Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem 2.1: Chapter Ii .. Definmons and Units
Problem 2.1: Chapter Ii .. Definmons and Units
Uploaded by
Liz ArfinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem 2.1: Chapter Ii .. Definmons and Units
Problem 2.1: Chapter Ii .. Definmons and Units
Uploaded by
Liz ArfinCopyright:
Available Formats
..
-
------- --···-•
Chapter II .. DEFINmONS AND UNITS
CHAPTER 2
Problem 2.1
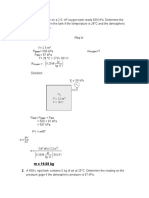
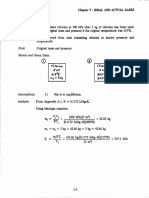
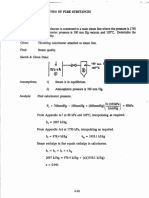
Referring to Figure 2.10, the atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa, and the pressure gages
A and B read 210 kPa (gage). Determine the absolute pressures in boxes A and B
in (a) kPa; (b) mm Hg absolute.
Given: Atmospheric pressure and readings of gages A and B.
Find: The absolute pressures in boxes A and B.
Sketch and Given Data:
210 kPct
Psurr = 100 kPa
6
A
Assumptions: None
Analysis: Determine pressures A and B in kPa, then convert to mmHg absolute.
(a) pBabs = pBgagc + psurr
= 210 kPa + 100 kPa = 310 kPa
PAabs = PAgage + PsurrA but PsurrA = PBabs
= 210 kPa + 310 kPa = 520 kPa
(b) lmmHg = 0.1333 kPa
PB = 310 kPa x lmmHg = 2325.6 mmHg absolute
abs 0.1333 kPa
PA = 520 kPa x lmmHg = 3901 mmHg absolute
abs 0.1333 kPa
2-1
You might also like
- Engineering Thermodynamics PDFDocument699 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics PDFZachNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Solutions 9th EdDocument150 pagesCH 3 Solutions 9th Edp-majidi91% (58)
- Fluid 9ed Solution ManualDocument919 pagesFluid 9ed Solution ManualAmr f100% (1)
- Solution Manual Refrigeration and Airconditioning (Stoecker and Jones) (Ed-2)Document161 pagesSolution Manual Refrigeration and Airconditioning (Stoecker and Jones) (Ed-2)anon_909426932100% (6)
- 1 Practice Problems (2 - 2)Document3 pages1 Practice Problems (2 - 2)IAN PAOLO BAUTISTA100% (1)
- 12.2 Thermodynamics 02 SolutionsDocument11 pages12.2 Thermodynamics 02 Solutionsjeruel sabacanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (Unknown) SolnDocument136 pagesFluid Mechanics (Unknown) SolnErik BaldadoNo ratings yet
- Engineering-Fluid-Mechanics-11th-Edition SolutionsDocument136 pagesEngineering-Fluid-Mechanics-11th-Edition Solutionskevin shiNo ratings yet
- Calculation Title: Seagas Pipeline Design - MinervaDocument1 pageCalculation Title: Seagas Pipeline Design - Minerva秦东旺No ratings yet
- Solution To Problem Set Fluid Mech PressureDocument6 pagesSolution To Problem Set Fluid Mech PressureMark Augusto V. AgusNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning - Module 23.1 SolutionsDocument9 pagesAir Conditioning - Module 23.1 SolutionsRuis Raphael HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part15 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part15 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Manómetro BásicoDocument3 pagesManómetro BásicoYisel Laura Cuevas ILisNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1: Basic Concept of ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesTutorial 1: Basic Concept of ThermodynamicsKaka ZettyNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Sol PDFDocument5 pagesTest 1 Sol PDFabhiNo ratings yet
- Ensc 461 Tutorial, Week#6 - Refrigeration Cycle: High Pressure Side P 700kpaDocument6 pagesEnsc 461 Tutorial, Week#6 - Refrigeration Cycle: High Pressure Side P 700kpaArchie Gil DelamidaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 05Document2 pagesAssignment 05Raj KothiyaNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Guía 6 Termodinámica - Balance de Energía en Sistemas Cerrados 2-2022Document41 pagesSolucionario Guía 6 Termodinámica - Balance de Energía en Sistemas Cerrados 2-2022Fernanda MuñozNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part33 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part33 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Answer's SchemeDocument27 pagesAssignment 1 Answer's Schemedangoy raulNo ratings yet
- 4HOMEWORKDocument6 pages4HOMEWORKBlue SkyNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant - Module 18.1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesSteam Power Plant - Module 18.1 SolutionsAnne Dominique QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Strength Notes 2 Axial StressDocument2 pagesStrength Notes 2 Axial StressNiña Elizabeth EjusaNo ratings yet
- Homework 8.1 Units of Pressure and Some Gas LawsDocument2 pagesHomework 8.1 Units of Pressure and Some Gas LawsDanielle Raven GarciaNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering Correlation Chemistry v4Document4 pagesBasic Engineering Correlation Chemistry v4jovanniNo ratings yet
- Transparansi PDRP (Gas) (English)Document10 pagesTransparansi PDRP (Gas) (English)M Rizki MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Carr Kobayashi Burrows ViscosityDocument3 pagesCarr Kobayashi Burrows ViscosityRichard GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Examples 1Document26 pagesExamples 1Gumball 8No ratings yet
- Given: Req'd:: 1. The Pressure Gage On A 2.5-mDocument5 pagesGiven: Req'd:: 1. The Pressure Gage On A 2.5-myeng botzNo ratings yet
- Sem218 W1 LECTURE3Document15 pagesSem218 W1 LECTURE3Akashi SilvaNo ratings yet
