Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 viewsMeters Task 1. Translate Into Russian
Meters Task 1. Translate Into Russian
Uploaded by
Андрей РоманенкоThe document discusses different electrical measurement devices:
- An ammeter measures current in amps and must be connected in series. A voltmeter measures potential difference in volts and must be connected in parallel.
- An ohmmeter measures resistance in ohms by connecting a known voltage source and measuring the resulting current. It is used to measure a circuit's resistance.
- Proper connection of the measurement device (in series for ammeters, parallel for voltmeters) is important to avoid altering the measured circuit. Ammeters require low resistance to not impact current.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Guideline 36 2021Document287 pagesGuideline 36 2021Shaliya KarunathilakaNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Practice Test: Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesStates of Matter Practice Test: Multiple ChoiceL'arc Will100% (1)
- Circuits1 1 Laboratory Meters and Power SupplyDocument2 pagesCircuits1 1 Laboratory Meters and Power SupplyJad DimabuyuNo ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument3 pagesHomeworkCanielNo ratings yet
- Expirement 1 - Fundamental Electrical MeasurementsDocument8 pagesExpirement 1 - Fundamental Electrical MeasurementsJhajha AlboniaNo ratings yet
- 3 X7 EBcf 78 Auzh Emn C5 ETDocument26 pages3 X7 EBcf 78 Auzh Emn C5 ETAnas AlamNo ratings yet
- AC & DC MetersDocument2 pagesAC & DC Metersk85yfbwhynNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Join @cbse10bystudentshelper On TelegramDocument26 pagesOhm's Law: Join @cbse10bystudentshelper On TelegramValerie CoxNo ratings yet
- EEE (Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument66 pagesEEE (Electrical & Electronics EngineeringHacker ChampNo ratings yet
- ElectricalDocument6 pagesElectrical3re0oooNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Lab 1-Introduction To Basic Electrical Measuring InstrumentsDocument7 pagesObjectives: Lab 1-Introduction To Basic Electrical Measuring Instrumentsßirũk Bmt100% (1)
- EE 442 Laboratory Experiment 2 Introduction To The Measurement of Voltage, Current, Resistance and Voltmeter LoadingDocument12 pagesEE 442 Laboratory Experiment 2 Introduction To The Measurement of Voltage, Current, Resistance and Voltmeter LoadingAdrien MunyanezaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measuring Instruments: (Voltmeter, Ammeter, and Ohmmeter)Document4 pagesElectrical Measuring Instruments: (Voltmeter, Ammeter, and Ohmmeter)angelo macatangayNo ratings yet
- Instituto Politécnico Nacional: Practice: 1 "Use of Ohmmeter, Voltmeter and Ammeter in Measurements D.C"Document11 pagesInstituto Politécnico Nacional: Practice: 1 "Use of Ohmmeter, Voltmeter and Ammeter in Measurements D.C"José Emmanuel Martínez CerónNo ratings yet
- LBYEC74 Lab Report 1Document17 pagesLBYEC74 Lab Report 1Earl Kristof Li Liao50% (4)
- Experiment 2Document7 pagesExperiment 2anasser0772No ratings yet
- 3.3. Ohmmeters: Ohmmeter Working PrincipleDocument3 pages3.3. Ohmmeters: Ohmmeter Working PrincipleEveNo ratings yet
- Moving Coil Meters: Voltmeter Ammeter OhmmeterDocument5 pagesMoving Coil Meters: Voltmeter Ammeter OhmmeterAtique KhanNo ratings yet
- AmmeterDocument115 pagesAmmetermhnmndrkNo ratings yet
- Ammeter: ObjectiveDocument26 pagesAmmeter: ObjectiveAnkhi BaroiNo ratings yet
- BEE LAB MANUAL FINAL1st SemesterDocument38 pagesBEE LAB MANUAL FINAL1st SemesterSaif KhanNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument2 pagesPhysicsGlazerie Quijano GalabinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 MendozaDocument20 pagesExperiment 1 MendozaBenj MendozaNo ratings yet
- AmmeterDocument31 pagesAmmeterakshayaNo ratings yet
- Electricity Equipment LAB: Lulav Saeed Sadiq Electricity and ElectronicDocument7 pagesElectricity Equipment LAB: Lulav Saeed Sadiq Electricity and ElectronicLulav BarwaryNo ratings yet
