Professional Documents
Culture Documents
15: Chemical Bonding: Key Chemistry Terms Using Bond Characteristics
Uploaded by
booty hole0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pagechemical bonding
Original Title
Chemical Bonding
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentchemical bonding
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 page15: Chemical Bonding: Key Chemistry Terms Using Bond Characteristics
Uploaded by
booty holechemical bonding
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat Sheet
15: Chemical Bonding
Key Chemistry Terms Using Bond Characteristics
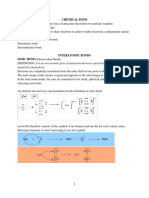
Ionic Bond: Bond formed from electrostatic attraction between Examples:
ions (charged atoms). Formed from metals with nonmetals. Identify the type of bond based on characteristics:
Covalent Bond: Bond formed between two nonmetals that NaCl
involve shared electrons. Ionic (metal & non-metal).
Polar covalent bond: Bond formed between two nonmetals— CH3COOH
uneven sharing of electrons. Covalent (non-metal & non-metal).
Metallic bond: Formed between metal atoms—electrons are Dissolves in water.
pooled between the networks of atoms. Polar covalent or ionic.
Polar bond: Bond between two atoms with a great difference Conducts electricity in solid state.
in electronegativities—uneven sharing of electrons resulting in a Metallic.
slightly positive region and a slightly negative region of the
bond. Conducts electricity dissolved in water.
Polar covalent.
Electronegativity: An atomic “pull” on electrons shared with
another atom.
Bond Polarity
Polar molecule: Molecule where the polar bonds do not cancel When nonmetals bond covalently with a large difference in
each other out in 3D orientation. electronegativity
Valence Bond Theory: Overlap of atomic orbitals form bond. Absolute value of differences:
Sigma () bond: First bond between two atoms formed from o 0 – 0.4 = covalent
head on overlap of orbitals (head-to-head overlap).
o 0.5 – 1.4 = polar covalent
Pi () bond: bond between two atoms from overlap of parallel
p orbitals (side-to-side overlap). o 1.5 – 4 = ionic
Symbolized with an arrow pointing towards the more
Characteristics of Bond Types electronegative element and a crossed tail by the less
Bond type Happens Electrons are electronegative element.
between
Ionic Metal & non-metal Transferred
Example:
Covalent Non-metals Shared
C–N
Polar Non-metals Shared Carbon electronegativity = 2.5
Covalent unevenly
Nitrogen electronegativity = 3.0
Metallic Metals pooled
Electronegativity difference of 0.5 = polar bond
Common characteristics:
C–N
Ionic: High melting points, most dissolve in water, conduct
electricity when dissolved in water, brittle.
Covalent: Low melting points, most do not dissolve in water,
do not conduct electricity when dissolved in water. Sigma and Pi Bonds
Polar covalent: Medium melting points, some dissolve in Each single bond is a sigma bond.
water, do not conduct electricity when dissolved in water. Each double or triple bond contains one sigma bond and then
Metallic: Soft, conduct heat and electricity, do not dissolve in pi bonds to form the second or third bond.
water.
Example:
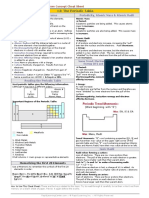
Electronegativity How many sigma and pi bonds are in the following?
There are 8 common elements that you should remember their H H
electronegativity ordering. | |
H–C=C–CC
Electronegativity Mnemonic: F(4.0) > O(3.5) > N(3.0) > Cl(3.0)
> Br(2.8) > S(2.5) > C(2.5) > H(2.1) = FON (fun) Clown Brings 6 sigma bonds & 3 pi bonds
Such CHaos.
Less common: I(2.5); P(2.1).
How to Use This Cheat Sheet: These are the keys related to this topic. Try to read through it carefully twice then recite it out on a
blank sheet of paper. Review it again before the exams.
