Professional Documents
Culture Documents
vn48 1009MeasuringAirflow PDF
Uploaded by
حسان السوفانيOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
vn48 1009MeasuringAirflow PDF
Uploaded by
حسان السوفانيCopyright:
Available Formats
Veris Application Note N48
Determining Air Flow
Introduction Air Densities at Different Elevations:
Air flow in cubic feet per minute (CFM) is a useful quantity to determine when Elevation (ft) Density (lb/ft3)
examining air quality issues. Calculate air flow in a duct by measuring the air flow 0 0.0745
velocity in feet per minute (FPM) and multiplying by the duct cross sectional area in 500 0.0732
square feet (ft2).
1000 0.0719
1500 0.0706
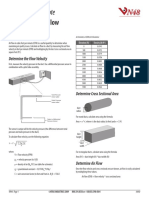
Determine the Flow Velocity 2000 0.0693
First, measure the velocity pressure in the duct. Use a differential pressure sensor in 2500 0.0680
combination with a pitot tube assembly.
3000 0.0668
3500 0.0656
A IR F
LOW 4000 0.0644
4500 0.0632
5000 0.0620
7500 0.0564
Total Pressure Determine Cross Sectional Area
(inner tube)
Static Pressure
(outer tube)
duct
radius
For round ducts, calculate area using the formula
Tubes to Differential
Pressure Sensor
Area = π * r2, where r is the duct radius (in feet) and π = 3.14.
The sensor’s output will be the velocity pressure (the difference between total
pressure and static pressure in the duct).
duct
To calculate flow velocity, use the following equation: height
V = C*
√ (2 * pw * gc)
ρ
duct
width
where: For rectangular ducts, calculate area using the formula
V = Flow velocity (FPM)
Area (ft2) = duct height (ft) * duct width (ft)
pw = velocity pressure (in. H20)
ρ = density of air (lbm/ft3) (see table for estimates) Determine Air Flow
gc = gravitational constant = 32.174 lbm*ft/lbfs2 Once the flow velocity and cross sectional area are known, air flow is easily calculated
by multiplying these values.
C = unit conversion factor (to feet and from in. H20) = 136.8
Air flow (CFM) = flow velocity * cross sectional area
VN48 Page 1 ©VERIS INDUSTRIES 2009 800.354.8556 or +1(0)503.598.4564 10092
Example
Calculate the air flow in a round duct with a 3 foot diameter at an elevation of 1000
feet above sea level. Assume the velocity pressure is 0.7 in. H2O.
First, calculate the flow velocity:
V = C*
√ (2 * pw * gc)
ρ
V = 136.8 * √ (2 * 0.7 in. H2O * 32.174 lbmft/lbfs2)
0.0719 lbmft3
V = 3424 FPM
Second, calculate the cross sectional area of the duct:
A = π * r2
A = π * (1.5 ft)2
A = 7 ft2
Third, multiply the two values:
Air flow (CFM) = flow velocity * cross sectional area
Air flow = 3424 FPM * 7 ft2
Air flow = 23,968 CFM
VN48 Page 2 ©VERIS INDUSTRIES 2009 800.354.8556 or +1(0)503.598.4564 10092
You might also like
- Determining Air Flow: Veris Application NoteDocument2 pagesDetermining Air Flow: Veris Application NoteAnonymous nfgoGdhYNo ratings yet
- Soler & Palau Static Pressure CalculatorDocument1 pageSoler & Palau Static Pressure CalculatorchillzoneNo ratings yet
- Static Pressure Calculator r3Document3 pagesStatic Pressure Calculator r3arshi_yusufNo ratings yet
- Flight Test Instrumentation: Proceedings of the Third International Symposium 1964From EverandFlight Test Instrumentation: Proceedings of the Third International Symposium 1964M. A. PerryNo ratings yet
- Static CalculationsDocument1 pageStatic CalculationsAnish BabuNo ratings yet
- Components for Pneumatic Control Instruments: The Static and Dynamic Characteristics of Pneumatic Resistances, Capacitances and Transmission LinesFrom EverandComponents for Pneumatic Control Instruments: The Static and Dynamic Characteristics of Pneumatic Resistances, Capacitances and Transmission LinesNo ratings yet
- ESP Calculation - Ventilation4uDocument4 pagesESP Calculation - Ventilation4uKaide Johar BohraNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument6 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentMohamed Gamal GemyNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- Static Pressure Calculator r3 Rev1610 27Document1 pageStatic Pressure Calculator r3 Rev1610 27Dwiki Yudia BasukiNo ratings yet
