Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The 4 Types of Thinking Skills, Explained! (2020) PDF
Uploaded by
ishmal khanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The 4 Types of Thinking Skills, Explained! (2020) PDF
Uploaded by
ishmal khanCopyright:
Available Formats
Ad
Start Here Topics
Create Magical Swirls
OPEN
About The Helpful
Professor
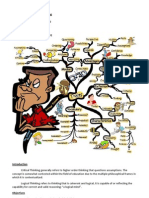
The 4 Types of
Thinking Skills,
Explained! (2020)
This website explores academic
topics for teachers and college
students. We adhere to strict
Definition of Thinking
editorial rules. Our writers are
PhD-level academics who are not
Skills paid for contributions. We are
strictly against academic cheating,
Thinking skills are the mental process involved in processing
including plagiarism and
information. There are four types of thinking skills: convergent or
collusion.
analytical thinking, divergent thinking, critical thinking and creative
thinking. We use these skills to help us understand the world
around us, solve difficult problems and puzzles, make logical
choices and develop our own values and beliefs.
The 4 Types of Thinking
Skills
The 4 types of thinking skills are:
1. Convergent Analytical Thinking
Convergent
thinking is the
process of coming
up with the best
answer to a
question using our
memory, resources
around us, or logic.
This thinking skill
does not require significant creativity or lateral thinking strategies.
Instead, it uses very straightforward thought processes. A
convergent thinker simply needs to apply already established
procedures and memory recall to reach the ‘correct’ answer.
Convergent thinking is very commonly used for standardized and
multiple choice tests. These sorts of tests simply assess our
knowledge and ability to apply knowledge to simple and logical
situations.
The key elements required to be a skilled convergent thinker are:
speed, accuracy and logic.
2. Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking is the exact opposite of convergent thinking. It
involves coming up to solutions, paths forward or new ideas when
there is no single correct answer. Questions like “should I study to
become a doctor or a lawyer?” may not have a simple answer. You
might be good at both, and both options might bring you
happiness and a good life. So, which option should you choose?
To come up with solutions to questions without clear answers, you
need to break down the possibilities and analyze each part. You
might create a pros and cons list, a venn diagram or a table to lay
out your options and consider each one in turn.
We often encourage divergent thinking from a very young age. For
example, we encourage children to play or simply ‘be playful’ in
order to discover how their world is complex and full of possibility.
3. Critical Thinking
Critical thinking involves analyzing something in order to form a
judgement about it. A critical thinker does not take the
assumptions of a topic for granted. Instead, the thinkers ‘critiques’
what they are viewing using their available intellectual knowledge.
Critical thinkers can use three processes to develop critical insights
on a topic: deduction, induction and abduction.
Deduction is the process of drawing conclusions based on the
facts at hand. You have all the facts available to you to come to a
clear and unambiguous conclusion about a topic. For example, a
doctor does blood tests to determine if someone has a virus. The
blood tests come back positive, so we can deduce that you
definitely have that virus.
Induction is the process of drawing conclusions based on a
generalization. You don’t have all the exact information at hand.
However, you are aware of patterns, clues and a methodology that
can help you induce the answer For example, you come to the
doctor exhibiting a fever, sneezing and coughing. The doctor
doesn’t do tests, but they induce that you probably have influenza
because your symptoms are characteristic of someone with the flu.
Abduction involves coming to a conclusion that is the most likely
or logical based on the small amount of knowledge that you have.
You can’t be sure of the answer, but you can guess. For example,
you may see that a cat is on the roof. The most logical answer is
that the cat got up there by climbing a nearby tree and jumping
from it to the roof, but you can’t be sure.
4. Creative Thinking
Creative thinking involves thinking about a topic in unusual,
unconventional and alternative ways to generate new ideas about
an established topic. A creative thinker will try to address an issue
from a perspective that hasn’t been used before.
While creative thinking may appear illogical, it is in fact a great
driver of human development. Creative thinkers identify gaps in
marketplaces or new, easier, faster and better ways of doing things.
When a creative thinker comes up with a great new way of
approaching an issue, their new method can become the new
orthodoxy.
