Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CynarPlc Turning Plastic Waste To Fuel PDF
Uploaded by
Trebob GardayaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CynarPlc Turning Plastic Waste To Fuel PDF
Uploaded by
Trebob GardayaCopyright:
Available Formats
By C ontinuing to use the site, you agree to the use of cookies.
You can change this and find out more by Accept Cookies
following this link
NEW S Energy firm signs euro 70m british deal... Home • Company Introduction • Contact Us • Cookies
Home
The Cynar Technology
The Company
The Cynar Technology Current situation of recycling of plastics
Video
Specification
Pyrolysis
Videos
Structure of the System
Media Operations
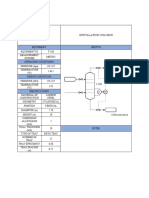
Contact Us Cynar ELP Technology - Process Flow Diagram
The system uses liquefaction, pyrolysis and distillation of plastics. The system can handle almost all
the End of Life Plastic that is currently being sent to landfills. A major advantage of the process is
its high efficiency. Each plant can produce up to 19k litres of fuel from 20 tonnes of End of Life
Plastic.
Current Situation of Recycling of Plastics
Various methodologies have been tried and tested to
process waste or end of life plastics for many years, with
recycling becoming the most common method reflecting the
needs of today. Plastics that cannot be processed are
handled by waste management companies mainly through
land-filling or incineration.
The building or expanding of incinerators has become
difficult due to opposition from governments and community
groups with environmental concerns, most notably the levels
of emissions.
Liquefaction of plastic is a superior method of reusing this
resource. These distillate products are excellent fuels and
make the C ynar Technology one of the best, economically
feasible and environmentally sensitive recycling systems in
the world today.
The synthetic fuels produced, given their low sulphur and high cetane qualities, will most likely be
utilised by the recycling organisations on-site for use in the vehicle fleet as SITA plan to do or
heavy equipment and generators.
Back to Top
Video
earthrise - Plastic Fuel
0:00 / 6:34
Back to Top
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process of thermal degradation of a material in the absence of oxygen. Plastic is
continuously treated in a cylindrical chamber and the pyrolytic gases condensed in a specially-
designed condenser system to yield a hydrocarbon distillate comprising straight and branched
chain aliphatics, cyclic aliphatics and aromatic hydrocarbons. The resulting mixture is essentially
equivalent to petroleum distillate. The plastic is pyrolised at 370ºC -420ºC and the pyrolysis gases
are condensed and liquid separated using fractional distillation to produce the liquid fuel products.
The essential steps in the pyrolysis of plastics
involves:
1. evenly heating the plastic to a narrow temperature
range without excessive temperature variations
2. purging oxygen from pyrolysis chamber,
3. managing the carbonaceous char by-product before
it acts as a thermal insulator and lowers the heat
transfer to the plastic
4. careful condensation and fractionation of the
pyrolysis vapours to produce distillate of good quality
and consistency
Back to Top
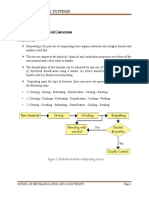
Structure of the System
The system consists of stock in-feed system, pyrolysis chambers, contactors, distillation, oil
recovery line and syn-gas..
End of Life Plastics are loaded via a hot-melt infeed system directly into main pyrolysis chamber.
Agitation commences to even the temperature and homogenise the feedstocks. Pyrolysis then
commences and the plastic becomes a vapour. Non-plastic materials fall to the bottom of the
chamber.
The vapour is converted into the various fractions in the distillation column, the distillates then pass
into the recovery tanks.
The System diverts the Syn Gas through a Scrubber and then back into the furnaces to heat the
pyrolysis chambers.
The cleaned distillates are then pumped to the storage tanks.
Back to Top
Operations
The heart of the pyrolysis system is the prime chamber,
which performs the essential functions of homogenisation
and controlled decomposition in a single process. The
process requires minimal maintenance and produces a
consistent quality distillate from End of Life Plastic..
The key to an efficient pyrolysis process is to ensure the
plastic is heated uniformly and rapidly. If temperature
gradients develop in the molten plastic mass then different
degrees of cracking will occur and products with a wide
distribution of chain lengths will be formed.
