Professional Documents
Culture Documents
KJKG KJKG K MKG 350 C C: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.Co - in
Uploaded by
SameerChauhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
KJKG KJKG K MKG 350 C C: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.Co - in
Uploaded by
SameerChauhanCopyright:
Available Formats
www.gatehelp.
com
CHAP 8 THERMODYNAMICS PAGE 347
State h (kJkg−1) s (kJkg−1 K−1) ν (m3 kg−1)
Steam : 4 MPa, 350cC 3092.5 6.5821 0.06645
Water : 15 kPa hf hg sf sg νf νg
225.94 2599.1 0.7549 8.0085 0.001014 10.02
h is specific enthalpy, s is specific entropy and ν the specific volume;
subscripts f and g denote saturated liquid state and saturated vapor state.
MCQ 8.18 The net work output (kJkg−1) of the cycle is
(A) 498 (B) 775
(C) 860 (D) 957
MCQ 8.19 Heat supplied (kJkg−1) to the cycle is
(A) 2372 (B) 2576
(C) 2863 (D) 3092
YEAR 2009 ONE MARK
MCQ 8.20 If a closed system is undergoing an irreversible process, the entropy of the
system
(A) must increase
(B) always remains constant
(C) Must decrease
(D) can increase, decrease or remain constant
MCQ 8.21 A frictionless piston-cylinder device contains a gas initially at 0.8 MPa and
0.015 m3 . It expands quasi-statically at constant temperature to a final
volume of 0.030 m3 . The work output (in kJ) during this process will be
(A) 8.32 (B) 12.00
(C) 554.67 (D) 8320.00
YEAR 2009 TWO MARKS
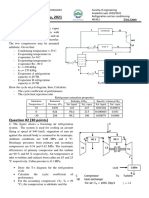
MCQ 8.22 A compressor undergoes a reversible, steady flow process. The gas at inlet
and outlet of the compressor is designated as state 1 and state 2 respectively.
Potential and kinetic energy changes are to be ignored. The following
notations are used :
ν = Specific volume and p = pressure of the gas .
The specific work required to be supplied to the compressor for this gas
compression process is
GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
www.gatehelp.com
PAGE 348 THERMODYNAMICS CHAP 8
2 2
(A) # pdν (B) # νdp
1 1
(C) ν1 (p2 − p1) (D) − p2 (ν1 − ν2)
MCQ 8.23 In an air-standard Otto-cycle, the compression ratio is 10. The condition at
the beginning of the compression process is 100 kPa and 27c C . Heat added
at constant volume is 1500 kJ/kg, while 700 kJ/kg of heat is rejected during
the other constant volume process in the cycle. Specific gas constant for air
= 0.287 kJ/kgK . The mean effective pressure (in kPa) of the cycle is
(A) 103 (B) 310
(C) 515 (D) 1032
MCQ 8.24 An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at
a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW. The entire
work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump
operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17cC
and 75cC . The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its
high temperature sink is
(A) 50 (B) 250
(C) 300 (D) 360
• Common Data For Q.25 and Q.26
The inlet and the outlet conditions of steam for an adiabatic steam turbine
are as indicated in the figure. The notations are as usually followed.
MCQ 8.25 If mass rate of steam through the turbine is 20 kg/s, the power output of
the turbine (in MW) is
(A) 12.157 (B) 12.941
(C) 168.001 (D) 168.785
MCQ 8.26 Assume the above turbine to be part of a simple Rankine cycle. The density of
water at the inlet to the pump is 1000 kg/m3 . Ignoring kinetic and potential
GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
You might also like
- THERMODYNAMICS TITLEDocument68 pagesTHERMODYNAMICS TITLEAnkit AnandNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 THERMODYNAMICS MCQs YEAR 2012-2009Document68 pagesCHAPTER 8 THERMODYNAMICS MCQs YEAR 2012-2009Kumar SahebNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: 3251.0 / KJ KG 15 Kpa 15 Kpa 225.94 / KJ KG 2598.3 / KJ KG 10 / KgsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics: 3251.0 / KJ KG 15 Kpa 15 Kpa 225.94 / KJ KG 2598.3 / KJ KG 10 / KgsSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics MCQs from GATE Previous Year PapersDocument2 pagesThermodynamics MCQs from GATE Previous Year PapersSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument68 pagesThermodynamicsAnuj SaliNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics MCQs and their solutionsDocument123 pagesThermodynamics MCQs and their solutionsVasantha SeelanNo ratings yet
- Common Data For Q. - 58 and Q.59: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument2 pagesCommon Data For Q. - 58 and Q.59: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- ME ThermodynamicsDocument58 pagesME ThermodynamicsprasobhaNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument57 pagesThermodynamicsANILNo ratings yet
- KJ KG: YEAR 2008 One Mark MCQ 8.27Document2 pagesKJ KG: YEAR 2008 One Mark MCQ 8.27SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument58 pagesThermodynamicsSushil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Du W Δ Δ Tds Du Pd Ν Du W Δ Q Du Pd Δ Ν: 0.003155 / Mkg 0.025 M 0.1 Mpa 10 KgDocument2 pagesDu W Δ Δ Tds Du Pd Ν Du W Δ Q Du Pd Δ Ν: 0.003155 / Mkg 0.025 M 0.1 Mpa 10 KgSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- 350 C C 350 C C: Common Data For Q. - 35, 36 and Q.37Document2 pages350 C C 350 C C: Common Data For Q. - 35, 36 and Q.37SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 7 Steam TurbineDocument5 pagesThermodynamics 7 Steam Turbinep_nicks89No ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument58 pagesThermodynamicsGanesh MandpeNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air-ConditioningDocument24 pagesRefrigeration and Air-ConditioningKumar SahebNo ratings yet
- Power Pant Question BookDocument105 pagesPower Pant Question BookJosweeh AndaweyNo ratings yet
- Gate ThermalDocument4 pagesGate Thermalrp0212No ratings yet
- 20 Years Power Plant GATE, IES & IAS Questions with AnswersDocument48 pages20 Years Power Plant GATE, IES & IAS Questions with Answerselajchet senniNo ratings yet
- NPTEL IIT Roorkee Steam Power Systems Assignment #1Document3 pagesNPTEL IIT Roorkee Steam Power Systems Assignment #1Suraj ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Ciclos Térmicos-Ciclo de Refrigeración: Diego Mejia Mayo Del 2013Document4 pagesCiclos Térmicos-Ciclo de Refrigeración: Diego Mejia Mayo Del 2013miguel angel tecse cariNo ratings yet
- 2000 KG 1250 K 450 K 303 K 0.5 / KJKGK: Year 2004 Two Marks MCQ 8.65Document2 pages2000 KG 1250 K 450 K 303 K 0.5 / KJKGK: Year 2004 Two Marks MCQ 8.65SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- INDUSTRIAL & POWER PLANT DESIGN ELEMENTSDocument11 pagesINDUSTRIAL & POWER PLANT DESIGN ELEMENTSJohn Babe CapiliNo ratings yet
- Tut 6,7,8 - 2013Document3 pagesTut 6,7,8 - 2013SourabhNo ratings yet
- Soal Soal ThermodynamicDocument7 pagesSoal Soal Thermodynamicharistk7No ratings yet
- Final Exam 20172018 Sem 2Document10 pagesFinal Exam 20172018 Sem 2Abdulrahman DesoukyNo ratings yet
- Tarea de Ciclo de Refrigeracion y Maquinas TermicasDocument4 pagesTarea de Ciclo de Refrigeracion y Maquinas TermicasRenzo Alexander RestrepoNo ratings yet
- Tarea de Ciclo de Refrigeracion y Maquinas TermicasDocument4 pagesTarea de Ciclo de Refrigeracion y Maquinas TermicasRenzo Alexander RestrepoNo ratings yet
- ME267 TermDocument41 pagesME267 TermMuhammad Imran HossainNo ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Ipd PPD Problem2Document16 pagesIpd PPD Problem2Josue Carubio Ricalde Jr.100% (1)
- EXAM - (M) 2018: Mechanical Engineering Paper - IIDocument12 pagesEXAM - (M) 2018: Mechanical Engineering Paper - IISandeep PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Exams PapersDocument23 pagesThermodynamics Exams PapersAbdul HafizNo ratings yet
- PPE Long Exam Steam Power BarcelonaDocument9 pagesPPE Long Exam Steam Power BarcelonaAko C. IvanNo ratings yet
