Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circular Measure Questions
Uploaded by
popoutOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circular Measure Questions
Uploaded by
popoutCopyright:
Available Formats
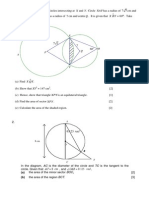
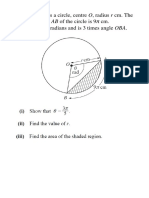
1. The figure shows a circle, center O, radius r cm.
The length of the arc AB of the
circle is 9 π cm. Angle AOB is θ radians and is 3 times angle OBA.
(i) Show that θ radians and is 3 times angle OBA. [2]
(ii) Find the value of r. [2]
(iii) Find the area of the shaded region. [3]
2. The diagram shows an isosceles triangle AOB and a sector OCDEO of a circle with
center O. The line AB is a tangent to the circle. Angle AOB = 1.8 radians and the
radius of the circle is 12 cm.
(i) Show that the distance AC = 7.3 cm to 1 decimal place. [2]
(ii) Find the perimeter of the shaded region. [6]
(iii) Find the area of the shaded region. [4]
3. In the diagram AD and BE are arcs of concentric circles O, where
OA =6 cm and AB = 8cm. The area of the region ABED is 32 cm 2.
The triangle OCF is isosceles with OC = OF = 20 cm.
(i) Find the angle θ in radians. [3]
(ii) Find the perimeter of the regions BCFE. [5]
4. The diagram shows a right-angled triangle ABC and a sector CBDC
of a circle with center C and radius 12 cm. Angle ACB =1 radian and
ACD is a straight line.
(i) Show that the length of AB is approximately 10.1 cm. [1]
(ii) Find the perimeter of the shaded region. [5]
(iii) Find the area of the shaded region. [4] (ii) 54.3(iii) 187
5. The diagram shows four straight lines, AD, BC, AC and BD. Lines
π
AC and BD intersect at O such that angle AOB is radians. AB is
6
an arc of the circle, center O and radius 10 cm, and CD is an arc
of the circle, center O and radius 20 cm.
(i) Find the perimeter of ABCD [4]
(ii) Find the area of ABCD [3] (i) 73.9, (ii) 231
6. In the diagram PQ and RS are arcs of concentric circles with center O and
angle POQ = 1 radian. The radius of the larger circle is X cm and the radius
of the smaller circle is y cm.
i)Given that the perimeter of the shaded region is 20 cm, express y in terms of x. [2]
ii)Given that the area of the shaded region is 16 cm 2, express y2 in terms of x2. [2]
iii)Find the value of x and y.[3] (i) y=3x−20(ii) y2=x2−32(iii) x=9;y=7
7. The diagram shows a square ABCD of side 16 cm. M is the mid-point of AB.
The points E and F are on AD and BC respectively such that AE = BF = 6 cm.
EF is an arc of the circle center M, such that angle EMF is i radians.
(i) Show that i = 1.855 radians, correct to 3 decimal places. [2]
(ii) Calculate the perimeter of the shaded region. [4]
(iii) Calculate the area of the shaded region. [3]
(ii) P=54.6(iii) A=115.25
8. The diagram shows two concentric circles, center O, radii 4 cm and 6 cm.
The points A and B lie on the larger circle and the points C and D lie on the
smaller circle such that ODA and OCB are straight lines.
(i) Given that the area of triangle OCD is 7.5 cm2, show that θ = 1.215
radians, to 3 decimal places. [2]
(ii) Find the perimeter of the shaded region. [4]
(iii) Find the area of the shaded region. [3]
(ii) 15.9(iii) 14.4
9. The diagram shows a circle, center O, radius r cm. The points A and B lie
on the circle such that angle AOB = 2θ radians.
(i) Given that the perimeter of the shaded region is 20cm, show that
10
r= [3]
θ+sin θ
(CIE 2012, s, paper 12, question 8)
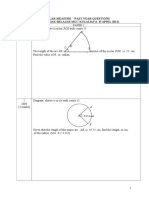
The figure shows a circle, centre O, with radius 10 cm. The
lines XA and XB are tangents to the circle at A and B respectively,
and angle AOB is 2π3 radians.