- Ammeter VoltmeterDocument17 pagesAmmeter Voltmeterfarihakanwal2021No ratings yet
- Postlab Report #1Document2 pagesPostlab Report #1Poyraz EmelNo ratings yet
- Ammeter ShortDocument2 pagesAmmeter ShortkappubhattNo ratings yet
- Ammeter, Voltmeter, DC Motor, Electric Generator, UPSDocument13 pagesAmmeter, Voltmeter, DC Motor, Electric Generator, UPSatiqurrehman0074No ratings yet
- Probing Guide - Questions For Electrical Circuits 1 Lab 1Document9 pagesProbing Guide - Questions For Electrical Circuits 1 Lab 1Marydelle SubitoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Electrical Instruments and MeasurementsDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Electrical Instruments and Measurementszxufra lumanglasNo ratings yet
- How To Connect An Ammeter (Amperemeter)Document2 pagesHow To Connect An Ammeter (Amperemeter)Jendral Deby IrawanNo ratings yet
- NOTES (2023-2024) Subject: PHYSICS Class: XII Experiment No.1: Ohm'S LawDocument5 pagesNOTES (2023-2024) Subject: PHYSICS Class: XII Experiment No.1: Ohm'S LawMichael IbrahimNo ratings yet
- What Is An OhmmeterDocument4 pagesWhat Is An OhmmeterballDISCOVERIES PHballDISCOVERIESNo ratings yet
- Instrument MeasurementDocument6 pagesInstrument MeasurementMarlon Desacula IINo ratings yet
- Most Expected Viva Questions - Physics PracticalsDocument14 pagesMost Expected Viva Questions - Physics Practicalsitzspam121fNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Q&ADocument6 pagesInstrumentation Q&AcloudNo ratings yet
- Electrical General Test Equipment OperationDocument2 pagesElectrical General Test Equipment OperationMarcin MecaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Familiarization With Electrical Measuring InstrumentsDocument10 pagesExperiment 1 Familiarization With Electrical Measuring InstrumentsCorps LaroprocNo ratings yet
- Epas G9 M Q3 W7-W8Document4 pagesEpas G9 M Q3 W7-W8ALLYSSA MAE PELONIANo ratings yet
- Measurement of CurrentDocument3 pagesMeasurement of CurrentAnkur MathurNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 How Things WorkDocument42 pagesUnit 4 How Things WorkDanielNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measuring InstrumentsDocument23 pagesElectrical Measuring InstrumentsRenegade PhantomNo ratings yet
- Viva Qns Solutions 15Document3 pagesViva Qns Solutions 15assentialNo ratings yet
- Unit Learning OutcomesDocument1 pageUnit Learning OutcomesAngelica Ulpindo BalubarNo ratings yet
- Multimeter - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument13 pagesMultimeter - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediad_richard_dNo ratings yet
- Ohmmeter: Design Evolution Precision Ohmmeters See Also References External LinksDocument3 pagesOhmmeter: Design Evolution Precision Ohmmeters See Also References External LinksMadhusudanan AshokNo ratings yet
- EIM 4th SemDocument5 pagesEIM 4th SemVishal Pandey M LE 06No ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document51 pagesPresentation 1Workineh AsefaNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument35 pagesPresentationApoorva SharmaNo ratings yet
- MAIN TOPIC Electrical Quantities in InstrumentationDocument68 pagesMAIN TOPIC Electrical Quantities in InstrumentationLoreto CorderoNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity. B TechDocument14 pagesBasic Electricity. B TechValentine Nwankwo100% (1)
- Phy Metre BridgeDocument25 pagesPhy Metre Bridgeadishrajesh0No ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument3 pagesOhms LawJuwariyah NafeesNo ratings yet
- OhmmeterDocument20 pagesOhmmeterAqeel HaiderNo ratings yet
- AmmeterDocument5 pagesAmmeterGilberto ManhattanNo ratings yet
- Measuring InsstrumentsDocument11 pagesMeasuring Insstrumentsamit singhNo ratings yet
- Intro To Circuits Lab #1: Anatomy of A BreadboardDocument5 pagesIntro To Circuits Lab #1: Anatomy of A BreadboardNishat AhamadNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1Document12 pagesExperiment No. 1Van LeronNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Progress Check I. Discuss The Basic Use of The Following MetersDocument5 pagesWeek 1 Progress Check I. Discuss The Basic Use of The Following MetersJoshua Ray CalagoNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Transformers VocabularyDocument3 pagesTransformers VocabularyАндрей РоманенкоNo ratings yet
