Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan: Dulay, David Audrey H. Saint Louis University Be OB Ward Duty Prof. Diadem Depayso
Uploaded by
Ericka Genove0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
114 views5 pagesThis nursing care plan is for a patient experiencing deficient fluid volume due to vomiting from pregnancy. The patient has vomited 10 times in 24 hours and cannot tolerate food or water. Goals are to achieve adequate fluid volume and normal potassium and urea lab results within 3 days. Interventions include monitoring vital signs, assessing skin turgor and urine color/output. Objectives are to increase fluid intake to 1.5-2L and achieve yellowish urine output within 8 hours and normal labs within 3 days. The rationales explain how dehydration affects the body and importance of rehydration.
Original Description:
Original Title
DULAY_NCP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis nursing care plan is for a patient experiencing deficient fluid volume due to vomiting from pregnancy. The patient has vomited 10 times in 24 hours and cannot tolerate food or water. Goals are to achieve adequate fluid volume and normal potassium and urea lab results within 3 days. Interventions include monitoring vital signs, assessing skin turgor and urine color/output. Objectives are to increase fluid intake to 1.5-2L and achieve yellowish urine output within 8 hours and normal labs within 3 days. The rationales explain how dehydration affects the body and importance of rehydration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
114 views5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Dulay, David Audrey H. Saint Louis University Be OB Ward Duty Prof. Diadem Depayso
Uploaded by
Ericka GenoveThis nursing care plan is for a patient experiencing deficient fluid volume due to vomiting from pregnancy. The patient has vomited 10 times in 24 hours and cannot tolerate food or water. Goals are to achieve adequate fluid volume and normal potassium and urea lab results within 3 days. Interventions include monitoring vital signs, assessing skin turgor and urine color/output. Objectives are to increase fluid intake to 1.5-2L and achieve yellowish urine output within 8 hours and normal labs within 3 days. The rationales explain how dehydration affects the body and importance of rehydration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
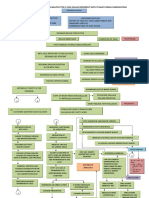
NURSING CARE PLAN
Dulay, David Audrey H.
Saint Louis University
Be OB Ward Duty
Prof. Diadem Depayso
NURSING DIAGNOSIS EXPLANATION OF THE GOALS AND INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
PROBLEM OBJECTIVES
Vomited up to 10 times in 24 Deficient Fluid Volume is defined GOAL: Monitor vital signs Dehydration alters body’s FULLY MET if able to maintain
hrs. and has not managed to as decreased intravascular, The patient will be able especially blood vital signs. For the blood normal fluid volume all
tolerate any food in 3 days interstitial and/or intracellular to achieve adequate pressure, pulse rate and pressure, first, when the throughout until discharge
Can only drink a few amounts of fluid. This refers to dehydration, fluid volume temperature body's cells lack water, the
water water loss alone without change brain sends a signal to the PARTIALLY MET if temporarily
Feels very weak and produces in sodium. Deficient fluid volume pituitary gland to secrete achieved, but then, becomes
small dark urine outputs. is a state or condition where the vasopressin, a chemical that deficient again
Dry mucus membranes fluid output exceeds the fluid causes constriction of the
Vital signs of: intake. It happens when water blood vessels to save fluids. NOT MET if patient never
Temperature- 37°C and electrolytes are lost as they On the other hand, achieved adequate fluid
BP- 115/68 mmHg exist in normal body fluids. Since dehydration also causes volume
HR- 96/min the patient is at her first higher viscosity of the
Urinalysis reveals: trimester, it is just normal for her blood, thus the increase in
Decreased Potassium= 3.0 to experience hyperemesis LTO: blood pressure. When these
mmol/L from the normal of 3.3- gravidarum wherein she suffers After 3 days of nursing happen, the heart will then FULLY MET if lab results show
4.1 mmol/L from extreme vomiting as a intervention, the compensate by contracting normal potassium and urea
Concentrated Urea= 8.2 mmol/L result of increase in HCG patient’s urinalysis will faster, the reason for levels after 3 days
from the normal of 2.4-4.3 hormone in the blood. Having reveal a normal increased pulse rate. Lastly,
mmol/L hyperemesis gravidarum forces potassium value to fluids regulate body PARTIALLY MET if lab results
her to vomit and excrete a lot of within 3.3-4.1 mmol/L temperature, so, the lack of show an increase in
Nsg. Dx: fluid from her body, hence the and urea level to within it results to inability to potassium level and a
Deficient fluid volume related to nursing diagnosis. 2.4-4.3 mmol/L from 3.0 regulate homeostasis decrease in urea level,
active fluid loss secondary to pregnancy mmol/L and 8.2 mmol/L, resulting to fever. If the however, are still not within
as manifested by vomiting 10 times in References: respectively patient’s vital signs increase, normal ranges or a normal
24 hrs. Wayne G., (2019, March 20). then, immediate level of just one
Deficient Fluid Volume. rehydration will be
Nurseslabs. Retrieved necessary. (Vascular NOT MET if lab results show
from: Institute. (2019, October 1). similar results or worse
https://nurseslabs.com/ The Importance of (lower potassium level and
deficient-fluid-volume/ Hydration for Your Heart. higher urea concentration)
Hyperemesis gravidarum: Retrieved May 15, 2020,
MedlinePlus Medical from
Encyclopedia. (n.d.). STO: https://share.upmc.com/20
Retrieved May 15, 2020, After 8 hours of nursing 14/09/importance-
from intervention, the patient hydration-heart/)
https://medlineplus.gov/ will be able to: Assess skin turgor, oral
ency/article/001499.htm mucosa and eyes Lack of fluid in the body will
1. Increase her result to drying of epithelial FULLY MET if fluid intake is
fluid intake to membrane like the mucous increased to as least 1.5L
1.5-2L from only and cutaneous membranes.
