Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Integumentary System: Epidermis: This Tough Layer of Cells Is The Outermost Layer
Integumentary System: Epidermis: This Tough Layer of Cells Is The Outermost Layer
Uploaded by
nitin garg0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views5 pagesThe document provides definitions and descriptions of terms related to the integumentary system and other biological systems. It defines the epidermis as the outer layer of skin made of keratin-filled cells and describes keratinization as the process that fills cells with keratin. It also defines the epiglottis as a cartilage flap that seals the windpipe during eating, and motile cilia as moving hair-like structures that keep airways clear.
Original Description:
This is related to Epidermis
Original Title
Epidermis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides definitions and descriptions of terms related to the integumentary system and other biological systems. It defines the epidermis as the outer layer of skin made of keratin-filled cells and describes keratinization as the process that fills cells with keratin. It also defines the epiglottis as a cartilage flap that seals the windpipe during eating, and motile cilia as moving hair-like structures that keep airways clear.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views5 pagesIntegumentary System: Epidermis: This Tough Layer of Cells Is The Outermost Layer
Integumentary System: Epidermis: This Tough Layer of Cells Is The Outermost Layer
Uploaded by
nitin gargThe document provides definitions and descriptions of terms related to the integumentary system and other biological systems. It defines the epidermis as the outer layer of skin made of keratin-filled cells and describes keratinization as the process that fills cells with keratin. It also defines the epiglottis as a cartilage flap that seals the windpipe during eating, and motile cilia as moving hair-like structures that keep airways clear.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
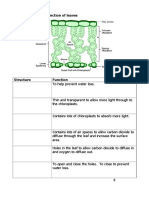
Integumentary system
Epidermis: This tough layer of cells is the outermost layer
of skin. It gets its toughness from a protein called keratin.
The epidermis has no blood supply and depends
on diffusion from the dermal cells for its metabolic needs.
Keratinization: The process by which vertebrate epithelial
cells become filled with keratin protein filaments, die, and
form tough, resistant structures such as skin, nails, and
feathers.
Epiglottis: It is a leaf-shaped flap of cartilage located
behind the tongue, at the top of the larynx, or voice box.
The main function of the epiglottis is to seal off the
windpipe during eating, so that food is not accidentally
inhaled.
Motile (or moving) cilia: They are found in the lungs,
respiratory tract and middle ear. These cilia have a
rhythmic waving or beating motion. They work, for
instance, to keep the airways clear of mucus and dirt,
allowing us to breathe easily and without irritation.
Floriculture: Floriculture the cultivation of flowers.
Tissue culture: It is the growth of tissues or cells in an
artificial medium separate from the organism. This is
typically facilitated via use of a liquid, semi-solid, or
solid growth medium, such as broth or agar. Tissue culture
commonly refers to the culture of animal cells and tissues,
with the more specific term plant tissue culture being used
for plants.
Silviculture: Silviculture the growing and cultivation of
trees.
Mariculture: Mariculture is the farming of
aquatic plants and animals in salt water.
Tachometer: It is an instrument designed to measure the
rotation speed of a shaft or disk. Tachometers
generally measure rotations per minute (RPM) though some
models also serve as rate meters and/or totalizers.
Barometer: It is a
scientific instrument
Tachom
used to measure air
eter
pressure.
Roemer: is a
temperature scale.
Mica: Mica is a mineral name given to a group of
minerals that are physically and chemically similar. They are
all silicate minerals, known as sheet silicates because they
form in distinct layers. Micas are fairly light and relatively
soft, and the sheets and flakes of mica are flexible.
Advection: It the transfer of heat or matter by the flow of
a fluid, especially horizontally in the atmosphere or the sea.
Diffusion: It is the net passive movement of particles
(atoms, ions or molecules) from a region in which they are in
higher concentration to regions of lower concentration. It
continues until the concentration of substances is uniform
throughout. Diffusion is an important process for living
things; it is how substances move in and out of cells.
