Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test Exam Basic Land Navigation Part 1: NAME - DATE
Uploaded by
Chu Nhật DuyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test Exam Basic Land Navigation Part 1: NAME - DATE
Uploaded by
Chu Nhật DuyCopyright:
Available Formats
NAME _____________________________________ DATE _____________
TEST EXAM
BASIC LAND NAVIGATION PART 1
1. Knowing these four basic skills, it is impossible to be totally lost; what are they?
a. Track Present Location / Determine Distance / Sense of Direction / How to Read a Topographic Map
b. Track Present Location / Determine Distance / Night Navigation / How to Read a Topographic Map
c. Track Present Location / Staying on Course / Sense of Direction / Terrain and Map Association
d. Track Present Location / Plan to Navigate / Sense of Direction / How to Read a Topographic Map
2. True False (circle one)
A 'deep-well' design is used to allow the compass to be used globally with little or no effect in accuracy
caused by a tilting compass dial.
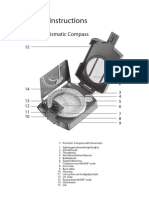
3. Label items by number, using the following list.
___ LANYARD RING ___ FIXED INDEX LINE
___ LENS ___ GRADUATED STRAIGHT EDGE
___ FLOATING DIAL ___ THUMB LOOP
___ BEZEL ___ SIGHTING WIRE
___ LUMINOUS SIGHT DOTS ___ LUMINOUS HEADING
___ LUMINOUS MAGNETIC ARROW ___ LUMINOUS BEZEL LINE
___ SIGHTING SLOT
4. Sighting Wire is?
a. Used with Sighting Slot, for sighting landmarks for an azimuth heading.
b. Used with Lens, for sighting landmarks for an azimuth heading.
c. Used with Luminous Sighting Dots, for sighting landmarks for an azimuth heading.
d. Used with Fixed Index Line, for sighting landmarks for an azimuth heading.
BASIC LAND NAVIGATION PART 1 PAGE 2
5. The Bezel Ring has the following features. (circle all that apply)
a. Device clicks when turned d. Turns clockwise (right) and counterclockwise (left)
b. Turns only clockwise (right) e. Rotates a full 360°
c. Each click equals 3° f. Luminous Bezel Line rotates with it
6. True False (circle one)
Luminous Bezel Line (when aligned with the Luminous Magnetic Arrow) is used to mark a course
(azimuth) direction during day or night navigation.
7. Current azimuth heading is read from?
a. Luminous Bezel Line
b. Luminous Magnetic Arrow
c. Fixed Index Line
d. Luminous Heading
8. Floating Dial black scale is?
a. In degrees and each degree mark equals 5°
b. In degrees and each degree mark equals 20°
c. In mils and each mil mark equals 5°
d. In mils and each mil mark equals 20°
9. Floating Dial red scale is?
a. In degrees and each degree mark equals 5°
b. In degrees and each degree mark equals 20°
c. In mils and each mil mark equals 5°
d. In mils and each mil mark equals 20°
10. True False (circle one)
The fake cheap lensatic compass has the same features as the GENUINE LENSATIC COMPASS, and is
as durable that it will never malfunction, unless you deliberately mistreat, or break the lensatic compass.
11. True False (circle one)
The GENUINE LENSATIC COMPASS is so durable that it should never malfunction, unless you
deliberately mistreat, or break the lensatic compass.
12. The Graduated Straight Edge is?
a. Used to take distance measurements from point “A” to point “B” on maps.
b. Used to take distance measurements from point “A” to point “B” on maps; in conjunction with the
distance bar scales on the map.
c. Used to take scale measurements from point “A” to point “B” on maps.
d. Used to take scale measurements from point “A” to point “B” on maps; in conjunction with the time
bar scales on the map.
13. True False (circle one)
The LENS can be used to start a fire in an emergency, when the sun is out and bright. The lens is designed
to strongly focus the sun rays. The strongly focused sun rays get hot enough to start a fire. Remember
this is a compass and a fire starter.”
14. True False (circle one)
The LENS is used to read the dial only and is not a fire starter.
