Professional Documents
Culture Documents
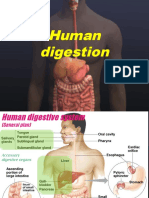
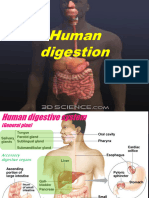
Summary of Digestion in Man: Mouth
Uploaded by
Amparin Solo AmparinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary of Digestion in Man: Mouth
Uploaded by
Amparin Solo AmparinCopyright:
Available Formats
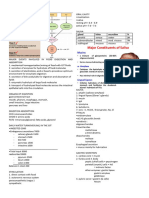
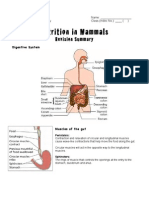
SUMMARY OF DIGESTION IN MAN
REGION OF GUT Gland and secretion Enzymes and optimum pH Food digested Products
and other activity
MOUTH Salivary gland Amylasa> Starch > >Maltosa
Mastication by jaws -saliva, pH 5-7 -Mucin lubricates food bolus
and tongue 1-2 litres daily
none none none -Food bolus move by
OESOPHAGUS peristalsis
Produce chyme that
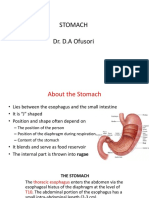
STOMACH Gastric gland, contain:
Churning action.
Temporary storage,
-stomach wall- Pepsin> Proteins> ->large peptides
1-3 h gastric juice, Hydrochloric acid> >Provide necessary acid
3-4 l daily pH 1, strongly acid pH for enzyme action and
>Bactericidal function
Absorption: water, salts,
vitamins and ethanol
Liver
-bile juice (bile salts)> none Lipids> Emulsified lipids
700cm3 -1,2 l daily Alters pH of stomach
contents
DUODENUM Produce CHYME containing
GLAND SECRETIONS Pancreas Sodium bicarbonate> Neutralize pH >pH 7-8 slighty alkaline
-pancreatic juice> Amylase p Starch> >maltose
700 cm3 daily Lipasa p Emulsified lipids> >fatty acids and glycerine
Trypsinogen p>(Trypsina) Large peptides> >small peptides
Produce cHYLE containing
Enterokinase>Trypsinogen> Changes intoTrypsin
Maltase i> Maltose> >Glucose
Glands in intestine Sucrase i> Sucrose> >Glucose and fructose
and duodenum wall. Lactase i> Lactose> >Glucosa and galactose
SMALL INTESTINE -intestinal juice, Lipasa i> Emulsified lipids> >fatty acids and glycerine
AND 200cm3 daily Erepsin i> Small peptides> >amino acids
DUODENUM Absorption: large surface
area, villi and microvilli,
main region for absorption
of vitamins, minerals,
aminoacids, glucose, fatty
acids and glycerine
Mucus lubricates faeces
Lining with pH 6-8 Water absorbed
LARGE INTESTINE
mucous glands no enzymes Bacteria synthesized
vitamin K and B groups
Produce faeces (*)
(*)Remember faeces mainly contain:
water (75%); bacteria (8%) ; lipids (6%); dietary fibre cellulose (2%), other substances (9%)
You might also like
- Digestion WiwiDocument23 pagesDigestion WiwiSCE1-0622 Amni Insyirah Binti Mohd NasarudinNo ratings yet
- GI SeminarDocument13 pagesGI SeminarshararohitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Food and DigestionDocument8 pagesChapter 4 - Food and Digestiononlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- Biology DigestionDocument14 pagesBiology DigestionhhhhhhhhhhhhhhNo ratings yet
- DIGESTIONDocument5 pagesDIGESTIONArdiene Shallouvette GamosoNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive PDFDocument1 pageHuman Digestive PDFsiyin limNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Gizi Andreanyta MelialaDocument105 pagesDigestive System Gizi Andreanyta Melialaannaafia69969No ratings yet
- Structure of Human DigestionDocument3 pagesStructure of Human DigestionChong Yu AnNo ratings yet
- Digesti Dan AbsorpsiDocument57 pagesDigesti Dan AbsorpsisariNo ratings yet
- DIGESTIONDocument6 pagesDIGESTIONRane MandapatNo ratings yet
- 9 Enzymes and DigestionDocument6 pages9 Enzymes and DigestionSheniqua GreavesNo ratings yet
- Digestion TransDocument10 pagesDigestion Transt4gjzhpfjcNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System - Physical & ChemicalDocument19 pagesThe Digestive System - Physical & ChemicalTrinity BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument257 pagesHuman PhysiologyAyushNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument32 pagesDigestion and AbsorptionFiqri NovianNo ratings yet
- Week 14: Digestion Chemistry: Intrinsic FactorDocument4 pagesWeek 14: Digestion Chemistry: Intrinsic FactorLore Anne Mhae SantosNo ratings yet
- 7.4 Chemical DigestionDocument4 pages7.4 Chemical DigestionPatrick AbidraNo ratings yet
- Pencernaan Dan Penyerapan: TriawantiDocument51 pagesPencernaan Dan Penyerapan: TriawantiAurellia ShafitriNo ratings yet
