Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermoplastic
Uploaded by
wisnu aji nugrohoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermoplastic
Uploaded by
wisnu aji nugrohoCopyright:
Available Formats
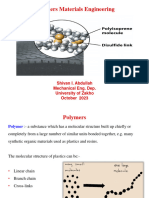
Thermoplastic materials are those materials that are made of polymers linked by
intermolecular interactions or van der Waals forces, forming linear or branched
structures.
A thermoplastic material it can be compared to a set of strings that are mixed on a table,
each of these string is represents a polymer, the greater degree of mixing of the strings
greater the effort will be made to separate the strings from each other, due the friction
that occurs between each of the cords offers resistance to separate, in this example the
friction represents the intermolecular forces that holds together the polymer.
Depending on the degree of the intermolecular interactions that occurs between the
polymer chains, the polymer can take two different types of structures, amorphous or
crystalline structures, being possible the existence of both structures in the same
thermoplastic material:
Amorphous structure - polymer chains acquire a bundled structure, like a ball of
thread disordered, amorphous structure that is directly responsible for the elastic
properties of thermoplastic materials.
Crystal structure - polymer chains acquire an ordered and compacted structure, it
can be distinguished mainly lamellar structures and micellar form. This crystal structure
is directly responsible for the mechanical properties of resistance to stresses or loads
and the temperature resistance of thermoplastic materials.
If the thermoplastic material has a high concentration of polymers with amorphous
structures, the material will have a poor resistance to loads but it will have an excellent
elasticity. But on the contrary, if the thermoplastic material has a high concentration of
polymers with a crystalline structure, the material will be very strong and even stronger
than thermoset materials, but with a little elasticity that provides the characteristic
fragility of these materials.
Properties of thermoplastic materials are:
It may melt before passing to a gaseous state.
Allow plastic deformation when it is heated.
They are soluble in certain solvents.
Swell in the presence of certain solvents.
Good resistance to creep.
Examples and applications of thermoplastic plastic materials:
High pressure polyethylene as applied to rigid material covered with electrical
machines, tubes, etc...
Low pressure polyethylene elastic material used for insulation of electrical cables,
etc...
Polystyrene applied for electrical insulation, handles of tools...
Polyamide used for making ropes, belts, etc...
PVC or polyvinyl chloride for the manufacture of insulation materials, pipes,
containers, etc...
Examples of thermoplastic adhesives:
Acrylates
Cyanoacrylates
Epoxy cured by ultraviolet radiation
Acrylates cured by ultraviolet radiation
Now that you know the thermoplastics materials, did you know that most packages that
contains soft drinks are made from thermoplastic materials?
You might also like
- Advanced Mechanics of Composite Materials and Structural ElementsFrom EverandAdvanced Mechanics of Composite Materials and Structural ElementsNo ratings yet
- 32vp297en PDFDocument112 pages32vp297en PDFMohamedNo ratings yet
- Types of MaterialsDocument13 pagesTypes of MaterialsHaider ManzoorNo ratings yet
- I - T - I ENGINEERS HANDBOOK I M 451145214 PDFDocument193 pagesI - T - I ENGINEERS HANDBOOK I M 451145214 PDFcpîndaru100% (1)
- Introduction To ElastomersDocument18 pagesIntroduction To ElastomersRaghav AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Electrode Selection Excel SheetDocument1 pageElectrode Selection Excel Sheetchandrakit047No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Polymer Engineering: Week-1Document52 pagesFundamentals of Polymer Engineering: Week-1muhammad shahadat awanNo ratings yet
- Polymers: Classification Based On SourceDocument4 pagesPolymers: Classification Based On Sourceatulkumargaur26No ratings yet
- Scaffolding Components PostersDocument3 pagesScaffolding Components PostersRavi Shankar TurlapatiNo ratings yet
- Energy Epp0500 PowerCableAccessories SouthEastEurope PDFDocument140 pagesEnergy Epp0500 PowerCableAccessories SouthEastEurope PDFElafanNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument34 pagesPolymersJerryco AlviarNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastic Materials Are Those Materials That Are Made of Polymers Linked by IntermolecularDocument1 pageThermoplastic Materials Are Those Materials That Are Made of Polymers Linked by IntermolecularVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. (1) Introduction of PolymersDocument21 pagesLecture No. (1) Introduction of PolymersKhalid AbeedNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument3 pagesPolymersjoe_huey_2No ratings yet
