Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EE1205 - Circuit Analysis
Uploaded by
Rameez FaroukOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EE1205 - Circuit Analysis
Uploaded by
Rameez FaroukCopyright:
Available Formats
EE1205 – CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
KINGS
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
PUNALKULAM.
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
QUESTION BANK
SUBJECT CODE : EE1205 SEM / YEAR : III / II
SUBJECT NAME : CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
UNIT - 1
DC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
PART – A (2 Marks)
1. Define charge and voltage?
2. Define current and power and mention its units?
3. What is the difference between emf and potential difference?
4. State and explain KCL.
5. State and explain KVL.
6. Define resistance and its unit.
7. Define active and passive networks.
8. Define ideal and practical voltage sources.
9. Define ideal and practical current sources.
10. Define mesh or loop and node analysis.
11. Write about network and network element.
12. Difference between time variant and time invariant sources.
13. Write about dependent and independent sources.
14. Define branch.
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
EE1205 – CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
PART – B (16 Marks)
15. Explain the voltage division in series circuit of two impedance. (16)
16. Explain the current division in parallel circuit of two impedance. (16)
17. Explain with the suitable example how to obtain
i. an equivalent current source from a given voltage source. (8)
ii. an equivalent voltage source from a given current source. (8)
18. Explain the loop analysis of analyzing a given network with a suitable
example. (16)
19. Briefly explain the node analysis of analyzing a given network with a suitable
example. (16)
20. Two storage batteries A and B are connected in parallel to supply a load of
0.3ohm.The open circuit emf of A is 11.7 volt and that of B is 12.3 volt.
The internal resistances are 0.06 ohm and 0.05 ohm respectively.
Find the current supplied to the load. (16)
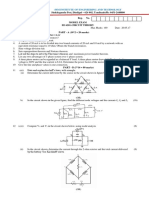
21. Apply KCL and KVL to the circuit shown in fig. (16)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
EE1205 – CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
22. Calculate the current through 8 ohm resistance using loop analysis. (16)
23. Find the current through branch A-B using mesh analysis. (16)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
EE1205 – CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
24. Find the node voltages V1, V2, V3 using node analysis method for the circuit
shown in figure. (16)
25. Find the current through each resistor of the circuit shown in fig.
using node analysis method. (16)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
EE1205 – CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
UNIT-2
NETWORK THEOREM AND DUALITY
PART – A (2 Marks)
1. Explain star and delta connection of impedances.
2. Explain Linearity theorem.
3. State Superposition theorem.
4. State Thevenin’s theorem.
5. State Nortan’s theorem.
6. State Maximum Power transfer theorem.
PART – B (16 Marks)
1. Derive the relation to convert the given star connected impedance to the
equivalent Delta. (16)
2. Derive the relation to convert the given Delta connected impedance to the
equivalent star. (16)
3. Briefly explain about
(i) Superposition theorem. (8)
(ii) Linearity theorem. (8)
4. Briefly explain about
(i) Thevenin’s theorem. (8)
(ii) Nortan’s theorem. (8)
5. Derive an expression for maximum power transfer theorem. (16)
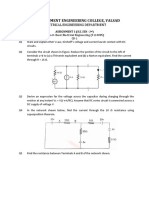
6. Find the current through branch AB by using superposition theorem. (16)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
EE1205 – CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
7. Find the current through 5 ohm resistance using Superposition theorem.
(16)
8. Find the current through 3 ohm resistance by using Thevenin’s theorem.
(16)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
EE1205 – CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
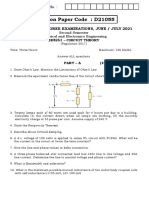
9. Find the current through 10 ohm resistance using Nortan’s theorem. (16)
10. Find the current through branch A-B by using (16)
a. Nortan’s theorem.
b. Thevenin’s theorem.
c. Superposition theorem.
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
EE1205 – CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
11. Using Thevenin’s theorem, find the current through RL =10 ohm in the
network shown in fig. Verify the answer by Nortan’s theorem. (16)
UNIT- 3
SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE ANALYSIS
PART – A (2 Marks)
1. State the advantages of AC supply over DC?
2. State the advantages of purely sinusoidal waveform as compared to
other non sinusoidal alternating waveforms.