Infrasonic rays: The term "infrasonic" applied to sound
refers to sound waves below the frequencies of audible
sound, and nominally includes anything under 20 Hz. Sources
of infrasound in nature include volcanoes, avalanches,
earthquakes and meteorites.
You might also like
- Lesson 5 Structure and Functions of Leaves Student WorksheetDocument3 pagesLesson 5 Structure and Functions of Leaves Student WorksheetEunice Xiiao Wenn100% (2)
- (L1) - Breathing and Gas Exchange-Aug 7, 2019Document36 pages(L1) - Breathing and Gas Exchange-Aug 7, 2019Geeta DhimanNo ratings yet
- The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument27 pagesThe Musculoskeletal SystemEduardoAlejoZamoraJr.No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument23 pagesBiologysammyusophNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument4 pagesAnaphyChyNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1.2 Gas Exchange and Transport SystemDocument8 pagesGen Bio 1.2 Gas Exchange and Transport SystemAizel Joyce DomingoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System NotesDocument4 pagesRespiratory System NotesFlare FlareonNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Organ System and Their FunctionsDocument78 pagesPlant and Animal Organ System and Their FunctionssannsannNo ratings yet
- Altm ks3Document30 pagesAltm ks3axellamae rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Gas ChangeDocument20 pagesGas ChangeBleebs CreigsNo ratings yet
- Cycle Test Revision 2.0Document4 pagesCycle Test Revision 2.0taminhthien2009No ratings yet
- Science Test RevisionDocument4 pagesScience Test Revisiontaminhthien2009No ratings yet
- Human Organ SystemDocument6 pagesHuman Organ SystemKNo ratings yet
- 18 OCTOBER, 2021 Monday. Biology Respiratory SystemsDocument9 pages18 OCTOBER, 2021 Monday. Biology Respiratory SystemsOyasor Ikhapo AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SurfacesDocument11 pagesRespiratory SurfacesNitesh KotianNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Gas Exchange BioDocument29 pagesGroup 4 Gas Exchange BioLJ Princess Mary MontenegroNo ratings yet
- U1L1 Gas Exchange01Document27 pagesU1L1 Gas Exchange01reamaedelectorNo ratings yet
- Life Science Study NotesDocument28 pagesLife Science Study Notes36050245No ratings yet
- University of The Punjab: BS-Chemistry 1st Semester-2021 Zoology-Invertebrates Diversity (ZOOL-101)Document6 pagesUniversity of The Punjab: BS-Chemistry 1st Semester-2021 Zoology-Invertebrates Diversity (ZOOL-101)basortusu13No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemsDocument41 pagesRespiratory SystemsDenzel MusaNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument10 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesRalph jhenzel UtonNo ratings yet
- Biology Lecture NotesDocument56 pagesBiology Lecture NotesMaisonette MichNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Re-Wps Office 21-1Document5 pagesMechanism of Re-Wps Office 21-1muichironezuko93No ratings yet
- Biology Preliminary Study NotesDocument23 pagesBiology Preliminary Study NotesNabiha SyedaNo ratings yet
- Bio Summary T2 Wk1Document7 pagesBio Summary T2 Wk1LilyNo ratings yet
- Palabras Del GlosarioDocument3 pagesPalabras Del GlosarioMilagros GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chicken HamborgerDocument5 pagesChicken HamborgerJulianaMarieBelicanoNo ratings yet
- Gas ExchangeDocument18 pagesGas ExchangemiatamayoqtNo ratings yet
- Agri 22.leon 3Document55 pagesAgri 22.leon 3Jackelene TumesaNo ratings yet
- Drei Javierto - Quarter 2 Week 4 Activity 4 Part 1 (GB)Document10 pagesDrei Javierto - Quarter 2 Week 4 Activity 4 Part 1 (GB)Andrei Sy JaviertoNo ratings yet