- Small Intestine and PancreasDocument52 pagesSmall Intestine and PancreasLutfi AuliaNo ratings yet
- 113 Trans Lipids Part 1.1Document6 pages113 Trans Lipids Part 1.1Rebecca Aira BalitonNo ratings yet
- The Small IntestineDocument16 pagesThe Small IntestineMichael NyaongoNo ratings yet
- Food Digestion (Equation)Document2 pagesFood Digestion (Equation)Nursakinah NajwahNo ratings yet
- 9 Nutrition-and-dietetics-IntroDocument51 pages9 Nutrition-and-dietetics-IntroPratiksha JhareeNo ratings yet
- BBB PDFDocument37 pagesBBB PDFaq educateNo ratings yet
- Digestive System SummaryDocument2 pagesDigestive System SummaryApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- PDF 1686404856729 7747998126007773086Document45 pagesPDF 1686404856729 7747998126007773086Pratiksha JhareeNo ratings yet
- 1 - Adult Gastrointestinal DisorderDocument17 pages1 - Adult Gastrointestinal DisorderNica EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Digestion in GI TractDocument3 pagesDigestion in GI TractAdnin ShereenNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption By-Dr. Suntia Saxena Part 2Document41 pagesDigestion and Absorption By-Dr. Suntia Saxena Part 2Divya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Mouth Salivary Glands: Aranilla, Hanako S. Homework-GitDocument2 pagesMouth Salivary Glands: Aranilla, Hanako S. Homework-GitHanako AranillaNo ratings yet
- Simple Non-Ruminants: Principles of Animal Nutrition Dr. Cristine W. MaramagDocument30 pagesSimple Non-Ruminants: Principles of Animal Nutrition Dr. Cristine W. MaramagMc Kjell Dagman RaveloNo ratings yet
- Presentation 05 Human DigestionDocument45 pagesPresentation 05 Human DigestionCarl (Carl)No ratings yet
- Presentation 05 Human DigestionDocument40 pagesPresentation 05 Human DigestionCarl (Carl)No ratings yet
- Alimentary Canal and Human Digestion 2015Document7 pagesAlimentary Canal and Human Digestion 2015Tharanga HewabuhageNo ratings yet
- Digestion SystemDocument2 pagesDigestion Systemأيمان كونNo ratings yet
- 2 Digestion and Absorption RB CAGMAT REVIEW Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument16 pages2 Digestion and Absorption RB CAGMAT REVIEW Anatomy and PhysiologyFatima AbirinNo ratings yet
- SCES3183 Nutrition For Human's EnzymesDocument18 pagesSCES3183 Nutrition For Human's EnzymesJacklin Ramli Jr.No ratings yet
- Digestive System: Arba P. RamadaniDocument39 pagesDigestive System: Arba P. RamadaniFitri Andriani IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Life Process Public LiveDocument29 pagesLife Process Public LiveMohammed RamzanNo ratings yet
- Digestion-Food Is BrokenDocument32 pagesDigestion-Food Is Brokenaerell manuelNo ratings yet
- 06 Nutrition in Humans NoteDocument12 pages06 Nutrition in Humans Notetarankaur401No ratings yet
- Enzyme: DigestionDocument5 pagesEnzyme: Digestion24 LOONG BAO XINl龙宝鈊No ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument63 pagesDigestive SystemFiqri NovianNo ratings yet
- 6.4 Food Digestion: Digestion in Small Intestine (Duodenum)Document7 pages6.4 Food Digestion: Digestion in Small Intestine (Duodenum)salsabilakamarudinNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Theraphy PDF 2Document1 pageNutrition and Diet Theraphy PDF 29xc2fc8hnqNo ratings yet
- Science PT3 PDFDocument5 pagesScience PT3 PDFKomagal KunaisekaranNo ratings yet
- Food Classes: FAT Water Vitamins, Minerals, & Roughage ProteinDocument25 pagesFood Classes: FAT Water Vitamins, Minerals, & Roughage Proteinuminoriah80% (5)
- Presentation 05 Human Digestion 1Document19 pagesPresentation 05 Human Digestion 1darontolentinoNo ratings yet
- (BIO) Chapter 4 - Nutrition in HumanDocument21 pages(BIO) Chapter 4 - Nutrition in Humantaco ghoulNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting in The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument14 pagesDrugs Acting in The Gastrointestinal SystemPrincess C. SultanNo ratings yet
- Rev Sci Summary DigestionDocument2 pagesRev Sci Summary Digestionprameeta100% (1)
- Digestion of CarbohydratesDocument1 pageDigestion of Carbohydrateskay yNo ratings yet
