Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology (2010) May Paper 2
Uploaded by
JewelleCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology (2010) May Paper 2
Uploaded by
JewelleCopyright:
Available Formats
TESTCODE OI2O7O2O
FORM TP 2010040 MAY/JUNE 2O1O
CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS C OUNC IL
SECONDARY EDUCATION CERTIFICATE
EXAMINATION
BIOLOGY
Paper 02 - General Proficiency
2L hours
2
READ THE FOLLOWING DIRECTIONS CAREFULLY.
1. ThispaperconsistsofSlXquestionsintwosections.AnswerAllquestions.
2. For Section A, write your answers in the spaces provided in this booklet.
3. For Section B, write your answers in the spaces provided at the end of
each question, in this booklet.
4. Where appropriate, answers should be illustrated by diagrams.
DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO.
Copyright O 2008 Caribbean Examinations Council@.
All rights reservecl.
01207020tF 2010
-2-
AnswerALL questions.
Do NOT spend more than 30 minutes on Question 1.
1. In an experiment on the plant species illustrated in Figure 1, the part identified as X was tested
in several plants after they had grown in three different light intensities.
Figure 1.. A plant species
(a) Sets of three plants for each light intensity were tested for the following: starch,
reducing sugar, protein, oil.
(Ð In the space provided below construct a table to show how the data from the
experiment might be collected.
(5 marks)
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
0r207020tF 20ro
T
3-
(iÐ Explain why a sample of three plants was used for each test.
(2 marks)
(b) In the space provided below, draw a labelled diagram of the appåratus that can be
used in an experiment to illustrate that Part Z will take in water for use by Part Y (in
Figure 1 on page 2).
(4 marks)
(c) One function of the plant part shown at Y is storage. Identify ONE organ in the human
body that serves the same function.
(L mark )
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
oI207020tF 20IO
-4-
(d) Humans also carry out other functions similar to that shown by the plant species
represented at Figure 1, for example, respiration. In investigating respiration in a human
being and a plant, explain how you would demonstrate that the process carried out by
both organisms is the same.
(3 marks)
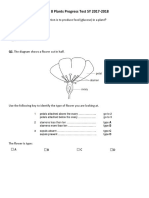
(e) Figure 2 represents the flower of the plant species shown in Figure 1.
Figure 2. Longitudinal section through the flower of the plant species
(Ð On the diagram in Fi gure2,label the following parts using the symbols indicated:
r p for the place where pollen is produced
r Q for the place that houses the ovum
o $ where pollen is deposited (3 marks)
(iÐ Suggest how this flower might be pollinated. Explain your answer.
(3 marks)
(Ð Some plant storage organs give rise to offspring. Suggest TV/O advantages to the plant
of having a storage organ that gives rise to both offspring and flowers.
(4 marks)
Total25 marks
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
01207020tF 20ro
a
-5-
) In an experiment on germinating seedlings, a group of Biology students made the drawings
shown in Figure 3 to illustrate the changes over a five-day period.
Figure 3. Stages in a germinating seedling
(a) Label on the drawing in Figure 3, THREE parts of the seedling shown on Day 5.
(3 marks)
(b) Outline the changes that took place in the seed to allow the development shown in
Figure 3.
(3 marks)
(c) (Ð The development shown by the seedling is a type of 'movement'. What is the
name given to this type of movement?
(1mark )
(iÐ State TWO ways in which the movement shown by the seedling differs from
that of an earthworm moving through its burrow.
(4 marks)
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
o1207020tF 2010
-6-
(d) (Ð rdentify TWo physicat factors that can cause an eârthworm to
move deeper into
its burrow.
(2 marks)
(iÐ Explain why moving deeper into its burrow is important to the earthworm.
(2 marks)
Total L5 marks
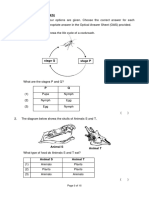
3. Figure 4 shows a terrestrial food web.
Ocelot 1\
/
rty)ner nira
Sq uirrel
,/\
/r
Caterpillar \
Ig uana
1
T,/
cr".rr,opp..
\
Plant materials,
letve$, frtrits, seeds
Figure 4. Terrestrial food web
(a) Identify, from the food we-b shown in Figure 4, a food chain with FoLrR
trophie levels,
Draw the food chain in the spaee provided below.
