Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Controversial Diets1
Uploaded by
Edrese AguirreOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Controversial Diets1
Uploaded by
Edrese AguirreCopyright:
Available Formats
CONTROVERSIAL DIETS
1. KETOGENIC DIET – technically used for epileptic patients in duration of 3 weeks
but become already a trending diet as it causes drastic change in weight loss due
to its high fat and very low carbohydrate.
A typical diet is composed of 50 – 60% carbohydrates but for a strict ketogenic
diet it is 4:1 ratio of serving (exchange) of fat to carbohydrate. This will result to:
1 exchange of fat = 9 Kcal x 4 = 36 Kcal for total of 40 Kcal per ratio of
1 exchange of carbohydrate = 4 Kcal fat and carbohydrate
This would mean 90 % for fat and only 10 % for carbohydrate
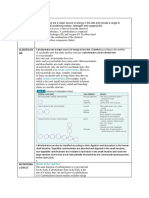
A very high fat food intake produces ketone bodies as result of ketosis
which leads to acidosis. An acidic blood results to OSTEOCLAST as
mechanism of homeostasis in which our Central Nervous System plays
vital role.
effector
low pH in the blood Central Nervous Osteoclast
(serves as System (depletion of
stimulant) calcium to balance
pH in the blood)
receptor Homeostasis
Osteoblast is the build-up of calcium in the bones (opposite of osteoclast).
Depleted calcium in the blood which can no longer accumulated by
osteoblast becomes Kidney stones.
Kidney stones are: calcium phosphate, calcium oxalate and uric acid.
2. ATKINS DIET – starts to a high protein and high fat but protein is adjusted
gradually so as the fat depends on the result of weight loss.
Low carbohydrate but high protein leads to conversion of protein nutrients
absorbed by our body to produce energy and this will lead to conversion of
amino acids to glucose (gluconeogenesis). If these happens by products
of gluconeogenesis will yield to by-products of ammonia (NH 3) but to be
excreted as blood urea nitrogen which may overworked liver and kidney
as well.
3. INTERMITTENT DIET – the person under this diet is only allowed to eat on
duration of 8 hours in for the whole day resulting to drastic weight loss due to
muscle mass wasting.
Glycogen is storage glucose in our liver. This only last 6 to 8 hours upon
its storage. After dinner and before sleep this will yield glucose in our body
and production of glucose for 2 hours which will give way to storage of
glucose in form of glycogen while in rest state (mostly sleeping).
But after our body needs energy source in form of glucose just like Atkins
diet, ammonia will be produced due to muscle mass wasting as proteins in
our body will be utilized for production of glucose. Thus, blood urea
nitrogen will also increase to as increased on the work load of liver and
kidney for release of NH3 in form of urea.
4. VEGETARIAN DIET – plant based meals consisting of variety of whole grains,
legumes, nuts, vegetables; eggs and dairy products included depends on the
type of modified diet but generally avoiding meat products as source of protein
nutrient.
Modified Vegetarian Diets:
a. Vegan or Total Vegetarian – designed for individuals aiming to exclude all
animal products. For instance, in avoidance of cow’s milk, soy milk is
consumed by these people engaging in this diet.
b. Lacto Vegetarian – modified vegetarian diet for those only ants to
consume plant foods and dairy products such as milk, cheese, yogurt, etc.
c. Lacto-Ovo Vegetarian – includes addition of eggs and dairy products for
these vegetarian people.
d. Semi – Vegetarian – for individuals who wants to consume protein but
only fish and chicken (white meat) to eat but still avoiding the red meat.
