Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sec-182. Agent' and Principal' Defined:-: Prepared by .... V.Shobha Rani., PLC
Uploaded by
law notes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views7 pagesOriginal Title
contracts II 25th April - - Copy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views7 pagesSec-182. Agent' and Principal' Defined:-: Prepared by .... V.Shobha Rani., PLC
Uploaded by
law notesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Sec-182.
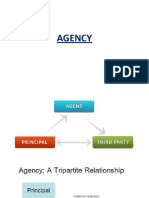
‘Agent’ and ‘Principal’ defined:- An “agent” is a
person employed to do any act for another, or to
represent another in dealings with third persons. The
person for whom such act is done, or who is so
represented is called the “principal”.
➢ Agency is a relationship constituted between one person
and a third party, by another person, representing or
acting on behalf of the former. Thus, when ‘A’
represents or acts on behalf of ‘B’, with ‘B’s authority
for the purpose of bringing ‘B’ into legal relations with a
third party, ‘C’, the relationship so constituted is called
Agency.
Prepared by ....V.Shobha Rani., PLC
Sec-183. Who may employ agent:- Any person who is of the
age of majority according to the law to which he is
subject, and who is of sound mind, may employ an
agent.
Sec-184. Who may be an agent:- As between the principal
and third persons, any person may become an agent, but
no person who is not of the age of majority and of sound
mind can become an agent, so as to be responsible to his
principal according to the provisions in that behalf
herein contained.
Sec-185 Consideration not necessary:- No consideration is
necessary to create an agency.
Prepared by ....V.Shobha Rani., PLC
1. Principal should be competent to contract: Sec183
➢ Principal must be of the age of majority according to the
law to which is subject and
➢ He must be of sound mind
➢ Since in an agency, the agent creates a contractual
relationship between his principal and the third persons,
it is necessary that the principal and the third person
should be competent to contract.
➢ If a person is not competent to contract and , therefore,
is incapable of making a contract, he cannot make a
contract through an agent either. A person can do only
such thing through an agent which he is himself
Prepared by ....V.Shobha Rani., PLC
personally capable of doing.
2. Agent need not be competent to contract: Sec184
➢ It is the agent who brings the principal into legal
relations with a third party.
➢ He is only a connecting link between the two.
➢ An agent never acts on his own behalf but always on
behalf of another who employs him.
➢ The act of the agent are deemed, in law, to be not his
own but of the principal and bind the principal.
➢ His function is over after a contract is established
between the principal and the third party.
➢ For the above reasons, law does not require that the
agent must be competent to contract. Prepared by ....V.Shobha Rani., PLC
3. Consideration for appointment not necessary: Sec185
➢ No consideration is necessary to create an agency.
➢ The provision of Section 185 cannot deprive an agent of
his legal remuneration.
➢ Generally an agent is remunerated by way of
commission for services rendered, but no consideration
is immediately necessary at the time of appointment.
Prepared by ....V.Shobha Rani., PLC
An agent occupies a position which is in many respects similar to that
occupied by a servant, bailee or trustee.
The distinction between an agent and a servant has been underlined by
the Supreme court in
Lakshminarayan Ram Gopal &sons Ltd. V Govt of Hyderabad
AIR1954 SC364
1. An agent has the authority to act on behalf of his principal and to
create contractual relations between the principal and a third
party. This kind of power is not generally enjoyed by a servant.
2. A principal has the right to direct what the agent has to do, but a
master has not only that right, but also the right to say how it is to
be done.
Conti... Prepared by ....V.Shobha Rani., PLC
3.The mode of remuneration is generally different. A servant is paid
by way of salary or wages, an agent receives commission on the
basis of work done.
4. A master is liable for a wrongful act of his servant, if it is
committed in the course of the servant’s employment. A principal
is liable for his agent’s wrong done within the “scope of
authority”
5. A servant usually serves only one master, but an agent may work
for several principals at the same time.
➢ The managing director of a company is an employee of the
company, but in the matter of the company’s relation with third
parties he occupies the position of an agent.