Cynar has signed an Agreement with Loughborough
University in the UK to Partner in the further
advancement/optimisation of the Cynar Technolgy
and is also looking at converting 'other' End of Life
Plastic feedstocks. This strategic partnership will
assist in ensuring that the Cynar Technology will
remain the world leader in the Pyrolysis of End of Life Plastics to Liquid Fuel.
Cynar ELP Technology - Process Flow Diagram
Back to Top
For further information
Contact Cynar Click Here
CYNAR PLC
Unit 601, C apital Tower, 91 Waterloo Road, London SE1 8RT
Tel: +353 (0) 57 868 0660 • Fax:+353 (0) 57 868 0640 • Email: info@cynarplc.com
Another great website by www.webintelligentmarketing.com
You might also like
- Ata 35Document38 pagesAta 35Geovanni Riquelme LooNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil Extraction From Waste PlasticDocument14 pagesCrude Oil Extraction From Waste PlasticRohit Raj100% (1)
- API Standards For Mechanical Rotating Machinery: September 2020Document4 pagesAPI Standards For Mechanical Rotating Machinery: September 2020khabiranNo ratings yet
- Atlas CopcoDocument90 pagesAtlas CopcoDejan Petkovski67% (3)
- Fuel From Waste PlasticDocument13 pagesFuel From Waste PlasticAnonymous VTbmrkb13bNo ratings yet
- Obtaining Fuels From Plastic Waste PDFDocument3 pagesObtaining Fuels From Plastic Waste PDFurfi ramadhani100% (1)
- AGA - Purging Principle and Practice PDFDocument158 pagesAGA - Purging Principle and Practice PDFsml100% (1)
- API 12j Two Phase Separator Sizing - Api Rp520 Relief Valve SizingDocument13 pagesAPI 12j Two Phase Separator Sizing - Api Rp520 Relief Valve SizingOmer EkerNo ratings yet
- 250 Piping Design GuideDocument779 pages250 Piping Design GuideBetty Giai Levra95% (21)
- Chan Scope and Dew Point Tester ManualDocument64 pagesChan Scope and Dew Point Tester ManualmercuryandmarsNo ratings yet
- Business Oppurtunities in Plastics Processing & Allied IndustriesDocument100 pagesBusiness Oppurtunities in Plastics Processing & Allied IndustriesNitin GuptaNo ratings yet
- Convert Plastic Waste into FuelDocument15 pagesConvert Plastic Waste into FuelSuresh VermaNo ratings yet
- Compressor 1Document25 pagesCompressor 1Trebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- APHDocument59 pagesAPHBrijraj Pandey100% (5)
- Chemical Recycling PETDocument14 pagesChemical Recycling PETApril ChaneyNo ratings yet
- Amine Sweetening Process DesignDocument12 pagesAmine Sweetening Process Designswapnil2603100% (2)
- BCG A Circular Solution To Plastic Waste July 2019 - tcm58 223960Document30 pagesBCG A Circular Solution To Plastic Waste July 2019 - tcm58 223960selcukNo ratings yet
- Plastic Energy - BASF Dialog ForumDocument12 pagesPlastic Energy - BASF Dialog ForumRajesh100% (1)
- Theory and Technology of Multiscale Dispersed Particle Gel for In-Depth Profile ControlFrom EverandTheory and Technology of Multiscale Dispersed Particle Gel for In-Depth Profile ControlNo ratings yet
- Thermo Fuel ProcessDocument9 pagesThermo Fuel ProcessSpoiler Alert100% (1)
- Conversion of Plastic Wastes in To FuelsDocument6 pagesConversion of Plastic Wastes in To FuelsannuunakiNo ratings yet
- Chemical recycling converts plastic waste into feedstockDocument2 pagesChemical recycling converts plastic waste into feedstockyamakunNo ratings yet
- Circular Economy: Economic System Aimed at Eliminating Waste and The Continual Use of ResourcesDocument27 pagesCircular Economy: Economic System Aimed at Eliminating Waste and The Continual Use of Resourcesendang dian lestariNo ratings yet
- Che198 Analytical Chemistry DrillsDocument18 pagesChe198 Analytical Chemistry DrillsTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- Che198 Analytical Chemistry DrillsDocument18 pagesChe198 Analytical Chemistry DrillsTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- Pyrolysis FPDocument6 pagesPyrolysis FPReymarkMachoNo ratings yet