- 13A03302122016Document2 pages13A03302122016EhteshTubeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Pallav AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer-11 PDFDocument1 pageHeat Transfer-11 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 2 2020 RevisedDocument3 pagesTutorial Topic 2 2020 RevisedTara PillayNo ratings yet
- Eng Therm and Fluid Mech E1 Level 4 Exam MAY 2021Document10 pagesEng Therm and Fluid Mech E1 Level 4 Exam MAY 2021Brody CrossNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper ME 604ADocument11 pagesSample Question Paper ME 604Amumtaz alamNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap10 P001Document29 pagesThermo 5th Chap10 P001welberTonetoMotaNo ratings yet
- Rankine Cycle Thermodynamics ProblemsDocument2 pagesRankine Cycle Thermodynamics Problemssuby0% (1)
- Final Exam 2020 - 2021 2nd TermDocument2 pagesFinal Exam 2020 - 2021 2nd Termas2899142No ratings yet
- Question 1. During An Experiment Conducted in A Room at 25Document11 pagesQuestion 1. During An Experiment Conducted in A Room at 25fivos_rgNo ratings yet
- rr222102 Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesrr222102 Engineering ThermodynamicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Applications - Test-1Document6 pagesThermodynamics and Applications - Test-1sap2279No ratings yet
- Problems Carnot and RankineDocument12 pagesProblems Carnot and RankineHassan SheikhNo ratings yet
- 18 Me 42Document2 pages18 Me 42Zeeshan SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- IC Engine Objective Questions and Answer by S K Mondal PDFDocument0 pagesIC Engine Objective Questions and Answer by S K Mondal PDFAjendra Singh100% (2)
- 51 ThermoDynamics ThermoDynamics PDFDocument5 pages51 ThermoDynamics ThermoDynamics PDFmozam haqNo ratings yet
- CHMT3040 2022 Semester Test 21 April 2022Document3 pagesCHMT3040 2022 Semester Test 21 April 2022Buyisile NyongwanaNo ratings yet
- Assignment AETD(1) (1)Document2 pagesAssignment AETD(1) (1)Pratham M JariwalaNo ratings yet
- GATE 2018 Thermodynamics QuestionsDocument4 pagesGATE 2018 Thermodynamics QuestionsPradyotNo ratings yet
- Nodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Mechanical Engineering Refrigeration and Air-ConditioningDocument20 pagesNodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Mechanical Engineering Refrigeration and Air-ConditioningVasantha SeelanNo ratings yet
- FD-201 Final Exam Fall 2020-21Document3 pagesFD-201 Final Exam Fall 2020-21Qamber pkNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- F D T D T: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageF D T D T: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-55Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-55SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-52Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-52SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Processes Associated State of Stress P. 3. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 4Document1 pageProcesses Associated State of Stress P. 3. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 4SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-53Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-53SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-54Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-54SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering Chapter on Metal Removal Rate and Rolling Load CalculationDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering Chapter on Metal Removal Rate and Rolling Load CalculationSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-46Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-46SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering Chapter Tool Life CalculationDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering Chapter Tool Life CalculationSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-45Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-45SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Column I Column II P. 4. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 3.: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageColumn I Column II P. 4. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 3.: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-53Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-53SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-51Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-51SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- α 12c t t φ r r α α t φ φ: Machining process Mechanism of material removal P. 2. Q. 3. R. 4. S. 1Document1 pageα 12c t t φ r r α α t φ φ: Machining process Mechanism of material removal P. 2. Q. 3. R. 4. S. 1SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- ADE Δ θ DE x x θ x x Z d x: Visit us at: www.nodia.co.inDocument1 pageADE Δ θ DE x x θ x x Z d x: Visit us at: www.nodia.co.inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- A N B N VT A VT B