Advantages/Disadvantages and Contraindication of Vegetarian Diets
a. Vegetarian diet is high source of protein that also promotes good bowel
movement.
b. Vegetarian diet contains low fat in which in the long run helps on the blood
chemistry in terms of
c. For Vegan diet since animal products were excluded, low biological
protein were only source of protein which does not have vitamins B 6
(pyridoxine), B9 (folate) and B12 (cobalamin) which are blood forming
vitamins and vitamin supplementation becomes necessity with these
people consuming this diet. Vitamin B3 (niacin) is also low and in the risk
of supplementation leads to niacin rush with danger of clinical
complication.
d. For Lacto-Ovo and Semi-Vegetarian diet, high biological source of protein
would be enough but not the blood forming vitamins such as pyridoxine,
folate and cobalamin were still lacking as these vitamins mentioned can
only be obtained in red meats. Still, supplementation for vitamins B 6, B9,
and B12 were still needed.
You might also like
- Macronutrients - ProteinsDocument35 pagesMacronutrients - ProteinsNurten Ayça AktaşNo ratings yet
- 2020 The Essential Diets - All Diets in One Book - Ketogenic, Mediterranean, Mayo, Zone Diet, High Protein, Vegetarian, Vegan, Detox, Paleo, Alkaline Diet and Much More: COOKBOOK, #2From Everand2020 The Essential Diets - All Diets in One Book - Ketogenic, Mediterranean, Mayo, Zone Diet, High Protein, Vegetarian, Vegan, Detox, Paleo, Alkaline Diet and Much More: COOKBOOK, #2No ratings yet
- Nutrition Nursing: ProteinsDocument38 pagesNutrition Nursing: ProteinsAngelyka Nicole Bengco David100% (1)
- The Power Of Exogenous Ketones: Learn Their Proven Benefits To Lose Weight And Improve Your Physical / Mental StateFrom EverandThe Power Of Exogenous Ketones: Learn Their Proven Benefits To Lose Weight And Improve Your Physical / Mental StateNo ratings yet
- Proteins: Ghina Assaf Chedid, MSC Fundamentals of Human NutritionDocument32 pagesProteins: Ghina Assaf Chedid, MSC Fundamentals of Human NutritionYouness Abou SalehNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Management for Liver DisordersDocument15 pagesNutritional Management for Liver DisordersFebby ShabrinaNo ratings yet
- كيمياء حياتية المرحلة الرابعة 2Document31 pagesكيمياء حياتية المرحلة الرابعة 2Abdala Al-MawlaNo ratings yet
- Group 6 - BOVINE KETOSIS (Repaired)Document12 pagesGroup 6 - BOVINE KETOSIS (Repaired)Solomon MbeweNo ratings yet
- Cancercleansequickstartguide 2018 PDFDocument13 pagesCancercleansequickstartguide 2018 PDFVinciane Baudoux100% (1)
- 07 Human NutritionDocument19 pages07 Human NutritionMalooka AlyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Proteins: in Greek: "To Take First Place"Document52 pagesChapter 3: Proteins: in Greek: "To Take First Place"Amani KayedNo ratings yet
- Liver-I LectureDocument57 pagesLiver-I LectureZaineb FarooqNo ratings yet
- Calcium Metabolism / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument23 pagesCalcium Metabolism / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academy100% (2)
- BiochemistryDocument17 pagesBiochemistryrohishaakNo ratings yet
- MennoDocument76 pagesMennoOmar GallozaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Ketogenic Diet and How Does It Affect On Testosterone and Cortisol Hormones?Document5 pagesWhat Is The Ketogenic Diet and How Does It Affect On Testosterone and Cortisol Hormones?Central Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- How Protein Fuels MetabolismDocument14 pagesHow Protein Fuels MetabolismCzarina G. CastilloNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Liver Disease: Understanding the Vital Role of the LiverDocument66 pagesNutrition and Liver Disease: Understanding the Vital Role of the LiverAzizRakhaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Supplements for AthletesDocument14 pagesCarbohydrate Supplements for AthletesOnyinye PreciousNo ratings yet
- NUTRITIONDocument12 pagesNUTRITIONJamuna PatelNo ratings yet
- The Optimal DietDocument5 pagesThe Optimal DietShaheena100% (2)
- VI Nutrition and The Surgical Patient: Caloric RequirementsDocument5 pagesVI Nutrition and The Surgical Patient: Caloric RequirementsIbrahem Y. NajjarNo ratings yet
