Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Economics Upsc 2021
Uploaded by
Pulkit Malik0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
145 views18 pagesOriginal Title
ECONOMICS UPSC 2021
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
145 views18 pagesEconomics Upsc 2021
Uploaded by
Pulkit MalikCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
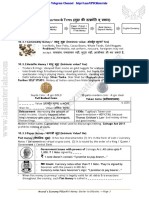
BARTER SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF COMMODITY METALLIC MONEY
1. Double Coincidence of MONEY MONEY Stamped gold nuggets using
wants PRIMARY Both intrinsic and dye.
2. High Search and Measure of Value extrinsic value. Indo Greek and Kushana
Transaction Cost As a medium of exchange Perishable, non- Kings- Issued Gold Coins
3. Perishable in transaction uniformity, Gupta Gold Coins: Most
CommoditiesLoose SECONDARY internationally spectacular
value with time. Store & transfer of value unaccepted, non-purity & Delhi Sultanate Kings:
4. No specialisation & Deferred Payments division of labour not Silver Tanka
division of labour CONTINGENT promoted. Sher Shah Suri: Rupiyah
5. Fungibility Problems Basis of Credit System, Iron nails, cocoa beans, Silver Coin
(Division: Yes; Mutual Financial Markets Akbar: Muhr
gold nuggets etc.
Substitution: No) Redistribution of National
Income
FULL BODIED COINS POOR QUALITY TOKEN COINS MODERN INDIAN
GUPTA COIN- 8g GOLD COINS 50 PAISA MODERN COINS
Intrinsic Value> Face Decrease in Roman- COIN- 4g STEEL Cupronickel metal used
Value Persian Empires lead to Intrinsic Value< Face to discourage the
DEBASEMENT: decrease in incoming Value melting.
decreasing the amount of gold. Tughlaq’s Token Coin Coinage Act 2011
metal in the coins. Experimentation: (not the
Trade was done for prohibits melting of
first to be introduced- China
Usually happen when species, pepper, silk and and Iraq issue paper money coins
king’s treasury gets sandalwood from India. first)
poor. Thus, lead to formation Hoarding of coins for metal
E.g. Aurangzeb, Roman of poor quality coins. Thomas Gresham’s Law-
Kings Bad money drives out good
money.
PAPER/ TOKEN/ LEGAL TENDER G-Sec, T-Bills, Shares, COINS in INDIA
REPRESENTATIVE Fiat money is legally Bonds, Demand Draft, Government issues with
MONEY valid for all debts & Cheque, ATM, Cards, powers of Coinage Act
Possess no intrinsic transactions throughout Bitcoins are neither Fiat all coins upto Rs.1000
value the country. money nor Legal Tender
FIAT MONEY FIDUCIARY MONEY Rupee 1 note signed by
Form of a coin/ currency People kept money with Financial Secretary.
note/ sometimes virtual merchant and merchant
crypto-coin provided a token. Rupee 1 does not
Issued by order of a Commemorative Coins: contain “I promise to
King/ Queen/
Fiat: Yes; Legal Tender: pay the bearer..”
Government/ Central
Bank No, until specified
CURRENCY NOTES in MEANING OF MODERN ERA LIMITED LEGAL
INDIA PROMISE CURRENCY NOTES TENDER
RBI issues with the COLONIAL ERA Zero Interest Payment beyond a
power of RBI Act, 1934 Converted to gold/ silver Bond/ Promissory Note limit can be refused.
all currency notes other worth the equal value in Anonymous Bond E.g. Coins
than Rupee 1. weight. Bearer. Coinage Act 2011
MODERN ERA Rs.1 or above coins
They are signed by RBI Converted to other token CURRENCY NOTES upto Rs. 1000
Governor notes of equal face FEATURES 50 paisa upto Rs. 10
value. 2000= 500 x 4 Read from handout. Below 50 paisa
Currency notes contain Not linked with gold. withdrawn
“I promise to…” Not inflation adjusted.