- Static Pressure Calculator r3 Rev1610 27Document1 pageStatic Pressure Calculator r3 Rev1610 27Wrya SaeedNo ratings yet
- Barge Resistance SoftwareDocument12 pagesBarge Resistance SoftwareJuniar Rizky Ardiansyah100% (1)
- Characterising Roof Ventilators: P 2 A Q CDocument4 pagesCharacterising Roof Ventilators: P 2 A Q CDhirendra Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Design. Ref - Decuments: API 650, 11TH - ED M09Document31 pagesDesign. Ref - Decuments: API 650, 11TH - ED M09hgagNo ratings yet
- Measure rectangular duct flow with aerodynamic foilDocument6 pagesMeasure rectangular duct flow with aerodynamic foilvaisakp777No ratings yet
- 6.0 Steam/Condensate Lines Preface: Chart D 3.1Document18 pages6.0 Steam/Condensate Lines Preface: Chart D 3.1Cristhian100% (1)
- Pump sizing spreadsheet calculates performanceDocument26 pagesPump sizing spreadsheet calculates performancesterling100% (1)
- Data - PhilipDocument21 pagesData - PhilipPhilip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- CW Pipe Thickness Calculation - 80% Vacuum - With RCCDocument39 pagesCW Pipe Thickness Calculation - 80% Vacuum - With RCCAshitava Sen0% (1)
- Burner CalculationDocument9 pagesBurner CalculationAbul QasimNo ratings yet
- Hydrological calculations for minor bridgeDocument30 pagesHydrological calculations for minor bridgeshshank guptaNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Vacuum System DesignDocument9 pagesAn Overview of Vacuum System Designhwang2100% (2)
- Simulacion Aero Enfriador PDFDocument40 pagesSimulacion Aero Enfriador PDFNicandroGonzalesNo ratings yet
- Pump Power ReqDocument8 pagesPump Power ReqNeil John CatapangNo ratings yet
- Valve SizingDocument6 pagesValve SizingVaibhav KuraleNo ratings yet
- Pumping and Piping Systems: Xavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan College of Engineering Cagayan de Oro CityDocument34 pagesPumping and Piping Systems: Xavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan College of Engineering Cagayan de Oro CityGab LibetarioNo ratings yet
- Fan LawsDocument39 pagesFan LawsbhatrkNo ratings yet
- AXIAL FLOW FAN TEST RIG PERFORMANCEDocument4 pagesAXIAL FLOW FAN TEST RIG PERFORMANCERajath ShettyNo ratings yet
- Hd-54 Single Stage Air CompressorDocument8 pagesHd-54 Single Stage Air CompressorErGiteshAroraNo ratings yet
- Bridge design discharge and afflux calculationsDocument5 pagesBridge design discharge and afflux calculationspraveenNo ratings yet
- Slab Bridge DesignDocument25 pagesSlab Bridge DesignEngineeri TadiyosNo ratings yet
- Vortex Flow Meters: Kaifeng AFT Instrument Co.,LtdDocument22 pagesVortex Flow Meters: Kaifeng AFT Instrument Co.,LtdgcortelliNo ratings yet
- HEURISTICSDocument6 pagesHEURISTICSlordyNo ratings yet
- ED4 Equillibrage VentiloDocument3 pagesED4 Equillibrage VentiloMohd SironNo ratings yet
- Simplified Numerical Modeling of Flow Downstream of an Axial ImpellerDocument4 pagesSimplified Numerical Modeling of Flow Downstream of an Axial ImpellerVincent RogNo ratings yet
- 3 Flow Rates and Pressure MeasurementsDocument20 pages3 Flow Rates and Pressure MeasurementsRiswan RiswanNo ratings yet
- Ansys Fluent Project in Advanced Fluid MechanicsDocument36 pagesAnsys Fluent Project in Advanced Fluid Mechanicsالسيد الميالي النجفيNo ratings yet
- Study of Subsonic Wind Tunnel and Its Calibration: Pratik V. DedhiaDocument8 pagesStudy of Subsonic Wind Tunnel and Its Calibration: Pratik V. DedhiaPratikDedhia99No ratings yet
- Drill String Design GuideDocument21 pagesDrill String Design GuideR GunalanNo ratings yet
- SW COLD PUMP CALCULATION (Rev.0)Document25 pagesSW COLD PUMP CALCULATION (Rev.0)Ardian20No ratings yet
- Department of Aeronautical Engineering Vi Semester 10AEL67 Aerodynamics Lab Manual Academic Year-2019 N S: U S N: S: BDocument40 pagesDepartment of Aeronautical Engineering Vi Semester 10AEL67 Aerodynamics Lab Manual Academic Year-2019 N S: U S N: S: BAkash MishraNo ratings yet
- Pressure Drop CalculationsDocument4 pagesPressure Drop CalculationsOmprakaash Mokide100% (1)
- Slab Bridge Design For WorkDocument27 pagesSlab Bridge Design For WorkEngineeri TadiyosNo ratings yet