(5 marks)
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
onaTg2nfF 2070
1
7-
(b) (Ð Identify, from the food web in Figure 4, ONE predator and ONE organism which
is likely to be its prey.
(2 marks)
(iÐ Identify TWO characteristics that will differentiate the predator population from
that of the prey.
(4 marks)
(c) (Ð Apart from predator/prey, identify ONE other relationship that may exist in a
food web, and provide an example.
(2 marks)
(ü) Give ONE advantage of having speeial relationships among organisms in a food
web.
(2 marks)
Total 15 marks
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
01207Q20fF 20rO
-8-
SECTTON B
AnswerALL questions.
write your ans\ilers in the spaces provided at the end of each question.
4. (a) (Ð Identify, with the aid of diagrams, the main stages in the life history of a narlçd
insect vector of disease.
(iÐ Explain how EACH srage in rhe life hisrory of the insecr you idenrified at (a)(i)
might be controlled to keep the vector popuration in check. (9 marks)
(b) (Ð Some sexually transmitted infections are caused by viruses and have been found
to be without cure. Explain why viral infections are usually very difficult, if not
impossible, to cure.
(iÐ Apart from the nature of the AIDS virus, what orFrER factors make the control
of this disease very difficult? (6 marks)
Total 15 marks
Space for diagrams
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
01207020tF 2010
- 11 -
5. (a) (Ð How is it possible for plants that have identical genetic make-up to show
differences?
(iÐ Suggest why it is sometimes necessary to breed plants with the same genetic
make-up.
(iiÐ Give ONE disadvantage of breeding an identical population of organisms.
(5 marks)
(b) When breeding programmes are deliberately used to control the characteristics of a
population of organisms, the process is called artificial selection.
Explain how this process is different from natural selection. (4 marks)
(c) (Ð Genetic engineering is a modern biological technology that has been used to
change the characteristics of certain organisms.
How does genetic engineering differ from artificial selection?
(iÐ Suggest TWO concerns people might have about using genetic engineering to
alter characteristics of organisms. (6 marks)
Total L5 marks
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
0t2070201F 2010
-14-
6. (a) (Ð With the aid of a diagram, explain how the hind limb in humans allows for
movement from one place to another.
(iÐ Give THREE advantages to humans of their ability to move from one place to
another. (9 marks)
(b) Flowering plants are usually anchored to one spot but both their gametes and seeds need
to be distributed or dispersed from one place to another.
(Ð Identify TWO means by which seeds are dispersed.
(iÐ Explain how any TV/O characteristics of a seed may be adapted for dispersal.
(6 marks)
Total L5 marks
Space for diagram
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
0t207020tF 20ro
You might also like
- Psle 2017Document36 pagesPsle 2017HanTeong57% (7)
- Grade 8 Plants Progress Test ReviewDocument16 pagesGrade 8 Plants Progress Test Reviewpixelhobo100% (1)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Appointment Letter Staff Nurse Job DescriptionDocument3 pagesAppointment Letter Staff Nurse Job DescriptionRenita ChrisNo ratings yet
- 2017 PSLE ScienceDocument43 pages2017 PSLE ScienceLily ColeNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology January 2007 P3Document4 pagesCSEC Biology January 2007 P3Makayla AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Perineal Care Procedure GuideDocument2 pagesPerineal Care Procedure GuideAlhadzra AlihNo ratings yet
- Will The Real SMART Goals Please Stand Up?: Robert S. Rubin Saint Louis UniversityDocument2 pagesWill The Real SMART Goals Please Stand Up?: Robert S. Rubin Saint Louis UniversityKyoko TakayanagiNo ratings yet
- June 2009 p2Document18 pagesJune 2009 p2Jada WilliamNo ratings yet
- Biology (2011) Jan Paper 2Document14 pagesBiology (2011) Jan Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology January 2006 P3Document4 pagesCSEC Biology January 2006 P3Cool things fuh schoolNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology June 2010 P2Document16 pagesCSEC Biology June 2010 P2Joy Boehmer100% (1)