- Carb Energy: Guide to Carbohydrates (CHODocument6 pagesCarb Energy: Guide to Carbohydrates (CHOIra Lilian DumadaugNo ratings yet
- Understanding The PancreasDocument10 pagesUnderstanding The PancreasijostlNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: 2 Eliminated 2 ConsumedDocument9 pagesNutrition: 2 Eliminated 2 ConsumedSenthereng MoaisiNo ratings yet
- Biochem 1Document42 pagesBiochem 1Ria CanteroNo ratings yet
- Proteins: Amino AcidsDocument3 pagesProteins: Amino AcidsVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- BCAAs Role in Nutrition and ExerciseDocument29 pagesBCAAs Role in Nutrition and ExerciseTasneem ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy For Accessory OrgansDocument83 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy For Accessory OrgansIan MendezNo ratings yet
- Impact of Surgical Nutrition on Patient OutcomesDocument54 pagesImpact of Surgical Nutrition on Patient OutcomesAmir SharifNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7: Chapter 4 Carbohydrates (Continued) Artificial SweetenersDocument5 pagesLecture 7: Chapter 4 Carbohydrates (Continued) Artificial SweetenersNikhil TutejaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate digestion and absorption in the small intestineDocument2 pagesCarbohydrate digestion and absorption in the small intestineChin ChanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Monosaccharides: Simple CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesMonosaccharides: Simple CarbohydratesfuckyouNo ratings yet
- Integration of Metabolism Integration of MetabolismDocument10 pagesIntegration of Metabolism Integration of MetabolismEdison LucianoNo ratings yet
- CALORIE CONTENT OF FOODSDocument2 pagesCALORIE CONTENT OF FOODSSusan MishraNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument56 pagesProteinsJessica SnowNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM DigestionDocument53 pagesBIOCHEM DigestionAngelika Perez CunanNo ratings yet
- 2.7 AssessmentDocument6 pages2.7 AssessmentVani DeswalNo ratings yet
- Ahn-Unit 2Document21 pagesAhn-Unit 2Dilshad TasnimNo ratings yet
- Proteins: Crucial Components of All Body TissuesDocument36 pagesProteins: Crucial Components of All Body Tissuesnherm6425No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Provision of FuelsDocument38 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism Provision of Fuelssjs6r8wwv9No ratings yet
- Starvation Induced Metabolic Alterations - Biochemistry For Medics - Clinical CasesDocument6 pagesStarvation Induced Metabolic Alterations - Biochemistry For Medics - Clinical CasesDianne Faye ManabatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 On Regulation of MetabolismDocument23 pagesLecture 11 On Regulation of MetabolismSaad KazmiNo ratings yet
- Protein Metabolism and Turnover ExplainedDocument23 pagesProtein Metabolism and Turnover ExplainedSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- Potassium: Nutrient InformationDocument2 pagesPotassium: Nutrient InformationGarv JainNo ratings yet
- SOST - Macronutrients and Micronutrients - 1844388031Document59 pagesSOST - Macronutrients and Micronutrients - 1844388031PATRICIA SAN PEDRONo ratings yet
- BRS BiochemistryDocument345 pagesBRS Biochemistrysxymd321100% (1)
- Dietary ProteinsDocument18 pagesDietary ProteinsIram AnwarNo ratings yet
- Balanced Diet and Human Diseases Biology GuideDocument19 pagesBalanced Diet and Human Diseases Biology GuideRameshNo ratings yet
- CC ChekDocument105 pagesCC ChekMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Nutritiondiettherapy Lectureprelimstomidterm 191112061026Document138 pagesNutritiondiettherapy Lectureprelimstomidterm 191112061026Augustine chandigaNo ratings yet
- Sport Supplement Fact Sheets Isolated Protein Supplement v3Document4 pagesSport Supplement Fact Sheets Isolated Protein Supplement v3Edwin VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- Minerals: A. Group I: Major Minerals 1. CalciumDocument11 pagesMinerals: A. Group I: Major Minerals 1. CalciumLiel TorresNo ratings yet