- Digestion & AbsorptionDocument18 pagesDigestion & AbsorptionDoghouseNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument10 pagesDigestion and Absorptionvivek kumarNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: Mechanical & Chemical Breakdown of Food For EnergyDocument26 pagesThe Digestive System: Mechanical & Chemical Breakdown of Food For EnergyRozaini OthmanNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument49 pagesDigestive SystemDaniel WakaWakaNo ratings yet
- Rev - Notes - ch06 - e Human NutritionDocument6 pagesRev - Notes - ch06 - e Human NutritionEsther WongNo ratings yet
- Biology - Course - Haidar RahhalDocument36 pagesBiology - Course - Haidar RahhalFatima SlimNo ratings yet
- Digestive Form 4Document43 pagesDigestive Form 4miraazizNo ratings yet
- Rabbit Nutrition PDFDocument252 pagesRabbit Nutrition PDFHuy Hoàng Lê100% (1)
- Monogastric: Single-Chambered StomachDocument4 pagesMonogastric: Single-Chambered StomachFarhan Rezki MNo ratings yet
- Small IntDocument59 pagesSmall IntCatalin SavinNo ratings yet
- Total Parenteral Nutrition: The Long and The Short of It: Duna PennDocument7 pagesTotal Parenteral Nutrition: The Long and The Short of It: Duna PennDsk IndryNo ratings yet
- Colostomy ClassDocument24 pagesColostomy Classshahulkp100% (1)
- What Is HirschsprungDocument4 pagesWhat Is HirschsprungMicah SaberNo ratings yet
- Posterior Fixation of Gastric Tube With Fibrin SeaDocument6 pagesPosterior Fixation of Gastric Tube With Fibrin Seaabdourahmane ndongNo ratings yet
- Medsurg ReviewerDocument6 pagesMedsurg Reviewersherlyn galvanNo ratings yet
- Developmental Lesson Plan: The Digestive SystemDocument21 pagesDevelopmental Lesson Plan: The Digestive Systemapi-526839782No ratings yet
- Enteric Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesEnteric Nervous Systemmehdi mafakheriNo ratings yet
- Estimasi Biaya Bedah DigestifDocument2 pagesEstimasi Biaya Bedah DigestifDei RahayuNo ratings yet
- The Liver: Anatomy and FunctionsDocument2 pagesThe Liver: Anatomy and FunctionsJharene BasbañoNo ratings yet
- SBI3U Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesSBI3U Digestive SystemMario AttallaNo ratings yet
- SCES3183 Nutrition For Human's EnzymesDocument18 pagesSCES3183 Nutrition For Human's EnzymesJacklin Ramli Jr.No ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Body OrientationDocument8 pagesActivity 2 - Body OrientationEuniece AnicocheNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Organ - Vermiform AppendixDocument3 pagesAbdominal Organ - Vermiform AppendixayooniaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Quiz AnswersDocument3 pagesGastrointestinal Quiz AnswersLyniel Anne de AsisNo ratings yet
- STOMACHDocument18 pagesSTOMACHOlaifa victorNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Microflora PPT 19.1.11.Document51 pagesGastrointestinal Microflora PPT 19.1.11.सुमेर सिंह मीणाNo ratings yet
- Lab Dept: Urine/Stool Test Name: Occult Blood, Stool: General InformationDocument4 pagesLab Dept: Urine/Stool Test Name: Occult Blood, Stool: General Informationnana kunaNo ratings yet
- Colonoscopy - : A Pictorial OverviewDocument29 pagesColonoscopy - : A Pictorial OverviewshravaniNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ExaminationDocument20 pagesAbdominal ExaminationRacquel WilsonNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube (NGT)Document31 pagesNasogastric Tube (NGT)annyeong_123No ratings yet
- Pancreatitis: David Minter, DO, FACOIDocument66 pagesPancreatitis: David Minter, DO, FACOINabeel ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Animals: DigestionDocument13 pagesNutrition in Animals: DigestionKalpavriksha1974No ratings yet
- Revised Case Report - HemorrhoidsDocument47 pagesRevised Case Report - Hemorrhoidschristina_love08100% (2)
- Gallbladder Specialist SurgeonDocument5 pagesGallbladder Specialist SurgeonGeorgia Top SurgeonsNo ratings yet
- Colonoscopy Categorisation Guidelines 2017Document2 pagesColonoscopy Categorisation Guidelines 2017ScribboddNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument40 pagesPancreasMuthannah MarawanNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy - Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesAnaPhy - Digestive SystemJan Mark SotoNo ratings yet