Professional Documents
Culture Documents
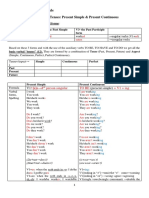
Tense: Past Continuous
Uploaded by
A. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLE0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesThe past continuous is used in English to talk about actions or events that were in progress at some time in the past. It is formed with “was” or “were” and a present participle.
FEEL FREE TO USE IT!
Original Title
TENSE: PAST CONTINUOUS
Copyright
© Attribution (BY)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe past continuous is used in English to talk about actions or events that were in progress at some time in the past. It is formed with “was” or “were” and a present participle.
FEEL FREE TO USE IT!
Copyright:
Attribution (BY)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesTense: Past Continuous
Uploaded by
A. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLEThe past continuous is used in English to talk about actions or events that were in progress at some time in the past. It is formed with “was” or “were” and a present participle.
FEEL FREE TO USE IT!
Copyright:
Attribution (BY)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
PAST CONTINUOUS
WHAT IS PAST CONTINUOUS?
The past continuous is used in English to talk about actions or events that were
in progress at some time in the past. It is formed with “was” or “were” and a
present participle.
--------------------------------------------------------------
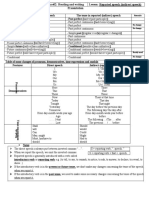
HOW TO FORM
Was/were Subject Was/were Ving Rest of sentence
- I was working now.
- You / We / They were working now.
- He / she / it was working now.
- I was working now.
- You / We / They were working now.
- He / she / it was working now.
was I - working now?
were You / We / They - working now?
was He / she / it - working now?
--------------------------------------------------------------
---- It used to express action at a particular moment in the past. The action started
before that moment but has not finished at that moment.
I started doing I was doing I finished doing
past past now
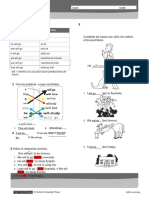
At 8 pm, I was in the middle of watching TV.
Past Continuous Tense + Simple Past Tense
We often use the past continuous tense with the simple past tense to say
something happened in the middle of something else. We can join the two ideas
with when or while. In the following example, we have two actions:
1. long action (watching TV), expressed with the past continuous tense
2. short action (telephoned), expressed with the simple past tense
I was watching TV when
you telephoned
past now future
- Long action: I was
watching TV at 8
pm.
- Short action: You
telephoned at 8 pm.
We can join these two actions by:
when + short action (simple past tense)
while + long action (past continuous tense)
There are four basic combinations:
I was watching TV when You telephoned
When You telephoned I was watching TV
You telephoned while I was watching TV
While I was watching TV You telephoned
REFERENCES AND RECOMMENDED READING
Azar, B. S. (1996). Basic English Grammar. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall
Regents.
Azar, B. S. (2003). Fundamentals of English Grammar: Chartbook: a
Reference Grammar. White Plains, NY: Longman.
Azar, B. S., & Hagen, S. A. (2009). Understanding and using English
grammar: Workbook. White Plains, N.Y.: Pearson Longman.
Ansell, M. (2000). Free English Grammar Second Edition.
Barduhn, S., & Hall, D. (2016). English for Everyone–English Grammar
Guide. New York: DK Publishing.
Murphy, R., Smalzer, W. R., & Nguyễn, T. T. (2000). Grammar in Use:
Intermediate. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Murphy, R., & Čhakramāt, S. (2002). Essential grammar in use (Vol. 20010).
