Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Chemistry of Milk v2
Uploaded by
Florentina BarbălatăOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Chemistry of Milk v2
Uploaded by
Florentina BarbălatăCopyright:
Available Formats
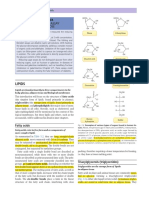
THE CHEMISTRY OF COW’S MILK
MILK’S COMPOSITION WHY IS MILK WHITE?
Milk is an emulsion of fat in water. It is also Milk contains hundreds of types of protein, of
a colloidal suspension of proteins. Other which casein is the main type. The milk proteins
compounds, including lactose and minerals, are form micelles. These micelles scatter light,
fully dissolved in the solution. causing milk to appear white.
WATER 87.5% CASEIN MICELLES
There are several models of casein micelle structure.
FAT 3.9% This diagram shows the supramolecular structure.
PROTEINS 3.4% CASEIN PROTEINS
LACTOSE & MINERALS 5.2% CALCIUM PHOSPHATE CLUSTER
FATS IN MILK LACTOSE & MILK
Droplets of fat in milk have an average size of 3–4 Lactose is a sugar found in milk. People who
micrometres. They consist mainly of triglycerides, are lactose intolerant are unable to digest it.
and also contain fat-soluble vitamins. Lactose can be fermented by microorganisms to
form lactic acid, causing the milk to sour.
H O R TRIGLYCERIDE HO O
OH
DIGESTION GALACTOSE
H C R R = fatty acid molecules HO O GLUCOSE
OH OH
H C O O
PALMITIC ACID 23.6–31.4% HO FERMENTATION
H3C
O
OH
H C OLEIC ACID 14.9–22.0% OH OH
OH
STEARIC ACID 10.4–14.6%
H O R LACTOSE LACTIC ACID
MYRISTIC ACID 9.1–11.9%
© Andy Brunning/Compound Interest 2018 - www.compoundchem.com | Twitter: @compoundchem | FB: www.facebook.com/compoundchem
Ci This graphic is shared under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives licence. BY NC ND
You might also like
- The Chemistry of MilkDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of MilknuriajiNo ratings yet
- Galactose: CH OH CH OHDocument13 pagesGalactose: CH OH CH OHCarla DionisioNo ratings yet
- Oligosaccharides: Dr. Md. Golam MortuzaDocument2 pagesOligosaccharides: Dr. Md. Golam MortuzaSamiya ZamanNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Red LipstickDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of Red LipstickDian Permata AdmNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Milk FatDocument9 pagesBiosynthesis of Milk FatFakhryansyahLuthfianNo ratings yet
- AI 71469 Chromatography Foods Beverages Carbohydrates AI71469 enDocument95 pagesAI 71469 Chromatography Foods Beverages Carbohydrates AI71469 enjuakfuenmayorNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Lactose From Milk: CHEM 334L Organic Chemistry Laboratory Revision 1.0Document9 pagesIsolation of Lactose From Milk: CHEM 334L Organic Chemistry Laboratory Revision 1.0Hasene Keskin100% (1)
- Isolation of LactoseDocument6 pagesIsolation of Lactosedrugdrug100% (2)
- Macromolecules 150911133121 Lva1 App6892Document88 pagesMacromolecules 150911133121 Lva1 App6892Carlos ErnacioNo ratings yet
- Modified Starches For The Food IndustryDocument5 pagesModified Starches For The Food IndustryMiguelArceMonroyNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculeDocument80 pagesBiomoleculexpogamer43No ratings yet
- Chemistry of MilkDocument44 pagesChemistry of Milkabdouam50% (2)
- Absorbation and Digestion of CarbohydratesDocument49 pagesAbsorbation and Digestion of CarbohydratesBehailu TsegayeNo ratings yet
- 5.milk LipidsDocument5 pages5.milk LipidsAbhijith S. PNo ratings yet
- Jagessar Vol43Document10 pagesJagessar Vol43Rica CagolNo ratings yet
- Starch Project UpdateDocument34 pagesStarch Project UpdateIsworo RukmiNo ratings yet
- Ee Minimap 17Document1 pageEe Minimap 17阮 孟强No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Structue and Function of MacromoleculesDocument71 pagesChapter 5 The Structue and Function of MacromoleculesKhoirunnisa LuthfiyyahNo ratings yet
- Ref G2 PolysaccharideDocument41 pagesRef G2 PolysaccharideLEE ZHI XUAN A21SC0118No ratings yet
- Kuliah II Komponen SelDocument44 pagesKuliah II Komponen SelTiar anggrainiNo ratings yet
- 39 Carbohydrates PDFDocument3 pages39 Carbohydrates PDFfaryal khan100% (1)
- Biomolecules-03 Allen Class NotesDocument25 pagesBiomolecules-03 Allen Class NotesRITESHNo ratings yet