- Study The VocabularyDocument5 pagesStudy The VocabularyАндрей РоманенкоNo ratings yet
- Ответы на задачи Измерит Приборы 2Document1 pageОтветы на задачи Измерит Приборы 2Андрей РоманенкоNo ratings yet
- Study The Vocabulary: TransformersDocument5 pagesStudy The Vocabulary: TransformersАндрей РоманенкоNo ratings yet
- Проводники и изоляторыDocument5 pagesПроводники и изоляторыАндрей РоманенкоNo ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument8 pagesSodapdfsdfbvshbdfNo ratings yet
- مصطفى محمدDocument8 pagesمصطفى محمدBoss barkatNo ratings yet
- 2dm2280 Digital Step DriverDocument22 pages2dm2280 Digital Step DrivermuhammedasifNo ratings yet
- 36 TD SST150Document2 pages36 TD SST150sisprointNo ratings yet
- Industry Leading Design in A Compact Package: E Line FamilyDocument27 pagesIndustry Leading Design in A Compact Package: E Line FamilyPhaniNo ratings yet
- Emerging Trends in Mechanical Engineering: Course Code - 22652 (AE/PG/PT/ME) Unit 2 - Process EngineeringDocument15 pagesEmerging Trends in Mechanical Engineering: Course Code - 22652 (AE/PG/PT/ME) Unit 2 - Process EngineeringKunal AhiwaleNo ratings yet
- Pulangi IV Hydroelectric PlantDocument3 pagesPulangi IV Hydroelectric PlantcatherineNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3Lala's gamingNo ratings yet
- Tech Specification, Section: CRP Page 21 of 40 C/Engg/Spec/Crp Rev No: 08Document1 pageTech Specification, Section: CRP Page 21 of 40 C/Engg/Spec/Crp Rev No: 08karthikNo ratings yet
- Recent Advancements and Developments For Electric Vehicle TechnologyDocument10 pagesRecent Advancements and Developments For Electric Vehicle TechnologyharshithaNo ratings yet
- فزیک طبی بخش حرارتDocument253 pagesفزیک طبی بخش حرارتSayed kazim hashimiNo ratings yet
- MEO Class 4 Exam - Electrical Oral Question & Answers PDFDocument6 pagesMEO Class 4 Exam - Electrical Oral Question & Answers PDFabhishek rathourNo ratings yet
- Fault Analysis On Distribution Feeders With High Penetration of PV SystemsDocument7 pagesFault Analysis On Distribution Feeders With High Penetration of PV SystemsLuis ÁtilaNo ratings yet
- Dates and Times With Lubridate::: Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesDates and Times With Lubridate::: Cheat SheetFelipe Balboa PolancoNo ratings yet
- Examinaton of phsics امتحان في مادة الفيزياء الجامعيةDocument3 pagesExaminaton of phsics امتحان في مادة الفيزياء الجامعيةmaanibrahimNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Properties PDFDocument34 pagesEstimation of Properties PDFLee860531No ratings yet
- Electric FluxDocument19 pagesElectric FluxroseNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic BasicsDocument124 pagesAerodynamic BasicsChanaka DilshanNo ratings yet
- Capacitor ElcoDocument5 pagesCapacitor ElcoRazi QurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Stirling Engine: Project by - S. Srikanth V. Prashaanth R. Srikkanth S. Srinivas Guided by - Mr. Senthil KumarDocument35 pagesStirling Engine: Project by - S. Srikanth V. Prashaanth R. Srikkanth S. Srinivas Guided by - Mr. Senthil Kumarhemanth7cNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument12 pagesProblem SolvingLouieBrent CaingatNo ratings yet
- CHM 1103 Lab - 2 - Student Report - Pdf.docxDocument4 pagesCHM 1103 Lab - 2 - Student Report - Pdf.docxjesseNo ratings yet
- VD Calculation L00 & B1 WWDBDocument1 pageVD Calculation L00 & B1 WWDBsajana jayasingheNo ratings yet
- Atd 8Document6 pagesAtd 8pri0322No ratings yet
- WWW - Hobby Hour - Com Electronics Resistorcalculator - PHPDocument5 pagesWWW - Hobby Hour - Com Electronics Resistorcalculator - PHPAntonio Tomba Chavez SomozaNo ratings yet
