Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Coiled Tubing Injector: Section 4
Uploaded by
Khalid ZaeemOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Coiled Tubing Injector: Section 4
Uploaded by
Khalid ZaeemCopyright:
Available Formats
Section 4
Coiled Tubing Injector
Table of Contents
Overview ................................................................................................................................................... 4-3
Tubing Injector Drive Assembly............................................................................................................... 4-4
Drive Chain Assembly........................................................................................................................... 4-4
Roller Chain Assembly.......................................................................................................................... 4-4
Timing Sprockets................................................................................................................................... 4-4
Skid and Support Structure.................................................................................................................... 4-4
Load Cell ............................................................................................................................................... 4-4
Load pin ................................................................................................................................................. 4-5
Circuit Description and Operating Principles........................................................................................ 4-5
Speed Selector ....................................................................................................................................... 4-5
Speed/Depth Sensor............................................................................................................................... 4-5
Drive Motors.......................................................................................................................................... 4-5
Gripper Cylinders and Blocks ............................................................................................................... 4-6
15K Injector ....................................................................................................................................... 4-6
30K Injector ....................................................................................................................................... 4-6
80K Injector ....................................................................................................................................... 4-6
Accumulator Pressure............................................................................................................................ 4-6
Benefits of Halliburton Injector Design.................................................................................................... 4-8
Preventive Maintenance ............................................................................................................................ 4-8
Monitor Condition of Chains................................................................................................................. 4-8
Lubrication of Chains .......................................................................................................................... 4-10
Injector Alignment Procedure.............................................................................................................. 4-10
15K and 30K injectors ..................................................................................................................... 4-10
60K Injector ..................................................................................................................................... 4-10
80K injector ..................................................................................................................................... 4-10
Rig-up Alignment ................................................................................................................................ 4-10
Injector Capacities................................................................................................................................... 4-11
Critical Design Parameters...................................................................................................................... 4-11
Injector Chain Inspection and Replacement Criteria .............................................................................. 4-15
Lubrication........................................................................................................................................... 4-15
Chain Critical Parameters.................................................................................................................... 4-15
Wear Characteristics that Contribute to Elongation ........................................................................ 4-15
Tension Failure ................................................................................................................................ 4-15
Fatigue Failure ................................................................................................................................. 4-15
Inspection Criteria ............................................................................................................................... 4-16
Routine Inspection with Chains on Injector..................................................................................... 4-16
4•1 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
Inspection of Chains after Disassembly........................................................................................... 4-16
Injector Pre/Job Inspection Checklist .................................................................................................. 4-17
Injector Post/Job Inspection Checklist ................................................................................................ 4-17
Test Your Knowledge ............................................................................................................................. 4-18
4•2 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
These two conditions can cause either a net
Overview downward load or a net upward vertical force (snub).
The formula for the net upward force is:
The Halliburton coiled tubing injector head is a Pressure x Cross Sectional Area of the
state-of-the-art mechanical apparatus that provides Tubing - Dead-Weight of Suspended Tubing
the reaction force and stability necessary for
The injector head assembly consists of the following
insertion and removal of continuous steel tubing in a
subassemblies, which are all positioned over the
well. It is designed to provide the thrust required,
wellhead:
through a friction drive system, to snub the tubing
into the well against pressure. It is also designed to • Tubing injector drive assembly
control the rate at which tubing is lowered into the
well if no pressure exists; and coming out of the • Tubing guide assembly
well, to lift the full weight and accelerate to • Load indicator
operating speed.
• Skid and support structure
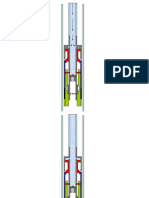
Fig. 1: Major components of Injector Guide.
Halliburton 4•3 Coiled Tubing Essentials
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
Tubing Injector Drive Timing Sprockets
Assembly The timing sprockets on the linear beams are
machined as a single assembly to prevent excessive
chain stretch, tooth wear and bearing wear.
The coiled tubing injector operates on the friction
drive principal. The tubing is squeezed between Note: Each shaft and sprocket are matched sets
opposing gripper blocks. Two direct-acting hydraulic and have timing marks, which must be aligned
cylinders connected to a movable take-up beam during any reassembly.
provide the applied normal force. A second beam is Failure to match timing marks may result in
mechanically fixed opposite the moving beam, and malfunction of the injector. All tapped holes have a
the tubing is gripped between the two beams. Two bi- spiroloc special thread form. Do not use a standard
directional hydraulic motors driving through torque- tap to the chase threads.
amplifying planetary gearheads generate the axial
force. (The 15K injector has a single motor.)