UNLIMITED LEGAL DEMONETISATION SPECIFIED BANK BANK MONEY/
TENDER OF FIAT MONEY NOTES (CESSATION DEPOSIT MONEY
No such restrictions 1946, 1978, OF LIABILITIES ACT, Paper orders: Cheque,
under RBI Act, 1934 8/11/2016 2017) Demand Draft.
RBI Act, 1934- Gazette notification- RBI not to honour “I Viceroy Ripon’s
Section 26: Every Finance Minister- promise…” on Negotiable
Bank Note is a legal Department of banned notes Instruments Act 1881:
tender in India. Can Economic Affairs Old notes cannot be Encourage Check usage
settle any amount. Banned “Specific stores except for & punish dishonour and
Financial Act 2017: Cash Bank Notes” of research, museum etc. forgery.
transaction for less than Rs. that too in limited Dishonour: Insufficient
Mahatma Gandhi Series
2 lakhs only quantity. money in drawer’s account.
BANK MONEY/ BANK MONEY/ AUTOMATIC TYPES OF CHEQUE
DEPOSIT MONEY DEPOSIT MONEY CLEARING SYSTEM Stale: Not withdrawn
2017 Amendment: Indian Financial 1) Optical Character in 3 months
20% interim System Code (IFSC): Recognition (OCR) Anti-dated: Before a
compensation @ Trial 11 alphanumeric 2) MICR Code: Magnetic specific date
Court. numbers to identify bank Ink Character Post-dated: After a
20% deposit before branch. Recognition. 9 digit code specific date
appeal in higher court Demand Draft: Sender written in iron oxide ink.
Open/ Bearer Check:
3 parts in cheque: has to pay before bank 3) CTS: NPCi’s Cheque If no crossing anyone
issues, thus, cannot be Truncation system:
1) Drawer (Sender) dishonoured.
can withdraw.
2) Drawee (Bank) scanned image If crossing Money will
Over Draft: Zero balance electronically sent. No only be sent to Payee’s
3) Payee (Recipent) but still withdraw as a loan theft and tempering. Account and no cash.
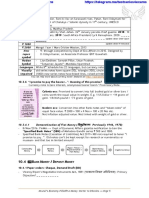
Middleman for Financial RBI FORMATION RBI FORMATION July, 1935: Banks to
Transactions b/w 1913: Commercial Banks 1934: RBI ACT enacted register 2nd Schedule
registered under of RBI ACT
Lender Borrower COMPANIES ACT st
1935: 1 April RBI CRR to be maintained.
No bound of reserve. OPERATED
Investor Entrepreneur 1943-49: CD Deshmukh.
1926: HILTON YOUNG 1st Indian Governor RBI
Governor: OSBORNE
Household Business Firm COMMISSION (Royal) 2nd FinMin
SMITH
recommended to set up RBI
Is known as: Viceroy: WILLINGTON
1948-49: GOI bought pvt.
Financial Intermediary 1929: Great Depression in shares under RBI transfer
Types: * Formal & USA, collapsed 450+ banks Low government ownership of OWNERSHIP ACT,
* Informal in India
1948 (RBI Parliament)
BANKING RBI CENTRAL RBI CENTRAL RBI CENTRAL
REGULATION ACT, BOARD BOARD BOARD
1949 COMPOSITION COMPOSITION COMPOSITION
RBI empowered Official Directors: Appointed by Financial Non Official Directors:
LicenseCompanies RBI Governor-25th- Sector Regulatory 2 Govt. Officials
New Bank Shaktikanta Das Appointment Search 10 Directors nominated
Permission Bank Max 4 Dy. Governor Committee (FSRASC) by Govt.