- Forced Convection in A Square Cavity With Inlet and Outlet PortsDocument11 pagesForced Convection in A Square Cavity With Inlet and Outlet PortsMoussa DiopNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Motion Responses of Ship Shape Floating Structure Using Diffraction PotentialDocument5 pagesPrediction of Motion Responses of Ship Shape Floating Structure Using Diffraction PotentialPatrick Silva OliveiraNo ratings yet
- PriceListHirePurchase Normal3august2020Document69 pagesPriceListHirePurchase Normal3august2020waqar ahmadNo ratings yet
Meters Task 1. Translate Into Russian
Meters Task 1. Translate Into Russian
Uploaded by
Андрей Романенко0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views3 pagesThe document discusses different electrical measurement devices:
- An ammeter measures current in amps and must be connected in series. A voltmeter measures potential difference in volts and must be connected in parallel.
- An ohmmeter measures resistance in ohms by connecting a known voltage source and measuring the resulting current. It is used to measure a circuit's resistance.
- Proper connection of the measurement device (in series for ammeters, parallel for voltmeters) is important to avoid altering the measured circuit. Ammeters require low resistance to not impact current.
Original Description:
Original Title
Измерительные приборы
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different electrical measurement devices:
- An ammeter measures current in amps and must be connected in series. A voltmeter measures potential difference in volts and must be connected in parallel.
- An ohmmeter measures resistance in ohms by connecting a known voltage source and measuring the resulting current. It is used to measure a circuit's resistance.
- Proper connection of the measurement device (in series for ammeters, parallel for voltmeters) is important to avoid altering the measured circuit. Ammeters require low resistance to not impact current.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views3 pagesMeters Task 1. Translate Into Russian
Meters Task 1. Translate Into Russian
Uploaded by
Андрей РоманенкоThe document discusses different electrical measurement devices:
- An ammeter measures current in amps and must be connected in series. A voltmeter measures potential difference in volts and must be connected in parallel.
- An ohmmeter measures resistance in ohms by connecting a known voltage source and measuring the resulting current. It is used to measure a circuit's resistance.
- Proper connection of the measurement device (in series for ammeters, parallel for voltmeters) is important to avoid altering the measured circuit. Ammeters require low resistance to not impact current.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Meters
Task 1. Translate into Russian:
1. One should take into consideration the difference between these circuits.
2. One should take into consideration that the ammeter is connected to the circuit
in series.
3. What should one take into consideration using the ohmmeter?
Task 2. Read and translate the text
Text: Meters
Any instrument which measures electrical values is called a meter. Among the
most common meters used there are the ohmmeter, the ammeter and the voltmeter.
An ammeter measures the current in amperes. The unit is named after Andre Marie
Ampere, a French scientist, who discovered a great number of facts about
electricity over a hundred years ago. The abbreviation for the ampere is amp. A
voltmeter measures the voltage and the potential difference in volts. The volt is
named after Alessandro Volta, an Italian scientist.
The current in a conductor is determined by two things, the voltage across the
conductor and the resistance of the conductor. Every material object offers some
resistance to the flow of an electron current through it. Good conductors like the
metals, copper, silver and aluminum offer very little resistance, while
nonconductors such as glass, wood and paper offer a very high resistance.
The unit by which resistance is measured is called the ohm. The resistance in
practice is measured with the ohmmeter.