BASIC LAND NAVIGATION PART 1 PAGE 3
15. True False (circle one)
When traveling, make sure that the rear sight is totally folded down as this will lock the floating dial and
prevent vibration, as well as protect the crystal and rear sight from being damaged.
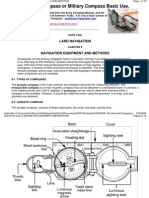
16. This is what you see in the lens, looking at the dial face. What are the Degrees and the Mils?
Degrees _____________ Mils ________________
17. This technique is used almost exclusively for sighting landmarks, and is the best for taking an accurate
azimuth bearing.
a. Center-Hold method
b. Hand-to-Chest method
c. Compass-to-Cheek method
d. Rear-to-Front Sight method
18. This technique is less precise, but is faster to use and can be used under all conditions of visibility.
a. Center-Hold method
b. Hand-to-Chest method
c. Compass-to-Cheek method
d. Rear-to-Front-Sight method
19. What methods are these?
a. _______________________________ b. _______________________________
BASIC LAND NAVIGATION PART 1 PAGE 4
20. Five basic colors are used for Topographic Maps. Match colors with features.
___ Brown 1. Vegetation
___ Black 2. Contour lines
___ Blue 3. Water
___ Green 4. Man made, roads, trails
___ Red 6. Highways
21. Maps are read for four basic kinds of information.
a. Colors / Map Scale / Direction / Identification
b. Direction / Symbols / Position / Identification
c. Altitude / Distance / Vegetation / Coordinates
d. Direction / Distance / Position / Identification
22. True False (circle one)
You must know the map scale to determine ground distances between objects or locations on the map, the
size of the area covered, and how the scale may affect the amount of detail being shown.
23. True False (circle one)
The LARGE scale map shows less land area, but more detail. And the SMALL scale map shows more
land area, but less detail.
24. True False (circle one)
Map scale is the relationship between distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the lensatic
compass Graduated Straight Edge measurement, not on the ground.
25. Match contour lines with land feature.
1.____ A.
2.____ B.
3.____ C.
4.____ D.
26. You need a way of expressing direction that is accurate, is adaptable to any part of the world, and has a
common unit of measure. North is the common unit of direction. Name the three types.
a. _____________________________
b. _____________________________
c. _____________________________
BASIC LAND NAVIGATION PART 1 PAGE 5
27. Select the TWO correct statements.
a. When using a map - use a protractor to measure GRID azimuth bearings.
b. When using a map - use a compass to measure GRID azimuth bearings.
c. When using the ground – use a Compass to Measure MAGNETIC azimuth bearings.
d. When using the ground – use a protractor to Measure MAGNETIC azimuth bearings.
28. The Protractor features? (circle all that apply)
a. Map has to be oriented d. Convert direction from ground to map
b. Map does not have to be oriented e. Plotting azimuths, position, UTM coordinates
c. Calculate direction from map to ground f. Determine azimuth by sighting a ground landmark
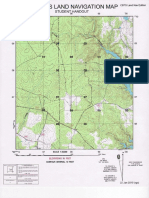
29. With the protractor’s edge aligned with the map GRID line and the center of the protractor aligned with
your location; what azimuth do you travel to reach the lake?
a. DEGREES ____________ b. MILS _____________
30. True False (circle one)
All members of the group should know the map’s location at all times.
31. True False (circle one)
It is hard to navigate accurately with a dirty, grimy, wet or damaged map. Take care of your map and it
will take care of you.
BASIC LAND NAVIGATION PART 1 PAGE 6
32. When orienting a map with the Lensatic Compass, which one below is correct? (circle one)
a. Using the MN line.
b. Using the True North line.
33. True False (circle one)
The purpose of the Lensatic Compass Lanyard Ring is to tie a string or rope loop to it; so you can keep it
around your neck or an attachment close to your chest, or a chest pocket for easy, quick access.
