Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 11k PDF
Module 11k PDF
Uploaded by
Baher WilliamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 11k PDF
Module 11k PDF
Uploaded by
Baher WilliamCopyright:
Available Formats
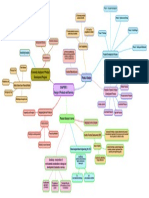
To determine ideas strategic fit
Gate 1: Idea Generation and initial
screening
Kill decisions that received poor
scoring in 1) - overly rigid STAGE 1: prelim assessment
process leads to lost opp's
Gate 2: Secondary screening
decisions
Detailed investigation, customer,
market & competitor analysis STAGE 2: business case prep
Gate 3: decisions on business New products categories: New to
Marketing plan development case the world (5%), New to firm, Line
extentions & Product Features are the
STAGE 3: Development improvements (89%) tangible/intangible attributes
Will the marketing plan lead to given to products by its
acceptance of product in the Gate 4: Post development review e.g Toothpaste
designers
market and is degree of decisions
acceptance sufficient to warant
further development STAGE 4: Testing & validation New product development Max distribution, consumer brand
Benefits are the solutions to Convenience goods and services & recognition advertising, instore
Process (Stagegate system)
customer problems or needs promotions
Try out In small geo areas
Gate 5: Precommercialisation delivered by the product
Field Test Market Test Market business analysis
Measures: e.g TV, cars
Awareness
Shopping goods and services Limited # of stores, personal
Trial Laboratory test markets Stage 5: Commercialisation selling, sellers usually offers
Repeat Buying New product development financing & post purchase
decisions Goods classification
1. Forgo market testing & directly
to rolloot region by region (use if e.g Stereo equip, Guitars
low risk)
Speciality goods and services limited distribution, high price,
brand & uniqueness emphasis
2. launch in 10% of country & rely
on fast sales results data
e.g medical services, insurance
Conduct post implementation Lengthening beyond its current Lengthens the product line by
review to assess how the launch range of variables, such as size, adding items within present range Unsought goods and services Personal selling, strong
is going & make adjustments price promotion
Objectives: to satisfy more
Upward stretch = trading up. customers, increase sales & Meets certain requirements
Line Stretching Line Filling Conformance
Downward stretch = adding profits, placate dealers & ward off
products to serve the lower end competition speed and ease of retaining
of the market e.g Merc & minicar Serviceability repair
Introducing new products that BARNEY - Come See A Purple
differ significantly from those in Aesthetics subjective
Line extensions Quite Fluffy Real Dinosaur
existing lines
Performance operating characteristics
- = Greater costs & financial risks Module 11
8 dimensions of quality of Quality
+ = new market segments, new Managing Product lines - goods
anchor points strategies Product Decisions Features
Perform satisfactory over a given
time
Use of a brand name established Reliability
in one product class as a vehicle
for enter another product class Brand extensions
e.g HP Durability Measure of the life of the product
Should b e reviewed regularly and Brand name is the part that can
b e vocalised (e.g Sony) Tangibles Appearance of physical
if poor contribution to product - Dropping products characteristics
drop it and focus on profitabile
products Competence, courtesy &
Assurance
Brand mark is not vocalised e.g a credibility
Selling product & also providing a symbol
Product systems 5 Dimensions of service quality
complementary product/service Reliability
as a package e.g HP sells printers (TARRE) Dependibility
Trademark is a brand or part of a
with ink catridges brand that legally belongs
exclusively to the seller Responsiveness
Branding Promptness & helpfulness
The company provides each 1. Observation
product with a distinctive name
4 major asset categories: Brand Empathy
name awareness, brand loyalty, Branding identifies and helps
+ = reduces company risk in that differentiate goods or services 2. capturing data
perceived quality & brand
failure not associated to other associations
brands 3. Reflection & analysis
Empathic design process to
- = can limit flexibility to changing Individual Branding uncover new customer needs
market conditions if brand name 4. Brainstorming & solutions
is e.g KFC - issue when fried not Qualitative product design &
considered healthy market research technique where
5. Developing prototypes customers are observed in their
Branding strategies own environment e.g focus
groups, interviews, surveys
Uses the same brand nameto - = Difficult as meaning of brand
cover a group of products name can evoke negative
associations in some countries.