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
You might also like
- TIMPURILE MODULUI INDICATIV-englezaDocument7 pagesTIMPURILE MODULUI INDICATIV-englezaioanacata100% (3)
- Adjectives PDFDocument25 pagesAdjectives PDFNemrac NemracNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Practice: Explanations and Exercises with KeyFrom EverandEnglish Grammar Practice: Explanations and Exercises with KeyNo ratings yet
- Lpe2501 Lecture Notes 7 (Week 13 - 14)Document27 pagesLpe2501 Lecture Notes 7 (Week 13 - 14)arif azahanNo ratings yet
- PPP LESSON PLAN FOR Sample TeachingDocument3 pagesPPP LESSON PLAN FOR Sample TeachingJa Moon MaiNo ratings yet
- Fuller Approach in Teaching ReadingDocument4 pagesFuller Approach in Teaching ReadingJC Viacrucis Juanero100% (3)
- Joaquin - DOWNLAD PDF Cambridge Latin Course Unit 1 North American 4th EditionDocument1 pageJoaquin - DOWNLAD PDF Cambridge Latin Course Unit 1 North American 4th EditionPuka PuhaNo ratings yet
- Tense: Present ContinuousDocument2 pagesTense: Present ContinuousA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- 5ASO Tenses - Deadlines Tue. 15 and Tue. 22 Nov.Document3 pages5ASO Tenses - Deadlines Tue. 15 and Tue. 22 Nov.n44v55cxmnNo ratings yet
- The Present Continuous TenseDocument21 pagesThe Present Continuous TenseAgus JosephNo ratings yet
- Past Simple and ContinuousDocument2 pagesPast Simple and ContinuousLaura Roman DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Handout 1Document3 pagesHandout 1edenamiriambutNo ratings yet
- The Simple Present and Present Continuous TenseDocument10 pagesThe Simple Present and Present Continuous TenseErlinda ApriliaNo ratings yet
- Content 1 - Lesson 3Document2 pagesContent 1 - Lesson 3Reign Chosen AyingNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Verb Tenses (Past Perfect Tense, Present Perfect Tense, Future Perfect Tense)Document8 pagesUnit 3: Verb Tenses (Past Perfect Tense, Present Perfect Tense, Future Perfect Tense)Adila WaheedaNo ratings yet
- The Simple Present and Present Continuous TenseDocument10 pagesThe Simple Present and Present Continuous TenseKim Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Past Simple and Past Continuous TensesDocument9 pagesPast Simple and Past Continuous TensesIvana JovanovicNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Present ContinuousDocument2 pagesPresent Simple Present ContinuousСніжана КерницькаNo ratings yet
- Tenses NotesDocument7 pagesTenses NotessasNo ratings yet
- The Present Continuous TenseDocument21 pagesThe Present Continuous TenseGuerrero AgeNo ratings yet
- The Present Continuous TenseDocument21 pagesThe Present Continuous TensedebbyNo ratings yet
- English Booklet (5th Year) 2021Document54 pagesEnglish Booklet (5th Year) 2021Debora AzcurraNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses ReviewDocument29 pagesVerb Tenses ReviewRocío García100% (1)
- Skripta Iz Engleskog Sa VezbamaDocument54 pagesSkripta Iz Engleskog Sa Vezbamaanica11No ratings yet
- English TensesDocument10 pagesEnglish TensesnawidrasoolyNo ratings yet
- PerfectDocument6 pagesPerfectNini CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect For SharingDocument10 pagesPresent Perfect For Sharingbella jangNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Time and TenseDocument5 pagesWeek 13 Time and TenseMihaela Codrina AntonNo ratings yet
- Forms (Affirmative - A/Negative - N Question - Q) USE Time PhrasesDocument4 pagesForms (Affirmative - A/Negative - N Question - Q) USE Time PhrasesSyairah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- 3.indirect SpeechDocument7 pages3.indirect SpeechzakNo ratings yet
- KEYSDocument16 pagesKEYSZemanic IzudinNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous InformationDocument7 pagesPast Continuous InformationHoskar Mendoza StanfordNo ratings yet
- The Present Continuous TenseDocument21 pagesThe Present Continuous TenseIanDragoneVenegasNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple (I Have Worked) : English Grammar TodayDocument26 pagesPresent Perfect Simple (I Have Worked) : English Grammar TodayEurico BrassoNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect Tense-1Document3 pagesThe Present Perfect Tense-1Zineb BouzaidNo ratings yet
- Prezentacija OdtDocument6 pagesPrezentacija OdtMarko DjokicNo ratings yet
- German Tense and AspectDocument28 pagesGerman Tense and AspectRaul PaulNo ratings yet
- The Past Continuous TenseDocument4 pagesThe Past Continuous TenseMuhamadNevyNo ratings yet
- Past ContinuousDocument4 pagesPast ContinuousRoshan UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: InglêsDocument5 pagesSimple Present: InglêsJuliaNo ratings yet
- Present Tenses: There Are 2 Basic Ways To Talk About PresentDocument13 pagesPresent Tenses: There Are 2 Basic Ways To Talk About PresentYujin IlNo ratings yet