END OF TEST (each question is worth 3 points)
BASIC LAND NAVIGATION PART 1 PAGE 7
You might also like
- BMC 3Document30 pagesBMC 3Tom AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Precision LensaticDocument16 pagesPrecision LensaticKuat SudrajatNo ratings yet
- Adventure Badge Notes For BoysDocument34 pagesAdventure Badge Notes For BoysMani Kumaresan Janarthanavel (Scss)No ratings yet
- Short QuestionsDocument8 pagesShort QuestionsPavneetNo ratings yet
- Land Nav GuideDocument33 pagesLand Nav GuidemarvNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physical Geography 2nd Edition Petersen Test BankDocument10 pagesFundamentals of Physical Geography 2nd Edition Petersen Test BankJordanWilliamspsgfa100% (18)
- Land Navigation Navigation Equipment and Methods: 9-1. Types of CompassesDocument13 pagesLand Navigation Navigation Equipment and Methods: 9-1. Types of CompassescrazybuttfulNo ratings yet
- HOPE 4 Module 4 Compass ReadingDocument9 pagesHOPE 4 Module 4 Compass ReadingJoross SabadoNo ratings yet
- 2021 22 Thane Essential Features of Maps-a15ZFAV6rLKyVDocument4 pages2021 22 Thane Essential Features of Maps-a15ZFAV6rLKyVD DandekarNo ratings yet
- Meridian Pro USADocument12 pagesMeridian Pro USAmstefanel71No ratings yet
- Navigation and Field Mapping: in This Chapter You Will Learn AboutDocument16 pagesNavigation and Field Mapping: in This Chapter You Will Learn AboutAndrew SeptiadiNo ratings yet
- H.O.P.E. 4 Module 4Document11 pagesH.O.P.E. 4 Module 4Rye IsshNo ratings yet
- Module 2 ActivityDocument4 pagesModule 2 ActivityGerald MontanoNo ratings yet
- Survey MCQ'S PDFDocument14 pagesSurvey MCQ'S PDFPavan Ps86% (7)
- pms475 Chap6aDocument16 pagespms475 Chap6aapi-257363586No ratings yet
- Military CompassDocument17 pagesMilitary Compassivan333ivanovic100% (1)
- Online Education Outdoor NavigationDocument32 pagesOnline Education Outdoor NavigationR. Mega MahmudiaNo ratings yet
- 4.1.1 - Lesson Plan - Introduction To Map ReadingDocument5 pages4.1.1 - Lesson Plan - Introduction To Map ReadingUlixes Maguate100% (1)
- Theory and PracticeDocument5 pagesTheory and PracticeRAUL BECERRONo ratings yet
- Operating Instructions: M-73 & M-88 CompassesDocument2 pagesOperating Instructions: M-73 & M-88 CompassesWilliam WoolleyNo ratings yet
- Land Navigation Part 1Document122 pagesLand Navigation Part 1sidney_henderson_2No ratings yet
- Historical Background of OrienteeringDocument2 pagesHistorical Background of Orienteeringleomille2No ratings yet
- Map Reading Hand OutDocument7 pagesMap Reading Hand OutWesley Jun MuñezNo ratings yet
- Air Cadet Publication: NavigationDocument52 pagesAir Cadet Publication: NavigationMarcus DragoNo ratings yet
- ACP 32 Volume 1 - Map ReadingDocument66 pagesACP 32 Volume 1 - Map Readingcockybundoo100% (1)
- How To Use A CompassDocument10 pagesHow To Use A CompassShaun JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Basic Military Compass EnhancedDocument19 pagesBasic Military Compass EnhancedPATRIOTSKULLZ100% (2)
- m73 Compass PDFDocument2 pagesm73 Compass PDFZoltan SomogyiNo ratings yet
- Landnav Module 1Document54 pagesLandnav Module 1ivan333ivanovicNo ratings yet
- Cartography WorksheetDocument3 pagesCartography WorksheetDario ŠakićNo ratings yet
- Cammenga Instruction US Military SheetsDocument16 pagesCammenga Instruction US Military SheetsHeimos GarciaNo ratings yet
