Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organisational Structure Overview
Uploaded by
Ritu Satyawan GuptaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organisational Structure Overview
Uploaded by
Ritu Satyawan GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
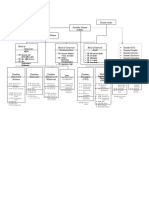
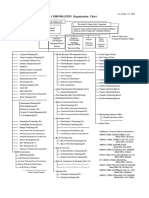
Annexure “A”: Organisaton Structure
Chairman
CEO BOD
CFO President President
(Account & Finance) (Operations) (Technical)
VP VP VP VP VP VP
(Internal Audit) CIO (Purchase)
VP
(Sales & Marketing) (Production) (Quality Control) (Design & Dev.)
(Logistics)
Manager Manager Manager Manager Manager Manager Manager Manager Manager Manager Manager Manager
(Internal Audit) (Finance) (Accounts) (I T) (Purchase) (Store) (Logistics) (HR/Adm.) (Regional) (Production) (Quality (Design & Dev.)
Control)
Manager
(Branch)
Shift In
charge
Assistants Assistants Assistants Assistants Assistants Assistants Assistants Assistants Assistants Supervisor Lab Assistants
Inspector
Laborers
RDPS LLP Page 1
Annexure “B”: Internal Audit questionnaire based on the COSO 2013 framework
Assessment Factor Indication of Stronger Controls Indication of Weaker Controls Assessment
Strong – Weak
1 2 3 4 5
Section 1 – Control Environment
1 - Integrity and Ethical Values
1.1 Acceptable business Individual department (operational staff) understand the Company's policies
Policies are poorly understood
practices. covering matters such as legitimate use of Company resources.
Individual department understand the Company's policies governing
1.2 Codes of conduct. relationships with sponsors, suppliers, creditors, regulators, the Policies are poorly understood.
commdepartmenty, and the public at large.
Individual department understand the Company's policies regarding
1.3 Conflicts of interests. Policies are poorly understood.
potential conflicts of interest.
Management does not set a good example and/or
Individual department sets a good example and regularly communicates high
1.4 Integrity. does not communicate high expectations
expectations regarding integrity and ethical values.
regarding integrity and ethical values.
2 – Commitment to Competence
Responsibilities are clearly defined in writing and communicated as Responsibilities are poorly defined or poorly
2.1 Job descriptions.
appropriate. communicated.
Individual department (operational staff) understand the knowledge and Management does not adequately consider
2.2 Knowledge and Skills.
skills required to accomplish tasks. knowledge and skill requirements.
Management is not adequately aware of
Individual department is aware of competency levels, and is involved in
2.3 Employee competence. competency levels, or does not actively address
training and increased supervision when competency is low.
problems.
3 – Management’s Philosophy and Operating Style
3.1 Communication with Individual department insists on full and open disclosure of financial or Management is secretive and reluctant to conduct
Employees and Staff. business issues with appropriate Employees and Staff personnel. business or deal with issues in an open manner.
There is active concern and effort to ensure compliance with the letter and Management is willing to risk the consequences of
3.2 Laws and regulations.
intent of laws and regulations. noncompliance.
Management is concerned with and exerts effort to get the job done right Management is willing to get the job done
3.3 Getting the job done.
the first time. without adequate regard to quality.
Exceptions to policy are infrequent. When they occur they must be approved Exceptions to policy are the norm and are rarely
3.4 Exceptions to policy.
and well documented. documented.
RDPS LLP Page 2
Assessment Factor Indication of Stronger Controls Indication of Weaker Controls Assessment
Strong – Weak
1 2 3 4 5
Management’s approach shows concern and appreciation for accurate and
3.5 Approach to financial
timely reporting. Budgeting and other financial estimates are generally Financial accountability is given low priority.
accountability.
conservative.
3.6 Emphasis on meeting Realistic budgets are established and results are actively monitored. Management either shows little concern (climate
budget and other financial Corrective action is taken as necessary. The department learns from, and of laxness), or makes unreasonable demands
and operating goals. does not repeat, mistakes. (climate of fear).
Decision-making processes are deliberate and consistent. Decisions are made Decision making is nearly always informal.
3.7 Approach to decision
after careful consideration of relevant facts. Policies and procedures are in Management makes arbitrary decisions with
making.
place to ensure appropriate levels of management are involved. inadequate discussion and analysis of the facts.
4 – Organizational Structure
Lines of responsibility are unclear or unnecessarily
4.1 Complexity of the Complexity of the structure is commensurate with the organization. Lines of
complicated for the size and activities of the
organizational structure. reporting are clear and documentation is up-to-date.
entity.
Documentation does not exist or is out-of-date.
4.2 Organization charts. Documentation exists and is up to date. The documented structure does not correspond
with actual responsibilities.
4.3 Size of the management Size is not appropriate (e.g., too many levels, too
Size is commensurate with the complexity of the department and its growth.
group. dispersed, or too "thin").
4.4 Stability of the
Low turnover. High turnover.
management group.
5 – Assignment of Authority and Responsibility
5.1 Delegation of authority
Decisions are dominated by one or a few
and assignment of Delegation of authority and assignment of responsibility is clearly defined.
individuals. Roles and responsibilities of middle
responsibility for operating Individuals are held accountable for results.
management are unclear.
and financial functions.
