Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Electronics Engineering Interview Questions & Answers PDF
Uploaded by
Satyam ShivanshOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Electronics Engineering Interview Questions & Answers PDF
Uploaded by
Satyam ShivanshCopyright:
Available Formats
Breaking News Up tp 93% Off - Launching Official Electrical Technology Store - Shop … OFFICIAL STORE WRITE FOR ET ADVERTISE
OFFICIAL STORE WRITE FOR ET ADVERTISE PRIVACY POLICY CONTACT US
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY 155k+ 2.3M 3,370
Subscribers Fans Followers
1,660 181k
Subscribers Followers
Home > Electronics > Basic Electronics > Basic Electronics Engineering Interview Questions & Answers
Basic Electronics EE Questions / Answers Electrical & Electronics Notes and Articles Electronics
Categories
Trending
Basic Electronics Engineering Interview Questions &
Select Category
Answers
Electrical Technology 3 12 minutes read
65+ Electronics Engineering Interview Questions & Answers
Electronics Engineering, like any other engineering job, has many technical questions. To shine
better at electronics engineering interview, you need to have a strong grip over the technical
questions. You need to keep yourself updated with electronics engineering interview questions
to outperform other candidates. You do not want someone who has no knowledge about technical
questions to outperform you in electronics engineering interview.
Related Post: Basic Electrical & Electronics Interview Questions & Answers
Here are some of the most asked basic Electronics Engineering interview questions.
What is Electronics Engineering?
Electronics engineering is a field of engineering which deals with the utilization of active and
passive electronic components to design a variety of different analog and digital circuits, devices,
and systems.
These devices are implemented in logic circuits, communication systems, robotics, microprocessors
and Artificial intelligence to perform useful tasks efficiently and for the betterment of human beings.
It usually deals with low current voltage (compared to Electrical Engineering) specifically between
-48v to 48v.
Related Question: What is the main Difference Between Electrical and Electronic Engineering?
What are Active and Passive components?
Active components are those electrical components which require an external source for its full
operation such as Diode, Transistor, Thyristor etc.
Passive components are those components which do not need any external source for its function.
Example of passive components is resistor, capacitor & Inductor.
Related Post: The Main Difference between Active and Passive Components (Examples)
What is a Resistor?
A resistor is an electronic component with two terminals, which resist or oppose the electrical
current in its path. It also develops a voltage drop across its terminals, which depends on the
current flowing through it. This voltage drop is calculated using the Ohm’s law: V= IR.
What is a Capacitor?
A capacitor is a two-terminal electronic component, which stores potential energy in the form of
charge. The property or ability of the capacitor to store charge is called capacitance and it is
measured in Farad. The stored charge q can be measured using the equation: q = CV
What is an Inductor?
An inductor is an electronic device, which resists the change in electrical current passing through it.
It stores energy in the form of the magnetic field when the current pass through it. The voltage drop
across an inductor can be calculated using: V = L (di/dt).
What is Practical & Ideal Voltage Source?
A voltage source having some internal resistance is called a practical voltage source. Due to this
resistance, there is a voltage drop. The supply voltage of the practical voltage source decreases
with an increase in the current.
If the internal resistance of a voltage source becomes zero the source is said to be an ideal voltage
source. And its voltage does not decrease with the increase in current.
Related Post: What is the differences between E.M.F and Voltage (P.d)
What is Practical & Ideal Current Source?
The ideal current source has infinite internal resistance. Its current does not depend on its supply
voltage.
A practical current source has a large internal resistance. Its supply current decreases with the
increase in its supply voltage.
What is Norton theorem?
Any combination of batteries and resistances in a linear circuit is equivalent to and can be
represented by an ideal current source and a resistor in parallel. You may follow the step by step
tutorial for solved examples through Norton’s Theorem.
What is Thevenin theorem?
Any combination of batteries and resistance in a linear circuit can be represented by a signal
voltage source and a resistor in series. You may follow the step by step tutorial for solved examples
through Thevenin’s Theorem.