‘few amounts’ Skin turgor of >2 sec. PARTIALLY MET if fluid intake
suggests dryness of the skin, is more then ‘few amounts’
thus dehydration. Same but is still under 1.5L
goes with dry mucous
membranes. If the patient NOT MET if fluid intake is still
displays these signs, then, ‘few amounts’
she must be dehydrated,
therefore, the need to
2. Excrete provide appropriate nursing FULLY MET if urine is colored
yellowish-amber interventions like yellowish to amber
colored urine rehydration and regulation
from being dark- of I.V. fluids. (Rice PARTIALLY MET if urine is
colored University. (2013, March 6). colored orange
Types of Tissues. Retrieved
May 15, 2020, from NOT MET if urine is still dark
http://pressbooks- in color
dev.oer.hawaii.edu/anatom
yandphysiology/chapter/typ
3. Expel a total es-of-tissues/) FULLY MET if urine output is
amount of at Note color and amount at least 240Ml
least 240 ml of of urine, as well as Change of urine color to a
urine from urinalysis results darker one and urine output PARTIALLY MET if urine
‘small amounts’ of less than 30ml/hour output is greater than ‘small
denote possible amount’ but does not reach
dehydration. Lack of fluid 240 mL
results to a more
concentrated urochrome in NOT MET if urine output is
the urine, thus the change still ‘small amount’
in color. Also, if there is
deficient fluid in the body, it
will also result to decrease
in urine output. If the
4. Display moist patient’s urine continues to FULLY MET if mucous
mucus be darker and lesser than membranes appear moist
membrane from usual, and her lab results
being dry show abnormalities in PARTIALLY MET if mucous
normal value like the excess membranes appear slightly
of urea, it may suggest that dry
she is still dehydrated,
hence the need for NOT MET if mucous
Ensure accurate intake rehydration. membranes still appear dry
and output recording
Intake and output records
show the amount of fluids
the patient takes in and out.
If the patient’s I&O record
shows that she is still
expelling more fluid than
what she takes, she may still
experience dehydration,
thus, the need to increase
Offer at least 1.5-2L of her fluid intake.
water
Offering water to the
patient and urging her to
consume it will replace the
fluids lost, hence
rehydrating her.
Rehydration will then help
in treating the patient and
return her normal body
functioning. Since the
patient has been vomiting a
lot, rehydrating it with at
least 1.5L of water will
Regulate I.V. fluid replace the lost fluids from
vomiting
I.V. fluids help in hydration.
Regulating the appropriate
amount of I.V. fluid entering
the body will help in
rehydrating the cells.
Ensuring the proper I.V.