3. Define (a).Instantaneous value (b).Time period.
4. Define (a).frequency (b).amplitude.
5. Define (a).cycle (b) Angular frequency.
6. Give the concept for effective value of an alternating quantity?
7. Define
(a) Form factor.
(b) Peak factor.
8. What is Power factor?
9. Define the following (a).Admittance (b) .Conductance (c) .Susceptance.
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
EE1205 – CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
PART – B (16 Marks)
1. Explain with neat diagram, generation of an alternating voltage? (16)
2. Derive the relation between
(a) RMS value & Maximum value. (8)
(b) Average value & maximum value for a purely sinusoidal alternating
quantity. (8)
3. Show that alternating quantity can be represented by a rotating phasor .(16)
4. Show that current through pure resistive circuit is in phase with applied
voltage. (16)
5. Show that the current through pure inductive lags applied voltage by 90`. (16)
6. Show that the current through pure capacitor leads applied voltage by 90` (16).
7. Show that (a). Current lags voltage in R-L series circuit (b). Current
leads voltage in R-C series Circuit ?
8. A 60HZ alternating voltage of 200V (rms) is applied independently to
(a). R=15 ohm (b). L= 0.5H (c) C=100(micro) F. Find the expression for
the instantaneous current in each case. Draw the phasor diagram in each case.
9. An alternating current i=320 sin (2 Π50t) a, is passed through a series Circuit
consisting of a resistance of 150 & an inductance of 0.31831 H. Find the
expression for the instantaneous value of the voltage across (a) Resistance
(b) Inductance (c) combination.
10. The waveform of the voltage ¤t of a circuit are given by C=80 sin (314t)
& i=10 sin (314t+ /6) Calculate the value of resistance, capacitance which are
connected in series to form the circuit.
11. A series circuit of 30 resistor,50mH inductor & 100micro F capacitor is
connected to a 150V,50Hz single phase supply as shown in fig. Calculate the
current, voltage across individual element and the over all power factor of the
circuit. Draw a neat phasor diagram showing I , VR, VL,VC and V
12. A RLC series of R=50, L=40mH & a capacitor is connected across a
415V,50Hz, a.c. supply .This RLC series circuit draws a circuit of10A.calculate
the value of Capacitor & power factor.
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
EE1205 – CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
UNIT – IV
TRANSISENTS AND RESONANCE IN RLC CIRCUITS
PART – A (2 Marks)
1. What is significance of initial conditions?
2. Write a note on initial conditions in basic circuit elements.
3. What is time constant?
4. Write a note on under damped, over damped and critically damped systems.
5. Define (i) rise time, (ii) time delay in respect of step response of second order
system.
6. What do you mean by resonance?
7. What is Q-factor?
8. What is anti-resonance?
9. Find the value of Q-factor for an Inductor & Capacitor.
PART – B (16 Marks)
1. Derive an expression for step response of series R-L circuit.
2. Derive an expression for step response of series R-C circuit.
3. Explain about current decay in source free series R-L circuit.
4. Explain the Discharge of capacitor through resistor in source free series
circuit.
5. In how many seconds after t=o has the current i(t) become one half of its initial
value in the given circuit shown in fig.
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
EE1205 – CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
6. Explain the step response of RLC circuit.
7. Find the expression for the current in a series RLC circuit fed by a D.C. voltage
of 20v with R=8, L=5H, C=1/8F. Assume the initial conditions to be zero.
8. Explain Series Resonance.
9. Briefly explain the frequencies for Maximum voltage across L & C.
10. A series RLC circuit consists of R=50, L=0.05H and C=0.05F. Calculate the
frequency of resonance. A variable frequency sinusoidal voltage of value 50v is
applied to the circuit. Find the frequency at which voltage across L & C is
maximum. Also calculate voltages across L & C at frequency of resonance.
Find maximum current in the circuit.
11. Briefly explain the parallel resonance.
12. A resistor & capacitor are in series with a variable inductor. When the circuit is
connected to 200v, 50Hz supply, the maximum current obtained by varying the
inductance is 0.314A. the voltage across capacitor, when the current in the
circuit is maximum is 800v. find the values of series circuit elements.
13. A parallel circuit has fixed C and variable inductor L. Q of inductor is 4. Find the
values of L & C for circuit impedance (100+j0) at f=2.4MHz. What is the
bandwidth at matched condition?