There are four sizes of Halliburton injectors: Skid and Support Structure
• 15K injector, which is used for small tubing up to
a 1.5 in. OD. It is commonly used on the Hyster The skid and support structure serve to balance the
unit or on the Bobtail units and has an axial load total load of the tubing injector assembly and
rating of 15,000 lb in either direction. workstring over the wellhead, also to secure the
tubing injector drive assembly and tubing guide
• 30K/38K injector, which is capable of generating assembly against lateral movement. The tubing
a 30,000-/38,000-lb axial load in an upward or injector drive is, however, free to move vertically
downward direction. within the guide frame to allow the load indicator to
function. The accumulator for the friction drive
• 60K injector, which is capable of generating
system of the head assembly is mounted to the skid.
60,000-lb axial load.
• 80K injector, which is capable of generating an
80,000-lb axial load at the maximum pressure Load Cell
capacity in both upward and downward
directions.
The load cell is located directly below the injector
inner frame. External load creates a pressure signal
that is transmitted to a load indicator gauge on the
Drive Chain Assembly operator’s console. The load cell is used on current
15K and 30K injectors and may be used with the 0 to
The drive chain should be assembled with the 30,000 weight indicator. The load cell should have a
connector links installed from alternate sides to 3/8- to 1/2-in. stand-off when properly pumped up.
provide even chain wear and loading. Failure to do
so may cause premature chain wear and damage.
Rotation of the cotter pin alignment indicates lack of
lubrication.
Roller Chain Assembly
The roller chain should be assembled with the
connector links installed from alternate sides.
Rotation of cotter pin orientation indicates lack of
lubrication. Check the rollers for cracks and wear.
Fig. 2: Load indicator.
4•4 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
Load pin full displacement or half displacement of hydraulic
oil to the injector motors.
The load pin is a bi-directional stain gauge and is Note: Always stop the injector and switch the
located on the bottom of the injector between the directional control valve to neutral when changing
inner and outer frame. A single or dual load pin speeds.
configuration can be used. There are two different
models of load pins presently in use. The signal from
the strain gauge is transmitted to a 9-in. analog meter Speed/Depth Sensor
and to a Unipro II in the operator’s compartment.
The optional Data Acquisition depth meter uses an
optical encoder to monitor the injector speed and
Circuit Description and depth. By sensing the rotation of the pipe mounted on
Operating Principles the outboard side of the injector, the encoder sends
electrical impulses to the UNIPRO II.
The injector receives hydraulic power from a separate Because some 15K and 80K injectors have single
power pack. Control is maintained from a control speeds, the separate speed selection function may not
console. The operator at the console controls injector apply. The 60K and 80K injectors use variable
speed and direction through the use of two bi- “displacement” pumps for speed control.
directional fixed displacement, hydraulic motors.
The injector uses pressure release/spring-set brakes
that are released by directing hydraulic pressure Drive Motors
through a shuttle valve to the release ports.
The injector drive motor(s) are supplied directly from
the four-way directional control valve located on the
Speed Selector power pack. Maximum supply pressures and flow
rates for the drive motors are as follows.
30K/38K injectors build after January 1987
incorporate an internal selector valve to allow either
Type of Injector Maximum Pressure Maximum
Supply Flow Rate
15K 2,500 psi 98 gal/min
30K/38K STANDARD 2,500 psi 98 gal/min
DNV 2,500 psi 98 gal/min
60K 4,000 psi 100 gal/min
80K STANDARD 6,000 psi 188 gal/min
DNV 3,500 psi 94 gal/min
4•5 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
necessary. However, at a pressure of 1,500 psi there
is a possibility of damaging thin-walled tubing.