- Slides 18 RegulationOfCellRespiration CellBiologyDocument17 pagesSlides 18 RegulationOfCellRespiration CellBiologyJulius FrondaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Pathways For Biocomposites From Vegetable Oils: Reena Vaidya, Gajanan N Chaudhari, Nitin RautDocument11 pagesSynthesis Pathways For Biocomposites From Vegetable Oils: Reena Vaidya, Gajanan N Chaudhari, Nitin RautAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Jam Making PDFDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of Jam Making PDFanton_428No ratings yet
- 26 Biomolecules Revision Notes Getmarks AppDocument30 pages26 Biomolecules Revision Notes Getmarks AppNitin BhandariNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates 27.8.20 FN 202Document39 pagesCarbohydrates 27.8.20 FN 202Mahmudur RahmanNo ratings yet
- FST 3210 Milk and Dairy Products Part OneDocument23 pagesFST 3210 Milk and Dairy Products Part OneAhmad MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Anaysis of MilkDocument14 pagesAnaysis of MilkSaman AkramNo ratings yet
- Lipids PDFDocument6 pagesLipids PDFGulam Muhammad AkhtarNo ratings yet
- A L Ahmad2003 Chitosan A NaturalDocument14 pagesA L Ahmad2003 Chitosan A NaturalHaziq MahmurNo ratings yet
- Fermentation On SucroseDocument11 pagesFermentation On SucroseGabu Figuracion100% (1)
- Sugar Alcohols: AnalysisDocument7 pagesSugar Alcohols: AnalysisTeera YimyooNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Carbohydrates II: ObjectivesDocument22 pagesChemistry of Carbohydrates II: Objectivesahmad671poNo ratings yet
- Karbohidrat: Dyke Gita Wirasisya, S.Farm., M.SC., Apt Program Studi Farmasi, Fakultas Kedokteran, Universitas MataramDocument37 pagesKarbohidrat: Dyke Gita Wirasisya, S.Farm., M.SC., Apt Program Studi Farmasi, Fakultas Kedokteran, Universitas Matarambrahmani ptrNo ratings yet
- Cir Sucrose Hal 25Document36 pagesCir Sucrose Hal 25Mellisa Laura MintoroNo ratings yet
- FC Lect Topic4d AY17-18 StudentDocument29 pagesFC Lect Topic4d AY17-18 StudentRaysonChooNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of BiomoleculesDocument91 pagesChemistry of BiomoleculesSidharth SamantarayNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0268005X12002810 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0268005X12002810 MainPPim ChNo ratings yet
- Farmakognosi 5Document36 pagesFarmakognosi 5Randi RasyidNo ratings yet
- Bio FactsheetDocument3 pagesBio Factsheetshannongiovanny7No ratings yet
- CD 4Document19 pagesCD 4زينب عيسىNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of MacromoleculesDocument70 pagesThe Structure and Function of MacromoleculesAhmadMaulanaIfanAkbasNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Cellularmetabolism 110727073536 Phpapp02 1Document52 pagesChapter4 Cellularmetabolism 110727073536 Phpapp02 1Jinan K. DianNo ratings yet
- Ch05 MacromoleculesCampbellDocument69 pagesCh05 MacromoleculesCampbellCarl Jasper AquinoNo ratings yet
- LT735 - 1333 - Chemysoap S 3R - Rev.04 - IDocument10 pagesLT735 - 1333 - Chemysoap S 3R - Rev.04 - Idaniel7327748No ratings yet
- Milk 1662 2006Document26 pagesMilk 1662 2006Geanina MozaNo ratings yet
- PL - Dhepe@ncl - Res.in Group Website: Http://academic - Ncl.res - In/pl - DhepeDocument13 pagesPL - Dhepe@ncl - Res.in Group Website: Http://academic - Ncl.res - In/pl - Dhepehiep237No ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument9 pagesBio MoleculesChetnaNo ratings yet
- Lactose: Lactose Is Milk Sugar and Is The Distinctive Carbohydrate of Milk. It Is A DisaccharideDocument11 pagesLactose: Lactose Is Milk Sugar and Is The Distinctive Carbohydrate of Milk. It Is A DisaccharideggfeyeraNo ratings yet
- 1 CHO - 1 - Def - Classfn - PDF - STDocument2 pages1 CHO - 1 - Def - Classfn - PDF - STSamiya ZamanNo ratings yet
- Hartmann1998 - High MW PLADocument45 pagesHartmann1998 - High MW PLAMathilda PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism in Dairy CowsDocument4 pagesLipid Metabolism in Dairy CowsEduardo BonilhaNo ratings yet
- 04 enDocument4 pages04 enimran LarNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Cellularmetabolism 110727073536 Phpapp02Document52 pagesChapter4 Cellularmetabolism 110727073536 Phpapp02onadandan4No ratings yet
- (Doi 10.1007/978!1!4613-0671-9 - 8) Skeist, Irving - Handbook of Adhesives Starch Based AdhesivesDocument14 pages(Doi 10.1007/978!1!4613-0671-9 - 8) Skeist, Irving - Handbook of Adhesives Starch Based Adhesivesguptarahul1992No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Biological MacromoleculesDocument32 pagesChapter 3 Biological MacromoleculeslolaNo ratings yet
- Acetic Pathway: Fatty Acids and PolyketidesDocument70 pagesAcetic Pathway: Fatty Acids and PolyketidesChessy Rima MustikaNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument33 pagesBiomoleculeskarmanyaraina4No ratings yet