- Air Vents, Vacuum Relief and Pressure Relief in Pressurized PipelinesDocument6 pagesAir Vents, Vacuum Relief and Pressure Relief in Pressurized PipelinesARSENo ratings yet
- Detailed Hydraulic CalculationsDocument9 pagesDetailed Hydraulic CalculationsV P GUPTANo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Package Engineering in Halliburton - Multi Chem Batch PlantDocument3 pagesCooling Tower Package Engineering in Halliburton - Multi Chem Batch PlantragulNo ratings yet
- Find Eq - Length (M) :: Manual Pressure Drop CalculationDocument7 pagesFind Eq - Length (M) :: Manual Pressure Drop Calculationcryptic postNo ratings yet
- NSW Pump Calculation 26-05-2017-r4Document28 pagesNSW Pump Calculation 26-05-2017-r4Ardian200% (1)
- Compressed Air Pipe Lines - Online Pressure Drop CalculatorDocument3 pagesCompressed Air Pipe Lines - Online Pressure Drop CalculatorJesús MontañoNo ratings yet
- Burner CalculationDocument6 pagesBurner CalculationAbul QasimNo ratings yet
- Duct Size Calculator (Si) Duct Size Calculator (Ip) : W H Galvanised 0.15Document4 pagesDuct Size Calculator (Si) Duct Size Calculator (Ip) : W H Galvanised 0.15Mohd Izham Idris100% (1)
- Flowmeter Apparatus (Venturi, Orifice, Rotameter)Document10 pagesFlowmeter Apparatus (Venturi, Orifice, Rotameter)meghaparinNo ratings yet
- 08_Modeling of Swirl Flow at the Exit of an Axial Flow FanDocument5 pages08_Modeling of Swirl Flow at the Exit of an Axial Flow FankcpatnaikNo ratings yet
- Electric Ducted Fan Theory Explained (EDFTDocument17 pagesElectric Ducted Fan Theory Explained (EDFTumunera2997No ratings yet
- AE6503 - QP CODE 50028 - Aerodynamics II Key - Nov 2017 PDFDocument25 pagesAE6503 - QP CODE 50028 - Aerodynamics II Key - Nov 2017 PDFRaahini IzanaNo ratings yet
- Air Flow in PipeDocument8 pagesAir Flow in Pipeตุ๊กตุ้ย ตัวกลมกลมNo ratings yet
- Mustafa PDFDocument1 pageMustafa PDFحسان السوفانيNo ratings yet
- Ventipac 200D Ventilator User'S ManualDocument66 pagesVentipac 200D Ventilator User'S Manualحسان السوفانيNo ratings yet
- Mustafa PDFDocument1 pageMustafa PDFحسان السوفانيNo ratings yet
- MusDocument1 pageMusحسان السوفانيNo ratings yet
- Determining Air Flow in CFM PDFDocument2 pagesDetermining Air Flow in CFM PDFNíthìsh GøwdåNo ratings yet
- Ventipac 200D Ventilator User'S ManualDocument66 pagesVentipac 200D Ventilator User'S Manualحسان السوفانيNo ratings yet
- O2 Valve CalprationDocument1 pageO2 Valve Calprationحسان السوفانيNo ratings yet
- MUSTAFADocument1 pageMUSTAFAحسان السوفانيNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Lionel QUETTIERDocument71 pagesMagnetic Resonance Imaging: Lionel QUETTIERFery B MulyonoNo ratings yet
- Turbine Engine Fundamentals ExplainedDocument114 pagesTurbine Engine Fundamentals ExplainedNaseer Abdaljabar0% (1)
- Sci409 - WS 8Document4 pagesSci409 - WS 8Hernel Sean CordaNo ratings yet
- SAKO SKI780 ManualDocument74 pagesSAKO SKI780 ManualJordi Garcia100% (1)
- 49E Hall-Effect Linear Position Sensor: 1. Ge Neral DescriptionDocument4 pages49E Hall-Effect Linear Position Sensor: 1. Ge Neral DescriptionJorge MorochoNo ratings yet
- Application of Undervoltage Protection To Critical Motors PDFDocument6 pagesApplication of Undervoltage Protection To Critical Motors PDFarisNo ratings yet
- DC Motor1 SolnDocument4 pagesDC Motor1 SolnGlazylynCortezPalo60% (5)
- R600a Iso Butane PT Chart PDFDocument2 pagesR600a Iso Butane PT Chart PDFAnjan Ahsanul Kabir0% (1)
- Engg Thermodynamics PDFDocument44 pagesEngg Thermodynamics PDFBrandon FunaNo ratings yet
- Rotational motion tutorialDocument2 pagesRotational motion tutorialShuhaila Hanis RosliNo ratings yet
- Z.gg#o-Yng - lS02.S2M-lcm-: Frequency WavelengthDocument2 pagesZ.gg#o-Yng - lS02.S2M-lcm-: Frequency WavelengthShlomoNo ratings yet
- Ecolink Flood FL007 150 200wDocument5 pagesEcolink Flood FL007 150 200wMohammad WildhanNo ratings yet
- Plugin-Modeling of Two Winding Voltage Regulating TransformersDocument8 pagesPlugin-Modeling of Two Winding Voltage Regulating TransformersmjailoviNo ratings yet