VT: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageA N B N VT A VT B VT: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering Chapter 10 Problems SolvedDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering Chapter 10 Problems SolvedSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-40Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-40SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-38Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-38SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering Solutions for GATE Exam PrepDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering Solutions for GATE Exam PrepSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-34Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-34SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-38Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-38SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- 175 MM 200 MM 200 MM 10 MM 10 / Ms : Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 page175 MM 200 MM 200 MM 10 MM 10 / Ms : Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-32 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-32 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-32 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-32 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Valency and Chemical Bond ValencyDocument2 pagesValency and Chemical Bond ValencyKanjariya AjayNo ratings yet
- Optically Detected Magnetic Resonance in HBN DefectDocument9 pagesOptically Detected Magnetic Resonance in HBN DefectHyeong Young HwangNo ratings yet
- Essential chemistry guideDocument56 pagesEssential chemistry guideFashana AdityaNo ratings yet
- Fouling in Heat Exchangers - PRDDocument47 pagesFouling in Heat Exchangers - PRDPradyumna DhamangaonkarNo ratings yet
- Enzyme KineticsDocument17 pagesEnzyme KineticsIsuru JayalathNo ratings yet
- Born-Haber Cycles: 16-18 YearsDocument12 pagesBorn-Haber Cycles: 16-18 YearsJoko SusiloNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 A Common Laboratory TechniquesDocument8 pagesActivity 2 A Common Laboratory TechniquesJearzy RufoNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Its All About WavesDocument4 pagesAnswer Key Its All About WavesyeiNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Lab Work 1. Chemical Kinetics. Chemical EquilibriumDocument5 pagesPurpose: Lab Work 1. Chemical Kinetics. Chemical EquilibriumFritz ManyauNo ratings yet
- Rubber Compound PropertiesDocument7 pagesRubber Compound PropertiesBhushan VermaNo ratings yet
- Artificial atmospheres test reportDocument8 pagesArtificial atmospheres test reportAs Ad Ali MutakinNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Benzoic AcidDocument6 pagesSynthesis of Benzoic AcidHakdogNo ratings yet
- CARBOWAX™ Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) 1000Document2 pagesCARBOWAX™ Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) 1000Anonymous vJPniV7No ratings yet
- Inorganic Notes - OrganomettalicsDocument26 pagesInorganic Notes - OrganomettalicsrohitNo ratings yet
- Unit-2: Phase DiagramDocument37 pagesUnit-2: Phase DiagramPrasad Govind KumbharNo ratings yet
- Micro EncapsulationDocument5 pagesMicro EncapsulationGajendra GowdaNo ratings yet
- Alkali Metals Trends and PropertiesDocument3 pagesAlkali Metals Trends and PropertiesHelp GloPosNetNo ratings yet
- Thermo Mock SolutionsDocument14 pagesThermo Mock Solutionsmanjeet gajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- Coolant Diesel EngineDocument2 pagesCoolant Diesel Enginemuhammad arifNo ratings yet
- Steam TrapDocument20 pagesSteam TrapMarie Saunders0% (1)
- FoE - Heat TransferDocument18 pagesFoE - Heat TransferPamela KennedyNo ratings yet
- Q2 A AnsDocument10 pagesQ2 A AnsKai Faha LukumNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Solids, Liquids and Gases (PowerPoint)Document29 pagesUnit-5 Solids, Liquids and Gases (PowerPoint)Núrùzzámàn KhäñNo ratings yet
- Manual For Accessory Kit To Electromagnetic Vibrator No. 2185.55Document2 pagesManual For Accessory Kit To Electromagnetic Vibrator No. 2185.55Harry RamzaNo ratings yet
- NEBB Psych Chart Sea Level 11x17Document1 pageNEBB Psych Chart Sea Level 11x17JojolasNo ratings yet
- IEC-60079-10-1-Ed.-3.0Document17 pagesIEC-60079-10-1-Ed.-3.0eman.rohayemNo ratings yet
- Dryers Problem and SolutionDocument4 pagesDryers Problem and SolutionAngielou Sialana100% (2)
- Introduction and General Overview of Cyclodextrin Chemistry: Jo Zsef SzejtliDocument12 pagesIntroduction and General Overview of Cyclodextrin Chemistry: Jo Zsef SzejtliCristina Martín JiménezNo ratings yet
- Richard Modern Physics Solved QuestionsDocument33 pagesRichard Modern Physics Solved Questionsmurugan_kribhcoNo ratings yet
- Mev Cm2/Mg (I.E., Mev/Cm Divided by Mg/Cm2)Document2 pagesMev Cm2/Mg (I.E., Mev/Cm Divided by Mg/Cm2)Raghu RamNo ratings yet