- Apolipoprotein LIPID-METABOLISM - 12.3Document86 pagesApolipoprotein LIPID-METABOLISM - 12.3clariza balmesNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of Keto DietDocument12 pagesHealth Benefits of Keto DietKhawaja Noman hasanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Liver: Alice SkoumalováDocument37 pagesBiochemistry of Liver: Alice Skoumalováandreas kevinNo ratings yet
- The Biochemistry of Digestion, Absorption and Detoxification by Prof. Dr. Hedef D. El-YassinDocument64 pagesThe Biochemistry of Digestion, Absorption and Detoxification by Prof. Dr. Hedef D. El-YassinSayhidoen CepexNo ratings yet
- Week 5 CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesWeek 5 CarbohydratesJoshua EclarinoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 Aguirre 1Document4 pagesAssignment 4 Aguirre 1Edrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document5 pagesAssignment 3Edrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- Stenmann'S Weavers Summer 2020: Singular / Plural NounsDocument5 pagesStenmann'S Weavers Summer 2020: Singular / Plural NounsEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- CHSM Scholarship Summer 2020 Idioms AssignmentDocument4 pagesCHSM Scholarship Summer 2020 Idioms AssignmentEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- Stenmann'S Weavers Summer 2020: Singular / Plural NounsDocument5 pagesStenmann'S Weavers Summer 2020: Singular / Plural NounsEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- Dance Creative StageDocument4 pagesDance Creative StageEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- Sample Certification On Deemed Paid Tax CreditDocument1 pageSample Certification On Deemed Paid Tax CreditEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- Pink Ballet Dance PosterDocument1 pagePink Ballet Dance PosterEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- Caused by The .: Dengue Dengue Fever Is ADocument2 pagesCaused by The .: Dengue Dengue Fever Is AEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- BIR RULING NO. 481-88: CD Technologies Asia, Inc. © 2018Document3 pagesBIR RULING NO. 481-88: CD Technologies Asia, Inc. © 2018Edrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- Module 5. Therapeutic Categories of DrugsDocument13 pagesModule 5. Therapeutic Categories of DrugsEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- Pink Ballet Dance PosterDocument1 pagePink Ballet Dance PosterEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- BIR RULING (DA-112-04) : EEI CorporationDocument2 pagesBIR RULING (DA-112-04) : EEI CorporationEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Introduction to Routes of AdministrationDocument40 pagesModule 4 Introduction to Routes of AdministrationEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- Blind Spot Amsler Grid AnalysisDocument4 pagesBlind Spot Amsler Grid AnalysisEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- Republic of Philippines Court of Tax Appeals Quezon: Davao City Water District, NoDocument21 pagesRepublic of Philippines Court of Tax Appeals Quezon: Davao City Water District, NoEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- HB 6765 - Digital Economy Tax Act Reformatted 21052020 2Document9 pagesHB 6765 - Digital Economy Tax Act Reformatted 21052020 2Edrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- Evidence AmendmentsDocument2 pagesEvidence AmendmentsEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- PALBooking ConfirmationDocument4 pagesPALBooking ConfirmationEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- BIR RULING NO. 481-88: CD Technologies Asia, Inc. © 2018Document3 pagesBIR RULING NO. 481-88: CD Technologies Asia, Inc. © 2018Edrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- Cta Eb CV 01023 D 2014sep16 Ref PDFDocument29 pagesCta Eb CV 01023 D 2014sep16 Ref PDFNoznuagNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces of Attraction (AGUIRRE)Document1 pageIntermolecular Forces of Attraction (AGUIRRE)Edrese Aguirre100% (1)
- Scholarship Committee Self Evaluation of Scholar For The SY 2019 / Second SemesterDocument4 pagesScholarship Committee Self Evaluation of Scholar For The SY 2019 / Second SemesterEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- PIT and Estate Tax Updates 2018Document16 pagesPIT and Estate Tax Updates 2018Niel Edar BallezaNo ratings yet