What is a Transistor?
A transistor is a three-terminal semiconductor device. It is can be used for amplifying or switching an
electrical signal.
How does the Transistor act as a Switch?
There are three useful regions of operation of a transistor namely saturation region, cutoff region &
active region.
In the active region, the transistor acts as an amplifier.
In the saturation region, the transistor acts as a closed switch.
In the cutoff region, the transistor acts as an open switch.
So to use a transistor as a switch, it needs to be operated in the saturation & cutoff region.
What is meant by Clipper and Clamper?
A clipper is a circuit that clips or cutoff voltage above or below a certain specified level. Positive
clipper cuts off a portion of positive half of a signal while negative clipper cuts off from the negative
half.
A clamper is a circuit that adds voltage in the positive or negative half of the signal to a specified
peak voltage. A clamper moves the whole signal up and down to reach the specified peak voltage.
What is SCR
Silicon controlled rectifier or thyristor is unidirectional semiconductor device but unlike diode, it
has three terminals Anode, Cathode & Gate. The SCR can be switched on & off using the gate
input.
What is Diode?
A diode is a unidirectional semiconductor device with two terminals called Anode & Cathode. A
diode can allow current in only one direction which is known as forward bias.
Difference between Silicon and Germanium Diode & why is Silicon diode
preferred?
The voltage drop of a silicon diode is 0.7v and that of germanium diode is 0.3v.
Silicon crystals are more resistant to heat than germanium.
Silicon diode has a high voltage rating than the germanium diode.
Silicon diodes are more preferable because silicon is available in abundant compared to
germanium.
What is the main difference between BJT and FET?
BJT stand for bipolar junction transistor and FET is the acronym for Field Effect Transistor.
BJT is bipolar that is there is a flow of both minority and majority charge carriers, while FET is
unipolar that is there is a flow of only majority carriers.
BJT is controlled using the input current (base current) while FET is controlled using the input
voltage (Gate voltage).
The input impedance of FET is much higher compared to BJT.
The three terminals of BJT is emitter, base & collector while FET is drain, gate & source
What is a Transformer?
A transformer is a static electrical device which transfers electrical energy from one circuit to
another circuit without any physical connection instead it uses the principles of electromagnetic
induction. A transformer either increase or decrease the input voltage & current.
Related Post: What is the difference between Power Transformers and Distribution Transformers?
What is Oscillator?
An oscillator is an electronic circuit which generates a periodic AC signal from a DC source. An
oscillator has no input. The output of oscillator can be sinusoidal or Square or a triangle wave.
What is Communication?
The transfer of information from one place to another place using some sort of medium is called
Communication. The information could be in any form such as a sound or visual or electrical signal
etc.
What is the Baseband Signal?
A signal consisting of significantly lower frequency (up to 10 kHz) is known as a baseband signal.
Example of the baseband signal is voice (300Hz to 3.5 kHz ), audio (20 Hz to 20 kHz) and a video
signal (0Hz to 4.5 MHz).
The baseband signal cannot be transmitted directly through the antenna. They are transmitted using
copper wire or fiber optics etc.
Related Post: Introduction to Signals, Types, Properties, Operation & Application
What is a Bandpass or Passband Signal?
A signal consisting of significantly higher frequencies (Higher than 100 kHz) is known as Passband
or BandPass signal. Bandpass signal does not contain any frequency lower than 100 kHz.
Bandpass signal can be directly transmitted through the antenna.
What is Modulation?
The process in which one of the characteristic parameter (amplitude, frequency, phase) of the
carrier signal varies linearly with respect to message signal’s amplitude is called modulation.
Related Post: Modulation – Classification and Types of Analog Modulation
Why do we need Modulation?
Modulation converts a baseband signal into a passband signal making it suitable for long distance
communication using an antenna.
Antenna size also depends on the frequency of the transmitting signal, so the modulation allows us
to use a small size antenna.
