Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignments Machine Tool Design
Uploaded by
abdullah 3mar abou reashaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignments Machine Tool Design
Uploaded by
abdullah 3mar abou reashaCopyright:
Available Formats
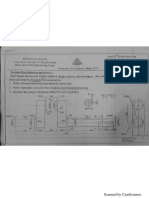
Benha University 4th Year Production (2019/2020)
Shoubra Faculty of Engineering Design of Machining and Forming
Mechanical Engineering Department Machine Tool
Assignment (1) Principles of Machine Tools
1. Illustrate graphically the main (working) and the auxiliary motions in some of machine
tools, (center lathe, milling, drilling, Shaping, grinding…)
2. What are the factors influence machine tool designs?
3. Why is it important to connect the electric motor and the machine tool by means of a belt
drive?
4. Determine the rpm of a lathe spindle if a work piece of diameter 100 mm is to be turned
at a cutting speed of 88 m/min.
5. A 175 mm long work piece is to be machined on a shaper which has a cutting stroke to
idle stroke velocity ratio of 0.85. Calculate the strokes/min of the shaping tool if the
cutting speed is 30 m min. Assume an approach and overshoot of 5 mm.
6. Find the forces needed to cut a steel work piece of diameter 200 mm, feed 3 mm/rev,
depth of cut 2mm at 100 m/min cutting speed, Then calculate the necessary power of the
motor of this machine tool if the total mechanical efficiency is taken 80%. Specific cutting
resistance is 8500 kg/cm2.
7. For a Center Lathe, it is required to calculate precisely the needed motor power. Given
the diameter of work-piece is 80 mm turned at 600 spindle rpm. The total mechanical
efficiency is 0.8. The feed is 0.2 mm/rev in the axial direction and no feed in the radial
direction. The tangential, radial and axial components of the cutting force were measured
on a dynamometer and found to be 3000, 800, and 1000 N respectively. Comment on
your result.
8. A 120 mm diameter work piece is being turned on a lathe at 400 rpm and a feed of 3
mm/rev. The tangential, radial, and axial components of the cutting force were measured
on a dynamometer and found to be 3250, 1200, and 1300 N respectively. Calculate the
power rating of the motor assuming a coefficient of efficiency of 0.85 for the drive.
9. For a lathe with the following specifications:
Min. Max.
Workpiece diameter (mm) 20 200
Feed rate (mm/rev) 0.3 3
Specific cutting pressure (kgf/mm2) 50 160
Depth of cut (mm) 0.1 2
Cutting speed (m/min) 20 100
Calculate the motor power rating. Draw a nomogram for different materials of workpiece
with reference to charts. Then determine the power requirements according to the
specifications given in the table above.
Dr. Gerges Edwar Mehanny Beshay
Benha University 4th Year Production (2019/2020)
Shoubra Faculty of Engineering Design of Machining and Forming
Mechanical Engineering Department Machine Tool
Assignment (2) Design of Gearbox
1. Draw the structural diagrams of a machine tool speed box for nmin = 44 rpm, nmax = 500
rpm in two stages and f = 1.41. Which layout is best and why?
2. It is required to design a gear box of 6 speeds, which satisfies the following specifications:
Maximum & minimum speeds: 710 & 125 rpm. Motor power = 10 kW at 1500 rpm. Draw
all possible structural diagrams and select the best one, then discuss why? Also draw a
layout of the gear box indicating the number of teeth of each gear and its module.
3. Draw the structural diagrams and layout for a machine tool gear box of a center lathe
satisfying the following conditions: Maximum cutting speed: 95 m/min. Minimum
cutting speed: 40 m/min. Maximum workpiece diameter: 200 mm. Minimum workpiece
diameter: 30 mm. Number of speeds: 9. Motor power: 7 kW at 1450 rpm. Find number
of teeth of each gear and the belt drive ratio.
4. Draw a structural diagram and layout for a gear box of a milling machine satisfying the
following conditions: Maximum cutting speed; 150 m/min. Minimum cutting speed: 40
m/min. Maximum cutter diameter: 350 mm. Minimum cutter diameter: 40 mm. Number
of speeds: 12. Motor power: 7 kW at 1450 rpm. Find number of teeth of each gear and
the belt drive ratio.
