Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circular Measure PDF
Uploaded by
Anna LeeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circular Measure PDF
Uploaded by
Anna LeeCopyright:
Available Formats
Circular Measure 1
CIRCULAR MEASURE
Radians Measure
r r
To measure angle we have : (i) Degree measure (ii) Radian measure
1 rad
If an arc of a circle is drawn such that it is the same length as the radius, then the angle
created is called one radian as shown in Fig. 1. r
Fig. 1
From the diagram you can see that dividing the circumference by the radius will give the
number of radians in one complete revolution. Therefore, the number of radians in one revolution is
These basic conversions are useful :
A circle contains A semi circle contains A right angle contains
2 radians radians radians
From the above we can derive the formulas of transforming degrees to radians, vice versa, by using
direct proportion as shown below :
From Degree to Radian measure From Radian to Degree measure
Examples :
1. Convert the following angles from degree to radians. Leave your answer in terms of :
(a) 180 (b) 22.50 (c) 360
2. Convert the following angles from radians to degree measure.
(a) rad (b) rad (c) 0.8 rad
MES LAILA PTEK 2011
Circular Measure 2
Length of an Arc
s
r
Length of an Arc, s = r
r
Examples :
1. In each of the following cases, find the length s :
a. b. 2 cm
1.8 rad
o
4 cm 300
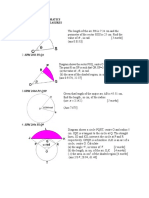
2. Figure 1 shows the sector AOB of radius 8 cm and a perimeter of 21 cm. A B
Find the angle AOB in radians.
8 cm 8 cm
Fig. 1 o
3. Figure 2 shows a sector OACB of a circle centre O and radius 5 cm. If the length of the chord AB is 8
cm, find
C
(a) in radians,
(b) The length of the arc ACB. 8 cm
A B
5 cm 5 cm
Fig. 2 o
4. A sector of a circle of radius 4 cm has an angle of 1.2 radians. Find the perimeter of the sector.
MES LAILA PTEK 2011
Circular Measure 3
Exercise 4A : Length of an Arc
Where the answer is not exact, 3 significant figure accuracy is sufficient.
1. In each of the following cases, find the arc length, s.
(a) (b) (c)
1.8 rad
220o
3 cm 1.2 rad
5 cm
4 cm
2. The length of an arc in a circle of radius 5 cm is 6 cm. Find the angle substended at the centre.
3. The angle subtended at the centre of a circle by an arc of length 2 cm is 60o.
4. A sector of a circle has radius r cm and angle radians. Find the value of correct to 3 significant
figures if the perimeter of the sector equals half the circumference of the circle.
5. Figure 2 shows a semicircle of centre O. Given the length of the arc AB is 4 cm and angle BOC is
radians, find
Fig. 2 B
(a) the radius of the circle, cm
rad
(b) the length of the arc BC.
C O A
6. In Figure 3 the chord AC of a circle centre O and radius 10 cm is 14 cm. Find C
(a) the angle subtended at the centre of the circle by the chord.
14 cm
O B
10 cm
(b) the length of the arc ABC.
Fig. 3
A
7. A chord AB is 8 cm long in a circle of radius 5 cm. Calculate
(a) the angle it subtends at the centre of the circle,
(b) the length fo the shorter arc AB.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ANSWERS :
(1) (a) 4.8 cm (b) 15.36 cm (c) 25.42 (2) 1.2 rad (3) 6 cm (4) 1.14 rad
(5) (a) 12 cm (b) 8 cm (6) (a) 1.55 rad (b) 15.5 cm (7) (a) 1.85 rad (b) 9.27 cm
MES LAILA PTEK 2011
Circular Measure 4
Area of a Sector of a Circle
In Figure 1, AOB is a sector of angle and radius r. The area of the sector A is
proportional to the angle subtended at the centre of the circle. A
r
i.e.
o
r B
Fig. 1
A=
A= or
=
Example
1. Figure 2 shows a sector of radius 6 cm and AOB = 0.9 rads. Find the area of the sector.
A B
6 cm
0.9 rad
Fig. 2 o
2. In Figure 3, OAB is a sector of a circle O and radius 8 cm. The mid-points of OA and OB are C and D
respectively. CD is a straight line. Given that AOB = 0.6 radians, calculate the area of the shaded
region.