Authority limits are clearly defined in writing and communicated as Policies and procedures covering authority limits
5.2 Authority limits.
appropriate. are informal or poorly communicated.
Signature authority is delegated without adequate
Appropriate limits have been placed on each delegation of signature
5.3 Delegated signature consideration. Delegated authority is not in line
authority. Management reviews and updates signature records as turnover
authority. with employee knowledge, training, or
occurs.
competence.
RDPS LLP Page 3
Assessment Factor Indication of Stronger Controls Indication of Weaker Controls Assessment
Strong – Weak
1 2 3 4 5
Key personnel are inexperienced. Management
5.4 Knowledge and Key personnel are knowledgeable and experienced. Management does not
delegates authority without regard to knowledge
experience. delegate authority to inexperienced individuals.
and experience.
Management provides the resources needed for employees to carry out Management does not provide necessary
5.5 Resources.
their duties. resources.
6 – Human Resource Policies and Practices
The hiring process is informal, and sometimes
A careful hiring process is in place. The Human Resources Department is
6.1 Selection of personnel. proceeds without adequate involvement by
involved in identifying potential employees based on job requirements.
higher-level supervisors.
On-the-job and other training programs have defined objectives. They are Training programs are inconsistent, ineffective, or
6.2 Training.
effective and important. are given low priority.
Regular supervision does not exist or is
Personnel are adequately supervised. They have a regular resource for
6.3 Supervision policies. ineffective. Employees are frustrated and feel
resolving problems.
they ‘have nowhere to go’ with issues.
Inappropriate behaviour is consistently reprimanded in a timely and direct Reprimands are not timely, direct, or are not
6.4 Inappropriate behaviour.
manner, regardless of the individual's position or status. consistently applied (climate of favoritism).
The evaluation process is ad hoc and inconsistent.
6.5 Evaluation of personnel. An organized evaluation process exists.
Performance issues are not formally addressed.
Compensation decisions are based on a formal process with meaningful
*6.6 Methods to compensate involvement of more than one level of management. The effect of Compensation decisions are ad hoc, inconsistent,
personnel. performance evaluations on compensation decisions is defined and or inadequately reviewed by management.
communicated.
6.7 Staffing of critical There is inadequate staffing and frequent periods
Critical functions are adequately staffed, with reasonable workloads.
functions. of overwork and "organizational stress."
6.8 Turnover. Particularly
High turnover. Management does not understand
turnover in financially Low turnover. Management understands root causes of turnover.
root causes.
responsible positions.
Section 2 – Risk Assessment
7 – Organizational Goals and Objectives
7.1 Department-wide A formal department-wide mission or value statement is established and A department-wide mission or value statement
objectives. communicated throughout the department. does not exist.
RDPS LLP Page 4
Assessment Factor Indication of Stronger Controls Indication of Weaker Controls Assessment
Strong – Weak
1 2 3 4 5
Factors that are critical to achievement of department-wide objectives are
7.2 Critical success factors. identified. Resources are appropriately allocated between critical success Success factors are not identified or prioritized.
factors and objectives of lesser importance.
Realistic objectives are established for all key activities including operations,
7.3 Activity-level objectives. Activity-level objectives do not exist.
financial reporting and compliance considerations.
7.4 Measurement of Department-wide and activity level objectives include measurement criteria Performance regarding objectives is not
objectives. and are periodically evaluated. measured. Targets are not set.
Management dictates objectives without
7.5 Employee involvement. Employees at all levels are represented in establishing the objectives.
adequate employee involvement.
7.6 Long and short-range Long and short-range plans are developed and are written. Changes in No organized planning process exists. There are
planning. direction are made only after sufficient study is performed. frequent shifts in direction or emphasis.
Detailed budgets are developed by area of responsibility following
Budgets do not exist or are "backed into"
7.7 Budgeting system. prescribed procedures and realistic expectations. Plans and budgets support
depending on desired outcome.
achievement of department-wide action steps.
7.8 Strategic planning for Planning for future needs is done well in advance of expected needs and The information system lags significantly behind
information systems. considers various scenarios. the needs of the business.
8 – Risk Identification and Prioritization
A process exists to identify and consider the implications of external risk
8.1 Identification and factors (economic changes, changing sponsor, student and
Potential or actual external risk factors are not
consideration of external commdepartmenty needs or expectations, new or changed legislation or
effectively identified or evaluated.
risk factors. regulations, technological developments, etc.) on department-wide
objectives and plans.
A process exists to identify and consider the implications of internal risk
8.2 Identification and
factors (new personnel, new information systems, changes in management Potential or actual internal risk factors are not
consideration of internal
responsibilities, new or changed educational or research programs, etc.) on effectively identified or evaluated.
risk factors.
department-wide objectives and plans.
The likelihood of occurrence and potential impact (monetary and otherwise)
8.3 Prioritization of risks. have been evaluated. Risks have been categorized as tolerable or requiring Risks have not been prioritized.
action.
In-depth, cost / benefit studies are performed before committing significant
8.4 Approach to studying risks. Risks are accepted with little or no study.
department resources.
RDPS LLP Page 5
Assessment Factor Indication of Stronger Controls Indication of Weaker Controls Assessment
Strong – Weak
1 2 3 4 5
Exposure is dealt with on a case by case basis.
8.5 Process for monitoring A risk management program is in place to monitor and help mitigate
Regular efforts or programs to manage risks do
risks. exposures.
not exist.