K.R.Kothandaraman V CIT, AIR1967 Mad143
Prepared by ....V.Shobha Rani., PLC
You might also like
- Contract of AgencyDocument20 pagesContract of AgencyGurunathan AmmasaiNo ratings yet
- Agency and RatificationDocument5 pagesAgency and RatificationAnubhav GargNo ratings yet
- Agency NotesDocument32 pagesAgency NotesPRAKHAR GUPTANo ratings yet
- AgencyDocument123 pagesAgencyManjeev Singh SahniNo ratings yet
- Agency Under Contracts-AcademiaDocument6 pagesAgency Under Contracts-AcademiaRouble SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Agency, ContractsDocument154 pagesAgency, ContractsKahmishKhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter X (Secs. 182 To 238) of The Indian Contract Act, 1872Document87 pagesChapter X (Secs. 182 To 238) of The Indian Contract Act, 1872Ujjwal AnandNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Agency and Modes of Creation of AgencyDocument10 pagesMeaning of Agency and Modes of Creation of AgencyShfq KhanNo ratings yet
- Agency Remaining Part PDFDocument30 pagesAgency Remaining Part PDFdsaquibNo ratings yet
- AgencyDocument128 pagesAgencyjyoti panditNo ratings yet
- Agency in Law of ContractDocument11 pagesAgency in Law of ContractYash Vardhan SinghNo ratings yet
- Contract of AgencyDocument6 pagesContract of AgencyRayapureddy Rohitha100% (2)
- All You Need To Know About The Agent-Principal Relationship: IpleadersDocument22 pagesAll You Need To Know About The Agent-Principal Relationship: IpleadersRaza RazaNo ratings yet
- Contract of Agency SectionsDocument11 pagesContract of Agency Sectionsdee deeNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Agency: Indian Contract Act, 1872Document14 pagesTopic 1: Agency: Indian Contract Act, 1872SUGANDHA YADAVNo ratings yet
- Law of Agency 2Document18 pagesLaw of Agency 2Senelwa AnayaNo ratings yet
- Contract of Agency MainDocument17 pagesContract of Agency MainAnjali BalanNo ratings yet
- Nalco Project - SritamDocument13 pagesNalco Project - SritamTrilo ChanNo ratings yet
- Agency Contract Part 1Document8 pagesAgency Contract Part 1mdkashifhayat78600No ratings yet
- Contract Project PDFDocument8 pagesContract Project PDFmirza ahrazNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Special ContractDocument13 pagesUnit 3 Special ContractKanishkaNo ratings yet
- Abdul Kadir Vs SalimaDocument19 pagesAbdul Kadir Vs SalimaAvinash MishraNo ratings yet
- Navaneeth Ss 1529: Section 191 of The Indian Contract Act, 1872Document10 pagesNavaneeth Ss 1529: Section 191 of The Indian Contract Act, 1872Navaneeth NeonNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act, 1872 Ms. NiharikaDocument6 pagesIndian Contract Act, 1872 Ms. NiharikasatyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction & CreationDocument34 pagesIntroduction & CreationirfafNo ratings yet
- Agent:: Agreement Between Principal and AgentDocument8 pagesAgent:: Agreement Between Principal and AgentIbrahim HassanNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii Agency-Definition - Creation of Agency - Kinds of Agents - Distinction Between Agent andDocument24 pagesUnit - Iii Agency-Definition - Creation of Agency - Kinds of Agents - Distinction Between Agent andAnilNo ratings yet
- Hari Priya-Hari Priya ContractsDocument9 pagesHari Priya-Hari Priya ContractsSAURABH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Contract of Agency-3Document11 pagesUnit 1 Contract of Agency-3thalapathy.7502No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - AgencyDocument47 pagesChapter 13 - AgencyRishabh NigamNo ratings yet