- Tense: Simple Present TenseDocument3 pagesTense: Simple Present TenseA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Tobe - in The Simple Present: Eventually Enrolls at Harvard UniversityDocument8 pagesTobe - in The Simple Present: Eventually Enrolls at Harvard UniversitybadoomtskNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument6 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentCanioNo ratings yet
- TENSESDocument2 pagesTENSESCony YapNo ratings yet
- The Past Continuous TenseDocument2 pagesThe Past Continuous TenseFirda ChaeraniNo ratings yet
- TOEFL Part III StructureDocument65 pagesTOEFL Part III StructurePatrick StevenNo ratings yet
- Modul 17 Past Perfect Continuous TenseDocument3 pagesModul 17 Past Perfect Continuous TenseStojanka ŽugićNo ratings yet
- TYPES OF TensesDocument19 pagesTYPES OF Tensesariesyue100% (2)
- Verb Tense Review: The Importance of TimeDocument32 pagesVerb Tense Review: The Importance of Timebaba ioana100% (1)
- Reported Speech, Teacher SheetDocument2 pagesReported Speech, Teacher SheetDARK SAD QUEENNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect 1Document3 pagesPresent Perfect 1J. LindellNo ratings yet
- Tenses UietDocument27 pagesTenses UietMohitNo ratings yet
- Introduction Present ContinuousDocument2 pagesIntroduction Present ContinuousMaría Cruz Rueda MesoneroNo ratings yet
- Engleski Jezik VremenaDocument5 pagesEngleski Jezik VremenaLuka DraščićNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect ProgresiveDocument4 pagesPresent Perfect ProgresiveCindy Lizeth Valle SalasNo ratings yet
- Presentation # 13 Ind.Document10 pagesPresentation # 13 Ind.Maria michelle Miranda MirandaNo ratings yet
- VERB TENSES ExplanationsDocument8 pagesVERB TENSES ExplanationsMihaela GradinaruNo ratings yet
- Gramatika Engleskog Jezika Sa VježbanjimaDocument73 pagesGramatika Engleskog Jezika Sa VježbanjimaSladjana SamardzicNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument4 pagesEnglish TensesToofanNo ratings yet
- Tense With CartoonsDocument63 pagesTense With Cartoonsbluediamond_12345100% (1)
- Tenses SummaryDocument79 pagesTenses Summaryandi besse cayyah100% (1)
- Assessment: Principles of AssessmentDocument9 pagesAssessment: Principles of AssessmentA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Assessment: Listening Comprehension AssessmentDocument10 pagesAssessment: Listening Comprehension AssessmentA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Assessment: Speaking Comprehension AssessmentDocument18 pagesAssessment: Speaking Comprehension AssessmentA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Assessment: Writing Comprehension AssessmentDocument20 pagesAssessment: Writing Comprehension AssessmentA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Assessment: Reading Comprehension AssessmentDocument10 pagesAssessment: Reading Comprehension AssessmentA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Systemic Functional Linguistics: Interpersonal MeaningsDocument24 pagesSystemic Functional Linguistics: Interpersonal MeaningsA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Systemic Functional Linguistics: Interpersonal MeaningsDocument35 pagesSystemic Functional Linguistics: Interpersonal MeaningsA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Assessment: Testing, Assessment, and Evaluation in Teaching (Iii)Document6 pagesAssessment: Testing, Assessment, and Evaluation in Teaching (Iii)A. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Speech ActDocument14 pagesSpeech ActA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLE100% (2)
- Systemic Functional Linguistics: Interpersonal MeaningsDocument35 pagesSystemic Functional Linguistics: Interpersonal MeaningsA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Pragmatics: Cooperative PrinciplesDocument14 pagesPragmatics: Cooperative PrinciplesA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Pragmatics: Concept of ImplicatureDocument9 pagesPragmatics: Concept of ImplicatureA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Speech ActDocument14 pagesSpeech ActA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLE100% (2)
- Assessment: Testing, Assessment, and Evaluation in Teaching (Ii)Document7 pagesAssessment: Testing, Assessment, and Evaluation in Teaching (Ii)A. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Assessment: Testing, Assessment, and Evaluation in Teaching (I)Document12 pagesAssessment: Testing, Assessment, and Evaluation in Teaching (I)A. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- English For Hotel: Confirming Customers To Check-Out From The HotelDocument6 pagesEnglish For Hotel: Confirming Customers To Check-Out From The HotelA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Language Function: ComplainingDocument3 pagesLanguage Function: ComplainingA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Language Function: Giving Orders, Advising and WarningDocument5 pagesLanguage Function: Giving Orders, Advising and WarningA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Language Function: Expressing and Eliciting Plans, Goals, and IntentionsDocument3 pagesLanguage Function: Expressing and Eliciting Plans, Goals, and IntentionsA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Language Function: Persuading and EncouragingDocument4 pagesLanguage Function: Persuading and EncouragingA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Language Function: Asking For, Granting and Withholding PermissionDocument4 pagesLanguage Function: Asking For, Granting and Withholding PermissionA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Language Function: RequestingDocument3 pagesLanguage Function: RequestingA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Language Function: SuggestingDocument4 pagesLanguage Function: SuggestingA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- English For Hotel: Understanding Guests Problems During Their Stay and Offering SolutionsDocument6 pagesEnglish For Hotel: Understanding Guests Problems During Their Stay and Offering SolutionsA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- English For Hotel: Responding To The Customer's NeedsDocument5 pagesEnglish For Hotel: Responding To The Customer's NeedsA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- English For Hotel: Checking and Confirming Customer Rooms' ReservationDocument10 pagesEnglish For Hotel: Checking and Confirming Customer Rooms' ReservationA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Language Function: Approving and DisapprovingDocument3 pagesLanguage Function: Approving and DisapprovingA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLE0% (1)
- Language Function: Showing Satisfaction and DissatisfactionDocument3 pagesLanguage Function: Showing Satisfaction and DissatisfactionA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Language Function: Expressing of FeelingsDocument4 pagesLanguage Function: Expressing of FeelingsA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- Language Function: Agreeing and DisagreeingDocument4 pagesLanguage Function: Agreeing and DisagreeingA. TENRY LAWANGEN ASPAT COLLENo ratings yet
- SNAP 2018 - Question Paper & Answer Key (Memory Based) : Section 1 - General EnglishDocument11 pagesSNAP 2018 - Question Paper & Answer Key (Memory Based) : Section 1 - General Englishsamyak jainNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English 6 (Figures of Speech)Document4 pagesLesson Plan in English 6 (Figures of Speech)Jhanne Khalie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- EspDocument6 pagesEspRicell Joy RocamoraNo ratings yet
- Ielts Foundation Course Handout 3Document2 pagesIelts Foundation Course Handout 3Đào Nguyễn Duy TùngNo ratings yet
- Legal Language and Plane EnglsihDocument7 pagesLegal Language and Plane EnglsihshubhamNo ratings yet
- Power Point Presentation Mother Tongue Based Models of Multilingual EducationDocument30 pagesPower Point Presentation Mother Tongue Based Models of Multilingual Educationservidadveronica100% (2)
- Chapter 1-Power SharingDocument3 pagesChapter 1-Power SharingVighnesh ParabNo ratings yet
- Term BaseDocument1 pageTerm BaseIulia MihalacheNo ratings yet
- Adverbs and Adverbs of Degree Grade 4 English Printable Worksheets w10Document2 pagesAdverbs and Adverbs of Degree Grade 4 English Printable Worksheets w10ibrahim fofana100% (1)
- Ingles IDocument4 pagesIngles Iisabel niebles arenasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Module 2021Document16 pagesLesson Plan Module 2021Cristo ReyNo ratings yet
- Logical Reasoning - ClassDocument4 pagesLogical Reasoning - ClassThanga RajaNo ratings yet
- Python Holiday HomeworkDocument3 pagesPython Holiday Homeworkfake bandaNo ratings yet
- Task 3 Comparatives and SuperlativesDocument5 pagesTask 3 Comparatives and SuperlativesCARLOS AUGUSTO RINCON PINZONNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Media NaturalnessDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Media NaturalnessJo-Ann SmithNo ratings yet
- Observation Report On Child Language AcquisitionDocument11 pagesObservation Report On Child Language AcquisitionArisha KabirNo ratings yet
- Error Analysis of Student Interns' Reflective Journals: Basis For A Grammar Remediation ClassDocument17 pagesError Analysis of Student Interns' Reflective Journals: Basis For A Grammar Remediation ClassBq. Puji CahayaNo ratings yet
- MMW Module-2Document25 pagesMMW Module-2Rochelly DamascoNo ratings yet
- Cloze Procedure Aw or Al Au Sounds HabilityDocument1 pageCloze Procedure Aw or Al Au Sounds HabilityRatiuCristiNo ratings yet
- Aptis TestDocument24 pagesAptis TestGracemmr100% (1)
- 3rd Meeting - Literature of Old English PeriodDocument9 pages3rd Meeting - Literature of Old English PeriodAgnes MonicaNo ratings yet
- Peta KonsepDocument1 pagePeta KonsepDikacukNo ratings yet
- Narrative Technique: Style Point of ViewDocument3 pagesNarrative Technique: Style Point of ViewEeshitaNo ratings yet
- Shevoroshkin 2004 (Topics in Milyan)Document14 pagesShevoroshkin 2004 (Topics in Milyan)tobiassoeborgNo ratings yet
- WP 2Document5 pagesWP 2api-659059757No ratings yet
- 21st ReviewerDocument5 pages21st ReviewerleibnagNo ratings yet