Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How clutches work in cars
Uploaded by
Khurram SherazOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How clutches work in cars
Uploaded by
Khurram SherazCopyright:
Available Formats
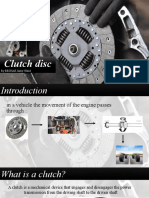
HOW DOES CLUTCHES WORKS
Clutches
Principle:
Automotive clutches depends on friction for their operation, whether it is to be solid friction
as in the conventional clutches, or fluid friction and inertia as utilized in the fluid coupling
and torque converter. The fluid serves the same purpose as the conventional clutch, but the
difference in the principles of operation makes it necessary to discuss the tow mechanisms
separately. Therefore, the first part of this discussion will be concerned with conventional
clutches.
Purpose:
A clutch in an automotive vehicle provides a means of connecting and disconnecting the
engine from the power transmission system. Because the internal combustion engine does
not develop a high starting torque, it must be disconnecting from the power train and
allowed to operate with out load until it develops enough torque to overcome the inertia of
the vehicle when starting from rest. The application of the engine power to the load must be
gradual to provide smooth engagement and to lesson the shock on the driving parts. After
engagement, the clutch must transmit all the engine power to the transmission without
slipping. Further, it is desirable to disconnect the engine from the power train during the
time the gears in the transmission are being the shifted from one gear ratio to another.
Operation
The transmission of power through the clutch accomplished by bringing one or more
rotating drive members secured to the crankshaft into gradual contact with one or more
driven members secured to the unit driven. These members secured to the unit being driven.
These members are either stationary or rotating spring pressure controlled by the driver
through the clutch pedal and suitable linkage. As spring pressure increases the friction
increases; therefore, when the pressure is light, the comparatively small amount of friction
between the members permits a great deal of slippage. As the spring pressure increases, less
slippage occurs until, when the full spring pressure is applied, the speed of the driving and
You might also like
- Small Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsFrom EverandSmall Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsNo ratings yet
- Brakes and ClutchesDocument20 pagesBrakes and ClutchesHuzaifa YousafNo ratings yet
- Vacuum ClutchDocument8 pagesVacuum Clutchprithvi mannNo ratings yet
- How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesFrom EverandHow to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Power Units and TransmissionDocument42 pagesPower Units and TransmissionAmarjeet RaiNo ratings yet
- Transmission and Steering Systems ExplainedDocument24 pagesTransmission and Steering Systems ExplainedSai RamNo ratings yet
- Clutch disc: Understanding how clutches workDocument7 pagesClutch disc: Understanding how clutches worksaberNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 - Transmission SystemDocument38 pagesLecture 03 - Transmission Systemcolonelsharif21No ratings yet
- How Automobile Clutches Work - Transmitting Power from Engine to WheelsDocument3 pagesHow Automobile Clutches Work - Transmitting Power from Engine to WheelsAshok Pradhan100% (1)
- ClutchhhDocument3 pagesClutchhhAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to clutches in automobilesDocument17 pagesIntroduction to clutches in automobileslokeshNo ratings yet
- Automatic Transmission Basics PDFDocument34 pagesAutomatic Transmission Basics PDFtambache69100% (1)
- ClutchesDocument60 pagesClutchesRoopesh BhatNo ratings yet
- What Is Clutch?Document2 pagesWhat Is Clutch?NizelCalmerinBaesNo ratings yet
- ClutchesDocument22 pagesClutchesravi100% (1)
- AutomaticDocument13 pagesAutomaticabdullah8508No ratings yet
- AE Unit 3 Transmission SystemDocument107 pagesAE Unit 3 Transmission Systemsemmat1802No ratings yet
- Main Components of Transmission SystemDocument11 pagesMain Components of Transmission SystemVJ CarbonellNo ratings yet