- Geography Skills Book GR 10,11,12 2022Document55 pagesGeography Skills Book GR 10,11,12 2022Julia100% (1)
- (A) Board Exam 2016Document13 pages(A) Board Exam 2016Row RowNo ratings yet
- Geography Mid 10 2014Document1 pageGeography Mid 10 2014Abdi MohammedNo ratings yet
- MathsTraks: Geometry: A Collection of Blackline Masters for ages 11-14From EverandMathsTraks: Geometry: A Collection of Blackline Masters for ages 11-14No ratings yet
- 3.1 Preliminary ExaminationDocument8 pages3.1 Preliminary ExaminationDave Florian BalanonNo ratings yet
- Plane Table Surveying NotesDocument25 pagesPlane Table Surveying Notesjamil ahmedNo ratings yet
- CVG2171 Course Outline Jan 2021Document2 pagesCVG2171 Course Outline Jan 2021Disala DesilvaNo ratings yet
- Gis For Environmental Applications A Practical Approach 1st Zhu Test BankDocument36 pagesGis For Environmental Applications A Practical Approach 1st Zhu Test Bankpockplot1eg6y100% (35)
- Orienteering PowerpointDocument28 pagesOrienteering PowerpointCaladhielNo ratings yet
- Department of Geography B.A. /B.Sc. (II Semester) Thematic Cartography (Practical) TopicDocument7 pagesDepartment of Geography B.A. /B.Sc. (II Semester) Thematic Cartography (Practical) TopicMansi SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit1test PDFDocument5 pagesUnit1test PDFurgazuNo ratings yet
- Brecon Navigation BookletDocument15 pagesBrecon Navigation BookletdirknuesinkNo ratings yet
- GE 101 Laboratory Manual: This Lab Manual Was Created by Sarah R. B. Stelmack and Kyle NicholsDocument92 pagesGE 101 Laboratory Manual: This Lab Manual Was Created by Sarah R. B. Stelmack and Kyle NicholsAtzhiri SánchezNo ratings yet
- Field Techniques Manual: GIS, GPS and Remote Sensing: - Section B: DataDocument34 pagesField Techniques Manual: GIS, GPS and Remote Sensing: - Section B: Datasbabic44No ratings yet
- CartoDocument5 pagesCartoLaarni HilarioNo ratings yet
- Preboard 2 TNP 2022Document8 pagesPreboard 2 TNP 2022Christorey MontegrandeNo ratings yet
- Term 1 Feb Controlled Test TVS Grade 11 - MEMODocument4 pagesTerm 1 Feb Controlled Test TVS Grade 11 - MEMONikhil DeolallNo ratings yet
- How To Use A CompassDocument7 pagesHow To Use A Compasskenneth mayao100% (1)
- Q3 MATH 7 Module 3 With Answer KeyDocument17 pagesQ3 MATH 7 Module 3 With Answer KeyRogelyn CustodioNo ratings yet
- RECTA DP 2 Instruction ManualDocument2 pagesRECTA DP 2 Instruction ManualxcpNo ratings yet
- Direction B181996 Student Handout: The Basic School Marine Corps Training Command Camp Barrett, Virginia 22134-5019Document33 pagesDirection B181996 Student Handout: The Basic School Marine Corps Training Command Camp Barrett, Virginia 22134-5019Abera FentahunNo ratings yet
- Function: Navigation at The Operational Level Competence: Plan and Conduct A Passage and Determine PositionDocument4 pagesFunction: Navigation at The Operational Level Competence: Plan and Conduct A Passage and Determine PositionAbu Nawshad100% (3)
- Final Exam Review1Document11 pagesFinal Exam Review1Keith Gruber100% (2)
- Digital Geography TrainingDocument76 pagesDigital Geography TrainingOODI MENAKERNo ratings yet
- How To Read a Nautical Chart: A Captain's Quick GuideFrom EverandHow To Read a Nautical Chart: A Captain's Quick GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- The Preparation of Illustrations for Reports of the United States Geological Survey With Brief Descriptions of Processes of ReproductionFrom EverandThe Preparation of Illustrations for Reports of the United States Geological Survey With Brief Descriptions of Processes of ReproductionNo ratings yet
- BUSI1633 - Strategy - For - Managers - 2021-22 - Report BDocument10 pagesBUSI1633 - Strategy - For - Managers - 2021-22 - Report BNguyen Phuong Mai (FGW HN)No ratings yet
- Greek - Tourism - Industry - Case Instructions - 2022-2023Document1 pageGreek - Tourism - Industry - Case Instructions - 2022-2023Chu Nhật DuyNo ratings yet
- Assigment 1 DraftDocument6 pagesAssigment 1 DraftChu Nhật DuyNo ratings yet
- Hoto Team M BÁN FILE KHÁCH HÀNGDocument6 pagesHoto Team M BÁN FILE KHÁCH HÀNGChu Nhật DuyNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Customer Retention in The Airline IndustryDocument21 pagesFactors Affecting Customer Retention in The Airline IndustryChu Nhật DuyNo ratings yet
- Disruptive Innovation Automotive Arun Mazurek PaterDocument17 pagesDisruptive Innovation Automotive Arun Mazurek PaterChu Nhật DuyNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement - Savage t11Document46 pagesFinancial Statement - Savage t11Chu Nhật DuyNo ratings yet
- Biz Environtment DraftDocument5 pagesBiz Environtment DraftChu Nhật DuyNo ratings yet
- Sell Products and Services To Customers For Personal Use. This Can Include Cruises, Clothing, Cars, Landscaping ServicesDocument1 pageSell Products and Services To Customers For Personal Use. This Can Include Cruises, Clothing, Cars, Landscaping ServicesChu Nhật DuyNo ratings yet
- hotcomic.net.txtDocument1 pagehotcomic.net.txtChu Nhật DuyNo ratings yet
- List of Regia Aeronautica Aircraft Used in World War IIDocument10 pagesList of Regia Aeronautica Aircraft Used in World War IIChu Nhật DuyNo ratings yet
- Template International Treaty Action Paper 03 - 1Document4 pagesTemplate International Treaty Action Paper 03 - 1Chu Nhật DuyNo ratings yet
- Encampment Land Navigation Student MapDocument1 pageEncampment Land Navigation Student MapJim Bob100% (1)
- Easy Step-By-Step Eisbein Recipe Learn To Make German Eisbein PDFDocument2 pagesEasy Step-By-Step Eisbein Recipe Learn To Make German Eisbein PDFChu Nhật DuyNo ratings yet
- Easy Step-By-Step Eisbein Recipe Learn To Make German Eisbein PDFDocument2 pagesEasy Step-By-Step Eisbein Recipe Learn To Make German Eisbein PDFChu Nhật DuyNo ratings yet
- SCP Foundation Iris Through The Looking Glass Volume 1 Dark PDFDocument243 pagesSCP Foundation Iris Through The Looking Glass Volume 1 Dark PDFChu Nhật Duy68% (22)
- The Geneva Conventions of August 12 1949Document224 pagesThe Geneva Conventions of August 12 1949International Committee of the Red Cross100% (2)
- German Warships DrawingDocument30 pagesGerman Warships DrawingChu Nhật DuyNo ratings yet
- 000 CoverDocument213 pages000 CoverChu Nhật DuyNo ratings yet
- IzumoDocument1 pageIzumoChu Nhật DuyNo ratings yet
- 빛공해 방지를 위한 조명기구 설치·관리 권고기준 가이드라인Document114 pages빛공해 방지를 위한 조명기구 설치·관리 권고기준 가이드라인ByungHoon JungNo ratings yet
- Fleishman AP 1975 - Towards A Taxonomy of Human PerformanceDocument23 pagesFleishman AP 1975 - Towards A Taxonomy of Human PerformanceCatalina Elena100% (2)
- SV1-10-4/4M/4R: - Solenoid ValveDocument2 pagesSV1-10-4/4M/4R: - Solenoid ValveCORTOCIRCUITANTENo ratings yet
- Dynamic Analysis of Gear Shifting MechanismDocument4 pagesDynamic Analysis of Gear Shifting MechanismMr. S. Thiyagu Asst Prof MECHNo ratings yet
- Xtivia Oracle Errors EbookDocument27 pagesXtivia Oracle Errors EbookVishal S RanaNo ratings yet
- Ca 3241Document1 pageCa 3241Tien LamNo ratings yet
- Math 1712Document11 pagesMath 1712fake emailNo ratings yet
- Low Shock Stage Separation System For Long Range Missile ApplicationDocument3 pagesLow Shock Stage Separation System For Long Range Missile ApplicationalexNo ratings yet
- Study of RGB Color Classification Using Fuzzy LogicDocument6 pagesStudy of RGB Color Classification Using Fuzzy LogicBhavin GajjarNo ratings yet
- 19-104 ResearchPaperDocument6 pages19-104 ResearchPaperGimhani KavishikaNo ratings yet
- Activate 1 BiologyDocument120 pagesActivate 1 BiologyMarina Belloni100% (1)
- Process: Add Menu Item Master, Definition, Price: Step ActionDocument7 pagesProcess: Add Menu Item Master, Definition, Price: Step ActionPrince HakimNo ratings yet
- Adaptive-Fuzzy Logic Control of Robot Manipulators S. Commuri and F.L. LewisDocument6 pagesAdaptive-Fuzzy Logic Control of Robot Manipulators S. Commuri and F.L. LewisNguyễn Thanh TùngNo ratings yet
- BalancesDocument8 pagesBalancescchauling6841No ratings yet
- Log TMBAG6NEXD0028904 210446km 130765miDocument6 pagesLog TMBAG6NEXD0028904 210446km 130765miSasa MitrovicNo ratings yet
- Schedule 90 Days Jee Main Crash Course MathongoDocument3 pagesSchedule 90 Days Jee Main Crash Course MathongoShrish DollinNo ratings yet
- Fast Web View PDF TomcatDocument2 pagesFast Web View PDF TomcatEddieNo ratings yet
- The Mathematical Gazette Volume 86 Issue 507 2002 (Doi 10.2307 - 3621155) Nick Lord - 86.76 Maths Bite - Sides of Regular PolygonsDocument3 pagesThe Mathematical Gazette Volume 86 Issue 507 2002 (Doi 10.2307 - 3621155) Nick Lord - 86.76 Maths Bite - Sides of Regular PolygonsEduardo CostaNo ratings yet
- 6-Engineering Drawing Transformations PDFDocument12 pages6-Engineering Drawing Transformations PDFibrahimsaleh20091884No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current QuestionsDocument2 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric Current QuestionsVinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Inspection and Testing of OC/EF Protection Relay: Relay Site Test ReportDocument3 pagesInspection and Testing of OC/EF Protection Relay: Relay Site Test ReportMASUD RANANo ratings yet
- Door SheetDocument9 pagesDoor SheetAnilkumarNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Hydraulic PumpsDocument15 pages1.3 Hydraulic Pumpsdoan lucNo ratings yet
- Optibelt OMEGA Product RangeDocument10 pagesOptibelt OMEGA Product Rangemoh ragehNo ratings yet
- SMM200 Derivatives and Risk Management 2021 QuestionsDocument5 pagesSMM200 Derivatives and Risk Management 2021 Questionsminh daoNo ratings yet
- 22 - GIS Testing PDFDocument9 pages22 - GIS Testing PDFwaqas_a_shaikh4348No ratings yet
- Fkeyrouz@ndu - Edu.lb: Systems Using MATLAB, Second Edition, Prentice Hall 2002Document2 pagesFkeyrouz@ndu - Edu.lb: Systems Using MATLAB, Second Edition, Prentice Hall 2002Elio EidNo ratings yet
- Peter and Wolf Resource Guide - Boston Philharmonic OrchestraDocument32 pagesPeter and Wolf Resource Guide - Boston Philharmonic OrchestraEmily Sharratt100% (5)
- Montfort Secondary School Chapter 21: Electromagnetism: Name: Date: ClassDocument12 pagesMontfort Secondary School Chapter 21: Electromagnetism: Name: Date: ClasssonghannNo ratings yet
- Telecom-02-00022-V2Document21 pagesTelecom-02-00022-V2husam hamidNo ratings yet