Using Modulation we can assign different frequencies to different signals which allow us to send
multiple signals using the same medium without interference.
Related Post: Types of Modulation Techniques used in Communication Systems
What is Demodulation?
The demodulation is a process of extracting the information or message signal from the received or
modulated signal.
What are the Types of Modulation?
Two main types of modulation are Analog modulation and Digital modulation.
Analog modulation is further divided into three types;
Amplitude modulation (AM): DSB-FC, DSB-SC, SSB-SC, SSB-FC, VSB
Frequency modulation (FM): NBFM, WBFM
Phase modulation (PM):
Whereas, Digital modulation is further divided;
Digital Amplitude modulation: ASK, PAM, QAM
Digital phase modulation: PSK, DPSK, OPSK
Digital Frequency modulation: FSK
Continuous phase modulation: GMSK, MSK, CPFSK
Trellis-coded modulation: PSK, QAM
What is the difference between AM and FM Modulation?
AM signals can be affected by noise as the information lies in the amplitude of the signal, while FM
is immune to noise because the information lies in the frequency of the signal.
The design of Transmitter and receiver for AM is very simple except for some cases like SSB.
While in FM, the transmitter and receiver have a complex design.
AM signal can travel long distances as compared to FM signals.
FM signal’s transmission consume more power as compared to AM signal’s transmission.
AM signal frequency ranges in KHz while FM signal frequency ranges in MHz
What is a Repeater in Telecommunication?
As we know that a transmitted signal loses its power when it travels long distances. To retain and
maintain its full power, the signal is boosted through a device known as a repeater for long distance
communication.
Usually, a repeater retransmits the identical signal but it may change the medium or frequency of
the signal according to the need.
What is the difference between Analog and Digital signal?
Analog signal has continuous time and continuous amplitude while digital signal has discrete time
and discrete amplitude.
Difference between Digital and Discrete signal.
Digital signal is a signal which has discrete time and discrete amplitude.
Discrete signal often known as the discrete-time signal is a signal, which has discrete time but
continuous (it can have any value) amplitude.
What is Sampling?
Sampling is a process of converting a continuous time signal into a discrete time signal but not a
digital signal.
What is the Nyquist Criteria for Sampling?
Suppose the maximum frequency of the analog signal is fmax then the Nyquist criteria suggest that
the sampling rate for this analog signal must be 2fmax or greater.
What is Aliasing?
Aliasing is a signal effect related to sampling. When a signal is sampled at a sampling rate less
than the required rate, the signal becomes indistinguishable from other signals and after
reconstruction, the signal does not look anything like the original signal. This effect is called
Aliasing.
Related Post: What is Quantization & Sampling? Types & Laws of Compression
What is a Filter?
A Filter is an electronic circuit that removes specific or unwanted frequency components from a
signal. The types of filters are:
Low pass filter
Bandpass filter
Band stop or band reject filter
High pass filter
Notch filter
Related Post:Types of Low Pass Filters – RL and RC Passive Filters & Examples
What is the Cutoff Frequency?
The cutoff frequency is the point in a filter’s frequency response where the pass band and stop band
meets. A filter rejects or passes frequency components below or above cutoff frequency depending
on the type of the filter.
The cutoff frequency is taken at -3db (Half power) of the maximum amplitude.
What is Passband?
The passband is the range of frequencies that can be passed through the filter without any
attenuation.
What is Stop band?
The stopband is the range of frequencies that are attenuated and cannot be passed through the
filter.
What is the Notch filter?
The notch filter is a type of band stop filter with very narrow stop band.
What is the difference between the Notch and Bandstop filter?
Band stop filter rejects a wide range of band while notch filter rejects a very narrow band. The notch
filter is used for suppressing powerful laser beams.
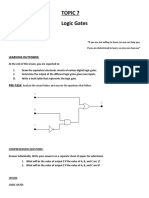
What is a Logic Gate?
A digital logic gate is an electronic device which implements the Boolean function. The boolean
function performs a logical operation on one or more than one binary numbers.