- AT121 – Automotive Clutch: Working Principle, Parts, Types and ProblemsDocument8 pagesAT121 – Automotive Clutch: Working Principle, Parts, Types and ProblemsDee DemNo ratings yet
- AE Unit 3 Transmission System NotesDocument15 pagesAE Unit 3 Transmission System Notessemmat1802No ratings yet
- Different Types of Clutch Explained in Detail Notes PDFDocument10 pagesDifferent Types of Clutch Explained in Detail Notes PDFMahihu KuriaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Transmission BasicsDocument238 pagesAutomatic Transmission BasicsSílvio Santos100% (2)
- Transmission Systems OverviewDocument168 pagesTransmission Systems Overviewriyaz ahmedNo ratings yet
- AT6501 UwDocument132 pagesAT6501 UwAjithNo ratings yet
- ClutchDocument4 pagesClutchboudy04No ratings yet
- 0.rahat Sir AutomobileDocument157 pages0.rahat Sir AutomobileTahammul Islam IbonNo ratings yet
- Automotive Transmission System - Slide 01-63Document89 pagesAutomotive Transmission System - Slide 01-63Arifur Rahman MSquareNo ratings yet
- Automotive Transmission SystemDocument94 pagesAutomotive Transmission SystemTanzim Rafat AyonNo ratings yet
- Advancements of Automatic Gear Transmission SystemsDocument21 pagesAdvancements of Automatic Gear Transmission SystemsKavindu UmayangaNo ratings yet
- TanoyDocument22 pagesTanoyOrtilano BryanNo ratings yet
- ClutchDocument24 pagesClutchJayson B. Cadelina100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Automatic TransmissionsDocument220 pagesFundamentals of Automatic TransmissionsAndrés Arias100% (7)
- Automotive Transmission QuestionsDocument8 pagesAutomotive Transmission QuestionsSahayaraj GabrielNo ratings yet
- Manual Transmission SystemsDocument57 pagesManual Transmission SystemsYerbol Kabyshev100% (1)
- CLUTCHES AND COUPLINGS: PNEUMATIC, MECHANICAL, AND FLEXIBLE TYPESDocument11 pagesCLUTCHES AND COUPLINGS: PNEUMATIC, MECHANICAL, AND FLEXIBLE TYPESSangharsh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Transmission PDFDocument21 pagesTransmission PDFMohanish ShahNo ratings yet
- Rohini 70563202173Document41 pagesRohini 70563202173Ss AMINE sSNo ratings yet
- Transmission System 3Document21 pagesTransmission System 3unofficialtuhinNo ratings yet
- Clutches: Sandeep Jaladhi 14955A0308 Mech IiiaDocument26 pagesClutches: Sandeep Jaladhi 14955A0308 Mech IiiaSandip KulkarniNo ratings yet
- What is a clutch and how does it work in vehiclesDocument2 pagesWhat is a clutch and how does it work in vehiclesHarish Padmanaban100% (1)
- Experiment No. 7: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 7: ObjectiveMoiz AamirNo ratings yet
- Clutch: Chapter-1 IntroductionDocument6 pagesClutch: Chapter-1 IntroductionNikhil DixitNo ratings yet
- Transmission System: Windmills Horse Steam Engines Pumping Milling HoistingDocument9 pagesTransmission System: Windmills Horse Steam Engines Pumping Milling Hoistingajay mauryaNo ratings yet
- Types and Classifications of Clutches in AutomobilesDocument10 pagesTypes and Classifications of Clutches in AutomobilesShambhuNath VermaNo ratings yet
- Automotive TransmissionDocument146 pagesAutomotive TransmissionTony Neal100% (1)
- Unit 2Document96 pagesUnit 2David GaddalaNo ratings yet
- AT21Document4 pagesAT21Pendi WaeeNo ratings yet
- Title: Automotive Powertrain Date: Objective: To Understand The Power Train Components of Automobiles Both Observation/TheoryDocument17 pagesTitle: Automotive Powertrain Date: Objective: To Understand The Power Train Components of Automobiles Both Observation/TheorybroNo ratings yet
- Types of ClutchesDocument18 pagesTypes of ClutchessyedshehzebNo ratings yet
- Automotive Transmission NewDocument147 pagesAutomotive Transmission NewhodvmkvecautoNo ratings yet
- Automobile Transmission Systems ExplainedDocument61 pagesAutomobile Transmission Systems ExplainedaravindNo ratings yet
- Title: Automotive Powertrain Date: Objective: To Understand The Power Train Components of Automobiles BothDocument6 pagesTitle: Automotive Powertrain Date: Objective: To Understand The Power Train Components of Automobiles BothbroNo ratings yet
- Transmission SystemDocument85 pagesTransmission SystempavanmeNo ratings yet
- Automobile EngieeringDocument28 pagesAutomobile EngieeringYogesh Kumar GaurNo ratings yet
- KSRTC Final ReportDocument47 pagesKSRTC Final ReportBoby Thomas100% (1)