+ = reduced costs & transfer of Family Branding strong local brands & heavy
customer satisfaction - easier to
investment required
launch product modifications,
impact of shelf facings / Globalisation
promotions
+ - most succesful e.gs are Coca
- = when it covers products that Cola, Nike, IBM
range in quality consumers Co-Branding
become confused, risk of
tarnishing the whole line is one uses multiple brand names with a
product bad single product or service offering
e.g Irish Bailey's cream Liquor Ice
cream
You might also like
- Pragmatic Framework RolesDocument6 pagesPragmatic Framework RolesZNo ratings yet
- Books of Accounts & Accounting RecordsDocument34 pagesBooks of Accounts & Accounting RecordsCA Deepak Ehn67% (3)
- Pragmatic Marketing FrameworkDocument2 pagesPragmatic Marketing Frameworkmailtoriteshpatnaik8255No ratings yet
- LWD For SLB PDFDocument21 pagesLWD For SLB PDFMohamed KableNo ratings yet
- Small Scale LNGDocument8 pagesSmall Scale LNGMelvin MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Innovation & RND Management: Value Analysis/Value Engineering & New Product DevelopmentDocument24 pagesInnovation & RND Management: Value Analysis/Value Engineering & New Product Developmenthikam anggaNo ratings yet
- Strategy and ConsultingDocument75 pagesStrategy and ConsultingRitu MendirattaNo ratings yet
- International Logistics Presentation FinalDocument32 pagesInternational Logistics Presentation Finalsoumyarm942No ratings yet
- CH-20-Introducing New Market OfferingsDocument24 pagesCH-20-Introducing New Market OfferingsBilal Raja100% (9)
- Cornell Johnson Casebook Consulting Case Interview Book康奈尔大学约翰逊商学院管理学院咨询案例面试Document97 pagesCornell Johnson Casebook Consulting Case Interview Book康奈尔大学约翰逊商学院管理学院咨询案例面试issac liNo ratings yet
- Pragmatic Framework Defintitions 1812.2Document2 pagesPragmatic Framework Defintitions 1812.2ZNo ratings yet
- Product ResearchDocument20 pagesProduct Researchjain_vikram90No ratings yet
- SAP Profitability Analysis ConfigurationDocument3 pagesSAP Profitability Analysis Configurationgurjitsingh823No ratings yet
- 1 Understanding and Analyzing Business TransactionsDocument2 pages1 Understanding and Analyzing Business Transactionsapi-299265916No ratings yet
- MODULE I - Introduction To Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementDocument51 pagesMODULE I - Introduction To Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementPrashansa Suman67% (3)
- Product Development Operations and Financial PlanDocument173 pagesProduct Development Operations and Financial Plani-Diptan Aku75% (4)
- Formula and Calculation of Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)Document7 pagesFormula and Calculation of Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)harpominder100% (1)
- Module 4 Loans and ReceivablesDocument55 pagesModule 4 Loans and Receivableschuchu tvNo ratings yet
- Best Practices Guide Cabin Retrofit and EIS Ed1Document45 pagesBest Practices Guide Cabin Retrofit and EIS Ed1SHERIEFNo ratings yet
- Guide To Customer DevelopmentDocument5 pagesGuide To Customer DevelopmentHoda Rashad100% (1)
- Chapter 8Document19 pagesChapter 8aastha gargNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing: New Product DevelopmentDocument11 pagesPrinciples of Marketing: New Product Developmentprativa subudhiNo ratings yet
- Chap 9Document14 pagesChap 9kusukundiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Design of Products and ServicesDocument1 pageChapter 3 Design of Products and ServicesAnthony KwoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 NPDDocument14 pagesUnit 1 NPDRoopa NandiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Developing Product StrategyDocument18 pagesUnit 2: Developing Product StrategyAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- New Product Development (Pertemuan II)Document14 pagesNew Product Development (Pertemuan II)The Infant FiniteNo ratings yet
- New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument25 pagesNew Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesRitesh KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- New Product Development and Test MarketingDocument22 pagesNew Product Development and Test MarketingnileshwahaneNo ratings yet
- New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument16 pagesNew Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- MM 2-5 New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument22 pagesMM 2-5 New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesvinaytoshchoudharyNo ratings yet
- New Product Development Process Lecture 1.2.4Document17 pagesNew Product Development Process Lecture 1.2.4gunjack477No ratings yet
- Om Mid Term Syllabus: Analysis DesignDocument135 pagesOm Mid Term Syllabus: Analysis DesignSameer69No ratings yet
- 3 Proses Pengembangan ProdukDocument10 pages3 Proses Pengembangan ProdukhilmaNo ratings yet
- 4 Step To EpiphanyDocument71 pages4 Step To Epiphanythikhjn2011No ratings yet
- Managing New Products: The Power of InnovationDocument34 pagesManaging New Products: The Power of InnovationwaqaasrumaniNo ratings yet
- New Product Development (NPD)Document29 pagesNew Product Development (NPD)Shubhranshu ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- New Product DevelopmentDocument23 pagesNew Product Development9013126157No ratings yet
- New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument21 pagesNew-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesHarshpreet TakkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 KBTUDocument19 pagesChapter 7 KBTUFarhangaizNo ratings yet
- New Product: A Product New To The World, The Market, The Producer, The Seller, or Some Combination of TheseDocument23 pagesNew Product: A Product New To The World, The Market, The Producer, The Seller, or Some Combination of ThesedharaparsawalaNo ratings yet
- Product Decisions: By: DR Shahinaz AbdellatifDocument21 pagesProduct Decisions: By: DR Shahinaz AbdellatifEman EmyNo ratings yet
- Business Acceptance Testing - Is Your Product User Ready?: Ashwin Kumar ChandrashekaraiahDocument8 pagesBusiness Acceptance Testing - Is Your Product User Ready?: Ashwin Kumar ChandrashekaraiahzanajoelleNo ratings yet
- Product Launch and EvaluationDocument27 pagesProduct Launch and EvaluationWasif UllahNo ratings yet
- U - Iii MMDocument37 pagesU - Iii MMverma.ganesh571No ratings yet
- New Product Planning Process: Situation AnalysisDocument11 pagesNew Product Planning Process: Situation AnalysisRaman KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Product Planning Process - 1Document75 pagesProduct Planning Process - 1Raman KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Market Information: MARKET RESEARCH: It Is For Discovering What People WantDocument4 pagesMarket Information: MARKET RESEARCH: It Is For Discovering What People WantMonal GehlotNo ratings yet
- New Product Development: Identifying Need Creating ValueDocument20 pagesNew Product Development: Identifying Need Creating ValueSharvaree TawareNo ratings yet
- Rahmawati CH 20 Introducing New Market OfferingsDocument24 pagesRahmawati CH 20 Introducing New Market OfferingslokioNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing: New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument14 pagesPrinciples of Marketing: New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategiesbhupesh joshiNo ratings yet
- MK430 - 2024 Lecture 3 - Slide Presentation For DayDocument39 pagesMK430 - 2024 Lecture 3 - Slide Presentation For DayelishmahNo ratings yet
- Market Projection "Evidence 2": Ana Isabel Dovales Oscar Ivan Sanchez Rivera Walter Alexander Riay SarmientoDocument10 pagesMarket Projection "Evidence 2": Ana Isabel Dovales Oscar Ivan Sanchez Rivera Walter Alexander Riay Sarmientoalexander riayNo ratings yet
- 5 Phrases in New Product ProcessDocument6 pages5 Phrases in New Product Processlekhanh2499No ratings yet
- 6 Chapter 6 9781786393814Document41 pages6 Chapter 6 9781786393814yunicenjeNo ratings yet
- RD2Document30 pagesRD2yomnaNo ratings yet
- Project Management ProcessDocument24 pagesProject Management ProcessRonald LopezNo ratings yet
- Demand-Led Plant Breeding Training ManualDocument34 pagesDemand-Led Plant Breeding Training ManualGana C RoverNo ratings yet
- PDCM - Slides For Chapter 2Document23 pagesPDCM - Slides For Chapter 2Prashant TyagiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - New Product DevelopmentDocument15 pagesChapter 10 - New Product Developmentkunal gargNo ratings yet
- Businessstudy Notes Chapter 11Document31 pagesBusinessstudy Notes Chapter 11MAYANK SINGH RAJPUTNo ratings yet