- Polymer IntroductionDocument11 pagesPolymer IntroductionmansourotaibiNo ratings yet
- Non Ferrous MaterialsDocument5 pagesNon Ferrous MaterialsSabirNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument7 pagesPolymersrayman9No ratings yet
- PolymersDocument10 pagesPolymersConrado DirectoNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete: Key CharacteristicsDocument13 pagesReinforced Concrete: Key CharacteristicsrisrizNo ratings yet
- Copolymers Are Polymers Composed of Two orDocument1 pageCopolymers Are Polymers Composed of Two orMatti NoNo ratings yet
- The University of The West Indies Faculty of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental EngineeringDocument5 pagesThe University of The West Indies Faculty of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental EngineeringLove LifeNo ratings yet
- Green Vintage Illustration Laboratory Business PresentationDocument31 pagesGreen Vintage Illustration Laboratory Business Presentationmarcmaglaqui30No ratings yet
- 3.0 PolymersDocument8 pages3.0 PolymersKhaembaNo ratings yet
- Branched Polymers Occur When Groups of Units Branch Off From TheDocument2 pagesBranched Polymers Occur When Groups of Units Branch Off From ThedummyNo ratings yet
- POLYMERSDocument64 pagesPOLYMERSSpoodsNo ratings yet
- Polymer and Composite Materials Study MaterialsDocument109 pagesPolymer and Composite Materials Study MaterialsSachi DhanandamNo ratings yet
- Materials and Processes For Agricultural and Biosystems EngineeringDocument16 pagesMaterials and Processes For Agricultural and Biosystems EngineeringMelanie D. Aquino BaguioNo ratings yet
- Polymer - PPTX 1Document103 pagesPolymer - PPTX 1Ratna ThakurNo ratings yet
- Characteristics, Applications and Properties of PolymersDocument2 pagesCharacteristics, Applications and Properties of PolymersGabriel Manalastas LapuzNo ratings yet
- Polymers Materials EngineeringDocument21 pagesPolymers Materials EngineeringHussein SaeedNo ratings yet
- Thanks Ja Labyu MwaDocument4 pagesThanks Ja Labyu MwaMichelle MendozaNo ratings yet
- When Subjected To TemperatureDocument9 pagesWhen Subjected To TemperatureAnbu M S TNo ratings yet
- 13 PolimerDocument54 pages13 PolimerJhonsonNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument3 pagesPolymersnabeelbirdNo ratings yet
- Name-Rishav Kumar REG NO-17BCM0026 Slot-E1 Course-Polymer Technology Course Code-Che1019 DATE-20-01-19Document10 pagesName-Rishav Kumar REG NO-17BCM0026 Slot-E1 Course-Polymer Technology Course Code-Che1019 DATE-20-01-19RishavNo ratings yet
- Non Metallic and PolymersDocument15 pagesNon Metallic and PolymersHemant PokhraNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Part-ADocument7 pagesUnit-Iv Part-AParameswara RajaNo ratings yet
- Ae684 Coatings2Document116 pagesAe684 Coatings2Naresh KumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT IV 20ME403 EMM (Non Metallic Materials) New 02.05.2022 (1) (2578)Document116 pagesUNIT IV 20ME403 EMM (Non Metallic Materials) New 02.05.2022 (1) (2578)Dark ranger YtNo ratings yet
- IAPD Plastics Intro1Document4 pagesIAPD Plastics Intro1eduardo_umNo ratings yet
- Linear, Branched and Cross-Linked Polymers: Technological Institute of The Philippines 363 P. Casal ST., Quiapo, ManilaDocument2 pagesLinear, Branched and Cross-Linked Polymers: Technological Institute of The Philippines 363 P. Casal ST., Quiapo, ManilaMarvin ParasNo ratings yet
- PLASTICvs POLYMERSDocument12 pagesPLASTICvs POLYMERSjincy vargheseNo ratings yet
- Polymers: Thermoplastics Thermosets Elastomers Synthetic FibersDocument14 pagesPolymers: Thermoplastics Thermosets Elastomers Synthetic Fibersmahua khagNo ratings yet
- InTech Thermoplastic ElastomersDocument19 pagesInTech Thermoplastic ElastomersRajeev Singh BaisNo ratings yet
- What Is A Polymer?: TL DR (Too Long Didn't Read)Document2 pagesWhat Is A Polymer?: TL DR (Too Long Didn't Read)SJia LimNo ratings yet
- Pages From Thermoplastic Elastomers - 2012Document18 pagesPages From Thermoplastic Elastomers - 2012Ahmadreza AminianNo ratings yet
- Modern Materials ChemicalsDocument19 pagesModern Materials ChemicalsUsama Majid100% (1)
- Publication 4 12613 5018Document17 pagesPublication 4 12613 5018a12b67scicbNo ratings yet
- Physical and Mechanical Properties of PolymersDocument70 pagesPhysical and Mechanical Properties of PolymersMadhava ReddyNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastics: Group III Cayabyab, Shield R. Espiritu, Micoh L. Mendoza, Maynard T. Radia, Rezvani MDocument20 pagesThermoplastics: Group III Cayabyab, Shield R. Espiritu, Micoh L. Mendoza, Maynard T. Radia, Rezvani MMaynard Trinidad MendozaNo ratings yet