fluids will result to her
rehydration
Enumerate other
sources of fluids like
fruits and healthy Giving the mother other
beverages options may help her in
taking more fluids. She can
choose foods or beverages
that she prefers which will
aid in rehydration. This will
make rehydrating more
enjoyable for her
Emphasize the
importance of
increasing the fluid Emphasizing makes the
intake mother more
knowledgeable about why
fluid intake is important,
thus, increasing
participation
REFERENCES: Wayne, G., Wayne, G., & Wayne. (2019, March 20). Deficient Fluid Volume – Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan. Retrieved from https://nurseslabs.com/deficient-fluid-volume/
You might also like
- Post Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care Plan PDFDocument2 pagesPost Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care Plan PDFA sison100% (1)
- Abruptio Placentae Case StudyDocument4 pagesAbruptio Placentae Case StudyMonchee YusonNo ratings yet
- Problem # 3: Threat of Cross Infection From A Communicable Disease CaseDocument3 pagesProblem # 3: Threat of Cross Infection From A Communicable Disease CaseRolandNo ratings yet
- Dysfunction at The First Stage of Labor: Prolonged Latent PhaseDocument5 pagesDysfunction at The First Stage of Labor: Prolonged Latent PhaseRam Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPEmmanuelRodriguezNo ratings yet
- NCP Case 3Document3 pagesNCP Case 3boomer SeargeNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputCarlojay IniegoNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument54 pagesHyperemesis GravidarumAngeli Luz BonaobraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment, Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Assessment, Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDiana MuañaNo ratings yet
- Post C-Section Delivery Care PlanDocument5 pagesPost C-Section Delivery Care Planᒙᕧᖇᕦᙏᖻ ᗴᔛᓦᗩᖆᗩNo ratings yet
- A Case Analysis OnDocument27 pagesA Case Analysis Onbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Baby Jason with Cleft Lip and PalateDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Baby Jason with Cleft Lip and PalatePatricia Ellyne DizonNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument3 pagesHyperemesis GravidarumAldrece Castroverde100% (1)
- Milestones of Fetal Growth and Development EssayDocument2 pagesMilestones of Fetal Growth and Development EssayZoe Dominique GudioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument33 pagesDrug Studyjefwy8No ratings yet
- PREECLAMPSIA Case ScenarioDocument2 pagesPREECLAMPSIA Case Scenariosabao kizuiteNo ratings yet
- Incompetent CervixDocument5 pagesIncompetent CervixNaidin Catherine De Guzman-Alcala100% (1)
- Neonatal Sepsis Case 2Document81 pagesNeonatal Sepsis Case 2Joanne Bernadette Aguilar100% (1)
- Drug Study (Mefenamic Acid, Beetab, Esomeprazole Aspirin, Citicoline Plavix)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Mefenamic Acid, Beetab, Esomeprazole Aspirin, Citicoline Plavix)Patricia LuceroNo ratings yet
- Nursing care for anticipatory grieving after pregnancy lossDocument1 pageNursing care for anticipatory grieving after pregnancy lossYsabelle GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Learning Derived (Lysha)Document1 pageLearning Derived (Lysha)Choy DavidNo ratings yet
- Case Study Benign Tumors of The Uterus: MyomaDocument3 pagesCase Study Benign Tumors of The Uterus: MyomaToto RyanNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta Risks, Signs, and TreatmentDocument10 pagesAbruptio Placenta Risks, Signs, and TreatmentDoc DudayNo ratings yet
- Premature Rupture of Membranes (Prom)Document12 pagesPremature Rupture of Membranes (Prom)KABERA RENE50% (2)
- Causes and Treatment of Severe Morning SicknessDocument1 pageCauses and Treatment of Severe Morning SicknessAldrece Castroverde100% (1)
- NCP AgnDocument2 pagesNCP Agnj3nann3No ratings yet
- Drug Name Generic Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contra Indication/precautions Adverse Effect Dosage Nursing InterventionsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Generic Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contra Indication/precautions Adverse Effect Dosage Nursing InterventionsTedd CamilingNo ratings yet
- FNCPDocument1 pageFNCPEillhoysiea MedranoNo ratings yet
- Nclex 1Document18 pagesNclex 1Arvin Campos0% (1)
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument2 pagesReview of Related LiteratureAlexa MurielNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Hyperemesis GravidarumMary Ruth CruzNo ratings yet
- Nutri101 - Patient Self-Management GoalsDocument6 pagesNutri101 - Patient Self-Management GoalsFhai Escio100% (1)
- TAHBSO ReportDocument4 pagesTAHBSO ReportsachiiMeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions for PreeclampsiaDocument5 pagesNursing Interventions for PreeclampsiaChloe Crystal DorojaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis: Aurelio, Lyca Mae M. BSN II-DDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Aurelio, Lyca Mae M. BSN II-DLyca Mae AurelioNo ratings yet