UNIT -5
COUPLED CIRCUITS AND TOPOLOGY
PART – A (2 Marks)
1. What is meant by coupled circuits?
2. Write a note on coefficient of coupling?
3. Write a note on dot convention?
4. What are magnetically coupled circuits?
5. What is graph of a network?
6. Give the difference between f-circuits & f- cut sets?
7. Give the principle of duality?
8. What is an incidence matrix?
9. What are the properties of complete incidence matrix?
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
EE1205 – CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
PART – B(16 Marks)
1. Explain self inductance.
2. Explain mutual inductance.
3. Explain the coefficient of coupling or magnetic coupling coefficient (k).
4. Explain linear transformer.
5. Explain Ideal transformer.
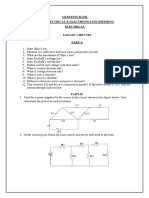
6. Write the voltage equation for the network shown in figure and determine the
effective inductance.
7. Write the loop equation for the network shown in the figure.
8. Explain the following terms with reference to network topology (1)co-tree
(2) Tree (3) Branch (4) Node (5) Twig (6) Link (7) Oriented graph (8). Incidence
matrix.
9. Explain the graphical method to draw the Dual network.
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
EE1205 – CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
10. For the oriented graph shown in the figure, draw tree & co tree. Determine
the tieset schedule.
11.Find the Dual network of the network given in figure.
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
EE1205 – CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
12. Linear graph of a network is shown in figure .For the given tree
(shown with firm line ) obtain the fundamental loop matrix.
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
You might also like
- Advanced Aerospace PropulsionDocument57 pagesAdvanced Aerospace Propulsionsid676No ratings yet
- Digital Electronics - Principal and Application PDFDocument723 pagesDigital Electronics - Principal and Application PDFKamal Bhattacharjee100% (2)
- Numerical Mathematics With MATLABDocument66 pagesNumerical Mathematics With MATLABReza Abazari87% (15)
- Methods In: ExperimenDocument503 pagesMethods In: ExperimenLuis H CamposNo ratings yet
- Mason - Applied Computational Aerodynamics PDFDocument450 pagesMason - Applied Computational Aerodynamics PDFDiana DumitrascuNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit AnalysisDocument12 pagesElectric Circuit AnalysisMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (ECE)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank (ECE)Manav JainNo ratings yet
- VLSI DESIGN Lab Manual Verilog+l-EditDocument55 pagesVLSI DESIGN Lab Manual Verilog+l-Editmario sanchezNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Question BankDocument18 pagesElectrical Circuits Question BankRacherla Mega RaniNo ratings yet
- Ee-1151-Circuit TheoryDocument20 pagesEe-1151-Circuit Theoryapi-19951707No ratings yet
- EE 1151 Circuit Theory Question BankDocument19 pagesEE 1151 Circuit Theory Question BankVIVEK AHLAWATNo ratings yet
- EE 1151 Circuit TheoryDocument26 pagesEE 1151 Circuit Theorybala_c84111No ratings yet
- Question Bank On Unit IDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank On Unit IanupamNo ratings yet
- Sr. No. Mark 7: Prepared by Prof. Suvas VoraDocument8 pagesSr. No. Mark 7: Prepared by Prof. Suvas Vorasanket soniNo ratings yet
- Part B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisDocument4 pagesPart B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisAnonymous Ndsvh2soNo ratings yet
- Kings: Question BankDocument26 pagesKings: Question BankRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Ee6201 CT U1 5 QBDocument10 pagesEe6201 CT U1 5 QBsakilakumaresanNo ratings yet
- PTEE6201 - CIRCUIT THEORY: KEY CONCEPTSDocument19 pagesPTEE6201 - CIRCUIT THEORY: KEY CONCEPTSSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- CT Important QuestionsDocument14 pagesCT Important QuestionsJacob JayaseelanNo ratings yet
- SSM EE Circuit Theory Model Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesSSM EE Circuit Theory Model Exam Questionsboomadev6321No ratings yet
- BEE Assignment Even 2020Document5 pagesBEE Assignment Even 2020Aditya PatelNo ratings yet
- Xii Derivation List-2023-24 2Document3 pagesXii Derivation List-2023-24 2prachurjyapadhiNo ratings yet