How to Maintain your
Thinking when School is
Over
You need to keep your mind active in order to maintain improve
your thinking skills. When I finished high school, I stopped thinking
mathematically. I stopped using calculus, trigonometry, geometry,
etc. in my daily life. Ten years on, my mathematical thinking is very
poor.
By contrast, I kept reading and writing in the ten years since
graduating high school. I am a much better creative and critical
thinker than I was when I was at high school. That’s because I
continued to exercise those parts of my mind on a regular basis.
Some ways to maintain your mind’s neural pathways include:
Doing Sudoku quizzes daily
Doing Crosswords daily
Reading a book per month
Completing mathematical quizzes regularly
Taking courses in community college
Doing brain exercise apps
How to Improve your
Thinking Skills
To improve your thinking skills, you need to go beyond just
maintaining your mind. You cannot just keep doing the same thing
day-in, day-out and expect to get better.
Instead, you need to exercise new parts of your brain by studying
regularly and keep creating new neural pathways in your mind. This
emphasizes the importance of education.
You always need to be thinking about things that are new and
difficult for you to understand.
The things that you learn need to be difficult. It’s through the
difficulty and discomfort in thinking that you are improving your
thinking. It’s just like going to the gym: no pain, no gain.
Some ways to improve your thinking include:
Taking college courses (or one of these alternatives) in
topics that you find very difficult
Taking classes in an online school
Learning using new learning strategies that make you
uncomfortable
Taking up new and diverse hobbies
The more you think, the better you will get at thinking. You’ll
become faster, more creative and overall better at thinking if you
practice and try out new strategies.
Tools to Help you Think
Better
There are also some tools that we call cognitive tools that help you
with your thinking skills. These tools don’t do the thinking for you,
but they help you with your thinking.
Thinking tools can help you think better by:
Helping you structure your thoughts
Giving you a blueprint or scaffold for finding new angles to
approach a topic
Providing prompts to move your thinking forward
Some tools that can help you think better include:
1. A Brainstorming Mind Map
A brainstorming mind map can be made with a simple piece of
paper. Simply write the topic at the top of the piece of paper and
scrawl any and all key things you can think about down onto the
paper.
During the brainstorming process, no ideas are bad ideas. You can
critique and dismiss some of your ideas later on; but the
brainstorming session can help get your mind moving.
2. A Radar Chart
A radar (or spider) chart is very similar to a brainstorming mind
map, but it also shows the links between concepts.
To create a spider chart, write the topic you’re thinking about in the
middle of the piece of paper.
When you come up with a new idea, write it near the middle of the
paper and draw a line from the topic in the center to the idea. If
you come up with new ideas or sub-ideas based on that first key
idea, you can write them down and draw a line from one idea to
the other. Whenever you come up with related ideas, you should
draw a line between them to show their relationship.
3. A Process Chart
A process chart shows the sequence of steps from a question to its
logical answer. Often in science and mathematics classes, you need
to provide your process chart to your teacher to show how you
came to your conclusions. You may hear your teacher tell you to
“show your thinking”!
4. A Spreadsheet
Even a simple spreadsheet using Excel or Google Sheets can help
with your thinking. It will help you lay out ideas into an easy-to-
read table to help you keep track of your thoughts, your processes
and your different categories. Categorizing ideas into columns and
rows can help you to identify new patterns in data.
5. A Pros and Cons List
A simple pros and cons list can help you to get your ideas out of
your brain and onto paper. Once it’s on paper, you can go through
the list systematically and compare the pros and cons directly with
one another. Once you’ve done this, you may have a better idea of
what conclusions to come to.
6. De Bono’s Six Thinking Hats
Another strategy for helping your thinking is to use De Bono’s Six
Thinking Hats. These are six metaphorical ‘hats’ that you can put
on. Each hat represents a different way to look at a topic. When you
‘put the hat on’, you have to think from the perspective of the hat.
The six hats are:
Red Hat: Think about your feelings, emotions and hunches
about a topic
White Hat: Think about the information that’s available to
you and what it can reveal about the topic
Yellow Hat: Think about the benefits and value in the
situation you’re thinking about.
Black Hat: Think about the risks, difficulties and challenges
that a situation you’re thinking about may cause.