- Contracts of AgencyDocument20 pagesContracts of AgencyMallikarjunaNo ratings yet
- CONTRACT OF AGENCY (EDITED) Summarised DocumentDocument10 pagesCONTRACT OF AGENCY (EDITED) Summarised DocumentShubham PhophaliaNo ratings yet
- Law of AgencyDocument11 pagesLaw of Agencyprabharun18No ratings yet
- Law of Contract (Karan)Document6 pagesLaw of Contract (Karan)Hardik ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 1.7 Law of AgencyDocument14 pages1.7 Law of AgencyGastor Hilary MtweveNo ratings yet
- Agency - Finer Details in The Indian ContextDocument6 pagesAgency - Finer Details in The Indian ContextKumar NaveenNo ratings yet
- Contract of Agency 5thDocument35 pagesContract of Agency 5thtaimoor akbarNo ratings yet
- BL Unit - IiDocument10 pagesBL Unit - IiRisha A.MNo ratings yet
- Contract of Agency ProjectDocument5 pagesContract of Agency Projectdhingra cafeNo ratings yet
- LAW AssignmentDocument5 pagesLAW AssignmentPrasanna KumarNo ratings yet
- TroductionDocument9 pagesTroductionAvinash GunnaNo ratings yet
- Law of Agency in Malaysia (Lecture 14) (Autosaved)Document25 pagesLaw of Agency in Malaysia (Lecture 14) (Autosaved)Kenneth Wen Xuan TiongNo ratings yet
- Contract of Agency MainDocument14 pagesContract of Agency MainIbrahim Hassan100% (1)
- Contract of AgencyDocument14 pagesContract of AgencyRamasayi Gummadi100% (1)
- Screenshot 2023-06-15 at 08.47.34Document11 pagesScreenshot 2023-06-15 at 08.47.34Ellyriana QistinaNo ratings yet
- Contract of AgencyDocument90 pagesContract of AgencyAadhitya NarayananNo ratings yet
- AGENCYDocument154 pagesAGENCYAdityaSharmaNo ratings yet
- Contract of AgencyDocument19 pagesContract of AgencyPinky BangarhNo ratings yet
- Part 1 AgencyDocument9 pagesPart 1 AgencyMark Anthony ParinasNo ratings yet
- AgencyDocument5 pagesAgencySha MatNo ratings yet
- The Formation of Agency and TerminationDocument18 pagesThe Formation of Agency and Terminationpiyush anandNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Answer: UNIT 3: Contract of AgencyDocument6 pagesQuestion Bank Answer: UNIT 3: Contract of Agencyameyk89No ratings yet
- Contract Assignment UtsavDocument10 pagesContract Assignment UtsavThe Untold StoryNo ratings yet
- WEEK 11 Reading MaterialsDocument5 pagesWEEK 11 Reading MaterialsVineetha Victor GonsalvezNo ratings yet
- The Formation of Agency and TerminationDocument14 pagesThe Formation of Agency and TerminationPriyesh Garg80% (5)
- Contract of Agency: Sec 56 of NCA, Any Person May Appoint Any Other PersonDocument31 pagesContract of Agency: Sec 56 of NCA, Any Person May Appoint Any Other PersonAyesha jamesNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide for Drafting of Conveyances in India : Forms of Conveyances and Instruments executed in the Indian sub-continent along with Notes and TipsFrom EverandA Simple Guide for Drafting of Conveyances in India : Forms of Conveyances and Instruments executed in the Indian sub-continent along with Notes and TipsNo ratings yet
- Life, Accident and Health Insurance in the United StatesFrom EverandLife, Accident and Health Insurance in the United StatesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Landlord And Tenant Relationship: Fast & Easy Solutions To Tenancy Problems; In Simple English, For EveryoneFrom EverandLandlord And Tenant Relationship: Fast & Easy Solutions To Tenancy Problems; In Simple English, For EveryoneRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Key Question: Where Do Tourists Prefer To Go? Why?Document30 pagesKey Question: Where Do Tourists Prefer To Go? Why?law notesNo ratings yet