- Beee (R 17) Short Question Bank 2017Document4 pagesBeee (R 17) Short Question Bank 2017upender raoNo ratings yet
- Assignment BEE CompleteDocument5 pagesAssignment BEE CompleteHarshit YadavNo ratings yet
- 9A02305 Electrical CircuitsDocument8 pages9A02305 Electrical CircuitssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank With Answers: BE 8253 - Basic Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation EngineeringDocument93 pagesQuestion Bank With Answers: BE 8253 - Basic Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation EngineeringRajeshNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits and Electron Devices Unit I Circuit Analysis Techniques Part-ADocument8 pagesElectric Circuits and Electron Devices Unit I Circuit Analysis Techniques Part-ASalai Kishwar JahanNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics EMI AC WorksheetDocument4 pages12th Physics EMI AC WorksheetlkNo ratings yet
- Shivaji University, KolhapurDocument9 pagesShivaji University, KolhapurNiranjan PatilNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code: 22115: B.E./B.Tech - Degree Examinations, April/May 2011 Regulations 2008Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Code: 22115: B.E./B.Tech - Degree Examinations, April/May 2011 Regulations 2008Vinodh GanesanNo ratings yet
- WWW - Studyhaunters.blogspot - In: Question Paper Code: 22115Document5 pagesWWW - Studyhaunters.blogspot - In: Question Paper Code: 22115Sriram JNo ratings yet
- Unit: 4 (Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents)Document16 pagesUnit: 4 (Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents)Tuition MasterNo ratings yet
- BEE Questions BankDocument2 pagesBEE Questions BankDhaval KhuntNo ratings yet
- 02 Basic Electrical Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering notesDocument93 pages02 Basic Electrical Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering notesMonika GNo ratings yet
- Division Principle For Two Resistors in ParallelDocument12 pagesDivision Principle For Two Resistors in ParallelRaja pandiyanNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields: 2006 Board QuestionsDocument50 pagesElectric Charges and Fields: 2006 Board Questionsgurveer sainiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Krishna School of Emerging Technology and Applied Research (KSET)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank: Krishna School of Emerging Technology and Applied Research (KSET)Vraj PatelNo ratings yet
- Mid Bee Paper Set 3Document6 pagesMid Bee Paper Set 3raghusabale1No ratings yet
- BEE New Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesBEE New Important Questionsaraq3501No ratings yet
- Circuit TheoryDocument31 pagesCircuit Theoryraj selvarajNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument12 pagesElectronic Devices and CircuitsAnandhi SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- 9A02305 Electrical CircuitsDocument8 pages9A02305 Electrical CircuitssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit 1Document2 pagesAssignment Unit 1Mamta Vinod TapariaNo ratings yet
- CT Assignment IDocument4 pagesCT Assignment ImosesalvinNo ratings yet
- Question Bank BeeDocument25 pagesQuestion Bank Beedhruv goraiNo ratings yet
- EE8251 - Circuit Theory (Q)Document4 pagesEE8251 - Circuit Theory (Q)vinothkumarNo ratings yet
- U20EE201 - CT - Model QPDocument4 pagesU20EE201 - CT - Model QPvinothkumarNo ratings yet
- QbankDocument50 pagesQbankSourabhGuptaNo ratings yet
- EEE SyllabusDocument11 pagesEEE Syllabussamarpit_anandNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: (10 2 20 Marks)Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10 2 20 Marks)Samraj JebasinghNo ratings yet
- Physics Shorthand Guide by Ri DaDocument5 pagesPhysics Shorthand Guide by Ri DaGAME DEVNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 WEBDocument18 pagesPhysics 1 WEBSsNo ratings yet
- 2129:St - Joseph College of Engineering, Nemili Model Exam Semester: Ii Dept: Eee/Ece Ee6201-Circuit TheoryDocument2 pages2129:St - Joseph College of Engineering, Nemili Model Exam Semester: Ii Dept: Eee/Ece Ee6201-Circuit TheoryAarim SIJININo ratings yet
- EEE Exclusive: Question Paper Code: 22115Document5 pagesEEE Exclusive: Question Paper Code: 22115aishuvc1822No ratings yet
- Question BankDocument45 pagesQuestion BankSaritha Reddy100% (1)