- Solar car aerodynamic design optimizes cooling and efficiencyDocument8 pagesSolar car aerodynamic design optimizes cooling and efficiencynicolas brizzioNo ratings yet
- Fluid System 04-Centrifugal PumpDocument104 pagesFluid System 04-Centrifugal Pumpapri melianes febriNo ratings yet
- Senior High School Department: Subject TeacherDocument1 pageSenior High School Department: Subject TeacherPit's AfallaNo ratings yet
- CT Bien Dong EMIC - Trung TheDocument44 pagesCT Bien Dong EMIC - Trung TheBảo ChâuNo ratings yet
- Presentation DC DrivesDocument42 pagesPresentation DC Drivesfaizan100% (1)
- Electric Dipole and Capacitance CalculationsDocument3 pagesElectric Dipole and Capacitance CalculationsAfsaribegum MohammadNo ratings yet
- WLA2 - C& S Electric LimitedDocument4 pagesWLA2 - C& S Electric LimitedChirag SomaiyaNo ratings yet
- Radiation Process and Properties Course ContentsDocument17 pagesRadiation Process and Properties Course ContentsJainil GajjarNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Fields AS Unit 4: Drawing Field DiagramsDocument6 pagesMagnetic Fields AS Unit 4: Drawing Field DiagramsL5YARBNo ratings yet
- Sony Tektronix 335 ServiceDocument198 pagesSony Tektronix 335 Service10Gyula10No ratings yet
- Keynote Speaker - Prof. S. Talukdar - Vehicle Induced Dynamic Response of A Bridge and Moving Load EstimationDocument6 pagesKeynote Speaker - Prof. S. Talukdar - Vehicle Induced Dynamic Response of A Bridge and Moving Load Estimationdigvijay singhNo ratings yet
- Avr - LX321-V1.2.1 - Eng - Ge 06Document16 pagesAvr - LX321-V1.2.1 - Eng - Ge 06Mamadou lyNo ratings yet
- Chapter #26-Capacitance & DielectricsDocument42 pagesChapter #26-Capacitance & DielectricsJi Hoon MyeongNo ratings yet
- PHET Capacitor Internet LabDocument2 pagesPHET Capacitor Internet Labsobre1982No ratings yet
- P64x EN AP A11Document92 pagesP64x EN AP A11Sakthi Krishnan0% (1)
- Implementation of Over-Voltage & Under-Voltage Protection SystemDocument54 pagesImplementation of Over-Voltage & Under-Voltage Protection Systemvajiravel407No ratings yet
- Hydraulics Chapter 3Document73 pagesHydraulics Chapter 3Yoni RebumaNo ratings yet
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (543)
- Upcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)From EverandUpcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- The Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesFrom EverandThe Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationFrom EverandPractical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeFrom EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Gas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsFrom EverandGas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Practical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionFrom EverandPractical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- C++ Programming Language: Simple, Short, and Straightforward Way of Learning C++ ProgrammingFrom EverandC++ Programming Language: Simple, Short, and Straightforward Way of Learning C++ ProgrammingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataFrom EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsFrom EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026From EverandThe Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Graphene Revolution: The Weird Science of the Ultra-thinFrom EverandThe Graphene Revolution: The Weird Science of the Ultra-thinRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- ARDUINO CODE: Mastering Arduino Programming for Embedded Systems (2024 Guide)From EverandARDUINO CODE: Mastering Arduino Programming for Embedded Systems (2024 Guide)No ratings yet
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialFrom EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Winning in 2025: Digital and Data Transformation: The Keys to SuccessFrom EverandWinning in 2025: Digital and Data Transformation: The Keys to SuccessNo ratings yet
- Off-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemFrom EverandOff-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemNo ratings yet