0% found this document useful (0 votes)
114 views1 pageRouth-Hurwitz Criterion Special Cases Guide
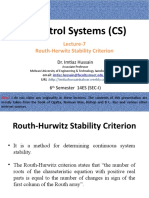
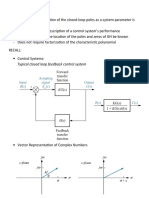
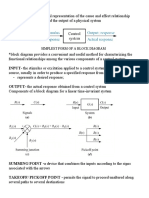
The document discusses two special cases of the Routh-Hurwitz criterion for determining stability of a system. The first case is when there is a zero only in the first column of a row. This is handled by replacing the zero with an epsilon and taking the limit as epsilon approaches zero. The second case is when there is an entire row of zeros. This is handled by differentiating the polynomial of the previous row and using the coefficients to replace the row of zeros. Two examples are provided to illustrate these cases.
Uploaded by
athenalavegaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
114 views1 pageRouth-Hurwitz Criterion Special Cases Guide
The document discusses two special cases of the Routh-Hurwitz criterion for determining stability of a system. The first case is when there is a zero only in the first column of a row. This is handled by replacing the zero with an epsilon and taking the limit as epsilon approaches zero. The second case is when there is an entire row of zeros. This is handled by differentiating the polynomial of the previous row and using the coefficients to replace the row of zeros. Two examples are provided to illustrate these cases.
Uploaded by
athenalavegaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd