Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MUSCULOSKELETAL
Uploaded by
Vero Steel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageThis document provides guidance on observing and assessing the musculoskeletal system. It outlines how to observe a client's gait and posture, inspect and palpate the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), and test range of motion. Normal findings include evenly distributed weight bearing, erect posture, smooth jaw movement, and full range of motion without pain. Abnormal findings may include limping, slouching, decreased jaw opening, swelling, tenderness, or restricted movement.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides guidance on observing and assessing the musculoskeletal system. It outlines how to observe a client's gait and posture, inspect and palpate the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), and test range of motion. Normal findings include evenly distributed weight bearing, erect posture, smooth jaw movement, and full range of motion without pain. Abnormal findings may include limping, slouching, decreased jaw opening, swelling, tenderness, or restricted movement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageMUSCULOSKELETAL
Uploaded by
Vero SteelThis document provides guidance on observing and assessing the musculoskeletal system. It outlines how to observe a client's gait and posture, inspect and palpate the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), and test range of motion. Normal findings include evenly distributed weight bearing, erect posture, smooth jaw movement, and full range of motion without pain. Abnormal findings may include limping, slouching, decreased jaw opening, swelling, tenderness, or restricted movement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
Observe gait. Observe the client’s gait as the
client enters and walks around the room.
Note: • Base of support • Weight-bearing
stability • Foot position • Stride and length and
cadence of stride • Arm swing • Posture
NORMAL: Evenly distributed weight.
Client able to stand on heels and toes.
Toes point straight ahead. Equal on both
sides. Posture erect, movements
coordinated and rhythmic, arms swing in
opposition, stride length appropriate.
ABNORMAL: Uneven weight bearing
is evident. Client cannot stand on heels
or toes. Toes point in or out. Client
limps, shuffles, propels forward, or has
wide-based gait.
Observe posture
Normal: posture is erect and
comfortable for age
Abnormal: slumped shoulders may
result from poor posture or from
depression. Abnormal curvatures of
spine. Include in lordosis (excessive
curvature of spine), kyphosis
(rounded thoracic convexity)
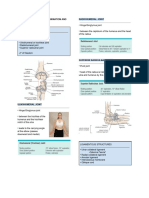
Inspect and palpate the TMJ. Have the client
sit; put your index and middle fingers just
anterior to the external ear opening
NORMAL: Snapping and clicking
may be felt and heard in the normal
client. Mouth opens 1–2 inches
(distance between upper and lower
teeth). The client’s mouth opens and
closes smoothly. Jaw moves laterally
1–2 cm. Jaw protrudes and retracts
easily.
ABNORMAL: Decreased ROM,
swelling, tenderness, or crepitus may be
seen in arthritis. Decreased muscle
strength with muscle and joint disease.
Decreased ROM, and a clicking,
popping, or grating sound may be noted
with TMJ dysfunction
Test ROM.
NORMAL: Jaw has full ROM against
resistance. Contraction palpated with no
pain or spasms.
ABNORMAL: Lack of full contraction
with cranial nerve V lesion. Pain or
spasms occur with myofascial pain
syndrome.
You might also like
- Achilles Tendon Rupture, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAchilles Tendon Rupture, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences: Sultan Kudarat State UniversityDocument8 pagesCollege of Health Sciences: Sultan Kudarat State UniversityGeremie Magno Mana-ayNo ratings yet
- Test For Back and Leg PainDocument8 pagesTest For Back and Leg PainJehazel BastianNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Musculoskelet Al SystemDocument93 pagesAssessment of Musculoskelet Al SystemJojo JustoNo ratings yet
- Hip (Word)Document32 pagesHip (Word)dwNo ratings yet
- Posterior and Gait: Presented By: Samantha Nicole T. MendozaDocument17 pagesPosterior and Gait: Presented By: Samantha Nicole T. MendozaSamantha Nicole MendozaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Musculoskeleta L SystemDocument103 pagesAssessment of Musculoskeleta L SystemDenniellePaulineKwon0% (1)
- Assessment of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument45 pagesAssessment of The Musculoskeletal Systemstudentme annNo ratings yet
- Inspection: Neck and Spine Have No Noted Deformities or Signs of InflammationDocument2 pagesInspection: Neck and Spine Have No Noted Deformities or Signs of InflammationgoodNo ratings yet
- Assessment MusculoskeletalDocument6 pagesAssessment Musculoskeletaldd marshall100% (1)
- Physical Assessment MSK Level 3 2019Document93 pagesPhysical Assessment MSK Level 3 2019Daniela OrtalNo ratings yet
- Cerebellar DisordersDocument51 pagesCerebellar DisorderswasimNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Musclo-Skletal SystemDocument25 pagesAssessment of The Musclo-Skletal SystemjacnpoyNo ratings yet
- Neurologic AssessmentDocument98 pagesNeurologic AssessmentJona Kristin EnclunaNo ratings yet
- Ortho Neuro ExamsDocument0 pagesOrtho Neuro ExamsMaybs Palec Pamplona-ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument160 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemAirene Aquino BusaniaNo ratings yet
- Assessing Head To Neck Part 1 - CNVSDocument36 pagesAssessing Head To Neck Part 1 - CNVSJayvee BillonesNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Hip Joint: Dr. Pallav AgrawalDocument66 pagesExamination of The Hip Joint: Dr. Pallav AgrawalJohn Agana AyamgaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System: Health AssessmentDocument43 pagesMusculoskeletal System: Health AssessmentEliezer Nuenay100% (1)
- VSR 511blameness PDFDocument162 pagesVSR 511blameness PDFkrishnaa100% (1)
- MSK PDFDocument90 pagesMSK PDFJay Rome100% (1)
- GALS Examination GuideDocument3 pagesGALS Examination GuideyapNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment Head and NeckDocument75 pagesPhysical Assessment Head and NeckDeeeee100% (2)
- PA1 HandoutDocument22 pagesPA1 HandoutIligan, JamaicahNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Joints and ExtremitiesDocument66 pagesExamination of The Joints and Extremitiesapi-25914483No ratings yet
- Far Eastern University Institute of NursingDocument5 pagesFar Eastern University Institute of NursingCheyenne Arville RoldanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Techniques Normal Findings Abnormal Findings A. Gait InspectionDocument12 pagesAssessment Techniques Normal Findings Abnormal Findings A. Gait Inspectionshannon c. lewisNo ratings yet
- Temporomandibular JointDocument3 pagesTemporomandibular JointFatima JamalNo ratings yet
- Cerebellar DisordersDocument29 pagesCerebellar DisordersArslan Aslam100% (1)
- Malunion and Non-UnionDocument12 pagesMalunion and Non-UnionHengkai NeoNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Elbow Region Examination and EvaluationDocument8 pagesLesson - Elbow Region Examination and EvaluationJULIANE MAE BALANGNo ratings yet
- CARE of ADOLESCENTSDocument15 pagesCARE of ADOLESCENTSaprilkate banagodosNo ratings yet
- HEAD and NECKDocument44 pagesHEAD and NECKDanica DaniotNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Musculo-Skeletal SystemDocument46 pagesAssessment of The Musculo-Skeletal SystemRaquel M. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology Examination: Physical Examination-N ManoliosDocument7 pagesRheumatology Examination: Physical Examination-N ManoliosRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- San Pedro College Physical Assessment GuideDocument2 pagesSan Pedro College Physical Assessment Guideallkhusairy6tuansiNo ratings yet
- Examination of Bone and Joint PathologyDocument89 pagesExamination of Bone and Joint PathologyMuhammad Thahir100% (1)
- Elbow PT AssessmentDocument31 pagesElbow PT Assessmentkrissh20No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Disorders - General and Specific: Yoan Rahmah Aprilia 1102013306Document21 pagesMusculoskeletal Disorders - General and Specific: Yoan Rahmah Aprilia 1102013306Yoan Rahmah ApriliaNo ratings yet
- L3 Musculoskeletal Assessment PDFDocument65 pagesL3 Musculoskeletal Assessment PDFElizabeth AbellaNo ratings yet
- Assessing The MusculoskeletalDocument5 pagesAssessing The MusculoskeletalYudi TrigunaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument36 pagesCerebral PalsyZulaikha Fadzil100% (1)
- Knee (Word)Document18 pagesKnee (Word)dwNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System: Health AssessmentDocument25 pagesMusculoskeletal System: Health AssessmentKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Genu Valgus Genu VarusDocument35 pagesGenu Valgus Genu VarusRatu FaniaNo ratings yet
- Neurological Eval SensoryDocument25 pagesNeurological Eval SensoryAyen FornollesNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of The Knee: Oleh: Dr. Darsuna Mardhiah Pembimbing: Dr. Deta Tanuwidjaja, SP - KFRDocument36 pagesPhysical Examination of The Knee: Oleh: Dr. Darsuna Mardhiah Pembimbing: Dr. Deta Tanuwidjaja, SP - KFRsingle_ladyNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Fractures QT PDFDocument42 pagesPediatric Fractures QT PDFyanNo ratings yet
- Health-Asessment-Finals 2Document92 pagesHealth-Asessment-Finals 2Ebun Rosa100% (1)
- Knee&Foot Part1Document28 pagesKnee&Foot Part1SarkawtNo ratings yet
- Ankylosing Spondylitis 1Document31 pagesAnkylosing Spondylitis 1Salman KhanNo ratings yet
- Fractures 2 3Document17 pagesFractures 2 3Prince RajNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Special TestDocument24 pagesOrthopaedic Special TestpradhanaadhityaNo ratings yet
- Leg and Ankle Problems in Primary Care: Briant W. Smith, MD Orthopedic Surgery TPMGDocument50 pagesLeg and Ankle Problems in Primary Care: Briant W. Smith, MD Orthopedic Surgery TPMGArmiya RamliNo ratings yet
- LL UL Musculoskeletal PE - PVD Varicose Veins ENT Headache PE PDFDocument187 pagesLL UL Musculoskeletal PE - PVD Varicose Veins ENT Headache PE PDFKalashini SenadheeraNo ratings yet
- Neurological History and ExaminationDocument30 pagesNeurological History and ExaminationMaria Agatha100% (1)
- Motor and Sensory Examination: Dr. Bandar Al Jafen, MD Consultant NeurologistDocument36 pagesMotor and Sensory Examination: Dr. Bandar Al Jafen, MD Consultant NeurologistJim Jose Antony100% (1)
- Low Back and SacrumDocument27 pagesLow Back and SacrumdwNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Neurological Examination OSCE GuideDocument15 pagesLower Limb Neurological Examination OSCE GuideLeen abusarhanNo ratings yet
- Journal ReviewDocument18 pagesJournal Reviewapi-347854786No ratings yet
- Sample Questions Research.Document6 pagesSample Questions Research.Vero Steel100% (1)
- Chapter 10: Nature of Research Design and MethodsDocument10 pagesChapter 10: Nature of Research Design and MethodsVero SteelNo ratings yet
- Cahpter 10Document1 pageCahpter 10Vero SteelNo ratings yet
- Childhood Diseases: By: Criszelle Angela Darroca Grade 3-HumilityDocument5 pagesChildhood Diseases: By: Criszelle Angela Darroca Grade 3-HumilityVero SteelNo ratings yet
- AndreaDocument1 pageAndreaVero SteelNo ratings yet
- Book, Hammer and The TongueDocument2 pagesBook, Hammer and The TongueVero SteelNo ratings yet
- Bill To Law and State Vs NationDocument3 pagesBill To Law and State Vs NationVero SteelNo ratings yet
- Nation and BayanDocument1 pageNation and BayanVero SteelNo ratings yet
- PathogenesisDocument1 pagePathogenesisVero SteelNo ratings yet
- What Are The Four Stages of RabiesDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Four Stages of RabiesVero SteelNo ratings yet
- Print CakesDocument1 pagePrint CakesVero SteelNo ratings yet
- Microbio Chap 1 2Document11 pagesMicrobio Chap 1 2Vero SteelNo ratings yet
- What Is Young Adulthood?: Piaget's Formal Operations StageDocument4 pagesWhat Is Young Adulthood?: Piaget's Formal Operations StageVero SteelNo ratings yet
- Postpartum: Postpartal Period / PuerperiumDocument17 pagesPostpartum: Postpartal Period / PuerperiumVero SteelNo ratings yet
- Adolescence:: The Developmental Stages of The LearnerDocument5 pagesAdolescence:: The Developmental Stages of The LearnerVero SteelNo ratings yet
- IGOROTDocument1 pageIGOROTVero SteelNo ratings yet
- Imminent Miscarriage: Pink, Red, or Dark BrownDocument3 pagesImminent Miscarriage: Pink, Red, or Dark BrownVero SteelNo ratings yet
- Remembering Rizal: Custodio, CoscolluelaDocument9 pagesRemembering Rizal: Custodio, CoscolluelaVero Steel89% (9)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (32)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (254)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (170)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesFrom EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1412)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceFrom EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (51)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (46)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (60)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- How to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingFrom EverandHow to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)