(i) Find the perimeter of the shaded region. [3]
(ii) Find the area of the shaded region. [4] (i) 55.6(ii) 68.5
(CIE 2013, s, paper 22, question 6)
The shaded region in the diagram is a segment of a circle with centre O and
radius r cm. Angle AOB=π/3 radians.
(i) Show that the perimeter of the segment is r(3+π)/3. [2]
(ii) Given that the perimeter of the segment is 26 cm, find the value of r and the
area of the segment. [5] (ii) r=12.7;A=14.6
(CIE 2014, s, paper 23, question 1)
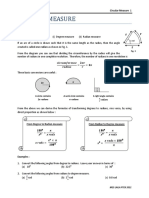
The diagram shows a sector of a circle of radius r cm. The angle of the sector is
1.6 radians and the area of the sector is 500 cm2.
(i) Find the value of r. [2]
(ii) Hence find the perimeter of the sector. [2]
25;90
(CIE 2014, w, paper 13, question 6)
The diagram shows a sector, AOB, of a circle centre O, radius 12 cm.
Angle AOB=0.9 radians. The point C lies on OA such that OC=CB.
(i) Show that OC=9.65 cm correct to 3 significant figures. [2]
(ii) Find the perimeter of the shaded region. [3]
(iii) Find the area of the shaded region. [3] P=22.8;A=19.4
(CIE 2014, w, paper 21, question 11)
The diagram shows a sector OPQ of a circle with centre O and
radius x cm. Angle POQ is 0.8 radians. The point S lies
on OQ such that OS=5 cm. The point R lies on OP such that angle ORS is a right angle. Given that the
area of triangle ORS is one-fifth of the area of sector OPQ, find
(i) the area of sector OPQ in terms of x and hence show that the value of x is 8.837 correct to 4
significant figures, [5]
(ii) the perimeter of PQSR, [3]
(iii) the area of PQSR. [2] P=19.8;A=25
(CIE 2012, w, paper 12, question 8)
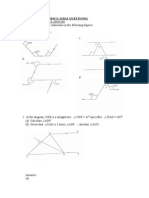
The diagram shows an isosceles triangle OBD in which OB=OD=18 cm
and angle BOD=1.5 radians. An arc of the circle, centre O and radius
10 cm, meets OB at A and OD at C.
(i) Find the area of the shaded region. [3]
(ii) Find the perimeter of the shaded region. [4] i) 86.6 (ii) 55.5
(CIE 2013, w, paper 21, question 10)
The diagram shows a circle with centre O and a chord AB. The radius of the
circle is 12 cm andangle AOB is 1.4 radians.
(i) Find the perimeter of the shaded region. [5]
(ii) Find the area of the shaded region. [4]
(i) 74.1(ii) 422
(CIE 2014, s, paper 12, question 7)
The diagram shows a circle, centre O, radius 8 cm. Points P and Q lie on the
circle such that the chord PQ=12 cm and angle POQ=θ radians.