- X-Ray: An of A Human Chest Area, With Some Structures LabeledDocument4 pagesX-Ray: An of A Human Chest Area, With Some Structures LabeledbbhoeeNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-28 at 3.39.31 PMDocument32 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-28 at 3.39.31 PMKumar KumarNo ratings yet
- Respiration PlantsDocument22 pagesRespiration Plantsnihalbolla2023No ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange: of GasesDocument10 pagesBreathing and Exchange: of GaseshellohelloworldNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesRespiratory SystemAdit KumarNo ratings yet
- EALSWeekkk14-15-16 DONEDocument27 pagesEALSWeekkk14-15-16 DONEAlejandro SantosNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument7 pagesRespiration NotesKrishna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Gas Exhange - Group 2 - 20240423 - 151553 - 0000Document20 pagesGas Exhange - Group 2 - 20240423 - 151553 - 0000dalandan293No ratings yet
- Sensory and Motor SystemDocument12 pagesSensory and Motor SystemrobertoNo ratings yet
- Breathing and ExchangeDocument40 pagesBreathing and ExchangeShambhaviNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms Part 2Document9 pagesRespiration in Organisms Part 2opsharpedgeNo ratings yet
- Homework EngDocument4 pagesHomework EngMigs TanNo ratings yet
- Science Revision NotesDocument13 pagesScience Revision NotesNoaNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review (Gen Bio 2)Document5 pagesPointers To Review (Gen Bio 2)jayrald cruzadaNo ratings yet
- 3 Environmental FactorsDocument21 pages3 Environmental Factorsrahul royNo ratings yet
- Gas ExchangeDocument15 pagesGas Exchangeneill arcaNo ratings yet
- AS Biology Unit 2 NotesDocument34 pagesAS Biology Unit 2 NotesMehreenSaeedNo ratings yet
- 1.6 EXCRETION-The Removal of WasteDocument13 pages1.6 EXCRETION-The Removal of WastesamiktshyagiriNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesRespiratory SystemRifai Alfarabi100% (1)
- DEFINE Homeostasis, Osmoregulation, Thermoregulation and Excretion. 1. HomeostasisDocument14 pagesDEFINE Homeostasis, Osmoregulation, Thermoregulation and Excretion. 1. HomeostasisStrange NazarNo ratings yet
- Science G K Info Shared LalaDocument32 pagesScience G K Info Shared LalaNatasha BeheraNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 2 Learning Activity Sheet Q4 W1 v. 2Document12 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY 2 Learning Activity Sheet Q4 W1 v. 2Pearl Lee MetiamNo ratings yet
- EarthwormDocument11 pagesEarthwormFabian GuadarramaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Anatomy - Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesComparative Anatomy - Respiratory SystemGeo ZahariaNo ratings yet
- Por If EraDocument5 pagesPor If EraRebecca SchmidtNo ratings yet
- 2009 Biology NotesDocument43 pages2009 Biology NotesRyan NostalgiNo ratings yet
- Transport SystemDocument10 pagesTransport Systemvictoriabodunde01No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument31 pagesRespiratory SystemMark Jhosua Austria GalinatoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Respiration - Reference Material - Shared in GCDocument7 pagesUnit 1 - Respiration - Reference Material - Shared in GCTarunNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document22 pagesGeneral Biology 2Lala ChanNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System PDFDocument25 pagesThe Respiratory System PDFbilly sauraNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning 1Document245 pagesMachine Learning 1nitin gargNo ratings yet
- ActivationsDocument8 pagesActivationsnitin gargNo ratings yet