Gripper Cylinders and Blocks
30K Injector
The 30K/38K injector contains two double-acting
hydraulic cylinders used to directly apply the normal
When using semi-circular gripper blocks, a pressure
force to the tubing through the gripper blocks on the
of 1,000 psi can be used on all tubing sizes and wall
gripper chains. The cylinders are connected to an
thicknesses without damage to the tubing. If slippage
accumulator, which is isolated by a pilot-operated
occurs, the pressure may be increased as necessary.
check valve so that gripper force is maintained in the
case of an input pressure loss. When using vee-blocks, a pressure of 750 psi should
be used.. Should slippage occur, the pressure can be
New style ‘V-Block’ gripper blocks have all the
increased as necessary. However, at a pressure of
advantages of our semicircular gripper blocks, plus
1,100 psi, there is a possibility of damaging thin-
the capacity to use the same chain assembly for a
walled tubing.
large range of tubing sizes. They are currently
available in two sizes for the 30K/38K injector, one
for use with 1 in - 1 3/4 in., one for use with 1 1/2 to 80K Injector
2 3/8 in. The 80K injector also has a set available to
run up to 3 1/2 in. tubing. The 80K Injector uses only the vee-block
configuration. Because of the considerable tubing
size range and available capacity of the 80K Injector,
it is recommended that the following equation be used
to determine beam pressure.
Beam Pressure = k x Expected Load
Example: The maximum expected load is 50,000 lb.
What is the suggested gripper pressure?
Beam Pressure = k x load
Beam Pressure = 0.01225 x 50,000 = 612 psi
Accumulator Pressure
At all times during coiled tubing operation, sufficient
hydraulic pressure should be applied to the cylinders The accumulator for the gripper cylinder/linear beam
to help prevent the tubing from slipping. This circuit should have a dry nitrogen pre-charge of 300
pressure will vary depending on the type of gripper psi for 1,000-psi beam pressure, up to 500 psi for a
blocks being used, tubing size, and tubing wall beam pressure of 1,500-psi. This provides
thickness. As a rule of thumb, the following approximately 50% fluid volume at the operating
guidelines are suggested. pressure. Verify the pre-charge pressure before each
job. Check that the system hydraulic pressure is zero
(0) when checking the pressure.
15K Injector
When using semi-circular gripper blocks, a pressure
of 1,000 psi can be used on all tubing sizes and wall
thickness without damage. If slippage occurs, the
pressure may be increased as necessary.
When using vee-blocks, use a pressure of 500 psi
starting at the surface and gradually increasing as
needed, not to exceed 1, 100 psi increase as
4•6 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
COILED TUBING INJECTORS WITH V-BLOCKS
HOISTING LOAD VS. BEAM PRESSURE
Hoisting Gripper Load P. Beam Pressure Required For: Hoisting
Load Required At Load
Friction Factor f 80K or 60K 1 ¼” (30K) Small
0.25 Injectors Injector 15K Injector
P=Q/(2f) p=P/127.6 p=P50.9 p=P/21
Q p p p p Q
Lb lb psi psi psi lb
1 2 3 4 5 6
1000 2000 200 300 400 1000
2000 4000 200 300 400 2000
3000 6000 200 300 400 3000
4000 8000 200 300 400 4000
5000 10000 200 300 476 5000
6000 12000 200 300 571 6000
7000 14000 200 300 667 7000
8000 16000 200 314 762 8000
9000 18000 200 354 857 9000
10000 20000 200 393 952 10000
11000 22000 200 432 1048 11000
12000 24000 200 472 1143 12000
13000 26000 204 511 1238 13000
14000 28000 219 550 1333 14000
15000 30000 235 589 1429 15000
16000 32000 251 629 1524 16000
18000 36000 282 707 18000
20000 40000 313 786 20000
22000 44000 345 864 22000
24000 48000 376 943 24000
26000 52000 408 1022 26000
28000 56000 439 1100 28000
30000 60000 470 1179 30000
32000 64000 502 1257 32000
34000 68000 533 1336 34000
36000 72000 $64 1415 36000
38000 76000 596 1493 38000
40000 80000 627 1572 40000
42000 84000 658 42000
44000 88000 690 Recommended P.Beam pressure 44000
46000 92000 721 are conservative, and they are 46000
48000 96000 752 based on friction factor of 0.25. 48000
50000 100000 784 Actual friction factor may be 50000
52000 104000 815 0.30 and even higher 52000
54000 108000 846 54000
56000 112000 878 56000
58000 120000 940 60000
62000 124000 972 62000
64000 128000 1003 64000
66000 132000 1034 66000
68000 136000 1066 68000
70000 140000 1097 70000
72000 144000 1129 72000
74000 148000 1160 74000
76000 152000 1191 76000
78000 156000 1223 78000
80000 160000 1254 80000
File: c:\tube\pro\beampr.wq1 02.22.93 AVA
4•7 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
• Rollers help distribute the bending stresses on the
Benefits of Halliburton tubing.