(i) Show that θ=1.696, correct to 3 decimal places. [2]
(ii) Find the perimeter of the shaded region. [3]
(iii) Find the area of the shaded region. [3]
P=48.7,A=178.5
You might also like
- SPM Circular Measure QuestionsDocument3 pagesSPM Circular Measure QuestionsRosmizar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Circular Measures Problems and SolutionsDocument3 pagesCircular Measures Problems and SolutionspizamNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure Enrichment Paper 2 Trials 2011Document6 pagesCircular Measure Enrichment Paper 2 Trials 2011Mushi MushiNo ratings yet
- Done Circular MeasureDocument12 pagesDone Circular MeasureSharvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Circular MeasureDocument15 pagesCircular MeasureJoann Ng100% (1)
- CIRCULAR MEASUREDocument9 pagesCIRCULAR MEASUREBawani shankerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Circular MeasureDocument9 pagesChapter 8: Circular MeasureHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Quiz: CIRCLE (Form 2)Document4 pagesQuiz: CIRCLE (Form 2)raudatunnur87No ratings yet
- Circular Measure PDFDocument6 pagesCircular Measure PDFAnna LeeNo ratings yet
- Add Math Form 5 Integration Collection of Trial SPM Questions 2012 Paper 2Document6 pagesAdd Math Form 5 Integration Collection of Trial SPM Questions 2012 Paper 2Eric Wong100% (1)
- Chapter 2 - Squares, Square Roots, Cubes and Cube RootsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 - Squares, Square Roots, Cubes and Cube RootssmkpthoeNo ratings yet
- Solid Geometry Form 2Document1 pageSolid Geometry Form 2pnt_buttercupNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure Problems SolvedDocument11 pagesCircular Measure Problems SolvedTerence RileyNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 8 Circular MeasureDocument9 pagesForm 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 8 Circular MeasureManisha Sekaran Muniandy80% (5)
- Form 3 Math Practice Test - Term 3Document3 pagesForm 3 Math Practice Test - Term 3zahidahosein50% (2)
- Chapter 6 IndicesDocument13 pagesChapter 6 Indicesnaza9775No ratings yet
- Mathematics Form 3 Kbat QuestionsDocument3 pagesMathematics Form 3 Kbat QuestionsMadelineLim69% (16)
- Soalan Kbat Add Math Form 5Document8 pagesSoalan Kbat Add Math Form 5Eric Mooi50% (2)
- Math MF2 Chapter 4 (Linear Equations I)Document1 pageMath MF2 Chapter 4 (Linear Equations I)compeil80% (5)
- Mathematics-Form 3-Chapter 3 Circle II by KelvinDocument7 pagesMathematics-Form 3-Chapter 3 Circle II by KelvinKelvinNo ratings yet
- AMATH Circular MeasureDocument21 pagesAMATH Circular MeasureLene100% (1)
- Review Exercise: (Form 2) Chapter 6-Pythagoras' TheoremDocument5 pagesReview Exercise: (Form 2) Chapter 6-Pythagoras' TheoremZulfitri Muhamad78% (9)
- KSSM Mathematics Form 2 Chapter 4 Polygons 4.2.4Document2 pagesKSSM Mathematics Form 2 Chapter 4 Polygons 4.2.4KSSM TSENo ratings yet
- (Worksheet) Lines & Planes in 3DDocument21 pages(Worksheet) Lines & Planes in 3DAmir Faisal75% (4)
- MATHEMATICS - CIRCLES FORM 2Document22 pagesMATHEMATICS - CIRCLES FORM 2graciezayn100% (6)
- Review Exercise: (Form 2) Chapter 5 - Ratios, Rates & Proportions IDocument3 pagesReview Exercise: (Form 2) Chapter 5 - Ratios, Rates & Proportions IZulfitri Muhamad100% (6)
- Add Math Index NumberDocument7 pagesAdd Math Index Numberkamil muhammadNo ratings yet
- Quiz f3Document10 pagesQuiz f3Hafizah PakahNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics Paper 2 SPM 2019 PDFDocument127 pagesAdditional Mathematics Paper 2 SPM 2019 PDFbrenwong@ymail.com50% (2)
- SPM Add Maths Pass Year QuestionsDocument61 pagesSPM Add Maths Pass Year QuestionsAvvy21No ratings yet
- 8 Circular MeasuresDocument12 pages8 Circular MeasuresNor Hanina100% (6)