RapidLearningCenter.com Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved
You might also like
- High School Chemistry - Core Concepts of Chemical BondingDocument1 pageHigh School Chemistry - Core Concepts of Chemical BondingDanilo Fronda Jr.No ratings yet
- 02 BondingDocument24 pages02 Bondingiron_trNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- Electronegativity Bond Polarity: Electronegativity of An ElementDocument12 pagesElectronegativity Bond Polarity: Electronegativity of An ElementSamNo ratings yet
- 2 The Chemistry of The ElementsDocument28 pages2 The Chemistry of The ElementsNazmi LatifNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Chemical Bonding 2021Document88 pagesUnit 4 Chemical Bonding 2021Damz RtgNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - 254 PDFDocument27 pagesChemical Bonding - 254 PDFGa AnNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - 254 PDFDocument27 pagesChemical Bonding - 254 PDFJatin SinglaNo ratings yet
- Covalent Ionic: Forms MoleculesDocument1 pageCovalent Ionic: Forms Moleculesash100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and BasesDocument13 pagesChapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and Bases黃向廷No ratings yet
- Core Chem Bonding Intro PresDocument43 pagesCore Chem Bonding Intro PresSHEILA MARIE CORTADO - UNDANNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Chemical Bonding and Structure PDFDocument13 pagesTopic 4 Chemical Bonding and Structure PDFSveta StepanovaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds GuideDocument10 pagesChemical Bonds GuideDesirie MarceloNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity and Polarity - FactsDocument9 pagesElectronegativity and Polarity - FactsAlshaimaa SolimanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding LNDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding LNCenjie Niña Hayag SongcalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Atomic BondingDocument23 pagesChapter 1 Atomic BondingLatisha AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Education Secondary Engagement Programme Grade 10 Chemistry Week 6 Lesson 2 Topic: Sub-Topic: ObjectivesDocument3 pagesMinistry of Education Secondary Engagement Programme Grade 10 Chemistry Week 6 Lesson 2 Topic: Sub-Topic: ObjectivesDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- 2 Atomic StructureDocument43 pages2 Atomic StructureRafael ArancibiaNo ratings yet
- 02 Chem X Icse Summary Chemical BondingDocument10 pages02 Chem X Icse Summary Chemical BondingShreyash ThamkeNo ratings yet
- Electron Dot Diagrams / Lewis Structures: Atom and Covalent Compound DiagrammingDocument50 pagesElectron Dot Diagrams / Lewis Structures: Atom and Covalent Compound DiagrammingJoan Clarice CorlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular GeometryDocument211 pagesChapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometryonline purchaseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Chemical BondingQutub KhanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding theories-SectionH-S Chatterjee PDFDocument110 pagesChemical Bonding theories-SectionH-S Chatterjee PDFAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Slides 2 Atomic Structure (Handout)Document40 pagesSlides 2 Atomic Structure (Handout)Seng Sy Keath100% (1)
- Forces of Attraction in MaterialsDocument33 pagesForces of Attraction in MaterialsRaymon Inolino IletoNo ratings yet
- Chap 1.2Document47 pagesChap 1.2Irfan AzaharNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument11 pagesAtomic StructureEnergy KojoNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesDocument9 pagesScience: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesAriel Lomugdang PatricioNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument37 pagesChemical BondingJenifer TaniaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsDocument4 pagesLecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsmartinNo ratings yet
- ° Polar and Non-Polar Covalent Bonds 3Document23 pages° Polar and Non-Polar Covalent Bonds 3Zayyan AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.4Document4 pagesLecture 1.4wemata7962No ratings yet
- Specialization: Physical Science: Environment: By: Prof. Crisanta A. OcampoDocument5 pagesSpecialization: Physical Science: Environment: By: Prof. Crisanta A. OcampoApril Joyce Ricamora NarcisoNo ratings yet