Standard spindle speeds and number of intervals for various values of φ:
Dr. Gerges Edwar Mehanny Beshay
Benha University 4th Year Production (2019/2020)
Shoubra Faculty of Engineering Design of Machining and Forming
Mechanical Engineering Department Machine Tool
6/17
3/17
6 7/10
Dr. Gerges Edwar Mehanny Beshay
Benha University 4th Year Production (2019/2020)
Shoubra Faculty of Engineering Design of Machining and Forming
Mechanical Engineering Department Machine Tool
Assignment (3) Design of Spindle
1. Calculate the cutting forces on a tungsten carbide tool when machining a 120 mm
diameter workpiece rotating at 400 rpm if the depth of cut is 2.5 mm and the feed rate is
1.1 mm/rev. Estimate the power required if the overall efficiency is 70% and the specific
cutting resistance is 7500 MPa. Calculate the spindle deflection in the direction of radial
component of the cutting force. Knowing that span length is 80 cm, overhang length is
30 cm, outer to inner diameter ratio is 2, radial to tangential force components ratio is 0.3,
bearings stiffness is 60000 kg/mm, and modulus of elasticity is 200 GPa.
2. While turning a 750 mm long workpiece of 100 mm diameter between centers, the radial
cutting force was found to be 1500 N when the tool was 200 mm from the tailstock.
Calculate the machine tool and system compliances if the stiffness of the saddle,
headstock and tailstock is 30000, 40000 and 25000 N/mm respectively.
3. Find the spindle diameters for the overhanging part, and the part between the antifriction
bearings, for the spindle shown in the figure. The spindle is powered by a 2.5 kW motor,
running at speeds ranging from 400 to 2400 rpm. The gear generates a radial separating
force of 1010 N. The spindle is subjected to fluctuating load and made of steel C45, the
permissible bending stress is 55 MPa. The reactive bending moment can be taken as 10%
of the bending moment due to overhanging load. You have to calculate the reactions,
draw S.F.D and B.M.D, then calculate the diameters. It is required to calculate the total
deflection at the nose of the spindle if the stiffness of the front and rear bearings are 100
and 65 N/μm respectively. (Dim mm)
180
450 120
4. A solid steel spindle transmits a torque of 40 kg.m through a gear of module 3 mm and
number of teeth of 80. The ratio a/b = 2 and compliances of front and rear bearings are
0.1 and 0.15 µm/kg respectively. Determine the optimum l/c ratio to ensure minimum
deflection of the spindle nose if force P1 = 150 kgf.
Dr. Gerges Edwar Mehanny Beshay
Benha University 4th Year Production (2019/2020)
Shoubra Faculty of Engineering Design of Machining and Forming
Mechanical Engineering Department Machine Tool
Assignment (4) Design of Guideways
1. Find the forces on flat guideways and the pressure between the saddle and guideways on
a lathe, if the guideways are 25 mm thick and 50 mm wide. The center distance between
the guideways is 400 mm. The machine has 110 mm height above the guideway top faces.
The machine is powered by 5.5 kW motor. The machine mostly shapes steel work pieces
at a speed 40m/min. The total frictional force Py is 30% of the cutting force Pz, the axial
force Px is 20% of the cutting force Pz, weight of the saddle is 500 N and its length is 250
mm. The maximum diameter of workpiece is 200 mm. Also, calculate the pulling force
Q, if the coefficient of friction between the slide ways and carriage is 0.2.
2. A center lathe has two flat cast iron slideways (figure 1) of equal width and height half
the width. While turning a 100 mm diameter workpiece, the tangential, radial, and axial
components of the cutting force were found to be 2.8, 1.25, and 1.18 kN respectively. The
lathe carriage weighs 1.5 kN and 300 mm long. Calculate the slideway width assuming
suitable values for affecting parameters. Knowing that the maximum pressure should not
exceed 0.8 MPa.