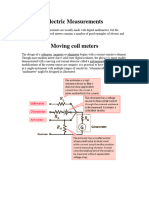
The ohmmeter is used to measure the value of resistance. It consists of а
milliammeter calibrated to read in ohms, а battery and resistors. The meter is
connected in parallel and the circuit is not opened when its resistance is measured.
The readings on the scale show the measured value. The ammeter is used to
measure the value of current. When the ammeter is used the circuit should be
opened at one point and the terminals of the meter should be connected to it. One
should take into consideration that the positive terminal of the meter is connected
to the positive terminal of the source; the negative terminal to the negative terminal
of the source. The ammeter should be connected in series. The readings on the
scale show the measured value.
A wattmeter measures electrical power in watts. Very delicate ammeters are often
used for measuring very small currents. A meter whose scale is calibrated to read a
thousandth of an ampere is called a milliammeter. One whose scale is calibrated in
millionth of an ampere is called a micro ammeter or galvanometer.
Whenever an ammeter or voltmeter is connected to a circuit to measure electric
current or potential difference the ammeter must be connected in series and the
voltmeter in parallel.
The ammeter is so connected that all of the electron current passes through it. To
prevent a change in the electron current when such an insertion is made, all
ammeters must have a low resistance. Most ammeters therefore have a low
resistance wire, called a shunt, connected across the armature coil. A voltmeter, on
the other hand, is connected across that part of the circuit for which a measurement
of the potential difference is required. If the 'potential difference between the ends
of the resistance R is wanted, the voltmeter is connected as shown.
Vocabulary:
meter- измерительный прибор
battery- батарея
scale- шкала
readings- показания на шкале (прибора)
terminal- клемма
positive- положительный
negative- отрицательный
to measure- измерять
to take into- consideration принимать во внимание
in this way- таким путем, таким образом
Task 3. Answer the questions.
1. What is the ammeter used for?
2. What is the voltmeter used for?
3. How is a voltmeter connected to the circuit?
4. What meter do we connect to the circuit in series?
5. Why must an ammeter have a low resistance?
6. What is the ohmmeter used for?
7. What terminals does а meter have?
8. Across what part of the circuit is a voltmeter connected?
9. Should the measured circuit be opened when the voltmeter is used?
10. Should the measured circuit be opened when the ammeter is used?
11. In what way should the voltmeter be connected to the circuit?
12. In what way should the ammeter be connected to the circuit?
13.What instruments are used to measure an electric current and potential
difference?
14. What is the difference between а voltmeter and an ammeter?
15.What common meters are used to measure the values in а circuit?
Task 4. Solve the following problems:
1. Suppose the ammeter scale reads 1.9 amp, the voltmeter scale reads 2.4 V; how
much is the value of resistance in the measured circuit?
2. Suppose the ohmmeter scale reads 75 ohms, the voltmeter scale reads 220 V;
how much is the value of current in the measured circuit?
3. Suppose that you have а series circuit consisting of three resistors and а voltage
source. R1=O.18 ohm, R2 =1.15 ohms, R3=2 ohms, I = 1О amp. Find the voltage
drop across each resistor; find the value of voltage in the circuit.
4. Two resistors are connected in series. R1 = 7,000, R2 = 2,200, I = 110 amp. Find
the voltage drop across each resistor.