- CAPE Biology 2010 U2 P2 PDFDocument19 pagesCAPE Biology 2010 U2 P2 PDFMarikaNo ratings yet
- HSB 2010 May-June P2 PDFDocument20 pagesHSB 2010 May-June P2 PDFA GOJONo ratings yet
- Bio 2023 Csec P2Document14 pagesBio 2023 Csec P2Amrita HarrilalNo ratings yet
- Csec HSB June 2007 p2Document17 pagesCsec HSB June 2007 p2Sachin BahadoorsinghNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology January 2009 P032Document10 pagesCSEC Biology January 2009 P032dd4f2ybpgzNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology June 2009 P2Document20 pagesCSEC Biology June 2009 P2Joy Boehmer50% (2)
- CSEC Biology January 2008 P2Document11 pagesCSEC Biology January 2008 P2Sheri-Ann AshmanNo ratings yet
- Biology 2010 U2 P2Document20 pagesBiology 2010 U2 P2Haylei And ChayilNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology January 2006 P042Document9 pagesCSEC Biology January 2006 P042Cool things fuh schoolNo ratings yet
- masegaDocument15 pagesmasegaMasega Daniel ManaliNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology January 2010 P2Document16 pagesCSEC Biology January 2010 P2kaitlynjagooNo ratings yet
- Csec HSB June 2006 p2Document13 pagesCsec HSB June 2006 p2Sachin BahadoorsinghNo ratings yet
- 2008 Biology CapeDocument13 pages2008 Biology CapeRuchi MarajhNo ratings yet
- PSLE Science 2012 Booklet ADocument24 pagesPSLE Science 2012 Booklet AVenetia TohNo ratings yet
- Biology f4t2 Pp3 MsDocument4 pagesBiology f4t2 Pp3 MssamuwelNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology January 2005 P042Document8 pagesCSEC Biology January 2005 P042Makayla AlexanderNo ratings yet
- PSLE Foundation ScienceDocument25 pagesPSLE Foundation ScienceNiladri ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- F3 - Bio - Final Exam - MCQs - For Ss - Final - 110526Document13 pagesF3 - Bio - Final Exam - MCQs - For Ss - Final - 110526jonas hoNo ratings yet
- CSEC Integrated Science June 2009 P2Document18 pagesCSEC Integrated Science June 2009 P2Sachin Bahadoorsingh0% (1)
- CAPE Biology 2003 U1 P1Document20 pagesCAPE Biology 2003 U1 P1Reshana SimonNo ratings yet
- Cape Biology 2004 U1 p2Document10 pagesCape Biology 2004 U1 p2rertwerNo ratings yet
- DSF 4 Biology P530 2Document3 pagesDSF 4 Biology P530 2Mwesigwa HannahNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology January 2008 P3Document4 pagesCSEC Biology January 2008 P3dd4f2ybpgzNo ratings yet
- CAPE Env. Science 2010 U1 P2Document15 pagesCAPE Env. Science 2010 U1 P2Christina Francis100% (1)
- E3 - Microorganisms and HumansDocument4 pagesE3 - Microorganisms and HumansBilly LamNo ratings yet
- PSLE Science 2013 Booklet ADocument20 pagesPSLE Science 2013 Booklet AVenetia TohNo ratings yet
- P5 Science SA1 2017 Henry Park Exam PapersDocument31 pagesP5 Science SA1 2017 Henry Park Exam Papersjanus.zhangNo ratings yet
- F1 End Term ExamsDocument86 pagesF1 End Term ExamsCyber Ishiara100% (3)
- First Term Organized Test Answer Sheets (2015/16) BiologyDocument4 pagesFirst Term Organized Test Answer Sheets (2015/16) BiologySharis LeeNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology January 2006 P2Document11 pagesCSEC Biology January 2006 P2Makayla AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Sce Year 4 Test PaperDocument4 pagesSce Year 4 Test PaperSangeetha SenappanNo ratings yet
- Annual Examination (2021–22) Subject – Science Class –VIIIDocument4 pagesAnnual Examination (2021–22) Subject – Science Class –VIIINiranjan KumawatNo ratings yet
- ExamsDocument7 pagesExamskulwayohana61No ratings yet
- ReseachDocument4 pagesReseachitangishaka alphonse100% (1)
- Evergreen - FDN Science - Prelim - 2020 - Booklet ADocument14 pagesEvergreen - FDN Science - Prelim - 2020 - Booklet AVenetia TohNo ratings yet
- Science Year 4 Assessment 2022 HOTS FinalDocument13 pagesScience Year 4 Assessment 2022 HOTS FinalHelwani IPGKTINo ratings yet
- Growth and DevelopmentDocument2 pagesGrowth and DevelopmentDenisNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology January 2015 P2Document20 pagesCSEC Biology January 2015 P2dd4f2ybpgzNo ratings yet