New Branch under SECTION 8 of headed by Cabinet 4 Directors: RBI’s Local
SLR RBI ACT Secretary IAS headed by Boards:
Interest of depositors BP Kanungo PM. N-S-E-W
Force elimination/ Mahesh Kumar Jain Delhi-Chennai-Kolkata-
merger of weak banks Tenure: 3 years, Mumbai
Michael Patra
……………. Reappointment Possible
RBI DEPARTMENTS RBI FUNCTIONS
1/04/17 Enforcement Controls Money Supply:
Department of RBI to M0
take centralized actions Controls Foreign
against violators. Exchange: FEMA
Banker to govt. & public
Not to be confused with debt
FinMin Enforcement Regulator of Banks &
Directorate uses FEMA NBFC under Banking
(Foreign Exchange Regulation Act, 1949 &
Management Act 1999), Payments System, 07
Prevention of Money Ombudsman, PSL
Laundering Act, 2002 Norms: Protect Public
You might also like
- Mission LBSNAA 2023Document105 pagesMission LBSNAA 2023shubham awhad100% (1)
- POLITY - Complete Study NoteDocument61 pagesPOLITY - Complete Study Notechhandak123No ratings yet
- Indian Art and CultureDocument4 pagesIndian Art and CultureAnonymous zyWGXsxhd4100% (1)
- Economy NCERT GISTDocument77 pagesEconomy NCERT GISTabhimanyuNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Quick Revision Polity 120 Days Upsc Perlims 2021 10pointerDocument8 pagesDay 1 Quick Revision Polity 120 Days Upsc Perlims 2021 10pointerAllindiatestNo ratings yet
- Art and CultureDocument108 pagesArt and CultureAdhir giriNo ratings yet
- Inspiring quotes on important issuesDocument21 pagesInspiring quotes on important issuessiddhant lodha100% (1)
- Mainspedia Ilp 2020 IasbabaDocument15 pagesMainspedia Ilp 2020 IasbabaKalyan valisetty0% (1)
- Mountain Passes in India Iasmania - Civil Services Preparation Online ! UPSC & IAS Study MaterialDocument4 pagesMountain Passes in India Iasmania - Civil Services Preparation Online ! UPSC & IAS Study MaterialsrikarNo ratings yet
- Key features of the Indian ConstitutionDocument44 pagesKey features of the Indian Constitutionmkrao_kiranNo ratings yet
- Indian Geography Notes From CDDocument240 pagesIndian Geography Notes From CDSatish Sunny100% (2)
- Art and Culture Notes From CDDocument196 pagesArt and Culture Notes From CDJishan Ahmed100% (1)
- India Physical GeographyDocument48 pagesIndia Physical GeographymkprabhuNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs APPDocument74 pagesCurrent Affairs APPHimanshu gupta100% (1)
- Ilp 2017 Set 2 Block 1 Polity Value Add 1Document102 pagesIlp 2017 Set 2 Block 1 Polity Value Add 1nidhi100% (1)
- INSIGHTSIAS PRELIMS TEST SERIES 2019 – GEOGRAPHY QUESTIONSDocument121 pagesINSIGHTSIAS PRELIMS TEST SERIES 2019 – GEOGRAPHY QUESTIONSGopal kumar100% (1)
- Dams in India Geography Notes For UPSCDocument2 pagesDams in India Geography Notes For UPSCsonuhd1995No ratings yet
- Mrunal (Culture) Indian Art, Architecture and Painting Schools (Mindmap Cum Note) MrunalDocument9 pagesMrunal (Culture) Indian Art, Architecture and Painting Schools (Mindmap Cum Note) Mrunalmerc7inNo ratings yet
- NCERT Complete Notes On History XI - XIiDocument282 pagesNCERT Complete Notes On History XI - XIiRajal Sharma100% (1)
- ANCIENT HISTORY Prelims Notes: Pugalur Incsription (1st Century AD) - Mentions 3 Madhuban Plate Inscription - HarshaDocument33 pagesANCIENT HISTORY Prelims Notes: Pugalur Incsription (1st Century AD) - Mentions 3 Madhuban Plate Inscription - HarshaMeghana RajputNo ratings yet
- Ancient India: The Harappan CivilizationDocument38 pagesAncient India: The Harappan CivilizationNishu ThimmaiahNo ratings yet