- Torque ConverterDocument11 pagesTorque ConverterWilliam KibbeNo ratings yet
- Gearboxes ClassDocument35 pagesGearboxes ClassNaveen Vachipalli100% (1)
- Design Progress 123Document24 pagesDesign Progress 123a61812344No ratings yet
- Study of Single Plate Clutch: Presented by:-PANKAJ SHARMADocument16 pagesStudy of Single Plate Clutch: Presented by:-PANKAJ SHARMAMonu JoshiNo ratings yet
- WATER QUALITYDocument37 pagesWATER QUALITYKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic Design: ELV, PMP, Risk AnalysisDocument14 pagesHydrologic Design: ELV, PMP, Risk AnalysisKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Annual Maximum Discharges: Guadalupe River at Victoria, Texas, 1935-2012Document5 pagesAnnual Maximum Discharges: Guadalupe River at Victoria, Texas, 1935-2012Khurram SherazNo ratings yet
- SPRINKLER IRRIGATION APPLICATION RATES AND DEPTHSDocument2 pagesSPRINKLER IRRIGATION APPLICATION RATES AND DEPTHSKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- County Soil Surveys: White Areas Are Water or Impervious Cover From Land DevelopmentDocument2 pagesCounty Soil Surveys: White Areas Are Water or Impervious Cover From Land DevelopmentKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- CelerityDocument2 pagesCeleritynidhalsaadaNo ratings yet
- Problem 3 On Homework 2: Gage Coordinates (Miles) Rainfall (Inches) 1 2 3 4Document10 pagesProblem 3 On Homework 2: Gage Coordinates (Miles) Rainfall (Inches) 1 2 3 4Jonathan M.No ratings yet
- Channel Flow RoutingDocument21 pagesChannel Flow RoutingKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Flowchart LevelingDocument1 pageFlowchart LevelingKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Solutions To HW#6 SP07Document6 pagesSolutions To HW#6 SP07Khurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Precision Land Grading Costs With On-Farm LaborDocument6 pagesPrecision Land Grading Costs With On-Farm LaborKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Managing Salinity in The Indus Basin of PakistanDocument9 pagesManaging Salinity in The Indus Basin of PakistanKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Evaporation Examples: (1) Energy Balance MethodDocument3 pagesEvaporation Examples: (1) Energy Balance MethodKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Darcy's Law For Flow Through Porous Medium, First Published in 1856Document4 pagesDarcy's Law For Flow Through Porous Medium, First Published in 1856Khurram SherazNo ratings yet
- How Does The Carburetor Works: A) TemperatureDocument5 pagesHow Does The Carburetor Works: A) TemperatureKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Water BalanceDocument25 pagesAtmospheric Water BalanceKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- How clutches work in carsDocument2 pagesHow clutches work in carsKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Valve DemonstrationDocument2 pagesValve DemonstrationKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document39 pagesUnit 7vijay_oraerp1711No ratings yet
- Valve DemonstrationDocument2 pagesValve DemonstrationKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- How Does The Carburetor Works: A) TemperatureDocument5 pagesHow Does The Carburetor Works: A) TemperatureKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Technogegggrma HydDocument8 pagesTechnogegggrma HydArun AroraNo ratings yet
- Fuel Efficiency Test Using Hydraulic DynamometerDocument1 pageFuel Efficiency Test Using Hydraulic DynamometerKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Python Lesson 1Document45 pagesPython Lesson 1DM TimaneNo ratings yet
- Ignition System of EngineDocument3 pagesIgnition System of EngineKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Increasing Water Productivity Eng - 1Document10 pagesIncreasing Water Productivity Eng - 1Khurram SherazNo ratings yet
- T 5109Document14 pagesT 5109akshayNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Domain (Thinking, Knowledge) Evaluation Synthesis Analysis Application Comprehension KnowledgeDocument3 pagesCognitive Domain (Thinking, Knowledge) Evaluation Synthesis Analysis Application Comprehension KnowledgeKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Overcoming Obstacles in Surveying ChainsDocument3 pagesOvercoming Obstacles in Surveying ChainsKhurram Sheraz100% (4)