- Topical Test Chapter 1 Math Form 1 Paper 2Document1 pageTopical Test Chapter 1 Math Form 1 Paper 2syukrie3100% (2)
- SPM Questions Transformations IIIDocument6 pagesSPM Questions Transformations IIIjuriah binti ibrahim0% (1)
- SPM AddMath Linear LawDocument21 pagesSPM AddMath Linear LawLeneNo ratings yet
- Test Paper Form 1 MathDocument13 pagesTest Paper Form 1 MathEsri9583% (6)
- Add Maths Form 4 Paper 1 Midterm 2012Document18 pagesAdd Maths Form 4 Paper 1 Midterm 2012Thiyaku MaruthaNo ratings yet
- Math MF2 Chapter 9 (Loci in Two Dimensions)Document6 pagesMath MF2 Chapter 9 (Loci in Two Dimensions)compeil100% (1)
- Maths F3 KSSM 2019Document132 pagesMaths F3 KSSM 2019蔡卷勋100% (5)
- Pythagoras' Theorem Topical Test Form 2Document2 pagesPythagoras' Theorem Topical Test Form 2ain nardirNo ratings yet
- Good Revision Modul Lulus Add MathDocument21 pagesGood Revision Modul Lulus Add MathLoh Chee WeiNo ratings yet
- Number Bases ExplainedDocument10 pagesNumber Bases ExplainedsiaoruiNo ratings yet
- Add MathsDocument5 pagesAdd MathsDzul JefriNo ratings yet
- SPM ADDITIONAL MATHS HOTS FUNCTIONSDocument13 pagesSPM ADDITIONAL MATHS HOTS FUNCTIONSsmkpthoe100% (1)
- Mathematics-Form 3-Chapter 1, 2, 3 & 4 by KelvinDocument10 pagesMathematics-Form 3-Chapter 1, 2, 3 & 4 by KelvinKelvin33% (3)
- Maths Questions IGCSEDocument26 pagesMaths Questions IGCSEDienta Alias100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Standard FormDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Standard FormWupo Ling100% (1)
- TRANSFORMATIONS Form 2Document34 pagesTRANSFORMATIONS Form 2Rosmah Abdullah87% (15)
- Final Year Exam Math Form 2Document13 pagesFinal Year Exam Math Form 2ashiela manaf33% (3)
- Normal Distribution Table SPMDocument1 pageNormal Distribution Table SPMsuraya che ahmadNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Mathematics Chapter 3Document3 pagesForm 4 Mathematics Chapter 3Chong Jie Mee50% (4)
- Solid Geometry Form 2Document18 pagesSolid Geometry Form 2graciezayn67% (3)
- Matematik K1 Modul KBSM SPM 2020Document275 pagesMatematik K1 Modul KBSM SPM 2020shafiqah azianNo ratings yet
- Circular Measures: Calculating Areas and Perimeters of Sectors and Circles (40Document4 pagesCircular Measures: Calculating Areas and Perimeters of Sectors and Circles (40SasiKalaRamayahNo ratings yet
- Topical Past Question On Circular Measure2Document8 pagesTopical Past Question On Circular Measure2Ebad AhmedNo ratings yet
- TrignometryDocument12 pagesTrignometryAbdo AbdalatifNo ratings yet
- Add Maths - Circular Measurement IIIDocument10 pagesAdd Maths - Circular Measurement IIIJohnLimNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure NADocument26 pagesCircular Measure NAJoann NgNo ratings yet
- Question's PDFDocument19 pagesQuestion's PDFAyaan NaveedNo ratings yet
- E (I) Circular Measures 1Document8 pagesE (I) Circular Measures 1Wong Jing KaeNo ratings yet
- Arc Length Area SectorDocument8 pagesArc Length Area SectorJohn GohNo ratings yet
- Workbook: Sunday, January 16, 2022 15:27Document1 pageWorkbook: Sunday, January 16, 2022 15:27popoutNo ratings yet
- Definitions and Concepts For CAIE Physics GCSEDocument25 pagesDefinitions and Concepts For CAIE Physics GCSEpopoutNo ratings yet
- March 2017 (v22) QPDocument2 pagesMarch 2017 (v22) QPpopoutNo ratings yet
- Question PaperDocument12 pagesQuestion PaperpopoutNo ratings yet
- 11595-Marked-Pilot - Textbook - Paper1 - History-Converted-Bangladesh Studies BookDocument30 pages11595-Marked-Pilot - Textbook - Paper1 - History-Converted-Bangladesh Studies BookpopoutNo ratings yet
- Possible Solutions For FloodDocument1 pagePossible Solutions For FloodpopoutNo ratings yet