- Write NowDocument158 pagesWrite Nowlaw notesNo ratings yet
- Contracts Law-IDocument117 pagesContracts Law-Ilaw notesNo ratings yet
- The Key To Wisdom Is Knowing All The Right Questions PDFDocument5 pagesThe Key To Wisdom Is Knowing All The Right Questions PDFlaw notes100% (1)
- The Key To Wisdom Is Knowing All The Right Questions PDFDocument5 pagesThe Key To Wisdom Is Knowing All The Right Questions PDFlaw notes100% (1)
- Regional Destination Patterns Q5Document17 pagesRegional Destination Patterns Q5law notesNo ratings yet
- Regional Destination Patterns Q5Document17 pagesRegional Destination Patterns Q5law notesNo ratings yet
- Destination Management: Unit IDocument111 pagesDestination Management: Unit Ilaw notesNo ratings yet
- EnvDocument9 pagesEnvlaw notesNo ratings yet
- Sem 2 Questions - Short QuestionsDocument13 pagesSem 2 Questions - Short Questionslaw notesNo ratings yet
- Qui Facit Per Alium Facit Per Se Is A Latin - Legal Term ThatDocument15 pagesQui Facit Per Alium Facit Per Se Is A Latin - Legal Term Thatlaw notesNo ratings yet
- 100 Landmark Cases in Constitutional Law PDFDocument18 pages100 Landmark Cases in Constitutional Law PDFadventure of Jay Khatri80% (10)
- Const AnswersDocument4 pagesConst Answerslaw notesNo ratings yet
- A Guide Illustrated With America's Favorite Comics: Dealing With Insults, Teasing and CritcismDocument49 pagesA Guide Illustrated With America's Favorite Comics: Dealing With Insults, Teasing and Critcismlaw notesNo ratings yet
- Written StatementDocument3 pagesWritten Statementlaw notesNo ratings yet
- Company Law PDFDocument36 pagesCompany Law PDFSvb CharyNo ratings yet
- Drafting Apperance and PleadingsDocument384 pagesDrafting Apperance and PleadingsDeepak Kumar100% (2)
- Law College Notes & Stuffs: For More Stuff Like This, Join HereDocument2,000 pagesLaw College Notes & Stuffs: For More Stuff Like This, Join Herelaw notes100% (2)
- SC Dismisses Plea Seeking Uniform Welfare Scheme For Lawyers in Distress Due To LockdownDocument22 pagesSC Dismisses Plea Seeking Uniform Welfare Scheme For Lawyers in Distress Due To Lockdownlaw notesNo ratings yet
- Law of Evidence Notes LLBDocument216 pagesLaw of Evidence Notes LLBSpeedie records83% (47)
- Indian Contract Act, 1872Document302 pagesIndian Contract Act, 1872Neha Kalra100% (3)
- 2355a PDFDocument933 pages2355a PDFsheshadiNo ratings yet
- Law College Notes & Stuffs: For More Stuff Like This, Join HereDocument2,000 pagesLaw College Notes & Stuffs: For More Stuff Like This, Join Herelaw notes100% (2)
- (BREAKING) Right To Default Bail Under Section 167 (2) CRPC Not Affected by SC Order Extending Limitation - Madras HC (Read Order) PDFDocument22 pages(BREAKING) Right To Default Bail Under Section 167 (2) CRPC Not Affected by SC Order Extending Limitation - Madras HC (Read Order) PDFlaw notesNo ratings yet
- SyllubusDocument5 pagesSyllubusV V Subba RaoNo ratings yet
- About Us: An Outline of Arriver's PhilosophyDocument11 pagesAbout Us: An Outline of Arriver's Philosophylaw notesNo ratings yet
- Alternate Dispute Resolution ADR Renaissance Law College NotesDocument70 pagesAlternate Dispute Resolution ADR Renaissance Law College NotesAaera Singh100% (1)
- 20 Topics For First Internal Family Law IIDocument1 page20 Topics For First Internal Family Law IIlaw notesNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law II Assigned Cases 2Document5 pagesConstitutional Law II Assigned Cases 2Dewm DewmNo ratings yet