- Applications and Processing of Polymers: Module-11Document20 pagesApplications and Processing of Polymers: Module-11Indranil BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Polymer Science and Its ApplicationsDocument25 pagesPolymer Science and Its ApplicationsPsyKen GrowTopiaNo ratings yet
- POLYMERSDocument11 pagesPOLYMERSSylviaChongNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument21 pagesPolymersSidad SalhNo ratings yet
- Polymers Based Type of Monomer Involved in The Structure: Homopolymer and CopolymerDocument5 pagesPolymers Based Type of Monomer Involved in The Structure: Homopolymer and CopolymerFlorelyn GocotanoNo ratings yet
- Polymers Group 3Document43 pagesPolymers Group 3Theodore JohnFer Buensuceso LicuananNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Composites:: Matrix (Used As Binder) With Another Material Are TheDocument25 pagesConcepts of Composites:: Matrix (Used As Binder) With Another Material Are ThePushparaj Vignesh0% (1)
- Unit II CMDDocument48 pagesUnit II CMDE HarshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 OF mATERIAL ENGINEERINGDocument6 pagesChapter4 OF mATERIAL ENGINEERINGaljhun fujitsuNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument9 pagesPolymersChhavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Nature of Chemical Attacks On Plastic and RubbersDocument7 pagesNature of Chemical Attacks On Plastic and RubberskayodeNo ratings yet
- Physics PresentationDocument13 pagesPhysics PresentationshafaqNo ratings yet
- Critical Success Factors For Construction Project: Articles You May Be Interested inDocument7 pagesCritical Success Factors For Construction Project: Articles You May Be Interested inTaddyBestNo ratings yet
- Personal Statement For PHD in Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 pagesPersonal Statement For PHD in Mechanical EngineeringSylvester JemigbeyiNo ratings yet
- Pensky Marten Flash Point Apparatus PDFDocument4 pagesPensky Marten Flash Point Apparatus PDFngdthgyyttrNo ratings yet
- Control de TemperaturaDocument10 pagesControl de TemperaturavidalNo ratings yet
- Advanced Silicide Based Materials - MoSi2Document13 pagesAdvanced Silicide Based Materials - MoSi2chandravadiyaketanNo ratings yet
- Leaflet ZRZT110-275 - LR - InekoDocument20 pagesLeaflet ZRZT110-275 - LR - InekoSandro RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Total Volume of Column Footing: Concrete WorksDocument4 pagesTotal Volume of Column Footing: Concrete Workssheralld salasNo ratings yet
- DC Blue Digital User ManualDocument5 pagesDC Blue Digital User ManualacinsaNo ratings yet
- Tata Indigo Petrol ManualDocument141 pagesTata Indigo Petrol Manualxtemp100% (3)
- Grid Connected Induction Generator and Self Excited Induction GeneratorDocument2 pagesGrid Connected Induction Generator and Self Excited Induction GeneratorSunil Jain0% (2)
- Bedroom Vocabulary Esl Matching Exercise Worksheets For KidsDocument5 pagesBedroom Vocabulary Esl Matching Exercise Worksheets For KidsAnonymous C49QaOVNo ratings yet
- Boehmer Catalogue Split-BodyDocument24 pagesBoehmer Catalogue Split-Bodysiddhesh_guessNo ratings yet
- Feed Mixer 420-12 490-14: Assembly, Operation and Parts ManualDocument63 pagesFeed Mixer 420-12 490-14: Assembly, Operation and Parts ManualErich illanes uribeNo ratings yet
- Frito Lay's PaperDocument9 pagesFrito Lay's Paperpunam89No ratings yet
- Organic Chemical TechnologyDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemical TechnologykayeNo ratings yet
- ERCO351 4-327608 2.0 03 - 05 - UkDocument20 pagesERCO351 4-327608 2.0 03 - 05 - UkRhomel TagalagNo ratings yet
- OpenScape Business V1, Service Documentation, Issue 20Document498 pagesOpenScape Business V1, Service Documentation, Issue 20Daniel German ArriagaNo ratings yet
- TLP Solutions: Our ActivitiesDocument16 pagesTLP Solutions: Our ActivitiesFrank DrennanNo ratings yet
- IKEA Catalogue 2012Document189 pagesIKEA Catalogue 2012Rafi UdeenNo ratings yet
- Fire Code 2013 PDFDocument1,033 pagesFire Code 2013 PDFKo PaukNo ratings yet
- Cpr-3 - Catalouge Rele RubberDocument2 pagesCpr-3 - Catalouge Rele Rubbermanuel100% (1)
- Civil Engineering Caste Region Seat Category Rank: OC AU Oc - Gen - Ur 24149Document32 pagesCivil Engineering Caste Region Seat Category Rank: OC AU Oc - Gen - Ur 2414935mohanNo ratings yet
- Commodity CodesDocument116 pagesCommodity Codesasif712No ratings yet
- India'S First Lead-Free Upvc PipeDocument20 pagesIndia'S First Lead-Free Upvc PipeSafeNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Operating CostDocument15 pagesVehicle Operating CostAbdulkareem Adeyinka100% (1)