You might also like
- Guideline 36 2021Document287 pagesGuideline 36 2021Shaliya KarunathilakaNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Practice Test: Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesStates of Matter Practice Test: Multiple ChoiceL'arc Will100% (1)
- Circuits1 1 Laboratory Meters and Power SupplyDocument2 pagesCircuits1 1 Laboratory Meters and Power SupplyJad DimabuyuNo ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument3 pagesHomeworkCanielNo ratings yet
- Expirement 1 - Fundamental Electrical MeasurementsDocument8 pagesExpirement 1 - Fundamental Electrical MeasurementsJhajha AlboniaNo ratings yet
- 3 X7 EBcf 78 Auzh Emn C5 ETDocument26 pages3 X7 EBcf 78 Auzh Emn C5 ETAnas AlamNo ratings yet
- AC & DC MetersDocument2 pagesAC & DC Metersk85yfbwhynNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Join @cbse10bystudentshelper On TelegramDocument26 pagesOhm's Law: Join @cbse10bystudentshelper On TelegramValerie CoxNo ratings yet
- EEE (Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument66 pagesEEE (Electrical & Electronics EngineeringHacker ChampNo ratings yet
- ElectricalDocument6 pagesElectrical3re0oooNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Lab 1-Introduction To Basic Electrical Measuring InstrumentsDocument7 pagesObjectives: Lab 1-Introduction To Basic Electrical Measuring Instrumentsßirũk Bmt100% (1)
- EE 442 Laboratory Experiment 2 Introduction To The Measurement of Voltage, Current, Resistance and Voltmeter LoadingDocument12 pagesEE 442 Laboratory Experiment 2 Introduction To The Measurement of Voltage, Current, Resistance and Voltmeter LoadingAdrien MunyanezaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measuring Instruments: (Voltmeter, Ammeter, and Ohmmeter)Document4 pagesElectrical Measuring Instruments: (Voltmeter, Ammeter, and Ohmmeter)angelo macatangayNo ratings yet
- Instituto Politécnico Nacional: Practice: 1 "Use of Ohmmeter, Voltmeter and Ammeter in Measurements D.C"Document11 pagesInstituto Politécnico Nacional: Practice: 1 "Use of Ohmmeter, Voltmeter and Ammeter in Measurements D.C"José Emmanuel Martínez CerónNo ratings yet
- LBYEC74 Lab Report 1Document17 pagesLBYEC74 Lab Report 1Earl Kristof Li Liao50% (4)
- Experiment 2Document7 pagesExperiment 2anasser0772No ratings yet
- 3.3. Ohmmeters: Ohmmeter Working PrincipleDocument3 pages3.3. Ohmmeters: Ohmmeter Working PrincipleEveNo ratings yet
- Moving Coil Meters: Voltmeter Ammeter OhmmeterDocument5 pagesMoving Coil Meters: Voltmeter Ammeter OhmmeterAtique KhanNo ratings yet
- AmmeterDocument115 pagesAmmetermhnmndrkNo ratings yet
- Ammeter: ObjectiveDocument26 pagesAmmeter: ObjectiveAnkhi BaroiNo ratings yet
- BEE LAB MANUAL FINAL1st SemesterDocument38 pagesBEE LAB MANUAL FINAL1st SemesterSaif KhanNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument2 pagesPhysicsGlazerie Quijano GalabinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 MendozaDocument20 pagesExperiment 1 MendozaBenj MendozaNo ratings yet
- AmmeterDocument31 pagesAmmeterakshayaNo ratings yet
- Electricity Equipment LAB: Lulav Saeed Sadiq Electricity and ElectronicDocument7 pagesElectricity Equipment LAB: Lulav Saeed Sadiq Electricity and ElectronicLulav BarwaryNo ratings yet
- Ammeter VoltmeterDocument17 pagesAmmeter Voltmeterfarihakanwal2021No ratings yet
- Postlab Report #1Document2 pagesPostlab Report #1Poyraz EmelNo ratings yet
- Ammeter ShortDocument2 pagesAmmeter ShortkappubhattNo ratings yet
- Ammeter, Voltmeter, DC Motor, Electric Generator, UPSDocument13 pagesAmmeter, Voltmeter, DC Motor, Electric Generator, UPSatiqurrehman0074No ratings yet
- Probing Guide - Questions For Electrical Circuits 1 Lab 1Document9 pagesProbing Guide - Questions For Electrical Circuits 1 Lab 1Marydelle SubitoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Electrical Instruments and MeasurementsDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Electrical Instruments and Measurementszxufra lumanglasNo ratings yet