3. If the right-hand slideway in problem 1 is replaced by a non-symmetrical Vee guideway,
with angles α and β, with the horizontal faces of guideway "C", Find the forces between
surfaces A, B and C if α = 50°.
Dr. Gerges Edwar Mehanny Beshay
Benha University 4th Year Production (2019/2020)
Shoubra Faculty of Engineering Design of Machining and Forming
Mechanical Engineering Department Machine Tool
4. A parting operation is being done on a center lathe having a combination of V and flat
slideways as shown in figure 2. Calculate the d/b ratio at which the saddle will lift from
face “A”. Assume h/b = 0.5, α = 50o. The resultant cutting force makes an angle of 37o
with the vertical and apex angle of the V-shaped side is 90o.
5. For a center lathe guide-way with the following specifications: The front side has an
unsymmetrical V-shape with inclined angles α & β with the horizontal. The widths of
surfaces are 24 mm and 20 mm for α & β inclinations respectively. The rear side is a flat
shape with a width 18 mm. The front and rear sides are spaced by a distance of 400 mm
and the swing of the workpiece from the slideway is 300 mm. The length of the active
sliding part which carries the cutting tool is 250 mm. You are required to check the
suitability of the slideway for correct performance. If the tangential, and radial cutting
forces are 2800 & 1200 N respectively, and workpiece diameter is 120 mm.
Dr. Gerges Edwar Mehanny Beshay
Benha University 4th Year Production (2019/2020)
Shoubra Faculty of Engineering Design of Machining and Forming
Mechanical Engineering Department Machine Tool
Assignment (5) Design of Hydraulic Drives
1. Design a hydraulic circuit suitable for operating the table of a milling machine having the
following specifications: Motor power: 16 HP. Maximum and minimum diameters of the
cutter are: 250 & 60 mm. Maximum cutting speed: 120 m/min. Maximum feed rate: 0.5
mm/tooth. No. of teeth: 10. Material specific cutting resistance: 9800 kg/cm2
2. A hydraulic shaping machine is used to machine a workpiece material of specific cutting
resistance of 9600 kg/cm2. If the piston rod is made of steel with allowable operating
stress of 800 kg/cm2, and the maximum cutting speed is 10 m/min. Design the required
hydraulic system for operating the machine ram.
Dr. Gerges Edwar Mehanny Beshay
You might also like
- Design of Transmission Systems Question BankDocument10 pagesDesign of Transmission Systems Question BankDesejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Machine Tool Engineering DesignDocument34 pagesMachine Tool Engineering DesignAshok Kumar UppariNo ratings yet
- Computer Control of Manufacturing Systems Y KorenDocument9 pagesComputer Control of Manufacturing Systems Y Korenbhagat1030% (1)
- Cam Lab 1Document40 pagesCam Lab 1Madhusudhan Rao KNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 CNC Machine Tools: StructureDocument17 pagesUnit 3 CNC Machine Tools: StructureRohit GhulanavarNo ratings yet
- Design of Transmission System Question BankDocument18 pagesDesign of Transmission System Question BankAravind50% (2)
- Ch-11 NC CNC DNC FMS Automation and RoboticsDocument191 pagesCh-11 NC CNC DNC FMS Automation and RoboticsPrateek BayalNo ratings yet
- 4363 111 Machine Design IDocument6 pages4363 111 Machine Design Iyogesh_b_k100% (2)
- 1 Cad Cam Intro PDFDocument40 pages1 Cad Cam Intro PDFWesleyNo ratings yet
- Problems s2Document6 pagesProblems s2zangue billy jamesNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Unit 1 Design PhilosophyDocument12 pagesMachine Design Unit 1 Design PhilosophyAnand Babu100% (3)
- Cadcam Geometric ModelingDocument31 pagesCadcam Geometric ModelingPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Tool GBDocument39 pagesDesign of Machine Tool GBrahul bachuteNo ratings yet
- Limit and Fit Data BooDocument18 pagesLimit and Fit Data Booविशाल पुडासैनीNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Crankshaft With Different CompositeDocument9 pagesDesign and Analysis of Crankshaft With Different CompositeSAI CHARANNo ratings yet