Internal expertise regarding risk and control issues
8.6 Consultation with external
External advisors are consulted as needed to supplement internal expertise. is inadequate. Assistance is never sought from
advisors.
outside sources.
9 – Managing Change
Management promotes the status quo, even
Management promotes continuous improvement and solicits input and
9.1 Commitment to change. when changes are needed to meet important
feedback on the implications of significant change.
business needs.
Management offers no resources to facilitate
9.2 Support of change. Management is willing to commit resources to achieve positive change.
change.
Mechanisms exist to identify, prioritize, and react to routine events (i.e.,
9.3 Routine change. turnover) that affect achievement of department-wide objectives or action Procedures are not present or are ineffective.
steps.
9.4 Economic change. Mechanisms exist to identify and react to economic changes. Procedures are not present or are ineffective.
Mechanisms exist to identify and react to regulatory changes (maintain
9.5 Regulatory change. membership in associations that monitor laws and regulations, participate in Procedures are not present or are ineffective.
Company forums, etc.).
Mechanisms exist to identify and react to technological changes and changes
9.6 Technological change. Procedures are not present or are ineffective.
in the functional requirements of the department.
Section 3 – Control Activities
10 – Written Policies and Procedures
10.1 Access to Company Departmentstaff have available up to date Company policy and procedures Company policy and procedures are not available
policies and procedures. and know how to use them. or are rarely used.
10.2 Department policies and The department has documented its own policies and procedures. They are
Department policies and procedures do not exist.
procedures. well understood by department staff.
11 – Control Procedures
11.1 Senior management Senior management monitors the department's performance against Senior management does not monitor
(Company ) reviews. objectives and budget. department performance.
RDPS LLP Page 6
Assessment Factor Indication of Stronger Controls Indication of Weaker Controls Assessment
Strong – Weak
1 2 3 4 5
11.2 Top level (department-
Reviews are made of actual performance compared to objectives and
wide) objective Analyses are not performed or management does
previous periods for all major initiatives. Management analyzes and follows
performance reviews by not follow up on significant deviations.
up as needed.
Individual department.
11.3 Top level (department-
Reviews are made of actual performance versus budgets, forecasts, and
wide) financial Analyses are not performed or management does
performance in prior periods for all major initiatives. Management analyzes
performance reviews by not follow up on significant deviations.
and follows up as needed.
Individual department.
11.4 Direct functional or activity
Performance reviews are made of specific functions or activities, focusing on
management by Individual No performance reviews occur.
compliance, financial or operational issues.
department.
11.5 Performance indicators. Unexpected operating results or unusual trends are investigated. Operating results and trends are not monitored.
Accounting statements and key reconciliations are completed timely. Reconciliations are not performed timely or
11.6 Accounting statements
Management performs a diligent review and signifies approval by signature regularly. Management does not carefully review
and key reconciliations.
and date. or formally approve statements or reconciliations.
Sponsored project accounts are reviewed and reconciled. PIs certify the
11.7 Sponsored project account Sponsored project accounts are not monitored;
expenditures timely. Individual department monitors the portfolio of
management. reconciliations and certifications are not timely.
sponsored accounts for compliance and fiscal responsibility.
Restrictions on use are well documented, and are understood by employees Restrictions are not clearly documented.
11.8 Use of restricted funds
who administer the funds. Usage is monitored by management, accounts are Restricted fund accounts are not monitored;
(gifts).
reconciled. usage may not match restrictions.
Controls exist to monitor the accuracy and completeness of information as
11.9 Information processing. No information processing controls are in place.
well as authorization of transactions.
Equipment, supplies, inventory, cash and other assets are physically secured Equipment, supplies, inventory, cash and other
11.10 Physical controls. and periodically counted and compared to the amounts shown on control assets are not protected. Control records do not
records. exist or are not up to date.
11.11 Training and guidance for Adequate guidance and training are provided to personnel responsible for
No training or guidance is provided.
asset custodians. cash or similar assets.
Financial duties are divided among different people (responsibilities for
No significant separation of financial duties
11.12 Separation of duties. authorizing transactions, recording them and handling the asset are
among different employees.
separated).
RDPS LLP Page 7
Assessment Factor Indication of Stronger Controls Indication of Weaker Controls Assessment
Strong – Weak
1 2 3 4 5
Department employees do not understand which
Department employees understand which records they are responsible to
11.13 Record retention. records they are responsible for maintaining. The
maintain and the required retention period. Records are appropriately filed.
filing system is inadequate.
A disaster response and recovery plan has been developed and is understood
11.14 Disaster response plan. No disaster response or recovery plan exists.
by key personnel.
12 – Controls over Information Systems
System operations are documented; software is appropriately acquired and
12.1 Local information systems maintained; access to the system, programs and data is controlled; the Inadequate controls over local information
and LANs. system is maintained in a secure environment; applications are appropriately systems or LANs.
developed and maintained.
The department controls its computer applications by diligent and timely
response to edit lists, rejected transactions and other control and balancing
12.2 Application controls. Application controls are not used.
reports. Controls ensure a high level of data integrity including
completeness, accuracy, and validity of all information in the system.
Key data and programs on LANs or desktop computers are appropriately
No formal back up procedures exist. Management
12.3 Back Up. backed up and maintained. Off-site storage is adequate considering possible
has not informed staff of back up requirements.
risks of loss.
RDPS LLP Page 8
Annexure “C”: Standard Risk Management approach based on the COBIT 5 framework for risks
EDM 03 – Evaluate, Direct and Monitor
Practice ID and Name Governance Practice
EDM03.01 Continually examine and make judgement on the effect of risk on the current and future use of IT in the enterprise. Consider whether the
Evaluate risk management. enterprise’s risk appetite is appropriate and that risk to enterprise value related to the use of IT is identified and managed.
EDM03.02 Direct the establishment of risk management practices to provide reasonable assurance that IT risk management practices are appropriate to
Direct risk management. ensure that the actual IT risk does not exceed the board’s risk appetite.
EDM03.03 Monitor the key goals and metrics of the risk management processes and establish how deviations or problems will be identified, tracked and
Monitor risk management. reported for remediation.
APO 12 – Align, Plan and Organise
Practice ID and Name Governance Practice
Process: 1. Establish and maintain a method for the collection, classification and analysis of IT risk-related data, accommodating multiple types of
Manage Risk events, multiple categories of IT risk and multiple risk factors.
2. Record relevant data on the enterprise’s internal and external operating environment that could play a significant role in the management
Practice ID: of IT risk.
APO12.01 3. Survey and analyse the historical IT risk data and loss experience from externally available data and trends, industry peers through industry-
Practice Name: Collection based event logs, databases, and industry agreements for common event disclosure.
of data 4. Record data on risk events that have caused or may cause impacts to IT benefit/value enablement, IT programme and project delivery,
and/or IT operations and service delivery. Capture relevant data from related issues, incidents, problems and investigations.
5. For similar classes of events, organise the collected data and highlight contributing factors. Determine common contributing factors across
multiple events.
6. Determine the specific conditions that existed or were absent when risk events occurred and the way the conditions affected event
frequency and loss magnitude.
7. Perform periodic event and risk factor analysis to identify new or emerging risk issues and to gain an understanding of the associated
internal and external risk factors.
Process: 1. Define the appropriate breadth and depth of risk analysis efforts, considering all risk factors and the business criticality of assets. Set the
Manage Risk risk analysis scope after performing a cost-benefit analysis.
2. Build and regularly update IT risk scenarios, including compound scenarios of cascading and/or coincidental threat types, and develop
Practice ID: expectations for specific control activities, capabilities to detect and other response measures.
APO12.02 3. Estimate the frequency and magnitude of loss or gain associated with IT risk scenarios. Take into account all applicable risk factors, evaluate
Practice Name: Analysis of known operational controls and estimate residual risk levels.
Risk 4 Compare residual risk to acceptable risk tolerance and identify exposures that may require a risk response.
5. Analyse cost-benefit of potential risk response options such as avoid, reduce/mitigate, transfer/share, and accept and exploit/seize.
Propose the optimal risk response.
6. Specify high-level requirements for projects or programmes that will implement the selected risk responses. Identify requirements and
expectations for appropriate key controls for risk mitigation responses.
7. Validate the risk analysis results before using them in decision making, confirming that the analysis aligns with enterprise requirements and
verifying that estimations were properly calibrated and scrutinised for bias.
RDPS LLP Page 9
Process: 1. Inventory business processes, including supporting personnel, applications, infrastructure, facilities, critical manual records, vendors,
Manage Risk suppliers and outsourcers, and document the dependency on IT service management processes and IT infrastructure resources.
2. Determine and agree on which IT services and IT infrastructure resources are essential to sustain the operation of business processes.
Practice ID: Analyse dependencies and identify weak links.
APO12.03 3. Aggregate current risk scenarios by category, business line and functional area.
Practice Name: Maintain a 4. On a regular basis, capture all risk profile information and consolidate it into an aggregated risk profile.
Risk Profile 5. Based on all risk profile data, define a set of risk indicators that allow the quick identification and monitoring of current risk and risk trends.
6. Capture information on IT risk events that have materialised, for inclusion in the IT risk profile of the enterprise.
7. Capture information on the status of the risk action plan, for inclusion in the IT risk profile of the enterprise.
Process: 1. Report the results of risk analysis to all affected stakeholders in terms and formats useful to support enterprise decisions. Wherever
Manage Risk possible, include probabilities and ranges of loss or gain along with confidence levels that enable management to balance risk-return.
2. Provide decision makers with an understanding of worst-case and most-probable scenarios, due diligence exposures, and significant
Practice ID: reputation, legal or regulatory considerations.
APO12.04 3. Report the current risk profile to all stakeholders, including effectiveness of the risk management process, control effectiveness, gaps,
Practice Name: Articulate inconsistencies, redundancies, remediation status, and their impacts on the risk profile.
Risk 4. Review the results of objective third-party assessments, internal audit and quality assurance reviews, and map them to the risk profile.
Review identified gaps and exposures to determine the need for additional risk analysis.
5. On a periodic basis, for areas with relative risk and risk capacity parity, identify IT-related opportunities that would allow the acceptance of
greater risk and enhanced growth and return.
Process: 1. Maintain an inventory of control activities that are in place to manage risk and that enable risk to be taken in line with risk appetite and
Manage Risk tolerance. Classify control activities and map them to specific IT risk statements and aggregations of IT risk.
2. Determine whether each organisational entity monitors risk and accepts accountability for operating within its individual and portfolio
Practice ID: tolerance levels.