- Production Management: Lecture No 5 Resource Person: Engr Muhammad Raheel ButtDocument40 pagesProduction Management: Lecture No 5 Resource Person: Engr Muhammad Raheel ButtZeeshan QaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document22 pagesChapter 11mahnoor javaidNo ratings yet
- Developing InnovationDocument30 pagesDeveloping InnovationSaranyaa Durai SingamNo ratings yet
- Sales Force Reward SystemDocument9 pagesSales Force Reward SystemUdruženje Behar Kulturno-edukativna AsocijacijaNo ratings yet
- Creating New Foods CH 1Document21 pagesCreating New Foods CH 1zin berNo ratings yet
- Product DevelopmentDocument30 pagesProduct DevelopmentJennifer Mae LangamanNo ratings yet
- Stage Gate ModelDocument4 pagesStage Gate ModelSreeparna SahaNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument10 pagesBusiness PlanKieanne BlackmanNo ratings yet
- 22 Drivers of Success in Product DevelopmentDocument67 pages22 Drivers of Success in Product DevelopmentUmar DarNo ratings yet
- Product Launch DoomedDocument17 pagesProduct Launch Doomednaughtysagi2No ratings yet
- RSPPLDocument1 pageRSPPLMohamed KableNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior Course Summary - Tamer 2011 - 2 of 2Document37 pagesOrganizational Behavior Course Summary - Tamer 2011 - 2 of 2Mohamed KableNo ratings yet
- Module 4 PDFDocument1 pageModule 4 PDFMohamed KableNo ratings yet
- Marketing EXAM CASE STUDY 1Document5 pagesMarketing EXAM CASE STUDY 1Mohamed KableNo ratings yet
- Ebs Exam Analysis-2Document39 pagesEbs Exam Analysis-2Mohamed KableNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document1 pageModule 9Mohamed KableNo ratings yet
- Finace Ex. Dec 2008Document4 pagesFinace Ex. Dec 2008Mohamed Kable50% (2)
- Analysis: OrganizationDocument6 pagesAnalysis: OrganizationDrAbhishek SarafNo ratings yet
- Telemarketing: - Calls Offering To Sell Goods or Services - Reduces CostDocument6 pagesTelemarketing: - Calls Offering To Sell Goods or Services - Reduces Costsudhir87No ratings yet
- Coke Contract. Texas A&M College StationDocument35 pagesCoke Contract. Texas A&M College StationCampaign to Stop Killer CokeNo ratings yet
- A 360 Approach To Time: CAS EDocument12 pagesA 360 Approach To Time: CAS EArpit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- CB Starbucks Grp6Document9 pagesCB Starbucks Grp6Tushar ShettyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 SummaryDocument4 pagesChapter 9 SummaryEugene OeiNo ratings yet
- Vodafone GroupDocument5 pagesVodafone GroupChirag DaveNo ratings yet
- CH 1 IntrotoimcDocument37 pagesCH 1 IntrotoimcamritabangaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Resources: Practice Multiple Choice Questions: Pre-Test #1: INTRODUCTIONDocument9 pagesFinal Exam Resources: Practice Multiple Choice Questions: Pre-Test #1: INTRODUCTIONShadreckLimpoKalimbweNo ratings yet
- Acctg. 6: Republic of The Philippines Sorsogon State College Castilla CampusDocument44 pagesAcctg. 6: Republic of The Philippines Sorsogon State College Castilla CampusRoxanne L. JayloNo ratings yet
- F13 Acct 311 Midterm 2 Solution For PostingDocument15 pagesF13 Acct 311 Midterm 2 Solution For PostingSteven Daniel DayNo ratings yet
- Excise Clearance For ExportsDocument24 pagesExcise Clearance For ExportsjeevanandamcNo ratings yet
- Deed of Absolute Sale SampleDocument2 pagesDeed of Absolute Sale SampleAnne Jana CiaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Sec BDocument2 pagesGroup 1 - Sec BRohanMohapatraNo ratings yet
- Order Types in SAPDocument88 pagesOrder Types in SAPRamesh MNo ratings yet
- School of Distance Education Examinations Time-Table For May 2012 ExaminationsDocument18 pagesSchool of Distance Education Examinations Time-Table For May 2012 ExaminationsAniel MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Trading Business Chapter 5Document40 pagesAccounting For Trading Business Chapter 5MUHAMMAD AMMAD ARSHAD100% (1)
- HBC 2117, Hps 2108 Cost AccountingDocument5 pagesHBC 2117, Hps 2108 Cost AccountingBennyhin OduorNo ratings yet
- Creating An Effective China "Cold Supply Chain": Current Status, Challenges and Implementation ConsiderationsDocument20 pagesCreating An Effective China "Cold Supply Chain": Current Status, Challenges and Implementation ConsiderationsfarhafarhaNo ratings yet