A
C
0.6 rad o
D
B 8 cm
Fig. 3
MES LAILA PTEK 2011
Circular Measure 5
3. In Figure 4, AD and BC are arcs of concentric circles of centre O. The length of the arc AD and BC are
10.5 cm and 16.8 cm respectively, and OD = 5 cm. Calculate the area of the shaded region ABCD.
16.8 cm
10.5 cm
A B
5 cm
o
Fig. 4
4. The diagram shows a semicircle OABC of centre O and radius 5 cm. BN is perpendicular to OA.
Given that the length of arc AB is 6 cm, find
B
a) Angle AOB in radians,
6 cm 6 cm
b) The area of the shaded region,
c) Express the area of the shaded region as a percentage of the area C O N A
of the semicircle.
MES LAILA PTEK 2011
Circular Measure 6
Exercise 4B : Area of Sector of Circles
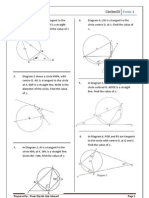
1. In each of the following cases, find the area of the sector :
(a) (b) (c)
o rad
300
1.6 rad
4 cm 5 cm
5 cm
o
2. The area of a sector of a circle is 9 cm2. If the radius is 6 cm, find the angle of the sector.
3. A sector of a circle has an angle of 2.25 rad and an area of 112.5 cm2. Find the radius of the circle.
4. The area of a sector of a circle is 15 cm2 and the length of its arc is 3 cm.
Calculate
(a) The radius of the sector,
(b) The angle of the sector.
5. The perimeter of a sector is 128 cm and its area is 960 cm 2. Find the possible values of the radius of
the sector and its angle.
6. The diagram shows a sector OAB of a circle centre O and radius 10 cm. BN is perpendicular to OA.
Given that BN = 8 cm, calculate
A
(a) Angle BON in radians
(b) The area of the shaded region. 10 cm
8 cm
o N B
7. In figure below , DOBC is a semicircle, centre O and radius 6 cm. CA is perpendicular to DOB where
AB is 2 cm. Calculate C
(a) the length of CA
(b) COA in radians, and
D 6 O A 2 B
(c) the perimeter of the shaded region.
(d) express the area of the shaded region as a percentage of the area of the semicircle.
MES LAILA PTEK 2011
You might also like
- Circular Measures Problems and SolutionsDocument3 pagesCircular Measures Problems and SolutionspizamNo ratings yet
- Add Math Circular MeasuresDocument12 pagesAdd Math Circular Measureskamil muhammad100% (1)
- Solid Geometry Form 2Document1 pageSolid Geometry Form 2pnt_buttercupNo ratings yet
- KSSM Mathematics Form 2 Chapter 4 Polygons 4.2.4Document2 pagesKSSM Mathematics Form 2 Chapter 4 Polygons 4.2.4KSSM TSENo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 IndicesDocument13 pagesChapter 6 Indicesnaza9775No ratings yet
- Circular Measure QuestionsDocument7 pagesCircular Measure QuestionspopoutNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure Problems SolvedDocument11 pagesCircular Measure Problems SolvedTerence RileyNo ratings yet
- Add Math Form 5 Integration Collection of Trial SPM Questions 2012 Paper 2Document6 pagesAdd Math Form 5 Integration Collection of Trial SPM Questions 2012 Paper 2Eric Wong100% (1)
- Solid Geometry Form 2Document18 pagesSolid Geometry Form 2graciezayn67% (3)
- Maths F3 KSSM 2019Document132 pagesMaths F3 KSSM 2019蔡卷勋100% (5)
- Done Circular MeasureDocument12 pagesDone Circular MeasureSharvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Quiz: CIRCLE (Form 2)Document4 pagesQuiz: CIRCLE (Form 2)raudatunnur87No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Standard FormDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Standard FormWupo Ling100% (1)
- Form 2 Math Chapter 10Document4 pagesForm 2 Math Chapter 10velavanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Algebraic FormulaeDocument12 pagesChapter 4 Algebraic FormulaeCik Yana50% (2)
- Additional Mathematics: Index NumbersDocument4 pagesAdditional Mathematics: Index NumbersSforazzura Suhaimi50% (2)