- Spec 2015 BiologyDocument21 pagesSpec 2015 BiologyEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- 2011 - Botany - Final YearDocument8 pages2011 - Botany - Final YearSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- UACE BIO PAPER TWO SET 4 2023-JusanDocument3 pagesUACE BIO PAPER TWO SET 4 2023-JusanCampbell OGENRWOTNo ratings yet
- F3 - Bio - Final Exam - MCQs - WT Ans - Final - 110526Document14 pagesF3 - Bio - Final Exam - MCQs - WT Ans - Final - 110526jonas hoNo ratings yet
- CAPE Env. Science 2012 U1 P2Document9 pagesCAPE Env. Science 2012 U1 P2Christina FrancisNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document12 pagesCH 10Olivia LinNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology January 2005 P3Document4 pagesCSEC Biology January 2005 P3Makayla AlexanderNo ratings yet
- CSEC Coordination Short Answer Exam QuestionDocument13 pagesCSEC Coordination Short Answer Exam QuestionTamicka BonnickNo ratings yet
- HKALE Ecology Question PaperDocument6 pagesHKALE Ecology Question PaperNeetenin NeeteninNo ratings yet
- Biology o Level Cells and Tissue Organisation QuestionsDocument11 pagesBiology o Level Cells and Tissue Organisation QuestionsTinah KianaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology June 2005 P2Document13 pagesCSEC Biology June 2005 P2Joy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemNo ratings yet
- Standard and Super-Resolution Bioimaging Data Analysis: A PrimerFrom EverandStandard and Super-Resolution Bioimaging Data Analysis: A PrimerNo ratings yet
- Spanish (2010) May Paper 2Document7 pagesSpanish (2010) May Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- Info Tech (2009) Jan Paper 2Document6 pagesInfo Tech (2009) Jan Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- Physics (2013) May Paper 2 PDFDocument19 pagesPhysics (2013) May Paper 2 PDFJewelleNo ratings yet
- Physics (2009) May Paper 2Document15 pagesPhysics (2009) May Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- Spanish (2009) May Paper 2Document7 pagesSpanish (2009) May Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (2010) May Paper 2Document15 pagesMathematics (2010) May Paper 2Jewelle100% (1)
- Physics (2010) May Paper 2Document12 pagesPhysics (2010) May Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- Spanish (2010) May Paper 1Document6 pagesSpanish (2010) May Paper 1Jewelle100% (1)
- Mathematics (2009) May Paper 2Document18 pagesMathematics (2009) May Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- Spanish (2009) May Paper 1Document6 pagesSpanish (2009) May Paper 1JewelleNo ratings yet
- CSECJanuary2013Physics SRDocument7 pagesCSECJanuary2013Physics SRcandy_kb17No ratings yet
- French (2009) May Paper 2Document8 pagesFrench (2009) May Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- Info Tech (2011) Jan Paper 3-2Document10 pagesInfo Tech (2011) Jan Paper 3-2JewelleNo ratings yet
- Physics (2011) Jan Paper 2Document16 pagesPhysics (2011) Jan Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- Info Tech (2010) Jan Paper 2 PDFDocument20 pagesInfo Tech (2010) Jan Paper 2 PDFJewelleNo ratings yet
- Info Tech (2009) Jan Paper 2Document6 pagesInfo Tech (2009) Jan Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- Info Tech (2011) Jan Paper 2Document9 pagesInfo Tech (2011) Jan Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- Form Caribbean Examinations Council: OI222O1ODocument6 pagesForm Caribbean Examinations Council: OI222O1OJewelleNo ratings yet
- Geography (2009) May Paper 2Document14 pagesGeography (2009) May Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- Geography (2010) May Paper 2Document11 pagesGeography (2010) May Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- French (2009) May Paper 1Document6 pagesFrench (2009) May Paper 1JewelleNo ratings yet
- French (2010) May Paper 2Document8 pagesFrench (2010) May Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- French (2010) May Paper 2Document8 pagesFrench (2010) May Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- File OrganizationDocument17 pagesFile OrganizationRajesh MishraNo ratings yet
- French (2009) May Paper 1Document6 pagesFrench (2009) May Paper 1JewelleNo ratings yet