- Definitions PDFDocument9 pagesDefinitions PDFAlexia LudlowNo ratings yet
- Properties of BondsDocument36 pagesProperties of BondsPaulNo ratings yet
- Engineering Material Presentation: Presented To: Engr. Nadeem Hassan Presented By: Abdul Rauf 2k17-Che-17Document70 pagesEngineering Material Presentation: Presented To: Engr. Nadeem Hassan Presented By: Abdul Rauf 2k17-Che-17Abdul Rauf ChNo ratings yet
- L3 Polar and Nonpolar Covalent MoleculesDocument33 pagesL3 Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Molecules1256- FRONDA, RHOVIC D.No ratings yet
- Q2 W4 Ionic BondingDocument30 pagesQ2 W4 Ionic BondingMARY JOY PIOSCANo ratings yet
- 04 Chemical Bonding Formula SheetsDocument9 pages04 Chemical Bonding Formula SheetsRushil PahwaNo ratings yet
- 02 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Chemical BondingDocument9 pages02 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Chemical BondingNatasha DalalNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaDocument8 pages1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaRS JNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds and Lewis StructuresDocument5 pagesChemical Bonds and Lewis Structuresnicole MenesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds: Lecturer: Dr. Yayooo Course Title: Organic ChemistryDocument50 pagesChemical Bonds: Lecturer: Dr. Yayooo Course Title: Organic Chemistryyayooo200450% (2)
- Q3 Module 3 Polar or Nonpolar: Prepared By: Engr. Erwin D. Rubio JRDocument25 pagesQ3 Module 3 Polar or Nonpolar: Prepared By: Engr. Erwin D. Rubio JRGumban Aaron Frances M.No ratings yet
- Concepts of Chemical BondingDocument48 pagesConcepts of Chemical BondingtalktotiffanychengNo ratings yet
- Module 01Document31 pagesModule 01Pacha Praneeth35No ratings yet
- Predict Polarity With Electronegativity DiffDocument2 pagesPredict Polarity With Electronegativity DiffRaymond LiuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Vy Bui, Lalein A. PajarilloDocument10 pagesChemical Bonding: Vy Bui, Lalein A. PajarilloNanette MoradoNo ratings yet
- Bonding: General ConceptsDocument41 pagesBonding: General ConceptsOlufifehanmi OsikoyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding1Document35 pagesChemical Bonding1drchewieNo ratings yet
- 6 C15 Notes CH4 Chemical BondsSTEM StudentsDocument12 pages6 C15 Notes CH4 Chemical BondsSTEM StudentsDONNA JEAN ACOJEDONo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 21Document16 pagesChemical Bond 21Thanks OdoiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 2016Document75 pagesChemical Bonding 2016MBOTAKE LawsonNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Chemical Bonding: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocument45 pagesConcepts of Chemical Bonding: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenBoNwoawaNo ratings yet
- Comparison On BondsDocument7 pagesComparison On Bondseliastadele7No ratings yet
- Atomic BondingDocument80 pagesAtomic BondingChan Chan M100% (1)
- Che 142 Chapter1 1.2, 1.3, 1.4Document52 pagesChe 142 Chapter1 1.2, 1.3, 1.4nur haslindaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure: 2.1. Fundamental Concepts of Chemical BondsDocument47 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure: 2.1. Fundamental Concepts of Chemical BondsNguyễn Quốc HưngNo ratings yet
- Apchemistrymastercheatsheet 140822185511 Phpapp01Document6 pagesApchemistrymastercheatsheet 140822185511 Phpapp01MPNo ratings yet
- 21: Acids and Bases: Key Chemistry TermsDocument1 page21: Acids and Bases: Key Chemistry Termsbooty holeNo ratings yet
- 18: Gas Laws: Key Gas Law Terms Attacking Strategy For Gas LawsDocument1 page18: Gas Laws: Key Gas Law Terms Attacking Strategy For Gas Lawsbooty holeNo ratings yet
- 19: Solutions: Key Solution Terms Concentrations of SolutionDocument1 page19: Solutions: Key Solution Terms Concentrations of Solutionbooty holeNo ratings yet
- Molecular GeometryDocument1 pageMolecular Geometrybooty holeNo ratings yet
- 16: Drawing Molecules - Lewis Structures: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat SheetDocument1 page16: Drawing Molecules - Lewis Structures: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat Sheetbooty holeNo ratings yet