What are basic Logic Gates?
There are seven basic logic gates. NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR gate.
What are derived Logic Gates?
Derived logic gates are those gate which can be made from these three basic logic gates NOT,
AND & OR.
NAND, NOR, XOR & XNOR are derived logic gates. Basic logic can be combined together to
make these gates.
What is a Universal Logic Gate?
A universal gate is a logic gate which can be solely used to implement any kind of boolean function.
There are two universal logic gates namely NAND & NOR gate.
What is Positive Logic and Negative Logic?
In digital logic, a Specific level of voltage is represented by binary numbers i.e.1 or 0 in other words,
True or False respectively.
In positive logic, the High-level voltage is represented by 1 or True & the low-level voltage is
represented by 0 or False.
In negative logic, the High-level voltage is represented by 0 or False & the low-level voltage is
represented by 1 or True.
What are Latches and Flip-Flops? Differences
Latch and flip-flop are memory devices with two stable states. They are used for storing data
(states) in sequential logic. The states are controlled using one or more than one control signals. It
can store one bit of data.
The main difference between a latch and flip-flop is that latch is triggered (change states) by the
level of input control signal & the flip-flop is triggered using the edge of input control signal known
as a clock signal.
So we can say that latches are level-triggered devices and flip-flops are edge-triggered devices.
Related Post: Digital Flip-Flops – SR, D, JK and T Flip Flops
What is a Level trigger and Edge trigger?
The level trigger means that the device will change its state according to the previous state, next
state input and the level (stable 1 or 0) of the control signal.
Edge trigger means that the device will change its state according to the previous state, next state
input and the edge (from +ve to –ve called “falling edge”, from –ve to +ve called “rising edge”) of the
clock signal.
What is Combinational and Sequential logic?
Combinational logic does not have a memory that is its current output depends only on the
current input.
While sequential logic has a memory and its current output depends on the previous output and
current input.
What is Ripple Carry Adder and Carry Look Ahead Adder?
These two Digital binary adders are differentiated based on the carry determining technique.
In ripple carry adder, the carry bits ripple through each individual adder while in a carry-look-ahead
adder, the carry bit is determined separately using a CLA (Carry look ahead) block.
CLA adder operates much faster than ripple adder as it bypasses many stages.
What is an Op-Amp?
Operational amplifier often known as op-amp is an active voltage amplifying component. It can
amplify voltage based on the difference of voltage between its two inputs.
What is Inverting and Non-inverting Amplifier?
When the input voltage signal is applied to a non-inverting terminal (+ve terminal) of the Op-amp,
the op-amp is said to be in a non-inverting configuration. Its gain is positive i.e. its output signal is
in-phase with the input signal.
In inverting op-amp configuration, the input signal is applied to the inverting terminal (-ve terminal)
of an op-amp. The gain of inverting op-amp is negative and the output signal is 180 degree out of
phase with respect to the input signal.
Related Post: What is Negative Feedback and Negative Feedback Amplifier Systems
What is the input and output Impedance of an Op-Amp?
The input impedance of op-amp between its differential inputs is very high usually in Mega Ohms
to Tera Ohms (ideally infinite). That is why the input current of an op-amp is very low (almost
negligible)
The output impedance of an op-amp is very low (ideally zero).
Even More Electronics Engineering Questions and Answers with Explanation
1. What is the Rule of Capacitor in AC and DC Circuit?
2. What is the difference between a battery and a capacitor?
3. What is the Difference between Unilateral and Bi-Lateral Circuits & Elements
4. What is The Main Difference between Linear and Nonlinear Circuit
5. What is the difference between AC and DC Resistance & How to calculate it?
6. How to Test a Diode using Digital & Analog Multimeter?
7. How to Test and remeber the direction of NPN and PNP Transistors?
8. How to calculate the value of resistor for LED’s ?
9. How to calculate or Find the value of SMD Resistors?
10. What is the difference between real ground and virtual ground?
11. What is Raspberry Pi?
12. What is Arduino?
13. What is ATMega?
14. What is GSM and How does it Work?
15. What is WiMAX?
Comparison & Differences
Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB & RCB, RCD or RCCB Circuit Breakers
Difference Between Active and Reactive Power
Difference between Analog and Digital Multimeter
Difference Between Capacitor and Supercapacitor
Difference Between a Battery and a Capacitor
Difference between Circuit Breaker and Isolator / Disconnector
Difference between Fuse and Circuit Breaker
Difference between Contactor and Starter?