- Pyrolysis of Plastic Waste - Opportunities and ChallengesDocument17 pagesPyrolysis of Plastic Waste - Opportunities and Challengesgavin meadeNo ratings yet
- CynarPlc - Turning Plastic Waste To FuelDocument3 pagesCynarPlc - Turning Plastic Waste To FuelShubham ArawkarNo ratings yet
- ppt tejuDocument17 pagesppt tejuTejas JawanjalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Plastic BreakdownDocument9 pagesChemistry Plastic BreakdownAndre ThomasNo ratings yet
- 2019_Cracking the problem of waste plasticsDocument2 pages2019_Cracking the problem of waste plasticsliliacul2000No ratings yet
- Artigo Cenibra Lodo Biológico 02 - 2021Document10 pagesArtigo Cenibra Lodo Biológico 02 - 2021Marcelo SilvaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214785321030285 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S2214785321030285 MainCarlos Aguilar TorresNo ratings yet
- Chemical Plant Design For The Conversion of PlastiDocument11 pagesChemical Plant Design For The Conversion of PlastiJohn KramouelNo ratings yet
- Technology Optimizes Plastics Waste ManagementDocument33 pagesTechnology Optimizes Plastics Waste ManagementSanjay Saxena AhmedabadNo ratings yet
- Alternate Fuel Preparation in Low Cost From Waste Plastic A ReviewDocument2 pagesAlternate Fuel Preparation in Low Cost From Waste Plastic A ReviewDana MateiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 3 Cynar Plastics To Fuel FINALDocument8 pagesCase Study 3 Cynar Plastics To Fuel FINALParth Garg100% (1)
- Plastic ManufacturingDocument31 pagesPlastic ManufacturingDipika KumariNo ratings yet
- IJREAMV06I0969019Document5 pagesIJREAMV06I0969019UNITED CADDNo ratings yet
- Research Paper -Team 6Document5 pagesResearch Paper -Team 6Mayankjain 2810No ratings yet
- A Review Paper On Plastic Recycle MachineDocument3 pagesA Review Paper On Plastic Recycle MachineerpublicationNo ratings yet
- 12.00 Kare Helge Karstensen SINTEFDocument137 pages12.00 Kare Helge Karstensen SINTEFParamananda SinghNo ratings yet
- Optimization of The Development of A Plastic Recycling MachineDocument15 pagesOptimization of The Development of A Plastic Recycling MachinePhilip ArpiaNo ratings yet
- Pyrolysis - of - Polystyrene - ProductosDocument30 pagesPyrolysis - of - Polystyrene - ProductosZ Fernandez UrbinaNo ratings yet
- Fuels From Plastic WastesDocument10 pagesFuels From Plastic WastesRock onNo ratings yet
- (Citation Han18 /L 1033) : Hul Techtonic Case SubmissionDocument2 pages(Citation Han18 /L 1033) : Hul Techtonic Case SubmissionAshi JainNo ratings yet
- Plastics RecycleDocument46 pagesPlastics RecycleMuhammad Kurniawan ArifmurtiNo ratings yet
- Recycling Technology: For Post-Consumer PlasticsDocument16 pagesRecycling Technology: For Post-Consumer PlasticsTimur SuleymanovNo ratings yet
- Effects of Heating Rate and Temperature On The Yield of Thermal Pyrolysis of A Random Plastic MixtureDocument12 pagesEffects of Heating Rate and Temperature On The Yield of Thermal Pyrolysis of A Random Plastic MixturePrathwiraj MeenaNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument6 pagesResearch PaperDhawalSoniNo ratings yet
- Case Study 3 Cynar Plastics To Fuel FINALDocument8 pagesCase Study 3 Cynar Plastics To Fuel FINALtalhaNo ratings yet
- Agrochemical ConversionDocument18 pagesAgrochemical ConversionMalli ReddyNo ratings yet
- Waste Plastic To Fuel: Zero Pollution Conversion TechnologyDocument9 pagesWaste Plastic To Fuel: Zero Pollution Conversion TechnologyMajik TayeNo ratings yet
- Optimization of catalytic pyrolysis processDocument4 pagesOptimization of catalytic pyrolysis processDana MateiNo ratings yet
- Additional Related LiteratureDocument2 pagesAdditional Related LiteratureDanae CamatNo ratings yet
- Thermalysis-Converting Waste Plastic To DieselDocument8 pagesThermalysis-Converting Waste Plastic To DieselRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Seminar TopicDocument4 pagesSeminar TopicChandana BJNo ratings yet
- Pal 2018Document14 pagesPal 2018adeeljutt1182No ratings yet