- Chapter 2 - Squares, Square Roots, Cubes and Cube RootsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 - Squares, Square Roots, Cubes and Cube RootssmkpthoeNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion EquationsDocument13 pagesForce and Motion EquationsniknadhiraNo ratings yet
- SPM Add Maths Pass Year QuestionsDocument61 pagesSPM Add Maths Pass Year QuestionsAvvy21No ratings yet
- SPM Circular Measure QuestionsDocument3 pagesSPM Circular Measure QuestionsRosmizar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Topical Test Chapter 1 Math Form 1 Paper 2Document1 pageTopical Test Chapter 1 Math Form 1 Paper 2syukrie3100% (2)
- Form 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 8 Circular MeasureDocument9 pagesForm 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 8 Circular MeasureManisha Sekaran Muniandy80% (5)
- MATHEMATICS - CIRCLES FORM 2Document22 pagesMATHEMATICS - CIRCLES FORM 2graciezayn100% (6)
- GCSE Maths Revision Guide: Calculating Areas and Perimeters of Circular Sectors, Segments and ArcsDocument7 pagesGCSE Maths Revision Guide: Calculating Areas and Perimeters of Circular Sectors, Segments and ArcszaedmohdNo ratings yet
- Maths Form 2 Chapter 1Document19 pagesMaths Form 2 Chapter 1Suelly Sabri100% (1)
- Trigonometry Test with 20 QuestionsDocument14 pagesTrigonometry Test with 20 QuestionsMohd TaufekNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Maths Lesson Plan 2021Document6 pagesForm 3 Maths Lesson Plan 2021Tcer ReenNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Physics Chapter 2 - Teacher'sDocument15 pagesForm 5 Physics Chapter 2 - Teacher'sPavithiran100% (4)
- Circles IIIDocument2 pagesCircles IIIHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Past SPM Maths Questions on Trigonometric Equations (2003-2009Document5 pagesPast SPM Maths Questions on Trigonometric Equations (2003-2009Siti Aizatie Ramli0% (1)
- Quiz Maths Form 2 - Chapter 5 on CirclesDocument5 pagesQuiz Maths Form 2 - Chapter 5 on CirclesBONG TZER WEI MoeNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 1-Form 3Document2 pagesExercise Chapter 1-Form 3shajohari40% (15)
- Add Maths Form 5 (Chapter 1: Progressions)Document1 pageAdd Maths Form 5 (Chapter 1: Progressions)api-22097564100% (4)
- Focus TG4 KSSM (Addmaths) Terbitan Penerbitan Pelangi SDN BHDDocument30 pagesFocus TG4 KSSM (Addmaths) Terbitan Penerbitan Pelangi SDN BHDRAUL MAHENDRAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Math MF2 Chapter 9 (Loci in Two Dimensions)Document6 pagesMath MF2 Chapter 9 (Loci in Two Dimensions)compeil100% (1)
- Circle I and IIDocument5 pagesCircle I and IILEE HUE KEAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Soalan Matematik Tingkatan 1 Kertas 1Document2 pagesSoalan Matematik Tingkatan 1 Kertas 1afiq8586No ratings yet
- CIRCULAR MEASUREDocument9 pagesCIRCULAR MEASUREBawani shankerNo ratings yet
- SPM Trigonometry Functions Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageSPM Trigonometry Functions Problems and SolutionsRosmizar AhmadNo ratings yet
- SPM Questions Transformations IIIDocument6 pagesSPM Questions Transformations IIIjuriah binti ibrahim0% (1)
- Calculating Areas and Circumferences of Circles and ShapesDocument3 pagesCalculating Areas and Circumferences of Circles and ShapesChris TeaNo ratings yet
- Exercise Alg FormulaeDocument6 pagesExercise Alg FormulaeLaavanes MurgayaNo ratings yet
- Quiz f3Document10 pagesQuiz f3Hafizah PakahNo ratings yet
- 8 Circular MeasuresDocument12 pages8 Circular MeasuresNor Hanina100% (6)