Difference Between Relay and Circuit Breaker
Difference between Power Transformers and Distribution Transformers?
Difference between Star and Delta Connections – Comparison Of Y/Δ
Difference between AC and DC Resistance & How to calculate it?
Difference Between Electrical and Electronic Engineering?
Difference between Active and passive Components ?
Difference between Linear and Nonlinear Circuit?
Difference between Real Ground and Virtual Ground?
Difference between Unilateral and Bi-Lateral Circuits & Elements?
Difference between a VOLTAMETER and a VOLTMETER?
Differences between E.M.F and Voltage (P.d)?
Difference Between Neutral, Ground and Earth?
Difference Between Conductor, Semiconductor and Insulator
Difference Between Conductor and Superconductor
Difference Between a Transformer and an Induction Motor
Some of the electronics engineering interview questions may be more casual like “why you choose
this field?” etc. but we are covering more technical question.
These are some of the basic electronic engineering interview questions. if you think there are
some questions related to electronics engineering interview that may have been asked or need to
be added, please, feel free to contact us or use the comment box below to include any questions
you like or interviewer asked in an interview for electronics engineering related job. Stay tuned for
more updates and questions related to electronics engineering interview as we will add even more.
Related EE Engineering Questions / Answers
Basic Electronics Engineering Interview Questions & Answers
Basic Electrical & Electronics Interview Questions & Answers
Tags Electrical Engineering Notes Electrical Engineering Questions & Answers Electronics Engineering Questions Answers
Electronics Notes How to
Facebook Twitter
Electrical Technology
All about Electrical & Electronics Engineering & Technology. Follow Electrical Technology on Facebook, Twitter ,
Instagram, Pinterest, YouTube, & Linkedin to get the latest updates or subscribe Here to get latest Engineering Articles
in your mailbox.
Types of Digital Logic Gates - Boolean Carrier Acquisition, Need for Carrier
Logic Truth Tables & Applications Acquisition & Techniques
Related Articles
How to Calculate/Find the How to Calculate the Battery How To Calculate Your
Rating of Transformer in kVA Charging Time & Battery Electricity Bill. Easy & Simple
(Single Phase and Three Charging Current – Example Explanation.
Phase)?
How to Find The Suitable Size Thevenin’s Theorem. Step by Why Transformer Rated In kVA,
of Cable & Wire for Electrical Step Procedure with Solved Not in KW?
Wiring Installation? – Examples Example
in British and SI System
3 Comments
Colin Mitchell
You say it is BASIC ELECTRONICS !!!! And then you ask: What is Thevenin theorem?
I have never used it in 40 years of teaching electronics.
Reply
Chandrashekhar v
Ya it’s good potions to develop my knowledge tq
Reply
Sehajbir Singh
Excellent resource for brushing up ECE. The differences and comparisons are an even deeper dive. I am going to spend
the next 10 days going through everything! Highly recommended.
Thank you
Cheers!
Sehaj
Reply
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Post Comment
Subscribe to our mailing list to get the new updates!