- French (2009) May Paper 2Document8 pagesFrench (2009) May Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- English A (2010) Jan Paper 2 PDFDocument7 pagesEnglish A (2010) Jan Paper 2 PDFJewelleNo ratings yet
- English A (2010) May Paper 2Document8 pagesEnglish A (2010) May Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- Form Caribbean Examinations Council: OI222O1ODocument6 pagesForm Caribbean Examinations Council: OI222O1OJewelleNo ratings yet
- English A (2011) Jan Paper 2Document8 pagesEnglish A (2011) Jan Paper 2JewelleNo ratings yet
- Dutch FarmDocument104 pagesDutch Farmdoc_abdullahNo ratings yet
- Come Back To Your Senses Use Your Body: Psychologyt LsDocument1 pageCome Back To Your Senses Use Your Body: Psychologyt LsMarina Moran100% (1)
- Aire Acondicionado Mazda 3 2006Document2 pagesAire Acondicionado Mazda 3 2006Jhon ConnorNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Breathing Exercise On Reducing Pain Perception and State Anxiety Among Primi ParturientsDocument8 pagesEffectiveness of Breathing Exercise On Reducing Pain Perception and State Anxiety Among Primi ParturientsPutra SpNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Drinking Water Quality Parameters (A Case Study of Hanumangarh Town)Document8 pagesAnalysis of Drinking Water Quality Parameters (A Case Study of Hanumangarh Town)Editor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Economic Case for Immobilizing EnzymesDocument25 pagesEconomic Case for Immobilizing EnzymesNikki ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Halal Policy PDFDocument1 pageHalal Policy PDFSaid SaidiNo ratings yet
- Different Surgical Modalities For Management of Postburn FL Exion Contracture of The ElbowDocument6 pagesDifferent Surgical Modalities For Management of Postburn FL Exion Contracture of The ElbowMadhuchandra HirehalliNo ratings yet
- Indian Medical Tourism Industry: A Pathway For The Healthy Future of IndiaDocument13 pagesIndian Medical Tourism Industry: A Pathway For The Healthy Future of IndiaPranjal MaluNo ratings yet
- Accessibility POC: October 26, 2017Document7 pagesAccessibility POC: October 26, 2017Ramesh BodukaniNo ratings yet
- Girl Scouts ActivitiesDocument5 pagesGirl Scouts ActivitiessluttybitchNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Units 8 12Document29 pagesChemistry Units 8 12reg speckNo ratings yet
- How To Judge A Dasha in JyotishDocument2 pagesHow To Judge A Dasha in JyotishRavan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fermentation Technology for Food Preservation and ProcessingDocument47 pagesFermentation Technology for Food Preservation and ProcessingAhmad Syamil Muhamad ZinNo ratings yet
- Yoga & Diet To Prevent DepressionDocument5 pagesYoga & Diet To Prevent DepressionDietician Mrunmayee DixitNo ratings yet
- Counter-pressure filler valve for beveragesDocument3 pagesCounter-pressure filler valve for beveragesbimalishaNo ratings yet
- Micro Bio Disease ListDocument168 pagesMicro Bio Disease Listspiff spacemanNo ratings yet
- DILEM 10 G (24VDC) MoellerDocument7 pagesDILEM 10 G (24VDC) MoellerElizabeth RamirezNo ratings yet
- WorkbookEdition 12 A Theory of HumorismDocument4 pagesWorkbookEdition 12 A Theory of HumorismMabel Ferr50% (2)
- General Psychology Mid Term ExamDocument2 pagesGeneral Psychology Mid Term Examapi-534780597No ratings yet
- Schlumber: Kevin: 16010072 Moch Rizky Setiawan: 16010068Document12 pagesSchlumber: Kevin: 16010072 Moch Rizky Setiawan: 16010068KevinNo ratings yet
- Cereal Based Functional BeveragesDocument7 pagesCereal Based Functional BeveragesCorina ParicanazaNo ratings yet
- Fuente As-IDocument4 pagesFuente As-IadalaviNo ratings yet
- RMD - Lightmix Modular CE IVD Assay BrochureDocument4 pagesRMD - Lightmix Modular CE IVD Assay BrochureDummy Tester JrNo ratings yet
- Impact of Excessive Mobile Phone Usage On Human JCSB 1000235Document5 pagesImpact of Excessive Mobile Phone Usage On Human JCSB 1000235nidNo ratings yet
- LC Used in ProteimicsDocument15 pagesLC Used in ProteimicsMandu ManNo ratings yet
- SWRO-200C Operation Manual AppendicesDocument38 pagesSWRO-200C Operation Manual AppendicestonbaldinNo ratings yet