- How To Connect An Ammeter (Amperemeter)Document2 pagesHow To Connect An Ammeter (Amperemeter)Jendral Deby IrawanNo ratings yet
- NOTES (2023-2024) Subject: PHYSICS Class: XII Experiment No.1: Ohm'S LawDocument5 pagesNOTES (2023-2024) Subject: PHYSICS Class: XII Experiment No.1: Ohm'S LawMichael IbrahimNo ratings yet
- What Is An OhmmeterDocument4 pagesWhat Is An OhmmeterballDISCOVERIES PHballDISCOVERIESNo ratings yet
- Instrument MeasurementDocument6 pagesInstrument MeasurementMarlon Desacula IINo ratings yet
- Most Expected Viva Questions - Physics PracticalsDocument14 pagesMost Expected Viva Questions - Physics Practicalsitzspam121fNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Q&ADocument6 pagesInstrumentation Q&AcloudNo ratings yet
- Electrical General Test Equipment OperationDocument2 pagesElectrical General Test Equipment OperationMarcin MecaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Familiarization With Electrical Measuring InstrumentsDocument10 pagesExperiment 1 Familiarization With Electrical Measuring InstrumentsCorps LaroprocNo ratings yet
- Epas G9 M Q3 W7-W8Document4 pagesEpas G9 M Q3 W7-W8ALLYSSA MAE PELONIANo ratings yet
- Measurement of CurrentDocument3 pagesMeasurement of CurrentAnkur MathurNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 How Things WorkDocument42 pagesUnit 4 How Things WorkDanielNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measuring InstrumentsDocument23 pagesElectrical Measuring InstrumentsRenegade PhantomNo ratings yet
- Viva Qns Solutions 15Document3 pagesViva Qns Solutions 15assentialNo ratings yet
- Unit Learning OutcomesDocument1 pageUnit Learning OutcomesAngelica Ulpindo BalubarNo ratings yet
- Multimeter - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument13 pagesMultimeter - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediad_richard_dNo ratings yet
- Ohmmeter: Design Evolution Precision Ohmmeters See Also References External LinksDocument3 pagesOhmmeter: Design Evolution Precision Ohmmeters See Also References External LinksMadhusudanan AshokNo ratings yet
- EIM 4th SemDocument5 pagesEIM 4th SemVishal Pandey M LE 06No ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document51 pagesPresentation 1Workineh AsefaNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument35 pagesPresentationApoorva SharmaNo ratings yet
- MAIN TOPIC Electrical Quantities in InstrumentationDocument68 pagesMAIN TOPIC Electrical Quantities in InstrumentationLoreto CorderoNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity. B TechDocument14 pagesBasic Electricity. B TechValentine Nwankwo100% (1)
- Phy Metre BridgeDocument25 pagesPhy Metre Bridgeadishrajesh0No ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument3 pagesOhms LawJuwariyah NafeesNo ratings yet
- OhmmeterDocument20 pagesOhmmeterAqeel HaiderNo ratings yet
- AmmeterDocument5 pagesAmmeterGilberto ManhattanNo ratings yet
- Measuring InsstrumentsDocument11 pagesMeasuring Insstrumentsamit singhNo ratings yet
- Intro To Circuits Lab #1: Anatomy of A BreadboardDocument5 pagesIntro To Circuits Lab #1: Anatomy of A BreadboardNishat AhamadNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1Document12 pagesExperiment No. 1Van LeronNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Progress Check I. Discuss The Basic Use of The Following MetersDocument5 pagesWeek 1 Progress Check I. Discuss The Basic Use of The Following MetersJoshua Ray CalagoNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Transformers VocabularyDocument3 pagesTransformers VocabularyАндрей РоманенкоNo ratings yet
- Study The VocabularyDocument5 pagesStudy The VocabularyАндрей РоманенкоNo ratings yet
- Ответы на задачи Измерит Приборы 2Document1 pageОтветы на задачи Измерит Приборы 2Андрей РоманенкоNo ratings yet
- Study The Vocabulary: TransformersDocument5 pagesStudy The Vocabulary: TransformersАндрей РоманенкоNo ratings yet