APO12.05 3. Define a balanced set of project proposals designed to reduce risk and/or projects that enable strategic enterprise opportunities,
Practice Name: Define Risk considering cost/benefits, effect on current risk profile and regulations.
Management Action
Portfolio
Process: 1. Prepare, maintain and test plans that document the specific steps to take when a risk event may cause a significant operational or
Manage Risk development incident with serious business impact. Ensure that plans include pathways of escalation across the enterprise.
2. Categorise incidents, and compare actual exposures against risk tolerance thresholds. Communicate business impacts to decision makers as
Practice ID: part of reporting, and update the risk profile.
APO12.06 3. Apply the appropriate response plan to minimise the impact when risk incidents occur.
Practice Name: Respond to 4. Examine past adverse events/losses and missed opportunities and determine root causes. Communicate root cause, additional risk
Risk response requirements and process improvements to appropriate decision makers and ensure that the cause, response requirements and
process improvement are included in risk governance processes.
RDPS LLP Page 10
Annexure “D” – Compliance checklist as per the ITAA 2008 as developed by the Data Security Council of India
Observa
Areas Reference to Assessment Questions Yes/ No/ tion Compliant/ R
Not
S.No. ITAA 2008 Sure/ Non- A
NA Compliant P
Definition of Body
1) Corporate Sec 43A Is the organization a ‘body corporate’ as defined in the IT (Amendment) Act, 2008 (ITAA 2008)?
Body Corporate – means any company and includes a firm, sole proprietorship, or other association of individuals
Definition engaged in commercial or
professional activities
2) Organization's Role Clarification Is the Organization aware of the privacy role it performs based on its functions, activities & business?
Issued u/s 43A
Provides services to its end customers (individuals – ‘providers of information’ under the ITAA 2008) under a direct
Role 1: Data Controller relationship and determined the
means and purpose of data collection and processing
Provides services to its clients (organizations) under a lawful contract having indirect relationship with the end
Role 2: Data Processor customers (providers of information)
as per the instructions from data controller; e.g. business process outsourcing service providers
Provides employment or other related services / benefits to its employees and / or enable employees to perform their
Role 3: Data Controller duties
Does the organziation deal (collect, process, store, transfer, access) with following categories of “sensitive personal data
3) Sensitive Personal Data or Sec 43A or information” (SPDI) as
Information (SPDI) defined under sec43A of the ITAA, 2008? Has it identified such functions, operations and actitivities that deal with SPDI?
Definiton of SPDI Rule 3 (u/s i. Password (Capable of providing information or access to SPDI listed below)
RDPS LLP Page 11
43A)
ii. financial information such as Bank account or credit card or debit card or other payment instrument details
iii. physical, physiological and mental health condition
iv. sexual orientation
v. medical records and history
vi. biometric information
vii. any of the detail relating to the above categories of or information received under above categories of SPDI by
SPDI the organization for
processing, stored or processed under lawful contract or otherwise
Any information that is freely available or accessible in public domain or furnished under the Right to Information Act,
Exceptions 2005 or any other law for the
time being in force shall not be regarded as sensitive personal data or information
4) Privacy Policy Rule 4 Does the organization have a privacy policy?
Requirements a) Is it published on the website of the organization?
b) Is the policy easily accessible?
RDPS LLP Page 12
c) Is the policy simple & easy to understand
d) Does it provide links to organization's practices and policies
e) Does it state?
i Type of SPDI being collected (refer question no. 3)
ii. Reason for collecting such information
iii. The intended usage of the provided information
iv. Disclosure policy and practices of the organization (refer question number 11)
v. Reasonable security practices and procedures adopted by the organization for securing SPDI
For organizations that act as data processors [refer Q 2 above], questions 5 to 11 (Rules 5 & 6 of Sections 43A in ITAA, 2008) are not applicable
5 Does the organization follow any due diligence to ensure SPDI is collected for a lawful purpose which is associated with
) Collection Limitation Rule 5 2(a) the function or activity of
the organization?
Due Diligence Rule 5 2(b) Does the organization follow any due diligence to ensure SPDI which is necessary for the above purpose is only collected?
When directly collecting SPDI from the provider of information, does the organization take reasonable steps to ensure
Informing the Providers of Rule 5(3) that the provider of
Information information is having knowledge about:
i. the fact that the SPDI is being collected
ii. the purpose for which SPDI is collected
iii. the intended recipients of SPDI
RDPS LLP Page 13
iv. the name & address of the agency which is collecting the SPDI
v. the agency tha will retain the SPDI
6 Does the organization take written consent from the provider of information regarding purpose of usage before collecting
) Consent Rule 5(1) and their SPDI?
Clarification
Modes for Obtaining Consent a. Letter
Issued u/s 43A
b. Fax
c. Email
d. Click in an online environment
e. Instant messaging
f. IVR
g. Any other mode of electronic communication
Does the organization provide an option to the provider of information to decline providing data or information sought to
Choice Rule 5(7) be collected for availing
service?
Consent Withdrawl Does the organization provide option to the provider of information to withdraw his / her consent given earlier?
7 Does the organization perform any due diligence to ensure that the usage of SPDI is consistent with the purpose for which
) Purpose Limitation Rule 5(5) has been collected?
8 Does the organization allow providers of information, as & when requested by them, the facility to review the SPDI they
) Access & Correction Rule 5(6) have provided?