- Internship Report FormatDocument2 pagesInternship Report FormatNati man100% (1)
- Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery Lab ManualDocument63 pagesKinematics and Dynamics of Machinery Lab ManualsaranNo ratings yet
- CAD-CAM Power Point PresentationDocument102 pagesCAD-CAM Power Point PresentationArgAshishGargNo ratings yet
- 3-Axis CNC Marble Cutting Machine Project ReportDocument84 pages3-Axis CNC Marble Cutting Machine Project ReportHammad Iftikhar HanifNo ratings yet
- c07 Catia v5r15 Transformation FeaturesDocument32 pagesc07 Catia v5r15 Transformation FeaturesNayefGhazaliNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Document2 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)jastraNo ratings yet
- Machine Design AssignmentDocument8 pagesMachine Design AssignmentSharthak GhoshNo ratings yet
- Mid Semester Exam Paper Contains 02 PagesDocument2 pagesMid Semester Exam Paper Contains 02 PagesBabuli KumarNo ratings yet
- Short Question Bank CADDocument3 pagesShort Question Bank CADnravin5No ratings yet
- Belt and Drive Analysis of Flour MillDocument16 pagesBelt and Drive Analysis of Flour Milllikhith saiNo ratings yet
- Design of Speed and Feed Gear BoxesDocument67 pagesDesign of Speed and Feed Gear BoxesBhotka BhutkiNo ratings yet
- ME 231 Computer Aided Machine DrawingDocument2 pagesME 231 Computer Aided Machine DrawingDeepakNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Element ProblemsDocument2 pagesDesign of Machine Element Problemsmaxpayne5550% (1)
- CNC Machines and Programming - CNC Lathe Tool Nose Radius CompensationDocument6 pagesCNC Machines and Programming - CNC Lathe Tool Nose Radius CompensationChanderprabh JainNo ratings yet
- Regenerative Braking SystemDocument34 pagesRegenerative Braking SystemJabiNo ratings yet
- Photochemical MachiningDocument9 pagesPhotochemical MachiningKAMALJEET SINGHNo ratings yet
- Ansys Lab ManualDocument87 pagesAnsys Lab Manualaravind174No ratings yet
- Question Bank Introduction To CAM: Noble Group of Institutions, JunagadhDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank Introduction To CAM: Noble Group of Institutions, JunagadhjanakNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines Experiments Student ManualDocument28 pagesTheory of Machines Experiments Student ManualHoneyNo ratings yet
- 2017HT30004 - Mechanical System Design - Assignment 2Document15 pages2017HT30004 - Mechanical System Design - Assignment 2Partha Pratim SarkarNo ratings yet
- CH 19Document21 pagesCH 19Sanjay Kumar100% (1)
- MT-II LAB ManualDocument44 pagesMT-II LAB ManualGANESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Bevel Gear - Force Analysis of Bevel GearDocument16 pagesBevel Gear - Force Analysis of Bevel GearRohit GhulanavarNo ratings yet
- Active Suspension System With Preview ControlDocument5 pagesActive Suspension System With Preview Controlrudey18No ratings yet
- Project Title ListDocument12 pagesProject Title ListShrishant PatilNo ratings yet
- Relationship between angle of twist, torque, length and diameterDocument6 pagesRelationship between angle of twist, torque, length and diameterAhsan MumtazNo ratings yet
- Numerical Control PDFDocument23 pagesNumerical Control PDFmishari67% (3)
- TRANSMISSION DESIGNDocument18 pagesTRANSMISSION DESIGNMURALI KRISHNAN RNo ratings yet
- Manual Part ProgrammingDocument38 pagesManual Part ProgrammingHot Shot100% (1)
- CAD important questions and tipsDocument5 pagesCAD important questions and tipsjeroldscdNo ratings yet
- Cad Lab Manual 2019-20Document71 pagesCad Lab Manual 2019-20Rambabu mokatiNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Gear Box TutorialDocument2 pagesMachine Design Gear Box TutorialRutvikLathia100% (1)
- Part-B1-Petrol Engine Connecting RodDocument5 pagesPart-B1-Petrol Engine Connecting RodN Dhanunjaya Rao BorraNo ratings yet
- 23 13 SA V1 S1 - CncmachinesassDocument4 pages23 13 SA V1 S1 - Cncmachinesassamulya68No ratings yet
