Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eddy Current:: Mutual Inductance
Uploaded by
Jaan JeeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eddy Current:: Mutual Inductance
Uploaded by
Jaan JeeCopyright:
Available Formats
Eddy current:
Eddy currents are currents which circulate in conductors like swirling eddies in a
stream. They are induced by changing magnetic fields and flow in closed loops,
perpendicular to the plane of the magnetic field. They can be created when a
conductor is moving through a magnetic field, or when the magnetic field
surrounding a stationary conductor is varying i.e. anything which results in the
conductor experiencing a change in the intensity or direction of a magnetic field can
produce eddy current.
Self-Inductance:
The property of the coil due to which it opposes the change of current
flowing through it. Inductance is attained by a coil due to the self-induced
emf produced in the coil itself by changing the current flowing through it .
The unit of inductance is Henry (H).
If the current in the coil is increasing, the self-induced emf produced in the coil will
oppose the rise of current, that means the direction of the induced emf is opposite to
the applied voltage If the current in the coil is decreasing, the emf induced in the coil
is in such a direction as to oppose the fall of current; this means that the direction of
the self-induced emf is same as that of the applied voltage. Self-inductance does not
prevent the change of current, but it delays the change of current flowing through it.
This property of the coil only opposes the changing current (alternating current) and
does not affect the steady current that is (direct current) when flows through it.
Mutual Inductance:
The property of the coil due to which it opposes the change of current in the
other coil, or you can say in the neighbouring coil. When the current in the
neighbouring coil changes, the flux sets up in the coil and because of this,
changing flux emf is induced in the coil. The unit of inductance is Henry (H).
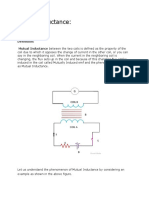
Two coils namely coil A and coil B are placed nearer to each other. When the switch
S is closed, and the current flows in the coil, it sets up the flux in the coil A and emf is
induced in the coil and if the value of the current is changed by varying the value of
the resistance (R), the flux linking with the coil B also changes because of this
changing current.
Thus this phenomenon of the linking flux of the coil A with the other coil, B is
called Mutual Inductance.
You might also like
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- The InductorDocument25 pagesThe InductorSureshraja9977No ratings yet
- Physics Project ElectromagnetismDocument24 pagesPhysics Project Electromagnetismaman100% (2)
- Mutual Inductance:: Definition: Mutual Inductance Between The Two Coils Is Defined As The Property of TheDocument4 pagesMutual Inductance:: Definition: Mutual Inductance Between The Two Coils Is Defined As The Property of TheRamixh IqbalNo ratings yet
- The InductorDocument25 pagesThe InductorSureshraja9977No ratings yet
- The InductorDocument67 pagesThe Inductorleonard1971No ratings yet
- Inductors Details StudyDocument45 pagesInductors Details StudyTanmay HazraNo ratings yet
- 1-The Inductor and The Effects of Inductance On A CoilDocument7 pages1-The Inductor and The Effects of Inductance On A Coilmehdi JrNo ratings yet
- Assigment of Capastor & InductorDocument24 pagesAssigment of Capastor & Inductorp pakistanNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Report On Electromagnetic InductionDocument6 pagesPhysics Project Report On Electromagnetic InductionSwarup RanjanNo ratings yet
- Electronics Tutorials WsDocument11 pagesElectronics Tutorials WsDev BuddyNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic InductionSanjay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic InductionLakshmi MenonNo ratings yet
- CH6 Formula SheetDocument11 pagesCH6 Formula SheetNancy SinghNo ratings yet
- Self InductanceDocument11 pagesSelf Inductanceحفيظو عبدالله100% (1)
- Elmachi1 - Lecture8 (Electrical Machines - Part 3)Document11 pagesElmachi1 - Lecture8 (Electrical Machines - Part 3)Trisha SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- Session 1.3 Common Electronic Components InductorsDocument19 pagesSession 1.3 Common Electronic Components InductorsNina VillonesNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction Physics Investigatory FileDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic Induction Physics Investigatory Filethe best ofNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: A Conductor by Changing Magnetic FieldDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: A Conductor by Changing Magnetic FieldshirlynNo ratings yet
- Self InductionDocument5 pagesSelf Inductionrizal123No ratings yet
- CertificateDocument17 pagesCertificatecᴘcтԍᴀмιɴԍ YTNo ratings yet
- Untitled 2Document2 pagesUntitled 2frawler22No ratings yet
- Physics Project (Investigatory Project 9)Document8 pagesPhysics Project (Investigatory Project 9)Ashu58% (19)
- Project Topic: To Study The Principle ofDocument14 pagesProject Topic: To Study The Principle ofAjay LalNo ratings yet