- Science: The Menstrual CycleDocument4 pagesScience: The Menstrual CycleLena Beth Tapawan YapNo ratings yet
- Uav Based Plant Disease Detection SystemDocument14 pagesUav Based Plant Disease Detection SystemTakudzwa MatangiraNo ratings yet
- 4 Pure BendingDocument42 pages4 Pure BendingOmarfirozNo ratings yet
- Moldex Realty, Inc. (Linda Agustin) 2.0 (With Sound)Document111 pagesMoldex Realty, Inc. (Linda Agustin) 2.0 (With Sound)Arwin AgustinNo ratings yet
- Science7 q2 Mod6of8 Asexual Sexualrep v2Document26 pagesScience7 q2 Mod6of8 Asexual Sexualrep v2Ishi OcheaNo ratings yet
- Buckthorpe Etal 23 Optimising Early Stage ACL Rehab ProcessDocument24 pagesBuckthorpe Etal 23 Optimising Early Stage ACL Rehab ProcessCole VincentNo ratings yet
- Sandvik Saf 31803 Tube and Pipe, Seamless: DatasheetDocument9 pagesSandvik Saf 31803 Tube and Pipe, Seamless: DatasheetPaul NeedhamNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument13 pagesAssignmentSwakshar DebNo ratings yet
- Inspirational Quotes General and ExamsDocument6 pagesInspirational Quotes General and Examsasha jalanNo ratings yet
- Solids Separation Study Guide: Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources Wastewater Operator CertificationDocument44 pagesSolids Separation Study Guide: Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources Wastewater Operator CertificationkharismaaakNo ratings yet
- Strange Christmas TraditionsDocument2 pagesStrange Christmas TraditionsZsofia ZsofiaNo ratings yet
- MetDocument41 pagesMetadityaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Vino Gano Ginger and Herbal Liquor On The Heamatological Parameters of The Wistar RatsDocument5 pagesEffect of Vino Gano Ginger and Herbal Liquor On The Heamatological Parameters of The Wistar RatsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Habitat Preference of Great Argus Pheasant ArgusiaDocument11 pagesHabitat Preference of Great Argus Pheasant ArgusiaFaradlina MuftiNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Psychology Core Concepts 7th Edition Zimbardo Test Bank PDFDocument13 pagesDwnload Full Psychology Core Concepts 7th Edition Zimbardo Test Bank PDFcomfortdehm1350100% (7)
- Water Chemistry - An Introduction To The Chemistry of Natural and Engineered Aquatic Systems-Páginas-483-492Document10 pagesWater Chemistry - An Introduction To The Chemistry of Natural and Engineered Aquatic Systems-Páginas-483-492jhonier guevaraNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To KennametalDocument40 pages1.1 Introduction To KennametalVig PankajNo ratings yet
- Initiation in Pre-Tantrasamuccaya Kerala Tantric Literature PDFDocument24 pagesInitiation in Pre-Tantrasamuccaya Kerala Tantric Literature PDFVenkateswaran NarayananNo ratings yet
- Water Vapor Permeability of Polypropylene: Fusion Science and TechnologyDocument5 pagesWater Vapor Permeability of Polypropylene: Fusion Science and TechnologyBobNo ratings yet
- DoomsdayDocument29 pagesDoomsdayAsmita RoyNo ratings yet
- Muharem Bazdulj - The Second Book (Writings From An Unbound Europe) - Northwestern University Press (2005) PDFDocument154 pagesMuharem Bazdulj - The Second Book (Writings From An Unbound Europe) - Northwestern University Press (2005) PDFjeff tehNo ratings yet
- Mono 108Document438 pagesMono 108pasaricaNo ratings yet
- Sikagrout®-214 Ae: Product Data SheetDocument3 pagesSikagrout®-214 Ae: Product Data Sheetmohammed rinshinNo ratings yet
- T 1246784488 17108574 Street Lighting Control Based On LonWorks Power Line CommunicationDocument3 pagesT 1246784488 17108574 Street Lighting Control Based On LonWorks Power Line CommunicationsryogaaNo ratings yet
- What A Wonderful WorldDocument3 pagesWhat A Wonderful Worldapi-333684519No ratings yet
- Exploded View & Parts Listing Air Operated Double Diaphragm PumpDocument2 pagesExploded View & Parts Listing Air Operated Double Diaphragm PumpCarlos AvalosNo ratings yet
- North Central Mindanao College: Maranding, Lala, Lanao Del NorteDocument8 pagesNorth Central Mindanao College: Maranding, Lala, Lanao Del NorteAnalyn FielNo ratings yet
- Massage Techniques in SpaDocument1 pageMassage Techniques in SpaALISA SAITANo ratings yet
- IMCI UpdatedDocument5 pagesIMCI UpdatedMalak RagehNo ratings yet
- Knowledge /28 Application / 22 Thinking / 12 Communication / 9Document8 pagesKnowledge /28 Application / 22 Thinking / 12 Communication / 9NmNo ratings yet