- Icontess - M.noviansyah A. Pyrolysis of Sawdust BriquettesDocument5 pagesIcontess - M.noviansyah A. Pyrolysis of Sawdust BriquettesNoviansyah AriditoNo ratings yet
- 11 March 2016Document46 pages11 March 2016Reena SinghalNo ratings yet
- Recycling Plastics: Mechanical vs Chemical ApproachesDocument2 pagesRecycling Plastics: Mechanical vs Chemical ApproachessateeshbondaNo ratings yet
- Suschem Sustainable Plastics Brochure-FINAL 2101Document53 pagesSuschem Sustainable Plastics Brochure-FINAL 2101Aimée CEmNo ratings yet
- Industrial Process Design and OperationsDocument24 pagesIndustrial Process Design and OperationsTemp AccountNo ratings yet
- CFA18 Waste To Value Part 1 and Part 2Document76 pagesCFA18 Waste To Value Part 1 and Part 2Ahmad SafrizalNo ratings yet
- CTRADEUSAIDDocument2 pagesCTRADEUSAIDXuan VienNo ratings yet
- Plastic Recycling ThesisDocument7 pagesPlastic Recycling Thesisamandabarbergilbert100% (2)
- Thermolysis of Plastic Waste - Reactor ComparisonDocument27 pagesThermolysis of Plastic Waste - Reactor ComparisonAndrew EfomzyNo ratings yet
- Agriculture: C F P C PDocument2 pagesAgriculture: C F P C PRahul MulayNo ratings yet
- Green-PVC With Full Recycled Industrial Waste and Renewably SourcedDocument15 pagesGreen-PVC With Full Recycled Industrial Waste and Renewably Sourcedpaulorp78No ratings yet
- Production of High Grade Liquid Fuel For CI Engine by Thermo-Catalytic Cracking of Waste PlasticDocument7 pagesProduction of High Grade Liquid Fuel For CI Engine by Thermo-Catalytic Cracking of Waste PlasticYulia Rodriguez LamarNo ratings yet
- Dryers for Sewage Sludge DehydrationDocument9 pagesDryers for Sewage Sludge DehydrationRrodriguezz22No ratings yet
- Modeling Biodiesel Esterification in a Packed Bed ReactorDocument2 pagesModeling Biodiesel Esterification in a Packed Bed ReactorTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- Plant Design and Feasibility Study of Dichloromethane Manufacturing Facility in The PhilippinesDocument11 pagesPlant Design and Feasibility Study of Dichloromethane Manufacturing Facility in The Philippinesmache dumadNo ratings yet
- Gardaya - Petition To Open - Che185Document1 pageGardaya - Petition To Open - Che185Trebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- Che198 Thermodynamics DrillsDocument8 pagesChe198 Thermodynamics DrillsTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- Integrated Green Energy Appendix 4E Report Details 644% Loss IncreaseDocument10 pagesIntegrated Green Energy Appendix 4E Report Details 644% Loss IncreaseTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- Econ 4Document27 pagesEcon 4Trebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study of Catalytic Cracking of Waste Plastic to Produce Fuel Oil in MalaysiaDocument10 pagesFeasibility Study of Catalytic Cracking of Waste Plastic to Produce Fuel Oil in MalaysiaTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- TIME VALUE OF MONEY PRINCIPLESDocument45 pagesTIME VALUE OF MONEY PRINCIPLESTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- Continuous CompoundingDocument30 pagesContinuous CompoundingDan PobleteNo ratings yet
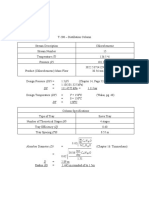
- Columns Spec SheetDocument4 pagesColumns Spec SheetTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- Columns CalcDocument10 pagesColumns CalcTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- PD Aspen 3 PDFDocument61 pagesPD Aspen 3 PDFTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- MseDocument2 pagesMseTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy: Study of Costs and BenefitsDocument18 pagesEngineering Economy: Study of Costs and BenefitsTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study of Catalytic Cracking of Waste Plastic to Produce Fuel Oil in MalaysiaDocument10 pagesFeasibility Study of Catalytic Cracking of Waste Plastic to Produce Fuel Oil in MalaysiaTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- Piro LiseDocument21 pagesPiro LiseFSBollNo ratings yet