Enter your Email address
Subscribe
© Copyright 2020, All Rights Reserved 2012-2020 by Electrical Technology
You might also like
- IES Bangalore Analog Electronics Old GATE ECE QuestionsDocument74 pagesIES Bangalore Analog Electronics Old GATE ECE QuestionsPrateek Khare100% (2)
- Driving Relays With stm32f407vgtx Microcontroller Using Uln2003 Relay DriverDocument12 pagesDriving Relays With stm32f407vgtx Microcontroller Using Uln2003 Relay DriverAnonymous Nlaa5HNo ratings yet
- 20 TOP PLC LAB VIVA Interview Questions and Answers PLC LAB VIVA Interview QuestionsDocument6 pages20 TOP PLC LAB VIVA Interview Questions and Answers PLC LAB VIVA Interview Questionsamrith h namboodiriNo ratings yet
- ANALOG COMMUNICATION LAB Questions and AnswersDocument10 pagesANALOG COMMUNICATION LAB Questions and AnswersMurthyNo ratings yet
- 8051 Interview QuestionsDocument8 pages8051 Interview QuestionsSudheer ReddyNo ratings yet
- Top 100 Electronic Devices and Circuits Interview QuestionsDocument15 pagesTop 100 Electronic Devices and Circuits Interview QuestionsEr PavankumarNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions Archives - Power Electronics A To ZDocument4 pagesInterview Questions Archives - Power Electronics A To ZAtul KumbharNo ratings yet
- 16 Bit Comparator Using 4 Bit ComparatorsDocument7 pages16 Bit Comparator Using 4 Bit ComparatorsSudhakara RaoNo ratings yet
- Short Question Answers Computer ScienceDocument5 pagesShort Question Answers Computer ScienceAnonymous sCZxIO100% (2)
- 40 Top Circuit Theorems and Conversions Questions and Answers PDFDocument3 pages40 Top Circuit Theorems and Conversions Questions and Answers PDFsayedNo ratings yet
- Electronic Engineering Applications of Two–Port Networks: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandElectronic Engineering Applications of Two–Port Networks: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Eee de Lab Manual DiplomaDocument80 pagesEee de Lab Manual Diplomasiri.pogula0% (1)
- ECE Interview Questions With AnswersDocument7 pagesECE Interview Questions With AnswersRohit Xavier100% (1)
- Introduction To C Programming Course MaterailDocument161 pagesIntroduction To C Programming Course Materailmohammedgousmujahid100% (1)
- It Workshop LAB MANUALDocument145 pagesIt Workshop LAB MANUALAvinash TalapulaNo ratings yet
- UbiSense User ManualDocument5 pagesUbiSense User ManualAshok Kumar100% (1)
- Ktu 2Document6 pagesKtu 2Jai JohnNo ratings yet
- Detailed Syllabus of ISRO Technical Assistant Electronics (ECE)Document6 pagesDetailed Syllabus of ISRO Technical Assistant Electronics (ECE)LoknathNo ratings yet
- C++ Programming LabDocument24 pagesC++ Programming LabManjusha KulkarniNo ratings yet
- NET Interview Questions and Answers OOPS IndiabixDocument9 pagesNET Interview Questions and Answers OOPS IndiabixAfshan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Interview Questions and AnswersDocument7 pagesBasic Electronics Interview Questions and AnswerssmydyNo ratings yet
- VHDL FaqDocument6 pagesVHDL FaqRavindra Mathanker100% (2)
- Basic Electronics Interview Questions and Answers GuideDocument8 pagesBasic Electronics Interview Questions and Answers GuideTynoh MusukuNo ratings yet
- Lap Manual Pspice PDFDocument17 pagesLap Manual Pspice PDFred_heartedNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument5 pagesSyllabusChandan Prasai100% (1)
- ET7102-Microcontroller Based System DesignDocument19 pagesET7102-Microcontroller Based System DesignbalaNo ratings yet
- Hardware Lab-I: (CS-217) Instruction ManualDocument36 pagesHardware Lab-I: (CS-217) Instruction Manualmaen2009No ratings yet