- Umc v. Dy Hian Tat, 28 Scra 161Document1 pageUmc v. Dy Hian Tat, 28 Scra 161Gabriel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Civil Law Digested Cases Leonen's 2012-2020Document208 pagesCivil Law Digested Cases Leonen's 2012-2020Sheryl Mae Addun Querobines100% (2)
- Batas Pambansa Bilang 68Document23 pagesBatas Pambansa Bilang 68RB BalanayNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 181132Document5 pagesG.R. No. 181132Tin LicoNo ratings yet
- Acting Registrars of Land Titles and Deeds of Pasay City, Pasig and Makati vs. RTC, Branch 57, Makati, MM.Document19 pagesActing Registrars of Land Titles and Deeds of Pasay City, Pasig and Makati vs. RTC, Branch 57, Makati, MM.Camille Yasmeen SamsonNo ratings yet
- The Law of AgencyDocument2 pagesThe Law of AgencyramboNo ratings yet
- ABELLA - Sheet2 - Veloso V CA (G.R. No. 102737. August 21, 1996)Document2 pagesABELLA - Sheet2 - Veloso V CA (G.R. No. 102737. August 21, 1996)Kiana AbellaNo ratings yet
- OBLICON - Novation - RequisitesDocument57 pagesOBLICON - Novation - RequisitesCGNo ratings yet
- Company LawDocument2 pagesCompany LawShrayee MukherjiNo ratings yet
- Lipat vs. BankingDocument3 pagesLipat vs. BankingNympa VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- N Srinivasa V Kuttukaran Machine Tools Ltd-AIR 2009 SC 2217Document6 pagesN Srinivasa V Kuttukaran Machine Tools Ltd-AIR 2009 SC 2217SwapnilRastogiNo ratings yet
- Arturo C. Calubad, Petitioner. Ricarcen Development Corp., RespondentDocument2 pagesArturo C. Calubad, Petitioner. Ricarcen Development Corp., Respondenthoney samaniego75% (4)
- Saw v. CADocument2 pagesSaw v. CABananaNo ratings yet
- Oblicon (First Meeting Cases)Document130 pagesOblicon (First Meeting Cases)StelaNo ratings yet
- Transpo Case DigestDocument10 pagesTranspo Case DigestSam FajardoNo ratings yet
- Defenses, StudicataDocument4 pagesDefenses, StudicatajaredNo ratings yet
- Bautista-Spille v. NICORP Management and Development Corp.Document6 pagesBautista-Spille v. NICORP Management and Development Corp.Rhona MarasiganNo ratings yet
- STRONGHOLD INSURANCE COMPANY, INC. v. RUNEDocument2 pagesSTRONGHOLD INSURANCE COMPANY, INC. v. RUNEEmmanuel Princess Zia Salomon100% (1)
- 2 Legal LiabilityDocument68 pages2 Legal LiabilityEmilia Ahmad Zam ZamNo ratings yet
- LTD NOTES ASGDocument26 pagesLTD NOTES ASGmark anthony mansuetoNo ratings yet
- SANJEEVNI BOOTI SLIDES For Business Law CA FoundationDocument80 pagesSANJEEVNI BOOTI SLIDES For Business Law CA FoundationMØBÅ 亗 HÌMÙ 7No ratings yet
- CPC II - Group B (Sem VIII - Batch 2016-21) - Project TopicsDocument5 pagesCPC II - Group B (Sem VIII - Batch 2016-21) - Project Topicsmansavi bihaniNo ratings yet
- Section 69 of The Indian Contract ActDocument3 pagesSection 69 of The Indian Contract ActheretostudyNo ratings yet
- Lloyd's Law Reports SHASHOUA AND OTHERS V SHARMADocument11 pagesLloyd's Law Reports SHASHOUA AND OTHERS V SHARMADeon FernandesNo ratings yet
- Duty of Reasonable CareDocument3 pagesDuty of Reasonable CareRoshi DesaiNo ratings yet
- Us V MilwaukeeDocument6 pagesUs V MilwaukeeElaine Atienza-Illescas100% (1)
- Paragas V Hrs. of BalacanoDocument9 pagesParagas V Hrs. of BalacanoNicole ClianoNo ratings yet
- Vicarious Liability Only Master ServantDocument20 pagesVicarious Liability Only Master ServantSandhya TMNo ratings yet
- Memorial For MootDocument27 pagesMemorial For Mootekankme53% (17)