Injector Design • Single point lifting bail can be used to apply
moderate tension to increase stability of the stack
up.
• Linear bearing beams apply uniform pressure to
the back side of the gripper chain
• Counter balance valves on both the in and out
ports provide fail safe protection in both
directions.
Preventive Maintenance
• High efficiency hydraulic motors utilizing a vane
on vane design provide more precise starting
torque control. This allows the operator to
slowly accelerate the pipe for accurate
Monitor Condition of Chains
positioning.
1. Check positions of cotter pins to determine if
• Automatic brakes set when hydraulic pressure is connector pins are rotating (Refer to Fig. 5). If
lost. pins appear to have rotated, this indicates
• Extensively tested tubing guides. For 1 in., 1 1/4 incorrect alignment, broken parts, and/or
in., and 1-1/2 in. tubing a 72 in. radius tubing improper lubrication.
guide is used. For 1 3/4 in., 2 in., and 2 3/8 in.
tubing a 96 in. radius tubing guide is used.
• Tubing guide portion swivels to maintain
orientation with the tubing reel and compensate
for fleet angle changes.
4•8 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
Fig. 5: Roller chain assembly showing the connector links installed from alternate sides.
Note: If the chain has stretched enough so that the Compressed length of the disc washers should be
tensioner is out as shown in Figure 7, then one roller 2.125 to 2.25 in. (for 30K) not including the flat
should be removed and a half link installed. This washers on each end (Refer to Fig. 6).
procedure is recommended only once per chain.
2. Check that Belleville washers on the gripper
chain tensioners are properly adjusted.
Fig. 6:
3. Visually check position of linear roller chain
tensioning arm. When the lower end of the
tensioning arm reaches a position of
approximately 1/2 in. past vertical (Fig. 7), the
linear roller chain should be removed and
shortened by one roller. This will require the use
of a special half link. Do not operate with roller
missing from profile. Removal of a half link and
roller should be done only once. Additional
stretch requires that the chain parts be replaced.
Note: When reassembling the chain, stagger
the connector links so that cotter pins are on
alternate sides.
4•9 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
Caution: Vee blocks may be damaged in this
procedure.
Note: The chains should be cleaned and lubricated
within 12 hr after each job is finished. Lubricant
should also be applied every 10,000 running feet.
Injector Alignment Procedure
15K and 30K injectors
The injector alignment should be checked
periodically and adjusted following the steps below,
if required. (New style 15K is self-aligning.)
1. Insert a straight, solid rod (1 in., 1 1/4 in., or 1
1/2 in. OD) 10 ft long through the tubing guide
base, the injector, and the stuffing box.
2. Position the injector within the frame by
adjusting the turnbuckles, until the rod is
centered in the tubing guide base and enters
straight into the stuffing box.
3. Unlock the 5/16-in. socket head locking bolts
and advance the fixed side pressure beam
adjustment screws until the gripper blocks make
even contact along the length of the rod. Lock the
screws in position by tightening the 5/16-in.
socket head bolts above these screws.
60K Injector
Fig. 7: Maximum distance for tensioner to The 60K Injector is self-aligning.
travel.
80K injector
4. The drive chains should not be disassembled The 80K injector is self-aligning.
except to replace worn or damaged parts.
5. Check for chain stretch outlined in the “Injector
Chain Inspection and Replacement Criteria”. Rig-up Alignment
When the injector is rigged up on the wellhead, either
Lubrication of Chains the hydraulic or stationary linear beam side must be
facing the reel to help prevent side loading the chains
that will decrease chain life and damage the linear
1. Apply sufficient pressure to beams so that the
beam side rails.
inner chain rotates with the drive chain.
2. Operate the injector at a slow speed. Apply 90
wt. climbing gear lube to inner chain and drive
chain so that chain parts are properly lubricated.
4 • 10 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
Injector Capacities
Injector Capacity Tubing OD Range
15K 15,000 lb 0.75 to 1.50 in.
30K/38K 15,000 lb (high speed)*
30,000 lb (low speed)* 1.0 to 2.375 in.
60K 60,050 1.25 to 2.375 in.
80K 80,000 lb 1.25 to 3.5 in.
Critical Design Parameters
Halliburton 15K Injector Critical Design Parameters
Size 1 in.