Does the organization have mechanisms in place that allow providers of information to modify / update / correct their
Mechanisms SPDI, if found to be outdated
and / or incorrect?
9 Does the organization ensure that the SPDI is not retained for a period longer than required for its lawful use or is
) Information Retention Rule 5(4) otherwise required by any other
law for the time being in force?
1
0 Has the organization designated a grievance officer to address any discrepancies & grievances raised by the providers of
) Grievance Officer Rule 5(9) information?
Publication on website Has the organization published the name and contact details of the grievance officer on its website?
Is the grievance officer mandated to redress the grievances of the providers of information within one month (maximum)
Resolution from the date of the
receipt of grievance?
1
1 Does the contract signed between the organization and providers of information mention the disclosure of SPDI to third
) Disclosure of Information Rule 6(1) parties?
If not, does the organization take prior permission of the providers of information before disclosing their SPDI to third
Prior Permission parties or publishing it?
Are there any legal obligations under which the organization needs to disclose the SPDI without informing or taking
Exceptions permission of the providers of
information?
Does the organization take due diligence to ensure that the SPDI is not published intentionally or unintentionally in public
Publishing in Public Domain Rule 6(3) domain, i.e., made
available to unauthorized persons or public?
Has the organization put in place the mechanisms / controls to ensure that the third party with which SPDI is shared does
Controls Rule 6(4) not disclose it further?
1Transfer of Information Rule 7 Does the organization follow due diligence to ensure that the same level of data protection (please refer Question 13) is
RDPS LLP Page 14
2
) adhered to by third parties
(which may be located in India or abroad) to whom the organization transfers SPDI for performance of a lawful contract
between the organization
and providers of information or where the providers of information have given their consent for such transfers?
1
3
) Security Practices Sec 43A Has the organziation implemented 'Reasonable Security Practices' for protecting SPDI?
Does the contract signed between organization & provider of information or between organization & third party contains
a. Agreement through provisions that specify
security practices and procedures designed to protect SPDI from unauthorized access, damage, use, modification,
contractual instruments disclosure or impairment?
Does the contract include:
i. Comprehensive documented information security policies & programs
ii. Managerial, technical, operational & physical security controls that are commensurate with the value of information
assets being protected and
the risk exposure
iii. Audit / assessment mechanisms for testing implementation of controls
Has the organization implemented documented information security policies & programs that contain managerial,
b. In absense of any Contract Rule 8(1), 8(2) technical, operational
& physical security controls that are commensurate with the value of information assets being protected and the risk
& 8(3) exposure?
Such security practices & procedures could be:
a. IS/ISO/IEC 27001
b. Codes of best practices of an industry association (where the organization is a member) that are duly approved &
notified by the central
government
Do such security practices & procedures get certified or audited by a government approved independent auditor, on a
Rule 8(4) regular basis (at least once
a year or as & when the organization undertakes significant up gradation of its processes & computer resources)?
c. Demonstration of Security Sec 43A Does the organization maintain the requisite records, logs, trails, etc. for demonstrating compliance?
Practices in case of security Can the organization demonstrate that it has implemented security controls as per the documented security policies &
programs?
incident / data breach
RDPS LLP Page 15
You might also like
- Organogram For ISO 14001Document2 pagesOrganogram For ISO 14001FaridUddin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Struktur TelkomDocument2 pagesStruktur TelkomRisky FajarNo ratings yet
- Head of Corporate Affair Head of Corporate Communication Head of Internal AuditDocument23 pagesHead of Corporate Affair Head of Corporate Communication Head of Internal AuditAgung RachmadanNo ratings yet
- Reference, Schazoo Org Hierarchy ChartDocument1 pageReference, Schazoo Org Hierarchy Chartsilah imanNo ratings yet
- Structure of Utility Stores Corporation of Pakistan (PVT) LTD at A GlanceDocument9 pagesStructure of Utility Stores Corporation of Pakistan (PVT) LTD at A GlanceMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- PDF of Bank OrganogramDocument1 pagePDF of Bank OrganogramAntar ShaddadNo ratings yet
- DSI Training ReportDocument50 pagesDSI Training ReportChaturanga WagaArachchigeNo ratings yet
- Struktur Organisasi PT ABC Utk Semua KelompokDocument2 pagesStruktur Organisasi PT ABC Utk Semua KelompokKholid HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- Struktur OrganisasiDocument27 pagesStruktur OrganisasiCipta DimensiaNo ratings yet