- Einfochips Interview QuestionsDocument1 pageEinfochips Interview Questionsshafi hasmani100% (1)
- CS 102 Lab 1Document18 pagesCS 102 Lab 1Abdulaziz Altararwah0% (1)
- IOT Using Arduino IDE to Monitor Temperature and HumidityDocument20 pagesIOT Using Arduino IDE to Monitor Temperature and HumidityPrabir dasNo ratings yet
- EMBEDDED SYSTEMS GUIDEDocument83 pagesEMBEDDED SYSTEMS GUIDEhareesh.makesu100% (1)
- How To Interfacing Sensor With LPC2148 ARMDocument8 pagesHow To Interfacing Sensor With LPC2148 ARMSubir MaityNo ratings yet
- Experiment-2: Aim: Familiarization With Networking Components-Hub Switch Repeater Router GatewayDocument3 pagesExperiment-2: Aim: Familiarization With Networking Components-Hub Switch Repeater Router GatewayKetanNo ratings yet
- Logic Gates FundamentalsDocument5 pagesLogic Gates FundamentalsEnitsuj Eam EugarbalNo ratings yet
- Digital Principle and System DesignDocument26 pagesDigital Principle and System Designainugiri100% (4)
- MOSFET - Working, Types, Operation, Advantages & ApplicationsDocument28 pagesMOSFET - Working, Types, Operation, Advantages & ApplicationsgezahegnNo ratings yet
- EC6712 Embedded Lab ManualDocument104 pagesEC6712 Embedded Lab ManualpasuarjNo ratings yet
- Iii B.Tech Ii Sem Eie (R18) : PLC Intermediate and Advanced FunctionsDocument83 pagesIii B.Tech Ii Sem Eie (R18) : PLC Intermediate and Advanced FunctionsSrinivas PapaniNo ratings yet
- Project Report DoorDocument48 pagesProject Report Doornehadudeja14100% (3)
- Collection of Cs Multiple Choice Questions McqsDocument40 pagesCollection of Cs Multiple Choice Questions McqsShuseel BaralNo ratings yet
- PP Innovative Features of Scripting LanguagesDocument20 pagesPP Innovative Features of Scripting Languages014 CSE Devamruth AG100% (1)
- 8051 Lab Experiments With SolutionDocument11 pages8051 Lab Experiments With SolutionInaamahmed13No ratings yet
- I-O PortsDocument20 pagesI-O PortsPradeep V DevNo ratings yet
- EC8462Document86 pagesEC8462ur's joeNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Interview QuestionsDocument3 pagesAnalog Communication Interview QuestionsShwetha LokeshNo ratings yet
- EC Lab Manual Frequency ResponseDocument32 pagesEC Lab Manual Frequency ResponseXavier50% (4)
- Types of Operating Systems - GeeksforGeeksDocument1 pageTypes of Operating Systems - GeeksforGeeksxitetNo ratings yet
- The Digital Encoder: 4-To-2 Bit Binary EncoderDocument10 pagesThe Digital Encoder: 4-To-2 Bit Binary EncoderJohn Brix BalisterosNo ratings yet
- CPP 1Document7 pagesCPP 1minaleNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Language of ComputersDocument94 pagesUnderstanding the Language of Computerskrishnagovind33No ratings yet
- VHDL Question BankDocument5 pagesVHDL Question BankSugam KatariaNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Interview Questions and AnswersDocument34 pagesAnalog Communication Interview Questions and AnswerssarveshNo ratings yet
- DSB SC Final ProjectDocument14 pagesDSB SC Final ProjectOscar Mauricio Sarmiento UrbinaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Component - Wikipedia PDFDocument1 pageElectronic Component - Wikipedia PDFSatyam ShivanshNo ratings yet
- 20 Electrical Engineering Interview Questions & Answers: Leave A CommentDocument1 page20 Electrical Engineering Interview Questions & Answers: Leave A CommentSatyam ShivanshNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Interview Questions and Answers PDFDocument1 pageBasic Electronics Interview Questions and Answers PDFSatyam ShivanshNo ratings yet