- 10 Must Read Books For IAS Aspirants - ByjusDocument13 pages10 Must Read Books For IAS Aspirants - ByjusKailashchoudhary09No ratings yet
- l0 p1 To p4 Upsc Gs PrepDocument112 pagesl0 p1 To p4 Upsc Gs PrepAnonymous YLd94rwO4fNo ratings yet
- India's Extent and SizeDocument151 pagesIndia's Extent and Sizeajinkya kamble100% (1)
- Newslive 23rdfeb2014 Telangana KilliDocument20 pagesNewslive 23rdfeb2014 Telangana KillideekshithNo ratings yet
- IASToppers PreCharge 2020 Art-Culture & History-1Document82 pagesIASToppers PreCharge 2020 Art-Culture & History-1AnkitDhakadNo ratings yet
- NCERT Notes on Prehistoric Rock Paintings and Indus Valley ArtsDocument62 pagesNCERT Notes on Prehistoric Rock Paintings and Indus Valley ArtsMathiraja.T100% (2)
- I Dian Geography NotesDocument16 pagesI Dian Geography NotesSrimanta AdakNo ratings yet
- Updated Art N Culture 2023Document116 pagesUpdated Art N Culture 2023R RajNo ratings yet
- Culture Complete Notes MrunalDocument51 pagesCulture Complete Notes Mrunalamarsinha198767% (6)
- Niti Aayog: Case Studies & Best PracticesDocument11 pagesNiti Aayog: Case Studies & Best PracticesUmang PathaniaNo ratings yet
- Indian GeographyDocument24 pagesIndian GeographySatish Shinde100% (1)
- Indian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsFrom EverandIndian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsNo ratings yet
- Money FunDocument1 pageMoney Funsingh RNNo ratings yet
- Module 3 MoneyDocument23 pagesModule 3 Moneyg.prasanna saiNo ratings yet
- Pillar 1 - Money, RBI, BankingDocument215 pagesPillar 1 - Money, RBI, Bankingshek ndNo ratings yet
- Economy Pillar - 1 - A1 (Money)Document27 pagesEconomy Pillar - 1 - A1 (Money)Our PastNo ratings yet
- Best Telegram Channels for Exam PDFs and Test SeriesDocument2 pagesBest Telegram Channels for Exam PDFs and Test SeriesWashim Alam50CNo ratings yet
- MoneyDocument49 pagesMoneyShalini Singh IPSANo ratings yet
- 08 Chapter 3Document79 pages08 Chapter 3Oii SaralNo ratings yet
- Notes in BankingDocument2 pagesNotes in BankingCYRELL ANDREA BUSTARDENo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Ghulam HaiderNo ratings yet
- Functions and Forms of MoneyDocument20 pagesFunctions and Forms of Moneyirfan444No ratings yet
- Money and Banking NotesDocument13 pagesMoney and Banking NotesYash ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Basic Finance - 021415Document3 pages1.2 Basic Finance - 021415Angel RamosNo ratings yet
- 12-13. Money MarketDocument45 pages12-13. Money MarketLakshmi NairNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Money and The Financial SystemDocument20 pagesWeek 4 Money and The Financial Systemelijah thonNo ratings yet
- Finance MIDTERMDocument2 pagesFinance MIDTERMPia SolNo ratings yet
- Bitcoin: (GS3) Money Laundering Interview Stage Mca/EcDocument78 pagesBitcoin: (GS3) Money Laundering Interview Stage Mca/EcPraveen KatepallyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, Concept of MoneyDocument18 pagesChapter 2, Concept of Moneymiracle123No ratings yet
- Classification of MoneyDocument8 pagesClassification of MoneyRajat KumarNo ratings yet
- Mamata L6 P1 BitcoinDocument66 pagesMamata L6 P1 BitcoinitsmohanecomNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Payment Systems in India: Barattes and Were Akin To Present Day Drafts or ChequesDocument5 pagesEvolution of Payment Systems in India: Barattes and Were Akin To Present Day Drafts or Chequesshweta9696No ratings yet
