10-Feb-2020 IIR - Bilinear Transformation ExamplesDocument9 pagesWINSEM2019-20 EEE2005 ETH VL2019205002607 Reference Material I 10-Feb-2020 IIR - Bilinear Transformation ExamplesdhoniNo ratings yet
- State of Nature Alternatives 1 2 3Document10 pagesState of Nature Alternatives 1 2 3Michael Allen RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Upload 0 Conditional 3RD LevelDocument4 pagesUpload 0 Conditional 3RD LevelDexy CacpataNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics Tutorial for EQT 272Document2 pagesProbability and Statistics Tutorial for EQT 272Jared KuyislNo ratings yet
- Фонетика Тест 1-4Document1 pageФонетика Тест 1-4Карина КамаловаNo ratings yet
- Cot Lesson Plan in Math 5 Q1Document11 pagesCot Lesson Plan in Math 5 Q1Gina VilloriaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Materials For Hydrogen ProductionDocument150 pagesAdvanced Materials For Hydrogen ProductionGhazanfar SheikhNo ratings yet
- Zhao Et Al 2012Document10 pagesZhao Et Al 2012Mohd Sofiyan Bin SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document10 pagesLecture 3Dr. Saad Saffah HresheeNo ratings yet
- Social EntrepreneurshipDocument21 pagesSocial EntrepreneurshipSree LakshyaNo ratings yet
- SPEX 201 Lab 1 - Motion Analysis Techniques - STUDENT - 2023Document8 pagesSPEX 201 Lab 1 - Motion Analysis Techniques - STUDENT - 2023tom mallardNo ratings yet
- EOY History Sec 1 2022Document8 pagesEOY History Sec 1 2022SherryNo ratings yet
- (Reuters Institute For The Study of Journalism) James Painter - Climate Change in The Media - Reporting Risk and Uncertainty-I. B. Tauris (2013)Document192 pages(Reuters Institute For The Study of Journalism) James Painter - Climate Change in The Media - Reporting Risk and Uncertainty-I. B. Tauris (2013)Thomas Ravelly Batista dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Spe 193796 MsDocument22 pagesSpe 193796 MsMurtibaahshe HDNo ratings yet
- Comparing Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDocument11 pagesComparing Male and Female Reproductive SystemsRia Biong TaripeNo ratings yet
- 11 Axis FormationDocument61 pages11 Axis Formationapi-3800038100% (1)
- PK Mitomycin C in LCMSDocument13 pagesPK Mitomycin C in LCMSRuthNo ratings yet
- Homo Deus PDFDocument14 pagesHomo Deus PDFThaw TarNo ratings yet
- Adequacy and Utilization of Instructional Resources For Skills Acquisiton in BrickDocument5 pagesAdequacy and Utilization of Instructional Resources For Skills Acquisiton in BrickSaidu NingiNo ratings yet
- Math6 q1 Mod5 AdditionofDecimals v4-SIGNEDDocument34 pagesMath6 q1 Mod5 AdditionofDecimals v4-SIGNEDARRIANE JOY TOLEDONo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1: Do and See The Surface Tension: 1. Describe The Shape of The Water On Top of The Coin. (5 Points)Document3 pagesLaboratory Activity 1: Do and See The Surface Tension: 1. Describe The Shape of The Water On Top of The Coin. (5 Points)Clarence Bautista100% (2)
- Global Citizenship Courseware SSP032 GCED 1Document24 pagesGlobal Citizenship Courseware SSP032 GCED 1siegaralphNo ratings yet
- Pragmatics Kel 2Document10 pagesPragmatics Kel 2i iNo ratings yet
- ADVANCED PRACTICE TEST 2Document7 pagesADVANCED PRACTICE TEST 2phươngNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Biology and Health: M. Gail K. Krickeberg J. M. Samet A. Tsiatis W. WongDocument579 pagesStatistics For Biology and Health: M. Gail K. Krickeberg J. M. Samet A. Tsiatis W. WongViníciusSeixasNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL APPROVAL FORMDocument2 pagesCHEMICAL APPROVAL FORMYosep SasadaNo ratings yet
- Vol 5, No 2 November, Pp. 99-111 P-ISSN 2549-4880, E-ISSN 2614-1310 Journal DOI: WebsiteDocument11 pagesVol 5, No 2 November, Pp. 99-111 P-ISSN 2549-4880, E-ISSN 2614-1310 Journal DOI: WebsiteSyarah RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Crude Oil Blends PDFDocument6 pagesAssessment of Crude Oil Blends PDFDanivian HigginsNo ratings yet
- Sep. Gravimetrica - CromitaDocument13 pagesSep. Gravimetrica - Cromitaemerson sennaNo ratings yet
- 9.06&9.01social Psychology JournalDocument17 pages9.06&9.01social Psychology JournalMatthew CheungNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme BI Penulisan PPT 5MDocument7 pagesMarking Scheme BI Penulisan PPT 5MTAN KOH SIANG MoeNo ratings yet