- Respi SystemDocument65 pagesRespi Systemapi-373599567% (3)
- Spontaneous AbortionDocument8 pagesSpontaneous Abortionsaber_fate_11No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Core CompetenciesDocument13 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Core CompetenciesMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- Incompetent NCPDocument1 pageIncompetent NCPMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- DP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Document6 pagesDP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Maemae SumalinogNo ratings yet
- NCP - Preeclampsia (A)Document6 pagesNCP - Preeclampsia (A)Ronel ResurricionNo ratings yet
- Kevin Kato Fischer Swot AnalysisDocument17 pagesKevin Kato Fischer Swot AnalysisKevin Kato Fischer100% (2)
- New FNCPDocument12 pagesNew FNCPIrene Soriano Bayubay0% (1)
- Postpartum Physical Assessment ParametersDocument5 pagesPostpartum Physical Assessment ParametersKathrina CraveNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Knowledge DeficitDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Knowledge DeficitRegine BautistaNo ratings yet
- AGE With Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAGE With Pa Tho PhysiologyChichi Licuben OresacamNo ratings yet
- Benign Febrile ConvulsionDocument10 pagesBenign Febrile ConvulsionJuan Luis C. SingsonNo ratings yet
- OB Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesOB Nursing Care PlanLiza Marie Cayetano AdarneNo ratings yet
- NCP Drug Study Group 1Document21 pagesNCP Drug Study Group 1Cassandra Grace Muerong Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMiru มิริวNo ratings yet
- Paragonimiasis Infection Causes and TreatmentDocument3 pagesParagonimiasis Infection Causes and TreatmentEjay Jacob RicamaraNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics and Gynecology Mock Simulation OutputDocument4 pagesObstetrics and Gynecology Mock Simulation OutputKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for AmebiasisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for AmebiasiskristennemarieNo ratings yet
- Occurs Most Often In:: Muscular DystrophyDocument4 pagesOccurs Most Often In:: Muscular DystrophyJiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram of CKD Sec. To DM Nephropathy, DM Type 2, DM FootDocument8 pagesSchematic Diagram of CKD Sec. To DM Nephropathy, DM Type 2, DM Footbeuwolfagate50% (2)
- Anemia Unspecified FinalDocument47 pagesAnemia Unspecified FinalMaria Paula BungayNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Cesarean DeliveryDocument4 pagesPhysiology of Cesarean DeliveryDante SalesNo ratings yet
- Managing Overweight through Diet and ExerciseDocument17 pagesManaging Overweight through Diet and ExerciseMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta NCP 2 FinalDocument19 pagesAbruptio Placenta NCP 2 FinalTin100% (1)
- Guinitaran, Christine Ann P. BSN 4 Abruptio Placenta Nursing Care PlanDocument19 pagesGuinitaran, Christine Ann P. BSN 4 Abruptio Placenta Nursing Care PlanGemmalene PaclebNo ratings yet
- Day 1Document10 pagesDay 1Ericka GenoveNo ratings yet
- 4 Hemoglobin Hematocrit and WBC CountDocument7 pages4 Hemoglobin Hematocrit and WBC CountEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO HEMATOLOGY: AUTOMATED CBCDocument4 pagesINTRODUCTION TO HEMATOLOGY: AUTOMATED CBCEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- 3 Reagent For Hemoglobin DeterminationDocument4 pages3 Reagent For Hemoglobin DeterminationEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- 1 MONDAY Jan 31 AfternoonkkDocument5 pages1 MONDAY Jan 31 AfternoonkkEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Ericka Genove - Final Term Activity - Art AppDocument4 pagesEricka Genove - Final Term Activity - Art AppEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Daily Time Records Summary for Jan-Mar 2020Document2 pagesDaily Time Records Summary for Jan-Mar 2020Ericka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Quality Assesment and Performance ManagementDocument10 pagesQuality Assesment and Performance ManagementEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Journal Ni Mokong1Document2 pagesJournal Ni Mokong1Ericka GenoveNo ratings yet