- Name of Student: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesName of Student: ObjectiveJay SuryaNo ratings yet
- Cs Lab Manual FinalDocument88 pagesCs Lab Manual FinalAathi KannanNo ratings yet
- Simulink LectureDocument32 pagesSimulink LecturelincolNo ratings yet
- Visualising AM ModulationDocument37 pagesVisualising AM ModulationELmokhtar HamrouniNo ratings yet
- Single Sideband SystemsDocument9 pagesSingle Sideband Systemswasif28No ratings yet
- Design of Fire Siren System Based On Power Line CarrierDocument15 pagesDesign of Fire Siren System Based On Power Line CarrierKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Satellite Radio - Seminar ReportDocument16 pagesSatellite Radio - Seminar ReportSagar Medikeri50% (2)
- Scientech 2209: Synchronous AM DetectorDocument1 pageScientech 2209: Synchronous AM Detectorlusoegyi 1919No ratings yet
- "Lab Reports": University of Engineering and TechnologyDocument51 pages"Lab Reports": University of Engineering and Technologyshahab khanNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital CommunicationDocument9 pagesAnalog and Digital CommunicationManish MahasethNo ratings yet
- 21ec401 Unit VDocument67 pages21ec401 Unit VsanthoshiniNo ratings yet
- DC to AC Inverter GuideDocument33 pagesDC to AC Inverter Guideबृजभूषणशर्माNo ratings yet
- Agni College of Technology Agni College of Technology Agni College of TechnologyDocument19 pagesAgni College of Technology Agni College of Technology Agni College of TechnologyparantnNo ratings yet
- CSADDocument3 pagesCSADGhe PataniNo ratings yet
- A DSP-Based Digital IF AM/FM Car-Radio ReceiverDocument4 pagesA DSP-Based Digital IF AM/FM Car-Radio ReceiverbmnaveenNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: CFD-G55Document54 pagesService Manual: CFD-G55angelsoyNo ratings yet
- 2021 Book AdvancesInConditionMonitoringADocument759 pages2021 Book AdvancesInConditionMonitoringAMUIN ABDULLAH-ALNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes From Peter Mclean, UTSDocument599 pagesLecture Notes From Peter Mclean, UTSMin Khine KyawNo ratings yet
- PWM Control of 3phase VsiDocument65 pagesPWM Control of 3phase VsiOm prakashNo ratings yet
- AM Envelope Detector SimulationDocument2 pagesAM Envelope Detector SimulationHazmie KunNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 (Communication System)Document2 pagesExperiment No. 1 (Communication System)RameezAmerNo ratings yet
- RADIO COMMUNICATIONS VHF and UHF PDFDocument56 pagesRADIO COMMUNICATIONS VHF and UHF PDFFABIAN100% (1)
- RCI-6300F HPTB Service ManualDocument45 pagesRCI-6300F HPTB Service ManualbellscbNo ratings yet
- TWTA Linearization: Need For LinearityDocument12 pagesTWTA Linearization: Need For LinearityAnanda KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Agilent 33250A ManualDocument336 pagesAgilent 33250A Manualfanj94No ratings yet
- Amplitude Shift KeyingDocument3 pagesAmplitude Shift KeyingamulyaNo ratings yet
- Pulse Amplitude Modulation & DemodulationDocument8 pagesPulse Amplitude Modulation & DemodulationRashed IslamNo ratings yet
- Ee4 01Document18 pagesEe4 01pabloNo ratings yet
- Difference Between PAMDocument17 pagesDifference Between PAMultra dubsNo ratings yet
- Short Answer Questions: Unit - I: Amplitude ModulationDocument8 pagesShort Answer Questions: Unit - I: Amplitude ModulationSrinivas PadalaNo ratings yet
- National Radio Systems Committee: NRSC-G101 AM Modulation-Dependent Carrier Level (MDCL) Usage Guideline April 2013Document20 pagesNational Radio Systems Committee: NRSC-G101 AM Modulation-Dependent Carrier Level (MDCL) Usage Guideline April 2013Enos Marcos BastosNo ratings yet