Green Hat: Think about the alternatives and creative
approaches you can apply to a topic.
Blue Hat: Think about the processes you can use and how
to manage the situation logically.
Final Thoughts
Thinking skills are necessary for getting along in life. They help you
do your job better, make smart decisions, and improve your own
life. You can classify your thinking skills into: convergent, divergent,
critical and creative skills. You could also use strategies such as De
Bono’s thinking hats, a pros and cons list or a process chart to help
you think.
Make sure you keep your mind active, try new things and do
quizzes to maintain your thinking skills throughout your life.
← Previous Post Next Post →
Privacy Policy Copyright © 2020 Helpful Professor
Terms of use
All the advice on this site is general in nature. Seek
Disclaimer: As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases. professional input on your specific circumstances. Students
should always cross-check any information on this site with
their course teacher.
You might also like
- Critical Thinking The Power To Think BeyondDocument27 pagesCritical Thinking The Power To Think Beyondanon_18159672167% (6)
- Critical ThinkingDocument34 pagesCritical ThinkingMarianne ElemosNo ratings yet
- LP Enttrep Mind 040052Document35 pagesLP Enttrep Mind 040052Analiz Irene CabagoNo ratings yet
- 5 Important Critical Thinking Skills To Master For StudentsDocument81 pages5 Important Critical Thinking Skills To Master For Students117. godlief erwin semuel migeNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument22 pagesCritical Thinkingotu kj50% (2)
- SBFS1103 Thinking Skills & Problem Solving c2017 1-2Document47 pagesSBFS1103 Thinking Skills & Problem Solving c2017 1-2Kakra Kirk-MensahNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Jemna PitogoDocument33 pagesPrepared By: Jemna PitogoJemna Ursal PitogoNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking: The Skills and Psychology of Questioning the ObviousFrom EverandCritical Thinking: The Skills and Psychology of Questioning the ObviousRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- 81 Fun Critical Thinking Activities PDFDocument7 pages81 Fun Critical Thinking Activities PDFNgọc Vũ NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Looking Thinking Classroom What Critical Thinking?: InonaDocument2 pagesLooking Thinking Classroom What Critical Thinking?: InonaMarcia PattersonNo ratings yet
- Creative and CriticalDocument11 pagesCreative and Criticalaries_rupaliNo ratings yet
- EDUCATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY THINKINGDocument6 pagesEDUCATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY THINKINGAreeba asgharNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking in Education: Activities and PerspectivesDocument29 pagesCritical Thinking in Education: Activities and PerspectivesGayathri deviNo ratings yet
- Conditions of Contract For: ConstructionDocument30 pagesConditions of Contract For: Constructionvladimir100% (2)
- Smu02b v300r002c02 User Manual 02Document248 pagesSmu02b v300r002c02 User Manual 02Jaime Andres Niño100% (2)
- Critical Thinking, Active Reading and Effective WritiveDocument15 pagesCritical Thinking, Active Reading and Effective Writiveterry505175% (4)
- Places of ArticulationDocument44 pagesPlaces of ArticulationYasser Mohammed Hamid AlrefaeeNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Current PDFDocument32 pagesMagnetic Effects of Current PDFAdarshNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking and Decision MakingDocument30 pagesCritical Thinking and Decision MakingmOHAN.S100% (2)
- Work Permit ManualDocument20 pagesWork Permit ManualRoni EnjelaniNo ratings yet
- Critical, Strategic and Intuitive Thinking Module PDFDocument16 pagesCritical, Strategic and Intuitive Thinking Module PDFJaycee Villaluz100% (1)
- Critical Thinking Word - Foundation5Document73 pagesCritical Thinking Word - Foundation5Saraswati Learning Center SLCNo ratings yet