- Проводники и изоляторыDocument5 pagesПроводники и изоляторыАндрей РоманенкоNo ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument8 pagesSodapdfsdfbvshbdfNo ratings yet
- مصطفى محمدDocument8 pagesمصطفى محمدBoss barkatNo ratings yet
- 2dm2280 Digital Step DriverDocument22 pages2dm2280 Digital Step DrivermuhammedasifNo ratings yet
- 36 TD SST150Document2 pages36 TD SST150sisprointNo ratings yet
- Industry Leading Design in A Compact Package: E Line FamilyDocument27 pagesIndustry Leading Design in A Compact Package: E Line FamilyPhaniNo ratings yet
- Emerging Trends in Mechanical Engineering: Course Code - 22652 (AE/PG/PT/ME) Unit 2 - Process EngineeringDocument15 pagesEmerging Trends in Mechanical Engineering: Course Code - 22652 (AE/PG/PT/ME) Unit 2 - Process EngineeringKunal AhiwaleNo ratings yet
- Pulangi IV Hydroelectric PlantDocument3 pagesPulangi IV Hydroelectric PlantcatherineNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3Lala's gamingNo ratings yet
- Tech Specification, Section: CRP Page 21 of 40 C/Engg/Spec/Crp Rev No: 08Document1 pageTech Specification, Section: CRP Page 21 of 40 C/Engg/Spec/Crp Rev No: 08karthikNo ratings yet
- Recent Advancements and Developments For Electric Vehicle TechnologyDocument10 pagesRecent Advancements and Developments For Electric Vehicle TechnologyharshithaNo ratings yet
- فزیک طبی بخش حرارتDocument253 pagesفزیک طبی بخش حرارتSayed kazim hashimiNo ratings yet
- MEO Class 4 Exam - Electrical Oral Question & Answers PDFDocument6 pagesMEO Class 4 Exam - Electrical Oral Question & Answers PDFabhishek rathourNo ratings yet
- Fault Analysis On Distribution Feeders With High Penetration of PV SystemsDocument7 pagesFault Analysis On Distribution Feeders With High Penetration of PV SystemsLuis ÁtilaNo ratings yet
- Dates and Times With Lubridate::: Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesDates and Times With Lubridate::: Cheat SheetFelipe Balboa PolancoNo ratings yet
- Examinaton of phsics امتحان في مادة الفيزياء الجامعيةDocument3 pagesExaminaton of phsics امتحان في مادة الفيزياء الجامعيةmaanibrahimNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Properties PDFDocument34 pagesEstimation of Properties PDFLee860531No ratings yet
- Electric FluxDocument19 pagesElectric FluxroseNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic BasicsDocument124 pagesAerodynamic BasicsChanaka DilshanNo ratings yet
- Capacitor ElcoDocument5 pagesCapacitor ElcoRazi QurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Stirling Engine: Project by - S. Srikanth V. Prashaanth R. Srikkanth S. Srinivas Guided by - Mr. Senthil KumarDocument35 pagesStirling Engine: Project by - S. Srikanth V. Prashaanth R. Srikkanth S. Srinivas Guided by - Mr. Senthil Kumarhemanth7cNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument12 pagesProblem SolvingLouieBrent CaingatNo ratings yet
- CHM 1103 Lab - 2 - Student Report - Pdf.docxDocument4 pagesCHM 1103 Lab - 2 - Student Report - Pdf.docxjesseNo ratings yet
- VD Calculation L00 & B1 WWDBDocument1 pageVD Calculation L00 & B1 WWDBsajana jayasingheNo ratings yet
- Atd 8Document6 pagesAtd 8pri0322No ratings yet
- WWW - Hobby Hour - Com Electronics Resistorcalculator - PHPDocument5 pagesWWW - Hobby Hour - Com Electronics Resistorcalculator - PHPAntonio Tomba Chavez SomozaNo ratings yet
- Forced Convection in A Square Cavity With Inlet and Outlet PortsDocument11 pagesForced Convection in A Square Cavity With Inlet and Outlet PortsMoussa DiopNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Motion Responses of Ship Shape Floating Structure Using Diffraction PotentialDocument5 pagesPrediction of Motion Responses of Ship Shape Floating Structure Using Diffraction PotentialPatrick Silva OliveiraNo ratings yet
- PriceListHirePurchase Normal3august2020Document69 pagesPriceListHirePurchase Normal3august2020waqar ahmadNo ratings yet