Speed Rating 192 ft/min, Factor = 2 ft/min/gal
Load Rating 19,300 lb, Factor = 7.72 lb/psi
Maximum Recommended Hydraulic Pressure 2,500 psi
Weight with Tubing Guide 4,200 lb
Tubing Guide Radius 48 in.
Motor Type Double Vane
Motor Quantity 1
4 • 11 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
Halliburton 30K Injector Critical Design Parameters
Tubing Sizes (With Interchangeable Gripper Blocks) 1 in., 1 ¼., and 1 ½ in.
Operating Loads (Push or Pull)
Continuous 24,000 lb at 2,500 psi hyd. Pressure
Intermittent 30,260 lb at 2,500 psi hyd. Pressure
Pressure Factor
Low Speed 12.104 lb/psi, (0.0826 psi/lb)
High Speed 6.052 lb/psi,k (0.1652 psi/lb)
Maximum Speed*
Low Speed 112 ft/min, 1.24 (ft/min)/(gal/min)
High Speed 224 ft/min, 2.48 (ft/min)/(gal/min)
Weight with Tubing Guide 5,500 lb (6,500 lb on 1989 or later models)
Tubing Guide Radius 72 in.
Motor Type Double Vane
Motor Displacement 9.5 in. 3/rev each motor
4 • 12 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
Halliburton 38K Injector Critical Design Parameters
Tubing Sizes (With Interchangeable Gripper 1 in., 1 1/4 in., 1 1/2 in., and 1 3/4
Blocks)
Operating Loads (Push or Pull)
Continuous 30,400 lb at 2,500 psi hyd. pressure
Intermittent 38,000 lb at 2,500 psi hyd. pressure
Pressure Factor
Low Speed 15.2 lb/psi, (0.0658 psi/lb)
High Speed 7.6 lb/psi, (0. 1316 psi/lb)
Maximum Speed*
Low Speed 82 ft/min, 0.836 (ft/min)/(gal/min)
High Speed 164 ft/min, 21.672 (ft/min)/(gal/min)
Weight with Tubing Guide 5,500 lb (6,500 lb on 1989 or later
models)
Tubing Guide Radius 94 in.
Motor Type Double Vane
Motor Displacement 13 in.3/rev each motor
4 • 13 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
Halliburton 80K Injector Critical Design Parameters
STANDARD DNV
Tubing Sizes 1.25 in. - 2.25 in. 1.25 in. - 2.25 in.
1.50 in. - 2.75 in. 1.50 in. - 2.75 in.
2.00 in. - 3.50 in. 2.00 in. - 3.50 in.
Operating Loads or Pull*
Continuous 71,600 lb, 5,000 psi. 73,200 lb, 3,000 psi.
Intermittent 85,600 lb, 6,000 psi. 85,366 lb, 3,500 psi.
Pressure Factor 14.32 lb/psi. 24.4 lb/psi.
Maximum Speed 188 ft/min, 188 gal/min 93.5 ft/min, 168 gal/min
Speed Factor 1 (ft/min)/(gal/min) 0.56 (ft/min)/(gal/min)
Weight
With Tubing Guide 16,000 lb 16,000 lb
Tubing Guide Radius 96 in. 96 in.
Motor Type Piston Double Vane
4 • 14 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
Injector Chain Inspection Wear Characteristics that Contribute
to Elongation
and Replacement
A. Normal Wear
Criteria
The rate of chain wear is greatly affected by
lubrication. When properly lubricated, load-bearing
The "gripper chains" on the injector are critical surfaces of the pin and bushing will look shiny and
elements that must be kept in good operating smooth. As long as the elongation is within the
condition. Failure of the chain may result in loss of allowable limit, the chain can be reused.
control of the pipe.
B. Excessive Wear
. It is essential that the chains are properly
If the load-bearing surfaces show discoloration
maintained, properly adjusted, and are promptly
(brown-red oxide), lubrication is insufficient
replaced when inspection reveals that they are worn
past the critical stage. Note: The injectors must be adjusted for proper
tension because the slack side blocks may
interfere with the frame. If the blocks hit the
Lubrication frame during operation, it may be necessary to
tighten the chain beyond the recommended level
given for optimum wear rate. In this case it will
One of the most important factors affecting chain life
be necessary to accept shorter chain life.
is proper lubrication. Lubrication provides cooling
and impact dampening at high speeds. Lubrication Do not overtighten the gripper chains.
also reduces corrosion and carries away foreign
matter, which is vital in abrasive environments. • Excessive slack: chain whips and creates noise.