- College of The Holy Spirit Manila Stenmanns Weavers Activity ReportDocument4 pagesCollege of The Holy Spirit Manila Stenmanns Weavers Activity ReportEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- ENTOPTIC-PHENOMENON Wih BordersDocument5 pagesENTOPTIC-PHENOMENON Wih BordersEdrese Aguirre0% (1)
- Concept Importance and Types of Starter Cultures in Dairy IndustryDocument21 pagesConcept Importance and Types of Starter Cultures in Dairy IndustryRohit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Desserts Evidence DessertDocument17 pagesDesserts Evidence Dessertpriya0% (1)
- For and against vegetarianismDocument2 pagesFor and against vegetarianismHossam AldishNo ratings yet
- 881 1982 1 SMDocument9 pages881 1982 1 SMariga aprialdiNo ratings yet
- Life of PiDocument1 pageLife of PiHector bartleyNo ratings yet
- Food Composition Activities in South AfricaDocument4 pagesFood Composition Activities in South AfricaAndres Fernando Silvestre SuarezNo ratings yet
- THESIS SYNOPSIS-K.Akshaya-311416251002Document19 pagesTHESIS SYNOPSIS-K.Akshaya-311416251002Omar FarookNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D Deficiency ThesisDocument4 pagesVitamin D Deficiency Thesisangelagibbsdurham100% (2)
- Solid Starts 50 Breakfast Menus For Babies and ToddlersDocument35 pagesSolid Starts 50 Breakfast Menus For Babies and Toddlersstefanii ngNo ratings yet
- Module-24: Rumen Microbes: Learning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesModule-24: Rumen Microbes: Learning ObjectivesSatish LokhandeNo ratings yet
- Try Out BigDocument32 pagesTry Out BignaufalNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Nutritional and Technological Quality Aspects of Minor CerealsDocument12 pagesComparative Study of Nutritional and Technological Quality Aspects of Minor Cereals张旭东No ratings yet
- Improve Sport Performance with Sport PhysiologyDocument19 pagesImprove Sport Performance with Sport Physiologylala liliNo ratings yet
- Canada's Good Food Heroes #1Document32 pagesCanada's Good Food Heroes #1foodmattersmanitobaNo ratings yet
- E.Science Grade 4Document180 pagesE.Science Grade 4Kisanet AbrhaNo ratings yet
- Food Exchange ListDocument9 pagesFood Exchange ListJerard VismanosNo ratings yet
- OCN Exam Flashcard Study System - OCN Test Practice Questions & Review For T-1Document1,255 pagesOCN Exam Flashcard Study System - OCN Test Practice Questions & Review For T-1NicoleNo ratings yet
- Lista Noua Synlab 2022Document190 pagesLista Noua Synlab 2022Maria AmaliaNo ratings yet
- IELTS Faculty Answer Key PDFDocument13 pagesIELTS Faculty Answer Key PDFGustavo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan Malnutrition)Document8 pagesTeaching Plan Malnutrition)Hazel Von S. Bravo100% (20)
- Extruder Examples 09Document37 pagesExtruder Examples 09Daniel SilvaNo ratings yet
- 100 Fantasy Fruits Vegetables Herbs and SpicesDocument3 pages100 Fantasy Fruits Vegetables Herbs and Spicesrmbandeira78100% (1)
- ConcoctionDocument44 pagesConcoctionROQUE SERENAS100% (1)
- SAMPLE 1 - Paper 01 - Section ADocument12 pagesSAMPLE 1 - Paper 01 - Section Achan chanNo ratings yet
- Tales of The Peculiar - Ransom RiggsDocument10 pagesTales of The Peculiar - Ransom RiggsKarina RichterNo ratings yet
- Coconut Almond Cake RecipeDocument2 pagesCoconut Almond Cake RecipeDew Masitha KusfiantiiNo ratings yet
- Replenishing The Nutrients Depleted by Drugs Holistic PharmacistDocument3 pagesReplenishing The Nutrients Depleted by Drugs Holistic PharmacistnepretipNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningDocument2 pagesCurriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningRitz Anton LimNo ratings yet
- Correct Grammar TestDocument11 pagesCorrect Grammar TestAdrianne Aldrin AlarcioNo ratings yet
- Online Doctor Consultation & Natural Treatment PortalDocument7 pagesOnline Doctor Consultation & Natural Treatment PortalKeerthi Vasan LNo ratings yet
- Summary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietFrom EverandSummary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Forever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellFrom EverandForever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellNo ratings yet