- Company Structure and ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesCompany Structure and ResponsibilitiesJose HabeahanNo ratings yet
- USC Proposed OrganogramDocument14 pagesUSC Proposed OrganogramMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Assistant Vice President-Kolkata Works (Technical Head) Assistant General Manager (Finance & Personnel In-Charge)Document1 pageAssistant Vice President-Kolkata Works (Technical Head) Assistant General Manager (Finance & Personnel In-Charge)chandan UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Organogram Hino PakDocument4 pagesOrganogram Hino PakSabeehuddin SafdarNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Architecture in Public Sector: Dr. S. Upendra Rao CTO State Bank of IndiaDocument10 pagesEnterprise Architecture in Public Sector: Dr. S. Upendra Rao CTO State Bank of IndiaS. Upendra RaoNo ratings yet
- Organizational Structure of Portal Steels IncDocument1 pageOrganizational Structure of Portal Steels Inczeline petallanoNo ratings yet
- Organisation Structure Bank of MauritiusDocument1 pageOrganisation Structure Bank of MauritiuscvikasguptaNo ratings yet
- Case 3: Pure Flex International Corporation Case 3: Pure Flex International CorporationDocument13 pagesCase 3: Pure Flex International Corporation Case 3: Pure Flex International CorporationAramae DagamiNo ratings yet
- Belmont Industries Case StudyDocument8 pagesBelmont Industries Case StudySaptarshi MaitraNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning KPIs for Measuring Corporate PerformanceDocument21 pagesStrategic Planning KPIs for Measuring Corporate PerformanceIbrahim KamaldeenNo ratings yet
- Retail OverviewDocument10 pagesRetail Overviewsam_sumitNo ratings yet
- Business Function in InsuranceDocument5 pagesBusiness Function in InsuranceRegiNo ratings yet
- Organogram PDFDocument1 pageOrganogram PDFztanjimNo ratings yet
- Management Services Notes Sir BradDocument18 pagesManagement Services Notes Sir BradMarynissa CatibogNo ratings yet
- Governance Objective: Value Creation: Benefits Realisation Resource Optimisation Risk OptimisationDocument6 pagesGovernance Objective: Value Creation: Benefits Realisation Resource Optimisation Risk OptimisationĐoàn Đức ĐềNo ratings yet
- 3kenya CaseDocument18 pages3kenya CaseJMPP12345No ratings yet
- Akhuwat Islamic MicrofinanceDocument1 pageAkhuwat Islamic MicrofinanceAbdul JabbarNo ratings yet
- CMQ-OE Certification Preparation LeadershipDocument75 pagesCMQ-OE Certification Preparation LeadershipMohammed SibghatullaNo ratings yet
- DeluxTool Case Study 2 ScribdDocument7 pagesDeluxTool Case Study 2 Scribdmsw112867No ratings yet
- Strategic Implementation and ControlDocument25 pagesStrategic Implementation and ControlBinod AdhikariNo ratings yet
- SSS Organizational StructureDocument23 pagesSSS Organizational StructureRenz BrionesNo ratings yet
- Abed Org ChartDocument8 pagesAbed Org ChartSyed Moiz Uddin AhmadNo ratings yet
- (Vacant) : Board of Directors Gujranwala Waste Management CompanyDocument1 page(Vacant) : Board of Directors Gujranwala Waste Management Companywaseemaslam_educationNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Cost Accounting For Managerial Planning Decision Making and Control Sixth Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Cost Accounting For Managerial Planning Decision Making and Control Sixth Edition PDFwilliam.bodrick959100% (35)
- Chairman and COO structureDocument1 pageChairman and COO structureTessa OktavianidahlanNo ratings yet
- HIVE ORGANIZATION CHARTDocument1 pageHIVE ORGANIZATION CHARTNoorul AmbeyaNo ratings yet
- USPS Org ChartDocument1 pageUSPS Org ChartbsheehanNo ratings yet
- Organizational Structure.Document6 pagesOrganizational Structure.Jeannie de leonNo ratings yet
- Humanresource Water StudyDocument5 pagesHumanresource Water StudyJanamora GonderNo ratings yet
- Organisational Structure - MitsubishiDocument1 pageOrganisational Structure - MitsubishiMỹ HoàiNo ratings yet
- Department Structure Telecom Companies: Michel ChamatDocument29 pagesDepartment Structure Telecom Companies: Michel ChamatLaxmi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Organisational Chart of Directorate General of Commercial Intelligence & Statistics (DGCIS)Document1 pageOrganisational Chart of Directorate General of Commercial Intelligence & Statistics (DGCIS)Drx Mehazabeen Kachchawala100% (1)
- STRUKTUR ORGANISASIDocument2 pagesSTRUKTUR ORGANISASIDewi Aprilia MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Direct Reporting Line Secondary Reporting LineDocument1 pageDirect Reporting Line Secondary Reporting LinePeter LoyensNo ratings yet
- Reval SDR, Inc. Organizational Structure: Lines of ResponsibilityDocument1 pageReval SDR, Inc. Organizational Structure: Lines of ResponsibilityomsumoNo ratings yet
- OrganizationDocument1 pageOrganizationSandeep MazumdarNo ratings yet
- Diagram: Proposed Organogram For IbankDocument7 pagesDiagram: Proposed Organogram For Ibankammad ahmadNo ratings yet