Adjust idlers or sprocket distances for proper
slack.
Chain Critical Parameters • Replace sprockets when teeth show excessive
wear or are hook-shaped. C. Galling.
For injector gripper chains (No. 140 with 1 3/4-in. Galling occurs as a result of inadequate lubrication or
pitch), all the connector links, side plates, and excessive operating speed. The mating surfaces of the
connector pins should be replaced when the measured pins and bushings actually weld together then break
length between the centers of seven links exceeds away as the joints flex over the sprockets.
12.62 in.
The injector uses gripper chain assemblies that are Tension Failure
comprised of 84 links of No. 140 chain. The nominal
length of each chain is therefore 147.00 in. When a
(When the chain is subjected to a one-time load
full chain is laid out on a table, the chain elements
greater than it can withstand). Normally, tension
must be replaced if the measured length is determined
failure can be identified by fractured side plates.
to exceed 151.4 in.
When replacing chain links, all the chain elements Fatigue Failure
(except for gripper blocks) should be replaced as a
unit. Do not mix new and worn links on the same
chain. Fatigue failures are a result of repeated cyclic loading
beyond the chain's endurance limit, or rated capacity.
Exception: Broken links can be replaced as a
temporary measure to allow completion of the job. Most of the chain failures on injectors are caused by
fatigue that results in fracture of one or more
connecting pins. The fatigue is a result of high
operating loads, lack of lubrication, and
contamination of the moving surfaces.
4 • 15 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
The roller chains should be examined regularly to Inspection of Chains after
determine if the wear has progressed to an Disassembly
unacceptable state.
1. Measure the overall length and check for
excessive elongation.
Inspection Criteria
2. If the chain is stretched beyond its limit, replace
all the chain parts with new parts. Do not mix
Routine Inspection with Chains on worn parts with new parts. The gripper blocks (or
Injector rollers) may be reused if they are not damaged.
Insert a solid round rod, whose diameter is equal to
Both the gripper chains and linear-bearing chains the tubing OD for the particular block, between two
should be visually inspected at least once every opposing blocks. Verify that the faces of the two
month. blocks do not touch. If the faces contact, the contour
of the radius is worn past the case thickness. The
block must be replaced. Worn gripper blocks must be
replaced in complete sets. Do not mix worn and new
gripper blocks on the same chains.
Injector Description Chain Size Pitch No. of Max.
(ASA No.) Links Allow
Length
15K Gripper Chain No. 100 1.25 10 12.87
Linear Beam Chain No. 60 0.75 16 12.36
30K Gripper Chain No. 140 1.75 7 12.50
Linear Beam Chain No. 80 1.00 12 12.36
60K Gripper Chain No. 160 2.00 6 12.36
Linear Beam Chain No. 80 1.00 12 12.36
80K Gripper Chain No. 200 2.50 5 12.87
Linear Beam Chain No. 1 00 1.25 10 12.87
4 • 16 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
Injector Pre/Job Inspection Checklist
( ) Visually Check For Damage.
( ) Visually Check For Hydraulic Leaks.
( ) Verify Lifting Slings And Shackles Are In Good
( ) Verify Correct Pin For Gooseneck Attachment Are Used.
( ) Check Chain lubrication
( ) Check Transmission Oil Level (Sight Glass).
( ) Check Accumulator Pre-Change
( ) Check Turnbuckles.
( ) Check Travel Lock Down Pins For Load Cell
( ) Check Condition Of Hoses And Fittings.
( ) Verify Drain Plugs Are In Drip Pan.
( ) Verify Drip Pan Is Clean and Dry
Injector Post/Job Inspection Checklist
( ) Clean Unit And Allow To Dry.
( ) Check Gear Oil Level In Head.
( ) Check Hydraulic Hoses and Fittings To Verify They Are In Good Condition And Have No Leaks
( ) Check Gripper Block Chains To Assure Cotter Pins Are Present And In-Line (Pins Not Rotated) On All
Alternative Pins.
( ) Check Linear Beam Chains To Assure All Cotter Pins Are Present And Are In-Line (Pins Not Rotated) On
All Alternative Pins.
( ) Check Turnbuckles And Inner Frame Mountings.