- 48 Critical Thinking QuestionsDocument10 pages48 Critical Thinking QuestionsZady ZalexxNo ratings yet
- Success Factors For Augmented Reality Business ModelsDocument36 pagesSuccess Factors For Augmented Reality Business ModelsAsutosh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking: The Concept and Power of Thinking CriticallyFrom EverandCritical Thinking: The Concept and Power of Thinking CriticallyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Imam Mahdi and Jesus Christ - 2023 ADDocument290 pagesImam Mahdi and Jesus Christ - 2023 ADSyed AbidiNo ratings yet
- Samsung Mobile: Market Share & Profitability in SmartphonesDocument15 pagesSamsung Mobile: Market Share & Profitability in SmartphonesTanmay WadhwaNo ratings yet
- Inglés AddesDocument16 pagesInglés AddesLucia JhoselynNo ratings yet
- CCT-Module Chapter-12 AngadananDocument62 pagesCCT-Module Chapter-12 AngadananRizette PaloganNo ratings yet
- Ej 1143316Document4 pagesEj 1143316Victor CantuárioNo ratings yet
- Crititcal Thinking - Robert PalDocument9 pagesCrititcal Thinking - Robert PalPalutziNo ratings yet
- Make Notes of Special and Important Points Regarding Definition of Critical Thinking As A Subject of Study and An Action To Learn in The Skills.Document11 pagesMake Notes of Special and Important Points Regarding Definition of Critical Thinking As A Subject of Study and An Action To Learn in The Skills.chanchal shahiNo ratings yet
- Module - 6 Thinking and Concept FormationDocument62 pagesModule - 6 Thinking and Concept Formationguptaa.akhillNo ratings yet
- BA Sem II Cognitive Psychology SLM-Module 3Document15 pagesBA Sem II Cognitive Psychology SLM-Module 3GPRNo ratings yet
- InteDocument30 pagesInteJayNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking and CreativityDocument6 pagesCritical Thinking and CreativityEl ghiate IbtissameNo ratings yet
- THINKINGDocument23 pagesTHINKINGLouis SpencerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Problem Solving in The Information Age: Lesson 1 - New Learning Skills 2Document8 pagesIntroduction To Problem Solving in The Information Age: Lesson 1 - New Learning Skills 2hayleykhoNo ratings yet
- 3 Mat Paket 2 Contoh Soal PembahasanDocument14 pages3 Mat Paket 2 Contoh Soal PembahasanMuhammad Misbakhul AbidNo ratings yet
- Thinking SkillsDocument3 pagesThinking SkillspaddybadriNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking SampleDocument26 pagesCritical Thinking SampleMarvin MoffattNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Reflective Writing and Critical Thinking, Educational PlatformDocument44 pagesUnit 1 Reflective Writing and Critical Thinking, Educational PlatformUmarNo ratings yet
- A3 - 3Q - Trends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21st CenturyDocument3 pagesA3 - 3Q - Trends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21st CenturySheina VillarozaNo ratings yet
- Thinking SkillsDocument10 pagesThinking SkillsIshika Rajesh ShahuNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Leticia S. Ong: Title: Logical and Critical ThinkingDocument3 pagesSubmitted By: Leticia S. Ong: Title: Logical and Critical ThinkingDanille Ivan OngNo ratings yet
- English 4 TerjemahanDocument7 pagesEnglish 4 TerjemahanSandra DewiNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking: Dr. Merry Indah Sari, M.Med - Ed Bagian Pendidikan Kedokteran Fakultas Kedokteran UnilaDocument17 pagesCritical Thinking: Dr. Merry Indah Sari, M.Med - Ed Bagian Pendidikan Kedokteran Fakultas Kedokteran Unilaikhlas taufikNo ratings yet
- Types of Knowledge & Thinking SkillsDocument2 pagesTypes of Knowledge & Thinking SkillsArchie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- Experience Psychology 2nd Edition King Solutions Manual DownloadDocument22 pagesExperience Psychology 2nd Edition King Solutions Manual DownloadEliza Webb100% (29)
- CRITICAL THINKING AND OTHER TYPES OF THINKINGDocument32 pagesCRITICAL THINKING AND OTHER TYPES OF THINKINGvictor paquiulNo ratings yet