- 14: The Periodic Table: Key Chemistry Terms Periodicity, Atomic Mass & Atomic RadiiDocument1 page14: The Periodic Table: Key Chemistry Terms Periodicity, Atomic Mass & Atomic Radiibooty holeNo ratings yet
- 13: Electron Configuration: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat SheetDocument1 page13: Electron Configuration: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat Sheetbooty holeNo ratings yet
- Hidroklortiazid Dan TelmisartanDocument3 pagesHidroklortiazid Dan TelmisartanRetno Rela MahananiNo ratings yet
- Amberlite Ira 410 CL L Anion SpecsDocument2 pagesAmberlite Ira 410 CL L Anion SpecsgsyaoNo ratings yet
- Ijca 60a (2) 220-227Document8 pagesIjca 60a (2) 220-227jorgeNo ratings yet
- Sea Transport of Ammonium Nitrate Based FertilizersDocument28 pagesSea Transport of Ammonium Nitrate Based FertilizersJEET yadav100% (1)
- Structures of Degradation Products and Degradation Pathways of A Atoxin B by High-Voltage Atmospheric Cold Plasma (HVACP) TreatmentDocument9 pagesStructures of Degradation Products and Degradation Pathways of A Atoxin B by High-Voltage Atmospheric Cold Plasma (HVACP) TreatmentbrunoNo ratings yet
- STM 211 Prat.Document74 pagesSTM 211 Prat.abdulqudus abdulakeem100% (3)
- Conical Tank Drain TimeDocument80 pagesConical Tank Drain TimemoulitechNo ratings yet
- AHU Instalation Manual YorkDocument36 pagesAHU Instalation Manual YorkBangto Yibsip50% (2)
- Convective Heat and Mass TransferDocument14 pagesConvective Heat and Mass TransferEr-Damodhiran MechNo ratings yet
- Normally Closed Solenoid Valves PDFDocument55 pagesNormally Closed Solenoid Valves PDFrahulNo ratings yet
- Fosfomycin Trometamol in Patients With Renal Insufficiency and in The ElderlyDocument10 pagesFosfomycin Trometamol in Patients With Renal Insufficiency and in The ElderlyInternational Medical PublisherNo ratings yet
- Alcohol & Phenol Markswise QuestionsDocument9 pagesAlcohol & Phenol Markswise QuestionsSachin GuptaNo ratings yet
- Microstructures, Mechanical Properties, and Fracture Behaviors of Metal-Injection Molded 17-4PH Stainless SteelDocument7 pagesMicrostructures, Mechanical Properties, and Fracture Behaviors of Metal-Injection Molded 17-4PH Stainless SteelCJPATAGAN100% (1)
- QCS 2010 Section 1 Part 22 Part 22 New Technologies and Innovations PDFDocument3 pagesQCS 2010 Section 1 Part 22 Part 22 New Technologies and Innovations PDFbryanpastor106No ratings yet
- Bellows Suction Cup NBR (Round) : SAB 30 NBR-60 G1/4-IGDocument2 pagesBellows Suction Cup NBR (Round) : SAB 30 NBR-60 G1/4-IGAndor TorokNo ratings yet
- Zaclon Galvanizing HandbookDocument127 pagesZaclon Galvanizing HandbookMohammed Abdallah100% (2)
- Antimicrobial Activites of Cow Dung Extracts AgainDocument4 pagesAntimicrobial Activites of Cow Dung Extracts AgainRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- TycoDocument69 pagesTycog4goharNo ratings yet
- Azeotropic dataIIDocument104 pagesAzeotropic dataIIDavid KyrejkoNo ratings yet
- This Is A Sample Cover Image For This Issue. The Actual Cover Is Not Yet Available at This Time.Document8 pagesThis Is A Sample Cover Image For This Issue. The Actual Cover Is Not Yet Available at This Time.Denise Maria CandidoNo ratings yet
- DD Cen TS 12037-2003Document34 pagesDD Cen TS 12037-2003DoicielNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport Mechanisms ExplainedDocument9 pagesCellular Transport Mechanisms Explainedelyza gwenNo ratings yet
- Export Business Plan For SLESDocument9 pagesExport Business Plan For SLESDivakar BindNo ratings yet
- 141 Darley254Document1 page141 Darley254Jose MelloNo ratings yet
- Occupational Asthma: Current Concepts in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and ManagementDocument19 pagesOccupational Asthma: Current Concepts in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and ManagementIrina Luciana DumitriuNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument10 pagesDrugsEphraim Remann D. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Raju Aji: "Suitable Post Inqa/ QC Inspector For Welding & Piping"Document5 pagesRaju Aji: "Suitable Post Inqa/ QC Inspector For Welding & Piping"alshifa40No ratings yet
- Lecture-1. Introduction To Pharmacology-1Document26 pagesLecture-1. Introduction To Pharmacology-1AbdulahiNo ratings yet
- Booster Korean Steam Generator ManualDocument26 pagesBooster Korean Steam Generator ManualUmar MajeedNo ratings yet
- J 05Document20 pagesJ 05Rochdi SahliNo ratings yet