( ) Lubricate All Chains With 90 Wt. Gear Lube With Tack Additive.
4 • 17 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
Coiled Tubing Injector
Test Your Knowledge
1. Name the four sizes of the Halliburton Injector.
2. If the cotter pins are rotated in the chains, what is this a sign of?
3. If the roller chain assembly has stretched enough so that the tensioner is out. What can be done to the chain and
still use it?
4. The load Cell should have how much standoff distance when pumped up?
5. How often should Injector Chains be cleaned and lubricated?
Within ____________ hrs. after the completion of the job or ____________ running feet.
6. What is used to release the brakes on the injector?
7. When the injector is rigged up on the wellhead, which way should it be facing?
8. How much N2 precharge pressure should be on the accumulator for 1000 psi? Beam pressure ____________
How much for 1500 psi? Beam Pressure____________.
9. What are the Washers called that are used on the Gripper Chain tensioners, and what is the compressed length
for the 30K injector?
10. Name two types of injector chain failure:
1.
2.
4 • 18 Coiled Tubing Essentials
Halliburton
© 1999, Halliburton
You might also like
- Completions Group: Engineering & Operation: Doc Id © Chevron 2005Document21 pagesCompletions Group: Engineering & Operation: Doc Id © Chevron 2005Khalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- When To Use The Data Converter ObjectDocument18 pagesWhen To Use The Data Converter ObjectKhalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- Plug, Top Latch-In Dual 4.500 X 6.625 PN 1831733Document2 pagesPlug, Top Latch-In Dual 4.500 X 6.625 PN 1831733mostafa rekabiNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Tubing Cutters Review Outcome PDFDocument2 pagesMechanical Tubing Cutters Review Outcome PDFKhalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- History and Overview of Coiled Tubing Services: Section 1Document9 pagesHistory and Overview of Coiled Tubing Services: Section 1Khalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- Packer Setting Sequence StepsDocument10 pagesPacker Setting Sequence StepsKhalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- Gas Lift ValvesDocument9 pagesGas Lift ValvesKhalid Zaeem100% (1)
- Setting ToolDocument41 pagesSetting ToolKhalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- Appendix E-Unipro-Ii™ Controller Hardware SetupDocument6 pagesAppendix E-Unipro-Ii™ Controller Hardware SetupKhalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- Gravel Pack With WordsDocument32 pagesGravel Pack With WordsKhalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- Gravel Pack With WordsDocument32 pagesGravel Pack With WordsKhalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- Geology: The Science Which Concerns The History of The Earth and It's Life, Especially As Recorded in The RocksDocument39 pagesGeology: The Science Which Concerns The History of The Earth and It's Life, Especially As Recorded in The Rocksraghavcracy8294No ratings yet
- TCP30210 PDFDocument1 pageTCP30210 PDFKhalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- Geology: The Science Which Concerns The History of The Earth and It's Life, Especially As Recorded in The RocksDocument39 pagesGeology: The Science Which Concerns The History of The Earth and It's Life, Especially As Recorded in The Rocksraghavcracy8294No ratings yet
- TCP30227Document1 pageTCP30227Khalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- TCP49251 CDocument1 pageTCP49251 CKhalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- Sand Management GuideDocument3 pagesSand Management GuideKhalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- TCP30234Document1 pageTCP30234Khalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- TCP30228Document1 pageTCP30228Khalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- Coiled Tubing I: Halliburton Energy Institute Duncan, OklahomaDocument1 pageCoiled Tubing I: Halliburton Energy Institute Duncan, OklahomaKhalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- TCP30281Document1 pageTCP30281Khalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- Injection of GasDocument5 pagesInjection of Gasmostafa rekabiNo ratings yet