- 2 Introduction To Financial Management 2023 SDocument37 pages2 Introduction To Financial Management 2023 SCarl AvilaNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Science: Seminar Presentation On Student Industrial Work Experience Scheme (Siwes)Document17 pagesFaculty of Science: Seminar Presentation On Student Industrial Work Experience Scheme (Siwes)Shafeeu MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Struktur OrganisasiDocument1 pageStruktur OrganisasiAhmad ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Deposit Insurance Corporation: Corp. Comm. DeptDocument1 pagePhilippine Deposit Insurance Corporation: Corp. Comm. DeptocssantiagoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managerial Accounting and Job Order Cost SystemsDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Managerial Accounting and Job Order Cost SystemsLadyAnne VillaricoNo ratings yet
- FS Chapter3.Homebody EscapadeDocument9 pagesFS Chapter3.Homebody EscapadeArchille Laraga JosephNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Assignment On Financial ManagementDocument22 pagesTerm Paper Assignment On Financial Managementyerosan mathewosNo ratings yet
- ROI Closing Presentation (EN)Document40 pagesROI Closing Presentation (EN)Akram MalikNo ratings yet
- Report On ZTBLDocument23 pagesReport On ZTBLFarrukh Gurmani100% (1)
- Struktur Organisasi Divisi KeuanganDocument3 pagesStruktur Organisasi Divisi KeuanganDWI ANDININo ratings yet
- Chapter One: China Civil Engineering Construction Coorperation (Ccecc) WasDocument24 pagesChapter One: China Civil Engineering Construction Coorperation (Ccecc) WasMoffat KangombeNo ratings yet
- Jan 19-Jan 20 KPI Forecast-TanvirDocument10 pagesJan 19-Jan 20 KPI Forecast-Tanvirislammajed08No ratings yet
- The Role of Projects in The Organization: ZahidDocument51 pagesThe Role of Projects in The Organization: ZahidTalha KhanNo ratings yet
- Mercruiser 4.3L Mpi SpecsDocument2 pagesMercruiser 4.3L Mpi Specssalvatore dalessandro100% (1)
- MITSUBISHI Elevator PDFDocument12 pagesMITSUBISHI Elevator PDFBirhami AkhirNo ratings yet
- Seven Tips For Surviving R: John Mount Win Vector LLC Bay Area R Users Meetup October 13, 2009 Based OnDocument15 pagesSeven Tips For Surviving R: John Mount Win Vector LLC Bay Area R Users Meetup October 13, 2009 Based OnMarco A SuqorNo ratings yet
- National Drinking Water Quality StandardDocument26 pagesNational Drinking Water Quality Standardiffah nazira100% (2)
- How Do I Create An Import DC ApplicationDocument10 pagesHow Do I Create An Import DC ApplicationPeter CheungNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements of An Entity That Have Been Reviewed by An AccountantDocument3 pagesFinancial Statements of An Entity That Have Been Reviewed by An AccountantQueen ValleNo ratings yet
- Measures of Position - Calculating Quartiles Using Different MethodsDocument6 pagesMeasures of Position - Calculating Quartiles Using Different Methodssergio paulo esguerraNo ratings yet
- South-Goa v1 m56577569830512348 PDFDocument16 pagesSouth-Goa v1 m56577569830512348 PDFXavierBoschNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic SystemDocument6 pagesAdrenergic SystemdocsNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Week 7Document5 pages2nd Quarter Week 7Lymieng LimoicoNo ratings yet
- NRSG 5800 SyllabusDocument5 pagesNRSG 5800 Syllabusapi-310557802No ratings yet
- Nick Bradbeer Thesis Master v11 Corrections REDACTEDDocument276 pagesNick Bradbeer Thesis Master v11 Corrections REDACTEDbatra_763079313No ratings yet
- Infineon-Motor Control Shield With IFX007T For Arduino-UserManual-V02 00-EnDocument15 pagesInfineon-Motor Control Shield With IFX007T For Arduino-UserManual-V02 00-EnMR. VAIBHAVSINGH VARMANo ratings yet
- Milk ManualsDocument18 pagesMilk ManualsLAKSHYA VERMA0% (1)
- Guide To Low Voltage Busbar Trunking Systems-BeamaDocument20 pagesGuide To Low Voltage Busbar Trunking Systems-BeamaGhayath Omer100% (1)
- Terms of Reference: Mataasnakahoy Senior High SchoolDocument13 pagesTerms of Reference: Mataasnakahoy Senior High SchoolAngelica LindogNo ratings yet
- Beteq2010 Part 1Document198 pagesBeteq2010 Part 1Zilmar JustiNo ratings yet
- Astm C11Document8 pagesAstm C11Fitria RindangNo ratings yet
- Eike Batista BiographyDocument9 pagesEike Batista BiographyGEORGEGeekNo ratings yet
- Model Question Papers SolutionDocument39 pagesModel Question Papers SolutionVinayaka Gombi100% (2)
- Airworthiness StandardsDocument15 pagesAirworthiness StandardsJason RossNo ratings yet
- Statistical Theory and Analysis in Bioassay OverviewDocument11 pagesStatistical Theory and Analysis in Bioassay OverviewEgbuna ChukwuebukaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Tourism in NepalDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On Tourism in Nepalgw0he255100% (1)
- DET-2 Service ManualDocument105 pagesDET-2 Service Manualkriotron50% (2)
- TIA PRO1 15 Drive With Startdrive ENGDocument35 pagesTIA PRO1 15 Drive With Startdrive ENGJoaquín RpNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Rectangular Travelling Wave (Unit Step Function at Transition Points-Typical CasesDocument1 pageBehaviour of Rectangular Travelling Wave (Unit Step Function at Transition Points-Typical CasesAngela VaughnNo ratings yet
- CALCULATE TRADE AND CASH DISCOUNTSDocument13 pagesCALCULATE TRADE AND CASH DISCOUNTSrommel legaspi71% (7)
- Safety Budget PlannerDocument12 pagesSafety Budget Plannersidhant nayakNo ratings yet
- The Best Chicken Quesadillas - Mel's Kitchen Cafe 4Document1 pageThe Best Chicken Quesadillas - Mel's Kitchen Cafe 4Yun LiuNo ratings yet
- GCC Lab ManualDocument61 pagesGCC Lab ManualMadhu BalaNo ratings yet