- Effective Questioning: West Lothian Council Educational Psychology ServiceDocument3 pagesEffective Questioning: West Lothian Council Educational Psychology ServiceTharun VinodNo ratings yet
- Types of Thinking FinalDocument15 pagesTypes of Thinking Finalasma mahmoodNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument59 pagesCritical ThinkingstpwebNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Cognition (Thinking and Intelligence) : - Thought and The BrainDocument61 pagesUnit 5: Cognition (Thinking and Intelligence) : - Thought and The BrainPuna Ram GhimireNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Process of Learning M.Ed.Document40 pagesUnderstanding The Process of Learning M.Ed.arunNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Development: A Stage Theory: With Implications For InstructionDocument8 pagesCritical Thinking Development: A Stage Theory: With Implications For InstructionNitigya ThakurNo ratings yet
- CAJUCOM - 033123 - Guiding Principles in The Selection and Organization of Subject Matter ContentDocument25 pagesCAJUCOM - 033123 - Guiding Principles in The Selection and Organization of Subject Matter ContentEILEEN MAY CAJUCOMNo ratings yet
- Final Presentation Int 322 Jada BrownDocument15 pagesFinal Presentation Int 322 Jada Brownapi-248118605No ratings yet
- Critical and Creative ThinkingDocument10 pagesCritical and Creative Thinkingyurvan3011No ratings yet
- Increase Students' Critical Thinking SkillsDocument10 pagesIncrease Students' Critical Thinking SkillsFlash BakerNo ratings yet
- Understanding local networks through strategic analysis and intuitive thinkingDocument8 pagesUnderstanding local networks through strategic analysis and intuitive thinkingRaymond ZafraNo ratings yet
- Research Paper - Creative ThinkingDocument5 pagesResearch Paper - Creative ThinkingvaradsanketNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document7 pagesModule 4NorhaidaNo ratings yet
- TNCT Module 2 Week 3Document5 pagesTNCT Module 2 Week 3Jocel CalugayNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Skills Are EssentialDocument8 pagesCritical Thinking Skills Are EssentialSarah NaderNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Thinking SkillsDocument22 pagesCognitive Thinking SkillsAjay J. VERMANo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking: Critical Thinking... The Awakening of The Intellect To The Study of ItselfDocument11 pagesCritical Thinking: Critical Thinking... The Awakening of The Intellect To The Study of ItselfLeonard Ruiz100% (1)
- Defining Critical ThinkingDocument5 pagesDefining Critical ThinkingDanNo ratings yet
- 1: The Lifetime of Electric Bulbs.: Let X Be Random Variable Having Values 25,15,18,20,20,12,9,16,15,30 Prove ThatDocument2 pages1: The Lifetime of Electric Bulbs.: Let X Be Random Variable Having Values 25,15,18,20,20,12,9,16,15,30 Prove Thatishmal khanNo ratings yet
- International Islamic University, Islamabad. Faculty of Management Sciences Spring 2020, Midterm ExamDocument1 pageInternational Islamic University, Islamabad. Faculty of Management Sciences Spring 2020, Midterm Examishmal khanNo ratings yet
- Macro Sample Course - Answer-BookletDocument25 pagesMacro Sample Course - Answer-Bookletishmal khanNo ratings yet
- 1: The Lifetime of Electric Bulbs.: Let X Be Random Variable Having Values 25,15,18,20,20,12,9,16,15,30 Prove ThatDocument2 pages1: The Lifetime of Electric Bulbs.: Let X Be Random Variable Having Values 25,15,18,20,20,12,9,16,15,30 Prove Thatishmal khanNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument3 pagesFinalishmal khanNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument3 pagesCourse Outlineishmal khanNo ratings yet
- Case Study Creative 1Document4 pagesCase Study Creative 1ishmal khanNo ratings yet
- C.T Group Assignment Bba 40 (B) PDFDocument23 pagesC.T Group Assignment Bba 40 (B) PDFishmal khanNo ratings yet