- Section 4 - Basic Hydraulics PDFDocument25 pagesSection 4 - Basic Hydraulics PDFKhalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- History and Overview of Coiled Tubing Services: Section 1Document9 pagesHistory and Overview of Coiled Tubing Services: Section 1Khalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- Coiled Tubing Technical Data: Section 18Document10 pagesCoiled Tubing Technical Data: Section 18Khalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- Power Pack: Section 8Document13 pagesPower Pack: Section 8Khalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- Section 7 - Definitions and Acrynyms PDFDocument19 pagesSection 7 - Definitions and Acrynyms PDFKhalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- Basic Bottomhole Assemblies (Bhas) : Section 13Document10 pagesBasic Bottomhole Assemblies (Bhas) : Section 13Khalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- History and Overview of Coiled Tubing Services: Section 1Document9 pagesHistory and Overview of Coiled Tubing Services: Section 1Khalid ZaeemNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Influence of Thixotropy On Stability of Cement GroutDocument9 pagesInfluence of Thixotropy On Stability of Cement GroutcementyNo ratings yet
- 1 STDocument40 pages1 STKomalNo ratings yet
- Brønsted-Lowry Theory of Acids and BasesDocument4 pagesBrønsted-Lowry Theory of Acids and Basescayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Mechanical Analysis - WikipediaDocument8 pagesDynamic Mechanical Analysis - WikipediamohsenNo ratings yet
- 20150714rev1 ASPACC 2015Document22 pages20150714rev1 ASPACC 2015HERDI SUTANTONo ratings yet
- PDFDocument228 pagesPDFGayan Madushan KandethanthriNo ratings yet
- Lightolier RFL Recessed Fluorescent Lighting Catalog 1981Document52 pagesLightolier RFL Recessed Fluorescent Lighting Catalog 1981Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Diode CircuitsDocument64 pagesChapter 3 Diode CircuitsAmged TahaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Separation of Mixtures - 0Document25 pages2.2 Separation of Mixtures - 0Arch Chellis OrongNo ratings yet
- TT IimDocument106 pagesTT IimrakeshNo ratings yet
- Ferrous: PrintedDocument40 pagesFerrous: PrintedsunsirNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam No. 4 2018 PDFDocument43 pagesPractice Exam No. 4 2018 PDFJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Radio Controls Setup GuideDocument52 pagesRadio Controls Setup GuideHaitham Mohamed100% (1)
- Electronicbekm 2023Document159 pagesElectronicbekm 2023Bekir MouradNo ratings yet
- 0580 IGCSE Mathematics - Useful FormulaeDocument3 pages0580 IGCSE Mathematics - Useful FormulaeSupermartin767No ratings yet
- Horizontal Single-Stage Centrifugal PumpsDocument52 pagesHorizontal Single-Stage Centrifugal PumpsMorgan HengNo ratings yet
- Worksheet MagnetismDocument3 pagesWorksheet MagnetismVenkyNo ratings yet
- Instructions for Combined Boiler CombustionDocument23 pagesInstructions for Combined Boiler CombustionMavio ViorelNo ratings yet
- St. Michael's School Syllabus for Class 8Document14 pagesSt. Michael's School Syllabus for Class 8Aila ParkarNo ratings yet
- Chemical EngineeringDocument9 pagesChemical EngineeringanushafiNo ratings yet
- JawapanDocument3 pagesJawapanYusfalina Mohd YusoffNo ratings yet
- Calculate the equivalent diameter of a 190 mm x 520 mm rectangular ductDocument10 pagesCalculate the equivalent diameter of a 190 mm x 520 mm rectangular ductKlaikangwol AnuwarnNo ratings yet
- VEML6075: Vishay SemiconductorsDocument11 pagesVEML6075: Vishay Semiconductorsyaumil akbarNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 CHEMISTRY Previous Year Question Paper 2011Document8 pagesICSE Class 10 CHEMISTRY Previous Year Question Paper 2011Madhu SudanNo ratings yet
- GR 9, Chem P-1Document23 pagesGR 9, Chem P-1kashif mohammedNo ratings yet
- Maths Mensuration Surface Area ConesThe title "TITLEMaths Mensuration Surface Area ConesDocument12 pagesMaths Mensuration Surface Area ConesThe title "TITLEMaths Mensuration Surface Area ConesWafi Bin Hassan The InevitableNo ratings yet
- Sludge Transfer Pump - Nmr-601 M13-G-0950A/B: Upgrade Pier Marine Facilities at TanajibDocument53 pagesSludge Transfer Pump - Nmr-601 M13-G-0950A/B: Upgrade Pier Marine Facilities at TanajibchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Cement CalculationsDocument25 pagesCement CalculationsKristi MicheleNo ratings yet
- 7 Things That Affect Your Vibration Frequency From The Point of View of Quantum PhysicsDocument12 pages7 Things That Affect Your Vibration Frequency From The Point of View of Quantum PhysicsLluisNo ratings yet
- Epofine 337 - Finehard 3918Document4 pagesEpofine 337 - Finehard 3918Karishma PrabhuNo ratings yet