- Mathematics Form 1 Chapter 6 & 7 QuizDocument1 pageMathematics Form 1 Chapter 6 & 7 Quizlaukhaisiang67% (3)
- Form 2 MathDocument10 pagesForm 2 MathLywee NeoNo ratings yet
- 2 Klon SPM Quad Eqn 2003 - 2014 - EdDocument32 pages2 Klon SPM Quad Eqn 2003 - 2014 - EdAnonymous 0fagPbbloNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Form 4 Paper 1 Midterm 2012Document18 pagesAdd Maths Form 4 Paper 1 Midterm 2012Thiyaku MaruthaNo ratings yet
- RatioDocument13 pagesRatioKatrine Jaya AndrewNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry SlidesDocument6 pagesTrigonometry SlidesElla O'NEILLNo ratings yet
- Arc and Area of SectorDocument5 pagesArc and Area of Sectorleena_louisNo ratings yet
- SATPREP Circular Measurement PracticeDocument5 pagesSATPREP Circular Measurement PracticeJoel SohNo ratings yet
- Institut Kemahiran MARA Sungai Petani, Kedah: Information SheetDocument6 pagesInstitut Kemahiran MARA Sungai Petani, Kedah: Information Sheetilzam_lilyNo ratings yet
- Level 3 Checklist - Are You Able To Achieve It? Math Vocab CornerDocument2 pagesLevel 3 Checklist - Are You Able To Achieve It? Math Vocab CornerGenesis Norbert AlconabaNo ratings yet
- Finding Perimeter of Sectors of a CircleDocument13 pagesFinding Perimeter of Sectors of a CircleSL TRAVELERNo ratings yet
- Formulae: Mathematics Form 2 Standardised Test 1: Circles Duration: 30 MinutesDocument4 pagesFormulae: Mathematics Form 2 Standardised Test 1: Circles Duration: 30 MinutesemiliaroslanNo ratings yet
- 1 Trigo Arc Length and Area of SectorDocument3 pages1 Trigo Arc Length and Area of SectorSanaNo ratings yet
- Circular MeasureDocument23 pagesCircular MeasureWOON RAY MINGNo ratings yet
- Calculating Perimeters and Areas of Circular SectorsDocument16 pagesCalculating Perimeters and Areas of Circular SectorsEdu 4 UNo ratings yet
- Sector and Segment of A Circle - Worksheets PackDocument5 pagesSector and Segment of A Circle - Worksheets PackRAMNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median, and ModeDocument18 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median, and ModeAnna LeeNo ratings yet
- What Is Rotational Symmetry?Document7 pagesWhat Is Rotational Symmetry?Anna LeeNo ratings yet
- Diagnostics TestDocument4 pagesDiagnostics TestAnna LeeNo ratings yet
- Mean, Median and Mode For Grouped Data: X FX F XDocument3 pagesMean, Median and Mode For Grouped Data: X FX F XAnna LeeNo ratings yet
- Intro To ProbabilityDocument29 pagesIntro To ProbabilityAnna LeeNo ratings yet
- Questions Simple ProbabilityDocument1 pageQuestions Simple ProbabilityAnna LeeNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure FORM 4 - LESSON PLANDocument10 pagesCircular Measure FORM 4 - LESSON PLANAnna LeeNo ratings yet
- Microsoft-Word-F4 c8 Circular Measures NewDocument10 pagesMicrosoft-Word-F4 c8 Circular Measures Newuzai88No ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median, and ModeDocument18 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median, and ModeAnna LeeNo ratings yet
- SPM Trial AddMath P1 by TopicDocument62 pagesSPM Trial AddMath P1 by TopicAnna LeeNo ratings yet
- Linear Law Linear Programming: By: Ting Hie Huong Lee Mee ChingDocument29 pagesLinear Law Linear Programming: By: Ting Hie Huong Lee Mee ChingAnna LeeNo ratings yet
- Linear LawDocument14 pagesLinear LawSiti Khadijah Noor ZariNo ratings yet
- Linear ProgrammingDocument11 pagesLinear ProgrammingAnna LeeNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Techniques BlogDocument44 pagesDifferentiation Techniques BlogMuhammad Mansor Burhan100% (2)
- Pak 21Document1 pagePak 21Anna LeeNo ratings yet