- Creative Thinking and Reasoning Course OutlineDocument3 pagesCreative Thinking and Reasoning Course Outlineishmal khanNo ratings yet
- Case Study Creative 1Document4 pagesCase Study Creative 1ishmal khanNo ratings yet
- Name: Ishmal Khan. Reg No. 5663-FMS/BBA/S19. Batch: Bba-40A Mid-Term. Introduction To PhilosophyDocument1 pageName: Ishmal Khan. Reg No. 5663-FMS/BBA/S19. Batch: Bba-40A Mid-Term. Introduction To Philosophyishmal khanNo ratings yet
- Creative Thinking and Reasoning Course OutlineDocument3 pagesCreative Thinking and Reasoning Course Outlineishmal khanNo ratings yet
- Case Study Creative 1Document4 pagesCase Study Creative 1ishmal khanNo ratings yet
- Handle Unemployment in Pakistan Through New Jobs and Education FundingDocument20 pagesHandle Unemployment in Pakistan Through New Jobs and Education Fundingishmal khanNo ratings yet
- Breakfast by John SteinbeckDocument5 pagesBreakfast by John Steinbeckishmal khanNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument16 pagesReportishmal khanNo ratings yet
- Organizational CultureDocument34 pagesOrganizational Cultureishmal khanNo ratings yet
- BBADocument2 pagesBBAishmal khanNo ratings yet
- Narcissism and Psychopathy FREE Guides To IssuesDocument4 pagesNarcissism and Psychopathy FREE Guides To Issueszadanliran100% (1)
- 5 Steps From Survey To Revenue InfographicDocument1 page5 Steps From Survey To Revenue InfographicBayCreativeNo ratings yet
- 3ABN World 2016 11LDocument27 pages3ABN World 2016 11LjavierNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary 3Document3 pagesVocabulary 3borahae 3000No ratings yet
- Dawn Ullmann - ReferenceDocument1 pageDawn Ullmann - Referenceapi-418750957No ratings yet
- HEIRS OF BATORI v. REGISTER OF DEEDS OF BENGUETDocument12 pagesHEIRS OF BATORI v. REGISTER OF DEEDS OF BENGUETFaustina del RosarioNo ratings yet
- A Bibliometric Analysis of Creativity in The Field of Business EconomicsDocument9 pagesA Bibliometric Analysis of Creativity in The Field of Business EconomicsDanielaNo ratings yet
- Area Under The Curve & Differential Equation: Theory and Exercise BookletDocument8 pagesArea Under The Curve & Differential Equation: Theory and Exercise BookletEr. Narender SinghNo ratings yet
- Concepts of TeachingDocument3 pagesConcepts of TeachingMoises Embalzado Bacus Jr.No ratings yet
- Kristeva and Feral - China, Women and The Symbolic - An Interview With Julia KristevaDocument11 pagesKristeva and Feral - China, Women and The Symbolic - An Interview With Julia KristevaLady MosadNo ratings yet
- Beyond The Wall - The Village Hero Character PlaybookDocument4 pagesBeyond The Wall - The Village Hero Character Playbookmagic_fyodorNo ratings yet
- The Innovator's Secret WeaponDocument9 pagesThe Innovator's Secret WeaponNaval VaswaniNo ratings yet
- Written Assignment Week 4Document5 pagesWritten Assignment Week 4Thai50% (2)
- 028 - Chapter 6 - L20 PDFDocument11 pages028 - Chapter 6 - L20 PDFRevathiNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab: Ahnaf Habib Khan 40079665 TJ-XDocument2 pagesPre-Lab: Ahnaf Habib Khan 40079665 TJ-XAhnafHabibKhanNo ratings yet
- Math 7 - Week 2 SummativeDocument1 pageMath 7 - Week 2 SummativeBrian Mary0% (1)
- Gomez FL Bar Complaint v. PerezDocument6 pagesGomez FL Bar Complaint v. PerezJudgeHSNo ratings yet
- Book of AbstractsDocument156 pagesBook of Abstractsdragance106No ratings yet
- ECKHOFF, Hanne & Dag Haug - Aspect and Prefixation in Old Church Slavonic PDFDocument45 pagesECKHOFF, Hanne & Dag Haug - Aspect and Prefixation in Old Church Slavonic PDFaurimiaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Jur ErbrinkDocument245 pagesThesis Jur Erbrinkgmb09140No ratings yet
- Ogham Gematria - Drawing Sephiroth6Document4 pagesOgham Gematria - Drawing Sephiroth6Simon StacheNo ratings yet
- PI2016 - Geotechnical Characterization of Clearwater Shales For DesignDocument8 pagesPI2016 - Geotechnical Characterization of Clearwater Shales For DesignmauricioNo ratings yet