- CHP#2 Forms of MoneyDocument20 pagesCHP#2 Forms of MoneyMuhammad HasnainNo ratings yet
- What is Money: The Economics of Banking and Financial MarketsDocument34 pagesWhat is Money: The Economics of Banking and Financial MarketsBryan AprilianoNo ratings yet
- BafinnnnDocument4 pagesBafinnnnkdot03433No ratings yet
- The Canadian Patriot Special: Republic or Colony?Document49 pagesThe Canadian Patriot Special: Republic or Colony?Matthew EhretNo ratings yet
- Mindanao Geo Reg. FormDocument2 pagesMindanao Geo Reg. FormChristine BernalNo ratings yet
- 4 Que vs. Law Union, G.R. No. L-4611Document4 pages4 Que vs. Law Union, G.R. No. L-4611thinkbeforeyoutalkNo ratings yet
- Demand LetterDocument2 pagesDemand LetterHimanshu RantiyaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of AccountingDocument72 pagesFundamental of AccountingGuruKPO67% (3)
- Insurance CompaniesDocument5 pagesInsurance CompaniesRajesh GawdeNo ratings yet
- 13.performance of Substantive Testing and Summary of Results of Substantive TestingDocument3 pages13.performance of Substantive Testing and Summary of Results of Substantive TestingKen Aaron DelosReyes PedroNo ratings yet
- Bill 11 October 2011Document6 pagesBill 11 October 2011UZNAPMNo ratings yet
- Insurance Sector in NigeriaDocument21 pagesInsurance Sector in NigeriaBaba Jide Oniwinde100% (1)
- GK Bullet - SBI PO (Mains) II PDFDocument33 pagesGK Bullet - SBI PO (Mains) II PDFgaurav singhNo ratings yet
- Town of Holden Beach: "Unofficial" Minutes & CommentsDocument17 pagesTown of Holden Beach: "Unofficial" Minutes & Commentscutty54No ratings yet
- Icici LiDocument15 pagesIcici Lijawad_mgNo ratings yet
- Supplier Bank DetailsDocument2 pagesSupplier Bank DetailsJoaquina BeloNo ratings yet
- Impact of Technological Advancement on Employee PerformanceDocument18 pagesImpact of Technological Advancement on Employee Performancesachin mohanNo ratings yet
- UBS Risk Management and Tax Evasion SolutionsDocument7 pagesUBS Risk Management and Tax Evasion SolutionsJoshua CabreraNo ratings yet
- Examples of Journal EntriesDocument7 pagesExamples of Journal EntriesParth VadulekarNo ratings yet
- IRCTC Ticket PrintingDocument1 pageIRCTC Ticket PrintingTuhin ChandraNo ratings yet
- Barangay KapasiganDocument7 pagesBarangay KapasiganJosell QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Swift Code Obligor Bank RiskpartDocument12 pagesSwift Code Obligor Bank RiskpartDee AZNo ratings yet
- Objective 4.02 Unpacked ContentDocument4 pagesObjective 4.02 Unpacked ContentHeather CovingtonNo ratings yet
- Cashless India EssayDocument2 pagesCashless India Essayer_ppravinNo ratings yet
- 3013618Document2 pages3013618GauriGanNo ratings yet
- Accounting Records Source DocumentsDocument3 pagesAccounting Records Source Documentsziad12321No ratings yet
- Micro FinanceDocument53 pagesMicro Financeamitharia100% (6)
- Punjab and Sind Bank Project MDocument78 pagesPunjab and Sind Bank Project MIbrahim Shaikh MNo ratings yet
- In FinacleDocument35 pagesIn FinacleSoniJimishNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh's Leading Mobile Banking ServicesDocument12 pagesBangladesh's Leading Mobile Banking ServicesTaymur Hasan MunnaNo ratings yet
- BelizeDocument8 pagesBelizeroger_roland_1No ratings yet
- Bol PDFDocument9 pagesBol PDFSiddhartha ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Billing StatemenDocument4 pagesBilling StatemenAriz LealNo ratings yet