- Instant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookFrom EverandInstant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyFrom EverandThe Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Metabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeFrom EverandMetabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeNo ratings yet
- The Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonFrom EverandThe Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- The Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingFrom EverandThe Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyFrom EverandThe Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyNo ratings yet
- Secrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainFrom EverandSecrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Body Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomFrom EverandBody Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Diet Trap Solution: Train Your Brain to Lose Weight and Keep It Off for GoodFrom EverandThe Diet Trap Solution: Train Your Brain to Lose Weight and Keep It Off for GoodNo ratings yet
- Sugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthFrom EverandSugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Summary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Keto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleFrom EverandKeto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Glucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarFrom EverandGlucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (350)
- The Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsFrom EverandThe Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (49)
- Allen Carr's Easy Way for Women to Lose Weight: The original Easyway methodFrom EverandAllen Carr's Easy Way for Women to Lose Weight: The original Easyway methodRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Happy Gut: The Cleansing Program to Help You Lose Weight, Gain Energy, and Eliminate PainFrom EverandHappy Gut: The Cleansing Program to Help You Lose Weight, Gain Energy, and Eliminate PainRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Grit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeFrom EverandGrit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Find Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeFrom EverandFind Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Rapid Weight Loss Hypnosis: Deep Sleep Your Way to Rapid Weight Loss, Healing Your Body and Self Esteem with Guided Meditations and Positive AffirmationsFrom EverandRapid Weight Loss Hypnosis: Deep Sleep Your Way to Rapid Weight Loss, Healing Your Body and Self Esteem with Guided Meditations and Positive AffirmationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- The Whole Body Reset: Your Weight-Loss Plan for a Flat Belly, Optimum Health & a Body You'll Love at Midlife and BeyondFrom EverandThe Whole Body Reset: Your Weight-Loss Plan for a Flat Belly, Optimum Health & a Body You'll Love at Midlife and BeyondRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (28)
- Glucose Goddess Method: A 4-Week Guide to Cutting Cravings, Getting Your Energy Back, and Feeling AmazingFrom EverandGlucose Goddess Method: A 4-Week Guide to Cutting Cravings, Getting Your Energy Back, and Feeling AmazingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Rapid Weight Loss Hypnosis: How to Lose Weight with Self-Hypnosis, Positive Affirmations, Guided Meditations, and Hypnotherapy to Stop Emotional Eating, Food Addiction, Binge Eating and MoreFrom EverandRapid Weight Loss Hypnosis: How to Lose Weight with Self-Hypnosis, Positive Affirmations, Guided Meditations, and Hypnotherapy to Stop Emotional Eating, Food Addiction, Binge Eating and MoreRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (17)
- Eat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouFrom EverandEat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouNo ratings yet
- How to Be Well: The 6 Keys to a Happy and Healthy LifeFrom EverandHow to Be Well: The 6 Keys to a Happy and Healthy LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)