- IV AcknowledgementDocument1 pageIV AcknowledgementEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Velazquez's Las MeninasDocument3 pagesAnalysis of Velazquez's Las MeninasEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type IIDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type IIEricka Genove100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMIDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMIEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- III IntroductionDocument4 pagesIII IntroductionEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- II Table of ContentsDocument1 pageII Table of ContentsEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- SLU College of Nursing case presentation on patient Angelina JuhiniDocument1 pageSLU College of Nursing case presentation on patient Angelina JuhiniEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Legend: - Precipitating Factors - Flow - Medical Diagnosis - Nursing Diagnosis - Lab Results - MedicationsDocument1 pageLegend: - Precipitating Factors - Flow - Medical Diagnosis - Nursing Diagnosis - Lab Results - MedicationsEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesHistology of The Urinary SystemEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnoses Prioritization: ND RDDocument1 pageNursing Diagnoses Prioritization: ND RDEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesHistology of The Urinary SystemEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- The Pituitary Gland: Notes on Anatomy, Embryology, and HistologyDocument9 pagesThe Pituitary Gland: Notes on Anatomy, Embryology, and HistologyEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- The Pituitary Gland: Notes on Anatomy, Embryology, and HistologyDocument9 pagesThe Pituitary Gland: Notes on Anatomy, Embryology, and HistologyEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Adrenal GlandsDocument4 pagesHistology of The Adrenal GlandsEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- MAQUET CARDIOHELP Disposables HLS - Module - Advanced PDFDocument2 pagesMAQUET CARDIOHELP Disposables HLS - Module - Advanced PDFXavi AnpiNo ratings yet
- PERSONS Finals Reviewer Chi 0809Document153 pagesPERSONS Finals Reviewer Chi 0809Erika Angela GalceranNo ratings yet
- Li Ching Wing V Xuan Yi Xiong (2004) 1 HKC 353Document11 pagesLi Ching Wing V Xuan Yi Xiong (2004) 1 HKC 353hNo ratings yet
- XDocument266 pagesXTrần Thanh PhongNo ratings yet
- RHS NCRPO COVID FormDocument1 pageRHS NCRPO COVID Formspd pgsNo ratings yet
- Haematology Notes - 3rd EdDocument100 pagesHaematology Notes - 3rd EdSally Brit100% (1)
- FileDocument284 pagesFileJesse GarciaNo ratings yet
- Malaysia's Trade Potential in Colourful AfricaDocument18 pagesMalaysia's Trade Potential in Colourful AfricaThe MaverickNo ratings yet
- Soal Upk B Inggris PKBM WinaDocument11 pagesSoal Upk B Inggris PKBM WinaCuman MitosNo ratings yet
- Hotel Housekeeping EQUIPMENTDocument3 pagesHotel Housekeeping EQUIPMENTsamahjaafNo ratings yet
- The Impact of StressDocument3 pagesThe Impact of StressACabalIronedKryptonNo ratings yet
- Live Performance Award Ma000081 Pay GuideDocument48 pagesLive Performance Award Ma000081 Pay GuideDan LijndersNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System Histology IDocument5 pagesFemale Reproductive System Histology ISolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Dip Obst (SA) Past Papers - 2020 1st Semester 1-6-2023Document1 pageDip Obst (SA) Past Papers - 2020 1st Semester 1-6-2023Neo Latoya MadunaNo ratings yet
- Journalize The Following Transactions in The Journal Page Below. Add Explanations For The Transactions and Leave A Space Between EachDocument3 pagesJournalize The Following Transactions in The Journal Page Below. Add Explanations For The Transactions and Leave A Space Between EachTurkan Amirova100% (1)
- RA8485 Animal Welfare Act (Carabao Slaughter)Document2 pagesRA8485 Animal Welfare Act (Carabao Slaughter)Jazreth Gaile100% (1)
- Solcon Catalog WebDocument12 pagesSolcon Catalog Webquocviet612No ratings yet
- Bio-Tank Guidelines for Indian RailwayDocument51 pagesBio-Tank Guidelines for Indian Railwayravi100% (2)
- Fitness WalkingDocument192 pagesFitness Walkingjha.sofcon5941100% (1)
- RTG E-One - Manual de Manutenção 41300-41303 (EN)Document328 pagesRTG E-One - Manual de Manutenção 41300-41303 (EN)Conrado Soares100% (1)
- Zygomatic Complex FracturesDocument128 pagesZygomatic Complex FracturesTarun KashyapNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Physical Properties of Refined Petroleum ProductsDocument36 pagesChemical and Physical Properties of Refined Petroleum Productskanakarao1No ratings yet
- InjectorDocument23 pagesInjectorBac Nguyen100% (1)
- Insects, Stings and BitesDocument5 pagesInsects, Stings and BitesHans Alfonso ThioritzNo ratings yet
- How To Become A Coffee Aficionado: Tips & Tricks: Kate Macdonnell Brewing Updated: Feb 06 2023Document17 pagesHow To Become A Coffee Aficionado: Tips & Tricks: Kate Macdonnell Brewing Updated: Feb 06 2023sadenaikeNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Part 1 CSIR JRF NET GATE DBT PDFDocument132 pagesLife Sciences Part 1 CSIR JRF NET GATE DBT PDFPavani Reddy68% (22)
- CHAPTER3 Foundations of Individual BehaviorDocument32 pagesCHAPTER3 Foundations of Individual BehaviorLynoj AbangNo ratings yet
- 57882d4608ae21394a0c7b00 PDFDocument574 pages57882d4608ae21394a0c7b00 PDFtualaNo ratings yet
- Strauss Dental Catalog 2013Document74 pagesStrauss Dental Catalog 2013d3xt3rokNo ratings yet
- of Types of Nuclear ReactorDocument33 pagesof Types of Nuclear Reactormandhir67% (3)