- Porous Material: It Is A Material Containing Pores (Voids) .: Totalizer: Totalizer A Device (Such As A Meter) ThatDocument5 pagesPorous Material: It Is A Material Containing Pores (Voids) .: Totalizer: Totalizer A Device (Such As A Meter) Thatnitin gargNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument3 pagesBloodnitin gargNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology Part 1 IGMPIDocument38 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology Part 1 IGMPIGaurav VatsNo ratings yet
- Seed Haematology: Challenges in Monocyte CountingDocument8 pagesSeed Haematology: Challenges in Monocyte CountingqualityNo ratings yet
- Diajukan Untuk Melengkapi Persyaratan Mencapai Gelar Dokter Spesialis Penyakit DalamDocument70 pagesDiajukan Untuk Melengkapi Persyaratan Mencapai Gelar Dokter Spesialis Penyakit DalamMohammad SutamiNo ratings yet
- Q1W2-Lesson 1-2 CIRCULATION OF BLOODDocument40 pagesQ1W2-Lesson 1-2 CIRCULATION OF BLOODKRISTA MAE BALANAYNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 16 - Digestion - and - Absorption Ncert SolutionDocument10 pagesChapter - 16 - Digestion - and - Absorption Ncert SolutionGuru KhanNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System and Body MetabolismDocument3 pagesThe Digestive System and Body MetabolismJonash MoralesNo ratings yet
- Immunohematology Harmening HIGHLIGHT 2222Document45 pagesImmunohematology Harmening HIGHLIGHT 2222flynnpunzNo ratings yet
- Untitled 2 4Document6 pagesUntitled 2 4nicksscribd7No ratings yet
- Immune Response in The Skin of AgingDocument7 pagesImmune Response in The Skin of AgingInmunoBlogNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Terms Used in PathologyDocument3 pagesGlossary of Terms Used in Pathologysamuel samarooNo ratings yet
- Zollinger Ellis Wps OfficeDocument15 pagesZollinger Ellis Wps OfficeAbhash MishraNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System - Brain and Spinal CordDocument8 pagesCentral Nervous System - Brain and Spinal CordArrianne Sjairra PimentelNo ratings yet
- Krok 1 Stomatology: Test Items For Licensing ExaminationDocument26 pagesKrok 1 Stomatology: Test Items For Licensing ExaminationhelloNo ratings yet
- Organelle Trading Card GameDocument1 pageOrganelle Trading Card Gamechabries100% (3)
- Graves Disease - HistologyDocument5 pagesGraves Disease - HistologySerenNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Organ 28-Jan-2022Document63 pagesFemale Reproductive Organ 28-Jan-2022Savita HanamsagarNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report in Histopathology November 6 - November 14, 2017Document3 pagesNarrative Report in Histopathology November 6 - November 14, 2017Mae ann barredoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lymphatic SystemDocument46 pagesAnatomy Lymphatic SystemJenise MuLatto Franklin100% (2)
- My Live 3 Questions (Tigiste)Document26 pagesMy Live 3 Questions (Tigiste)Hab AnneNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CancerDocument30 pagesPathophysiology of CancerAyoub ZeinEddinNo ratings yet
- Placenta FunctionsDocument46 pagesPlacenta Functionsvenkata sryanamala50% (2)
- Ovarian TumorsDocument73 pagesOvarian Tumorsabhishekrajpurohit275No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The SkinDocument30 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The SkinNancy VargasNo ratings yet
- ANA101 Respiratory System DR GIEDocument44 pagesANA101 Respiratory System DR GIEMarian Kyla MarianoNo ratings yet
- Cells and Systems: Unit 1 TestDocument4 pagesCells and Systems: Unit 1 TestJayNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Nutrition in AnimalDocument10 pagesClass 7 Nutrition in Animalcrapjorust123100% (2)
- NERVOUS SYSTEM (IB-DP BIOLOGY) - Multiple Choice Type QuestionsDocument5 pagesNERVOUS SYSTEM (IB-DP BIOLOGY) - Multiple Choice Type QuestionsVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Non Keratinizedmucosa Non KeratinocytesDocument29 pagesLecture 2 Non Keratinizedmucosa Non KeratinocytesAMIT GUPTANo ratings yet