- Question Bank Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering ElectricalDocument9 pagesQuestion Bank Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering Electricalcsvtu notesNo ratings yet
- Physics Test - Half Test - I: Topic: - NCERT BOOK-1Document4 pagesPhysics Test - Half Test - I: Topic: - NCERT BOOK-1ChetanNo ratings yet
- Physics 3Document6 pagesPhysics 3Aadit “ThePROkiller”No ratings yet
- 9A02305 Electrical CircuitsDocument8 pages9A02305 Electrical CircuitssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Single Pahse Ac Additional QuestionDocument7 pagesSingle Pahse Ac Additional QuestionYuvaraj BadigerNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory exam questions on ideal current sources, unilateral networks, co-trees, phasors, RMS values, reactive power, Norton's theorem, resonance, Laplace transforms, PSPICE simulationsDocument4 pagesCircuit Theory exam questions on ideal current sources, unilateral networks, co-trees, phasors, RMS values, reactive power, Norton's theorem, resonance, Laplace transforms, PSPICE simulationslokeshwarrvrjcNo ratings yet
- Bee 14 Question BankDocument10 pagesBee 14 Question BankprakashkerurNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Modeling Turbulent Flows: Boundary Conditions Mesh Density and Spatial Distribution Solution ProcedureDocument109 pagesModeling Turbulent Flows: Boundary Conditions Mesh Density and Spatial Distribution Solution ProcedurepuneshwarvermaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis of Reacting Flows Using Finite Rate Chemistry ModelsDocument1 pageNumerical Analysis of Reacting Flows Using Finite Rate Chemistry ModelsRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Numerical Modeling of Supersonic Combustion: Validation and Vitiation Studies Using FLUENTDocument1 pageNumerical Modeling of Supersonic Combustion: Validation and Vitiation Studies Using FLUENTRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Principles of Helicopter FlightDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Helicopter Flightapi-26338869100% (2)
- H2 - O2 Mech Very Very ImpDocument36 pagesH2 - O2 Mech Very Very ImpRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Compressible Flow 3. Flow Through Nozzles and DuctsDocument4 pagesCompressible Flow 3. Flow Through Nozzles and DuctsRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Characteristic MethodDocument11 pagesCharacteristic MethodmassooudNo ratings yet
- Propeller Theory: 1) Simple Propeller Theories: Screw-Nut PrincipleDocument21 pagesPropeller Theory: 1) Simple Propeller Theories: Screw-Nut PrincipleRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- AerodynamicsDocument7 pagesAerodynamicsRavindar_Singh100% (1)
- Implementation of A 19 Species Methane Global Mechanism Into FLUENTDocument1 pageImplementation of A 19 Species Methane Global Mechanism Into FLUENTRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Subsonic Compress Ible Flow Over Air FoilsDocument3 pagesSubsonic Compress Ible Flow Over Air FoilsRidwan FadlikaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering. LevenspielDocument15 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering. LevenspielcespinaNo ratings yet
- AircraftDocument7 pagesAircraftrehanadilNo ratings yet
- Notes On CFD FundamentalsDocument5 pagesNotes On CFD FundamentalsD.ViswanathNo ratings yet
- Scramjets: by Emily Davis and Raechel TanDocument24 pagesScramjets: by Emily Davis and Raechel TanRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Numerical Approach in Combustion and Propulsion Technologies Takita KDocument11 pagesNumerical Approach in Combustion and Propulsion Technologies Takita KRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- TIP Scramjet Engines FinalDocument12 pagesTIP Scramjet Engines FinalStephen Songjin LimNo ratings yet
- Wind Tunnel Testing: Provided by TryengineeringDocument11 pagesWind Tunnel Testing: Provided by TryengineeringRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- v y u x: ρ is the φ,Document25 pagesv y u x: ρ is the φ,Rameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- NASA Research Helps Improve Tennis Ball AerodynamicsDocument7 pagesNASA Research Helps Improve Tennis Ball AerodynamicsRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Partial Differential Equations in MATLABDocument23 pagesPartial Differential Equations in MATLABAsterix100% (20)