- Econ 2Document28 pagesEcon 2LutherDumasNo ratings yet
- PD Aspen 4 PDFDocument10 pagesPD Aspen 4 PDFTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- PD Aspen 4 PDFDocument10 pagesPD Aspen 4 PDFTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study of Catalytic Cracking of Waste Plastic to Produce Fuel Oil in MalaysiaDocument10 pagesFeasibility Study of Catalytic Cracking of Waste Plastic to Produce Fuel Oil in MalaysiaTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- Piro LiseDocument21 pagesPiro LiseFSBollNo ratings yet
- PD Aspen 3 PDFDocument61 pagesPD Aspen 3 PDFTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- PD Aspen 1Document6 pagesPD Aspen 1Trebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- PD Aspen 1Document6 pagesPD Aspen 1Trebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- PD Aspen 1Document6 pagesPD Aspen 1Trebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function PDFDocument53 pagesCell Structure and Function PDFTrebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering Fluid Mechanics - K. Muralidhar and G. BiswasDocument20 pagesAdvanced Engineering Fluid Mechanics - K. Muralidhar and G. BiswasAli Adnan100% (1)
- Module 5 in Physical ScienceDocument8 pagesModule 5 in Physical ScienceDarlyn MontillaNo ratings yet
- Argon PDFDocument18 pagesArgon PDFPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Food Processing - Evaporation Elevates Boiling PointsDocument2 pagesFood Processing - Evaporation Elevates Boiling PointsharshitNo ratings yet
- Coal LiquificationDocument28 pagesCoal LiquificationAugust mishraNo ratings yet
- Tokimec Vane PumpDocument8 pagesTokimec Vane PumpHydroacero SasNo ratings yet
- 48" X 15' Three Phase Test SeparatorDocument2 pages48" X 15' Three Phase Test Separatorpraash bhattNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration System DesignDocument8 pagesRefrigeration System DesignJustine BoqsNo ratings yet
- A New Model For Modern Production DeclinDocument14 pagesA New Model For Modern Production DeclinMinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- STR 2011 2 e 14 Menon eDocument4 pagesSTR 2011 2 e 14 Menon ePrashanthMNairNo ratings yet
- Effects of helium gas flow rate on arc shape, molten pool behavior and penetration in aluminum alloy DCEN TIG weldingDocument15 pagesEffects of helium gas flow rate on arc shape, molten pool behavior and penetration in aluminum alloy DCEN TIG weldingJoão Paulo NascimentoNo ratings yet
- SFE Review: Advantages of Supercritical Fluid Extraction in Food AnalysisDocument5 pagesSFE Review: Advantages of Supercritical Fluid Extraction in Food AnalysisNuradila Athirah LockmanNo ratings yet
- Lampiran C Speifikasi AlatDocument190 pagesLampiran C Speifikasi AlatAbdul Kadir LinggaNo ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance Manual - SFFECO Fire Pumps - 2012Document44 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual - SFFECO Fire Pumps - 2012mukhtarahmadaNo ratings yet
- Uniphos Kwiksense Digital Smart Gas Transmitter: Salient FeaturesDocument3 pagesUniphos Kwiksense Digital Smart Gas Transmitter: Salient Featuresraushan mishraNo ratings yet
- Petrol Price in Ludhiana - Ludhiana Petrol Price Today - Petrol Cost Trend in LudhianaDocument6 pagesPetrol Price in Ludhiana - Ludhiana Petrol Price Today - Petrol Cost Trend in LudhianaBINNo ratings yet
- 6C0034Document5 pages6C0034Joshua prabuNo ratings yet
- Correlation of Sauter Mean Diameter and Critical HDocument13 pagesCorrelation of Sauter Mean Diameter and Critical HOliver AmedNo ratings yet
- Pumps 303 AssDocument68 pagesPumps 303 AssGkou DojkuNo ratings yet
- Beko Brochure CLEARPOINT FiltersDocument10 pagesBeko Brochure CLEARPOINT FiltersJuan BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Valvulas Solenoides para Gas ASCODocument2 pagesValvulas Solenoides para Gas ASCOCarlos Ramos MorenoNo ratings yet