- Linear ProgrammingDocument11 pagesLinear ProgrammingAnna LeeNo ratings yet
- Essay WritingDocument2 pagesEssay WritingAnna LeeNo ratings yet
- KMC2014 - CadetDocument4 pagesKMC2014 - CadetAnna LeeNo ratings yet
- Differences in Left Ventricular and Left Atrial FuDocument10 pagesDifferences in Left Ventricular and Left Atrial FueugeniaNo ratings yet
- Zenopus ClassicDocument32 pagesZenopus Classicserenity42No ratings yet
- Hydromechanical Piercing Perforation: Oil Service Innovation TechnologiesDocument8 pagesHydromechanical Piercing Perforation: Oil Service Innovation TechnologiesЕлена ПаниотNo ratings yet
- IAL Edexcel Pure Math 1 January 2020Document28 pagesIAL Edexcel Pure Math 1 January 2020Mohamed Said Daw100% (4)
- Memorial Garden Policies and Guidelines St. Mark's Episcopal Church, Raleigh, North CarolinaDocument7 pagesMemorial Garden Policies and Guidelines St. Mark's Episcopal Church, Raleigh, North Carolinaestela maria dulaganNo ratings yet
- G5 C11 TestDocument6 pagesG5 C11 TestvictoriaNo ratings yet
- QRP Yu1lm SDR-RX TXDocument299 pagesQRP Yu1lm SDR-RX TXD BNo ratings yet
- 2a CTRL DecDocument75 pages2a CTRL Decramanathan balamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Detecting Oil Spills from Remote SensorsDocument7 pagesDetecting Oil Spills from Remote SensorsFikri Adji Wiranto100% (1)
- Catalogus 2010 ENGELSDocument52 pagesCatalogus 2010 ENGELShacikadiNo ratings yet
- Experiment# 3 Projectile Motion (Tasks 3 and 4)Document18 pagesExperiment# 3 Projectile Motion (Tasks 3 and 4)Hafiz MuhammadNo ratings yet
- CaseStudy AmtrakDocument14 pagesCaseStudy Amtraksnob_kNo ratings yet
- Interpuls Novinki 2014Document64 pagesInterpuls Novinki 2014BaklanovaSVNo ratings yet
- Computer Engineering SyllabusDocument47 pagesComputer Engineering SyllabusLily ChanNo ratings yet
- Circuits Review P2Document44 pagesCircuits Review P2José CastilloNo ratings yet
- Script For TSB GRDDocument9 pagesScript For TSB GRDJuvel OrquinazaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Monitoring of The Humber Bridge UsingDocument7 pagesExperimental Monitoring of The Humber Bridge Using정주호No ratings yet
- 07 IRIS NV PCB OtherDocument15 pages07 IRIS NV PCB OtherArnaldo cordovaNo ratings yet
- EE 102 Cabric Final Spring08 o Id15Document10 pagesEE 102 Cabric Final Spring08 o Id15Anonymous TbHpFLKNo ratings yet
- Meralco Bill 330370940102 04142023Document2 pagesMeralco Bill 330370940102 04142023Jha CruzNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 6 LAS Q4Document127 pagesMathematics 6 LAS Q4Jake Padua100% (1)
- ĐỀ SỐ 2Document98 pagesĐỀ SỐ 2van hoa nguyenNo ratings yet
- General Description: Effective Distance Depends On Antenna, Tag and EnvironmentDocument2 pagesGeneral Description: Effective Distance Depends On Antenna, Tag and EnvironmentSHASHANK BHUSHANNo ratings yet
- Permeability Test Constant Head MethodDocument10 pagesPermeability Test Constant Head MethodLouise LuyNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Nature of ReligionDocument41 pagesUnderstanding The Nature of Religioneden l. abadNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Entry: OSHA Standard 1910.146Document38 pagesConfined Space Entry: OSHA Standard 1910.146SKH CultureNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Chemical EquilibriumDocument29 pagesChapter 14 Chemical EquilibriumlynloeNo ratings yet
- Wda 201Document72 pagesWda 201MoussaNo ratings yet
- Giddings & Lewis Sect08 HydDocument24 pagesGiddings & Lewis Sect08 HydAngel AdautaNo ratings yet
- When Ceramic Sociology Meets Material SCDocument10 pagesWhen Ceramic Sociology Meets Material SCJosé Renato TeixeiraNo ratings yet