- Theory of Propulsion - Equations of Motion and CombustorsDocument40 pagesTheory of Propulsion - Equations of Motion and CombustorsRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Development of A Supersonic Aerodynamic Test Section Using Computational ModelingDocument7 pagesDevelopment of A Supersonic Aerodynamic Test Section Using Computational ModelingRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- AAE 512 Computational AerodynamicsDocument2 pagesAAE 512 Computational AerodynamicsRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Ph.D. / M.S.: Ordinances AND RegulationsDocument36 pagesPh.D. / M.S.: Ordinances AND RegulationsRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Age of PropellersDocument15 pagesAge of PropellersRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Fuels: 朱信 Hsin Chu Professor Dept. of Environmental Engineering National Cheng Kung UniversityDocument52 pagesGaseous Fuels: 朱信 Hsin Chu Professor Dept. of Environmental Engineering National Cheng Kung UniversityvictorNo ratings yet
- FilterDocument20 pagesFilterAsheque IqbalNo ratings yet
- HW2 SolDocument7 pagesHW2 Soluzair ahmadNo ratings yet
- ED Project ReportDocument8 pagesED Project Reportabdul hananNo ratings yet
- Renesas Technology Corp. announces name change from Mitsubishi brandsDocument10 pagesRenesas Technology Corp. announces name change from Mitsubishi brandsTahar BenacherineNo ratings yet
- OP200Document16 pagesOP200Asad AhmedNo ratings yet
- A SemiconductoresDocument19 pagesA Semiconductoresajcl_1987No ratings yet
- Datasheet PDFDocument12 pagesDatasheet PDFmhenley8059No ratings yet
- Differential Amplifier 1Document4 pagesDifferential Amplifier 1Eslam ElnagarNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronic Circuit: Prof. Shouribrata ChatterjeeDocument1 pageAnalog Electronic Circuit: Prof. Shouribrata ChatterjeechadNo ratings yet
- Ka5S-Series: KA5S0765C/KA5S0965/KA5S12656/KA5S1265 Fairchild Power Switch (FPS)Document16 pagesKa5S-Series: KA5S0765C/KA5S0965/KA5S12656/KA5S1265 Fairchild Power Switch (FPS)Arte Y MecatrónicaNo ratings yet
- Analog ModuleDocument1 pageAnalog ModuleTrần TàiNo ratings yet
- EEE3352 Test 1Document6 pagesEEE3352 Test 1Carlos YoongNo ratings yet
- Even Parity Bit GeneratorDocument18 pagesEven Parity Bit GeneratorKeith FernandesNo ratings yet
- Designing Combinational Logic Gates in CMOSDocument21 pagesDesigning Combinational Logic Gates in CMOSMonica MagnateNo ratings yet
- 2-Channel Secondary Monitoring IC: Issue Date: File Name: Total PagesDocument10 pages2-Channel Secondary Monitoring IC: Issue Date: File Name: Total PagesParedão FrankensteinNo ratings yet
- Lab - 1 Amplitude Modulation and Demodulation: 1.1 ObjectiveDocument13 pagesLab - 1 Amplitude Modulation and Demodulation: 1.1 Objectivetendua_13No ratings yet
- GaN DriverDocument42 pagesGaN DrivermosTfa dehghanyNo ratings yet
- 2SC2078 SpecsDocument3 pages2SC2078 Specsgerler jhony hernandez rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 MOSFET AmplifiersDocument41 pagesChapter - 3 MOSFET AmplifiersNguyễn Phước Định TườngNo ratings yet
- A Novel Method For Digital Signal Conditioning Using Resistive and Capacitive Sensor - EditedDocument5 pagesA Novel Method For Digital Signal Conditioning Using Resistive and Capacitive Sensor - EditedManjusha SreedharanNo ratings yet
- 4-DAC Dan ADCDocument36 pages4-DAC Dan ADCAchmad IlhamNo ratings yet
- Amplifier Design: Bilateral Design of Amplifier With Conjugately Matched (Design For Maximum Gain)Document12 pagesAmplifier Design: Bilateral Design of Amplifier With Conjugately Matched (Design For Maximum Gain)jascnjNo ratings yet
- 03 JM EFIE ControllerDocument1 page03 JM EFIE Controllerskyman05100% (1)
- Validation of MODICON 3-2 Receiver Board Operation - LJ Create PDFDocument3 pagesValidation of MODICON 3-2 Receiver Board Operation - LJ Create PDFAnonymous FKMfvCbNo ratings yet
- Collins PTT Line Interface For ICOM IC-706 FamilyDocument2 pagesCollins PTT Line Interface For ICOM IC-706 FamilyJim FischerNo ratings yet
- Switch-Mode Power Converter Compensation Made Easy: Robert SheehanDocument38 pagesSwitch-Mode Power Converter Compensation Made Easy: Robert Sheehanjimmyboy111No ratings yet
- LimiterDocument2 pagesLimiterBoedi SetijoNo ratings yet