- Course Outline Mechanics Machines ME3033Document4 pagesCourse Outline Mechanics Machines ME3033Mohammad Faraz AkhterNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Flanged Bolt CouplingDocument11 pages5.2 Flanged Bolt CouplingShayneBumatay0% (1)
- DME Lesson Plan As Per NBADocument3 pagesDME Lesson Plan As Per NBASabareesan Subramanian0% (1)
- Turning Parameters ExplainedDocument29 pagesTurning Parameters ExplainedMuhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- Creo Lab Project ReportDocument6 pagesCreo Lab Project ReportTanzeel M. SharifNo ratings yet
- Sheets - Sep 2013Document13 pagesSheets - Sep 2013Mohamed OsamaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial: Government Enginerring College, Valsad Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument12 pagesTutorial: Government Enginerring College, Valsad Mechanical Engineering DepartmentSURYA S96No ratings yet
- DMM-III Assignment TestDocument2 pagesDMM-III Assignment TestSaibabu SoloNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Shaft DesignDocument2 pagesAssignment On Shaft DesignRitesh SinghNo ratings yet
- نسخة من Final - ExamDocument2 pagesنسخة من Final - Examabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Value EngineeringDocument7 pagesValue Engineeringabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- LEC3 Lubrication 2021Document19 pagesLEC3 Lubrication 2021abdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- 2016 q6Document1 page2016 q6abdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- مسألة ٣Document7 pagesمسألة ٣abdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- مسألة ٤Document5 pagesمسألة ٤abdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Scan Doc by CamScannerDocument1 pageScan Doc by CamScannerabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Automatic ControlDocument26 pagesAdvanced Automatic Controlabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions 2222Document13 pagesRevision Questions 2222abdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Karnaugh MapsDocument10 pagesKarnaugh Mapsabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Final 2017Document3 pagesFinal 2017abdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 002 - PLCDocument6 pagesLecture 002 - PLCabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document14 pagesCH 3abdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 MRPDocument5 pagesSheet 2 MRPabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- CNC QuestionsDocument1 pageCNC Questionsabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Al2O3/SiC particle reinforced aluminium composites dry sliding wearDocument10 pagesAl2O3/SiC particle reinforced aluminium composites dry sliding wearabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- تطبيقات عملية PDFDocument30 pagesتطبيقات عملية PDFMohamed YahyaNo ratings yet
- حل الميد تيرم cncDocument2 pagesحل الميد تيرم cncabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- A Review On Fabrication & Characterization of Hybrid Aluminium Metal Matrix CompositeDocument6 pagesA Review On Fabrication & Characterization of Hybrid Aluminium Metal Matrix Compositeabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Sliding Wear Properties of A Composite of Aluminum 2024 Powder Reinforced With Heat Treatment and Silicon CarbideDocument12 pagesSliding Wear Properties of A Composite of Aluminum 2024 Powder Reinforced With Heat Treatment and Silicon Carbideabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Statistics Chapter Exploring Data, Samples & PopulationsDocument24 pagesIntroduction to Statistics Chapter Exploring Data, Samples & Populationsabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Invoice 1109Document1 pageInvoice 1109abdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Wear and Friction Properties of Epoxy-Polyamide Blend Nanocomposites Reinforced by MwcntsDocument7 pagesWear and Friction Properties of Epoxy-Polyamide Blend Nanocomposites Reinforced by Mwcntsabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- محاضرة