- Electomagnetic Induction:-Faraday's Law: Project ReportDocument17 pagesElectomagnetic Induction:-Faraday's Law: Project ReportSushantSinghNo ratings yet
- Self InductionDocument7 pagesSelf InductionShakawat Hossain ShifatNo ratings yet
- Pysics InvestigatoryDocument8 pagesPysics InvestigatoryAyush XI-ANo ratings yet
- Ch31&32 Electromagnetism SlidesDocument38 pagesCh31&32 Electromagnetism SlidesVent101No ratings yet
- Below: Mutual Inductance and Basic OperationDocument39 pagesBelow: Mutual Inductance and Basic OperationDevendra KapoorNo ratings yet
- What Is Inductor and Inductance - Theory of Inductor - Electrical4uDocument12 pagesWhat Is Inductor and Inductance - Theory of Inductor - Electrical4uteju2812No ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuits TheoryDocument26 pagesMagnetic Circuits TheoryRamkesh MeenaNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument9 pagesAbstractSimranNo ratings yet
- Mu PhysicsDocument12 pagesMu PhysicsMONISHNo ratings yet
- Self InductDocument22 pagesSelf Inductsiva balanNo ratings yet
- Elect Roma Gneti SM: How Electric Current Produce A Magnetic FieldDocument8 pagesElect Roma Gneti SM: How Electric Current Produce A Magnetic FieldIsmail MzavaNo ratings yet
- Year 12 E-Note PhyDocument77 pagesYear 12 E-Note Phyjeffersonawesome28No ratings yet
- Case Study 5 EmiDocument12 pagesCase Study 5 EmiSANJAY RNo ratings yet
- Electromgnetic InductionDocument5 pagesElectromgnetic InductionGhanshyam SinghNo ratings yet
- Induced Emf PDFDocument4 pagesInduced Emf PDFVenkata SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Physics Project-WPS OfficeDocument12 pagesPhysics Project-WPS OfficeDeepu KumariNo ratings yet
- Self Induction and Mutual InductionDocument24 pagesSelf Induction and Mutual InductionRavi Ranjan89% (9)
- Emi Notes (Cbse Class 12 2021-22)Document5 pagesEmi Notes (Cbse Class 12 2021-22)Shaku JoshiNo ratings yet
- Self Inductance of A CoilDocument8 pagesSelf Inductance of A CoilUnknown RiderNo ratings yet
- Self Inductance of A CoilDocument7 pagesSelf Inductance of A CoilIANDU PCNo ratings yet
- Concept of Electricity EnerationDocument7 pagesConcept of Electricity EnerationAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 EMIDocument52 pagesChapter 3 EMIMayank MeghaniNo ratings yet
- Iitm Diploma 1st Year FeeeDocument62 pagesIitm Diploma 1st Year Feeeblackgoku1512007No ratings yet
- Phy Topic 2 F4Document12 pagesPhy Topic 2 F4Kandrossy GlassNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Project For Class XIIDocument19 pagesPhysics Practical Project For Class XIIPallab Samanta66% (129)
- CHAPTER 31 Faraday S LawDocument27 pagesCHAPTER 31 Faraday S LawSattishZeeNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument21 pagesElectromagnetic InductionParth GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Project For Class XIIDocument18 pagesPhysics Practical Project For Class XIIManoj Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Lect 22Document7 pagesLect 22Girish RoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 NotesDocument20 pagesChapter 15 NotesMian EjazNo ratings yet
- Mod2 AC Circuits Provided by MaamDocument72 pagesMod2 AC Circuits Provided by Maamanishdeshmukh369No ratings yet
- Chapter 3B Electromagnetic InductionDocument6 pagesChapter 3B Electromagnetic InductionTaonga NhambiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument23 pagesUntitledArnab DasNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: Electro MagnetDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: Electro MagnetAbdulRehmanNo ratings yet
- 1unit 2Document4 pages1unit 2suresh krishnanNo ratings yet
- FA19-BEE-048 (Muhammad Hassaan) PDFDocument6 pagesFA19-BEE-048 (Muhammad Hassaan) PDFJaan JeeNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and Measurements by David A Bell 3rd Edition Chapter 8 Solution Manual PDFDocument4 pagesInstrumentation and Measurements by David A Bell 3rd Edition Chapter 8 Solution Manual PDFJaan JeeNo ratings yet
- Fatima Jinnah: "No Individual or People Can Achieve Anything Without Industry Suffering, and Sacrifice." - Fatima JinnahDocument1 pageFatima Jinnah: "No Individual or People Can Achieve Anything Without Industry Suffering, and Sacrifice." - Fatima JinnahJaan JeeNo ratings yet
- FA19-BEE-048 (Muhammad Hassaan)Document6 pagesFA19-BEE-048 (Muhammad Hassaan)Jaan JeeNo ratings yet
- Practical 2Document15 pagesPractical 2Jaan JeeNo ratings yet
- Name: Muhammad Hassaan Reg #: FA19-BEE-048 Section: 1A Submitted To: Sir Engr. Sabeeh MalikDocument9 pagesName: Muhammad Hassaan Reg #: FA19-BEE-048 Section: 1A Submitted To: Sir Engr. Sabeeh MalikJaan JeeNo ratings yet
- Name: Muhammad Hassaan Reg #: FA19-BEE-048 Section: 1A Submitted To: Sir Engr. Sabeeh MalikDocument9 pagesName: Muhammad Hassaan Reg #: FA19-BEE-048 Section: 1A Submitted To: Sir Engr. Sabeeh MalikJaan JeeNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Developments in Pakistan Form 1947-1955Document3 pagesConstitutional Developments in Pakistan Form 1947-1955Jaan JeeNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuit Analysis Numerical ProblemsDocument9 pagesElectronic Circuit Analysis Numerical ProblemsJaan JeeNo ratings yet