- Equilibium & Pressure - Summarized Concepts For IGCSEDocument11 pagesEquilibium & Pressure - Summarized Concepts For IGCSEpopoutNo ratings yet
- Political Problems of Post War PakistanDocument7 pagesPolitical Problems of Post War PakistanpopoutNo ratings yet
- 04 - Angles and Angle MeasureDocument4 pages04 - Angles and Angle MeasureRolando QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Math Test - No Calculator: 25 Minutes, 20 QuestionsDocument34 pagesMath Test - No Calculator: 25 Minutes, 20 QuestionsWarot Methaphiphat90% (10)
- 2-D Kinematics and Newton's Laws Projectile MotionDocument19 pages2-D Kinematics and Newton's Laws Projectile MotionRay ChuaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 - Radian Measure: Degrees. There Is Another Unit of Measurement For Angles That Is Frequently Used Because ItDocument4 pages4.1 - Radian Measure: Degrees. There Is Another Unit of Measurement For Angles That Is Frequently Used Because ItBetty WangNo ratings yet
- Gyro Compasses SR 120 - mk37 PDFDocument163 pagesGyro Compasses SR 120 - mk37 PDFMarine Electronics Quick SupportNo ratings yet
- PHY 400 - Chapter 6 - Rotational MotionDocument30 pagesPHY 400 - Chapter 6 - Rotational MotionJacob OrtizNo ratings yet
- CEP233 - M01 - Definition Classification and Types of SurveysDocument15 pagesCEP233 - M01 - Definition Classification and Types of SurveysPam NunagNo ratings yet
- Adj TotaDocument29 pagesAdj TotaMohamed Reda El-sayedNo ratings yet
- Plane TrigonometryDocument547 pagesPlane TrigonometrygrvchikNo ratings yet
- Ail 7Document10 pagesAil 7dbzrulesNo ratings yet
- Basic Survey Lecture Notes - NCCDocument93 pagesBasic Survey Lecture Notes - NCCIgnatius ZiwaNo ratings yet
- Ometric Design of Highway PDFDocument48 pagesOmetric Design of Highway PDFTadi Fresco Royce75% (4)
- Handoutspdf PDFDocument49 pagesHandoutspdf PDFashar khanNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument84 pagesTrigonometryMARYBETH DIABORDONo ratings yet
- MHF4U OutlineDocument10 pagesMHF4U OutlineFrederick Zhang100% (1)
- AS Level Trigonometry Revision GuideDocument7 pagesAS Level Trigonometry Revision GuidePrudhvi JoshiNo ratings yet
- Sin & Cos - The Programmer's PalsDocument24 pagesSin & Cos - The Programmer's PalsRicardo De Oliveira AlvesNo ratings yet
- Radians and DegreesDocument19 pagesRadians and DegreesBassem KhalidNo ratings yet
- 5.2. Circular Motion PDFDocument3 pages5.2. Circular Motion PDFjmsonlNo ratings yet
- Serway Capitulo I PDFDocument18 pagesSerway Capitulo I PDFMoises LeijaNo ratings yet
- CLASSIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF TRIANGLESDocument8 pagesCLASSIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF TRIANGLEScharmaine padorNo ratings yet
- CE 1111 - Mathematics of EngineeringDocument56 pagesCE 1111 - Mathematics of EngineeringChristian LaronaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam in Pre-CalculusDocument4 pagesFinal Exam in Pre-CalculusMaeNo ratings yet
- Surveying ch2Document5 pagesSurveying ch2NancyRossNo ratings yet
- Vector Power in Alternating-Current CircuitsDocument35 pagesVector Power in Alternating-Current CircuitselectrosciNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate The Angular VelocityDocument11 pagesHow To Calculate The Angular VelocityParasaram SrinivasNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Radian and Degree MeasureDocument21 pages4.1 Radian and Degree MeasureJet EstefaniNo ratings yet
- PythonsupplementDocument190 pagesPythonsupplementKb TheBest100% (1)
- Circular MeasuresDocument11 pagesCircular MeasuresHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Study Resources: A-Level Physics (Worksheets)Document10 pagesStudy Resources: A-Level Physics (Worksheets)Baraa KhaledNo ratings yet