العداداتDocument3 pagesمحاضرة العداداتabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Chapter (5) Di Fsidl Dsidls T Design of Spindles and Spindle SupportsDocument16 pagesChapter (5) Di Fsidl Dsidls T Design of Spindles and Spindle Supportsabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 004 - PLCDocument2 pagesLecture 004 - PLCabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- First Page PDFDocument1 pageFirst Page PDFabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- Invoice 1109Document1 pageInvoice 1109abdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- ISO 90012015checklist - tcm14 57745 PDFDocument25 pagesISO 90012015checklist - tcm14 57745 PDFDaniela Muñoz SaldiasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Lathes - Metal Arts PressDocument8 pagesChapter 7 - Lathes - Metal Arts Pressabdullah 3mar abou reashaNo ratings yet
- NRLM Skills PresentationDocument23 pagesNRLM Skills PresentationVinod Kumar NooluNo ratings yet
- L 08092 9Document5 pagesL 08092 9DmitryNo ratings yet
- What Is Knowledge WorkerDocument4 pagesWhat Is Knowledge WorkerAarti GundooaNo ratings yet
- Intergreen TimeDocument2 pagesIntergreen TimeMd Didarul AlamNo ratings yet
- Cessna 185 Familiarisation CourseDocument5 pagesCessna 185 Familiarisation CourseAmmar A. AlliNo ratings yet
- BANOVADocument44 pagesBANOVAGabriel HiNo ratings yet
- Analyze and Design Sewer and Stormwater Systems with SewerGEMSDocument18 pagesAnalyze and Design Sewer and Stormwater Systems with SewerGEMSBoni ClydeNo ratings yet
- Bank Management System Project ReportDocument72 pagesBank Management System Project ReportGokila GokilaNo ratings yet
- Stahl Service Manual Sf35226423 - Google SearchDocument2 pagesStahl Service Manual Sf35226423 - Google SearchAlvaroNo ratings yet
- Acoplamentos de Lamela de Aço ROBA-DSDocument72 pagesAcoplamentos de Lamela de Aço ROBA-DSFernando KonitzNo ratings yet
- Comp ConDocument2 pagesComp ConUmbrellamonNo ratings yet
- Modifications To The Mean Maximum Pressure SystemDocument17 pagesModifications To The Mean Maximum Pressure Systemkanteron6443No ratings yet
- DrainageDocument42 pagesDrainagekingjames90100% (3)
- Pascal's Principle Formula - Definition and ExamplesDocument4 pagesPascal's Principle Formula - Definition and Examplesahmed mahamedNo ratings yet
- HW-6, Ch-14Document9 pagesHW-6, Ch-14Natalie NinachuuNo ratings yet
- 20 Safety Rules for Working with Electrical EquipmentDocument23 pages20 Safety Rules for Working with Electrical EquipmentJoshua Ignatius EyanaNo ratings yet
- Spartan 25Document4 pagesSpartan 25Marco RgNo ratings yet
- Quizlet FinalDocument34 pagesQuizlet FinalAshive MohunNo ratings yet
- F310 Load and Torque CellDocument2 pagesF310 Load and Torque CellAsad HafudhNo ratings yet
- Design of Sewerage SystemDocument51 pagesDesign of Sewerage SystemZac Francis Daymond91% (11)
- Aindumps.1z0 808.v2015!10!08.by - Minnie.58qDocument66 pagesAindumps.1z0 808.v2015!10!08.by - Minnie.58qmaile4scribdNo ratings yet
- PlugindocDocument26 pagesPlugindocJohnny RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Concrete StructuresDocument432 pagesChapter 5 Concrete StructuresrizwanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sequential CircuitsDocument2 pagesAssignment Sequential CircuitsPavan SaiNo ratings yet
- 1.addition of 8 Bit Numbers 2.subtraction of 8 Bit Numbers: Microprocessor 8086 CodesDocument2 pages1.addition of 8 Bit Numbers 2.subtraction of 8 Bit Numbers: Microprocessor 8086 Codesprajwal patilNo ratings yet
- Package SsDocument2 pagesPackage SsNagaraj VjNo ratings yet
- Recommended Tweaks For IIS 8Document7 pagesRecommended Tweaks For IIS 8thiyagu_808No ratings yet
- Approved Drawing of Boundary WallDocument1 pageApproved Drawing of Boundary WallAnup Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Bill of Material For PCUDocument2 pagesBill of Material For PCUIqraSaeedNo ratings yet
- Business Exam SolutionsDocument15 pagesBusiness Exam SolutionsClement DonovanNo ratings yet