- Brochure HON - C210 PDFDocument6 pagesBrochure HON - C210 PDFManuel GerardoNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual Refrigeration and Airconditioning Stoecker and Jonesed 2 CompressDocument161 pagesSolution Manual Refrigeration and Airconditioning Stoecker and Jonesed 2 CompressskyyyxsageNo ratings yet
- Chapter V - Ideal and Actual Gases: 350 KpcaDocument1 pageChapter V - Ideal and Actual Gases: 350 KpcaLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- ME 311 Thermo I Fall 2014 Homework 5 Solutions PDFDocument1 pageME 311 Thermo I Fall 2014 Homework 5 Solutions PDFIllion IllionNo ratings yet
- Tme 213 Classwork SolutionsDocument15 pagesTme 213 Classwork SolutionsEnenamahNo ratings yet
- ME 113 S09 HW2 SolutionDocument3 pagesME 113 S09 HW2 SolutionallyhawNo ratings yet
- Vapor PressureDocument32 pagesVapor PressureStephen Rey CaldeaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document4 pagesProblem Set 1daejung1025No ratings yet
- D3SIGNCRlTERlA of BuildingDocument4 pagesD3SIGNCRlTERlA of BuildingRiaNo ratings yet
- Reflux 819 FoDocument20 pagesReflux 819 FoToniNo ratings yet
- Carr Kobayashi Burrows GasViscosityDocument2 pagesCarr Kobayashi Burrows GasViscosityChoiriahAgustinaSaritikaPutrianiNo ratings yet
- Carr Kobayashi Burrows GasViscosityDocument2 pagesCarr Kobayashi Burrows GasViscosityduyvkNo ratings yet
- Carr Kobayashi Burrows GasviscosityDocument2 pagesCarr Kobayashi Burrows Gasviscosityvictor javier nuñez100% (1)
- Presentation ReportDocument8 pagesPresentation ReportJackson ChongNo ratings yet
- BUGNAY, Jula ClaireDocument6 pagesBUGNAY, Jula Claireyeng botzNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer Es 31: Laboratoty Activity Bugnay, Jula Claire E. Bsaeng'G 4ADocument6 pagesThermodynamics and Heat Transfer Es 31: Laboratoty Activity Bugnay, Jula Claire E. Bsaeng'G 4Ayeng botzNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Chapter 2 Problems: V 0.002 M V 0.2 MDocument13 pagesSolutions To Chapter 2 Problems: V 0.002 M V 0.2 MJoanne DelosreyesNo ratings yet
- HW1 9Document6 pagesHW1 9Eduardo VCNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Engineering Fluid Mechanics 11th Edition Elger Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Engineering Fluid Mechanics 11th Edition Elger Solutions Manual PDFstrungrowett0m9ze100% (14)
- Borgnakke's Fundamentals of Thermodynamics: Global EditionDocument67 pagesBorgnakke's Fundamentals of Thermodynamics: Global Edition정윤서No ratings yet
- Combustion Chapter 6Document22 pagesCombustion Chapter 6Future HazeNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part11 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part11 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap03P102Document20 pagesThermo 5th Chap03P102Marilyn EspinozaNo ratings yet
- ES 31 - Thermodynamics and Heat TransferDocument5 pagesES 31 - Thermodynamics and Heat Transferyeng botzNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part88 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part88 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Chapter Id - Conservation of Mass and EnergyDocument1 pageChapter Id - Conservation of Mass and EnergyLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Properties of Pure Substances: Chapter IVDocument1 pageProperties of Pure Substances: Chapter IVLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part75 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part75 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part81 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part81 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Chapter V - Ideal and Actual Gases: 350 KpcaDocument1 pageChapter V - Ideal and Actual Gases: 350 KpcaLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part66 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part66 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part51 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part51 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Chapter V - Ideal and Actual Gases: Problem 5.5Document1 pageChapter V - Ideal and Actual Gases: Problem 5.5Liz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Mass and Energy: Problem 3.37Document1 pageConservation of Mass and Energy: Problem 3.37Liz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part87 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part87 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Problem 3.13: Chapter Iii - Conservation of Mass and EnergyDocument1 pageProblem 3.13: Chapter Iii - Conservation of Mass and EnergyLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Mass and Energy: Problem 3.33Document1 pageConservation of Mass and Energy: Problem 3.33Liz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.5: Chapter Iv - Properties of Pure SubstancesDocument1 pageProblem 4.5: Chapter Iv - Properties of Pure SubstancesLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.1: Chapter Iv - Properties of Pure SubstancesDocument1 pageProblem 4.1: Chapter Iv - Properties of Pure SubstancesLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part91 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part91 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part79 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part79 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Problem 3.41: Chapter Ill - Conservation of Mass and EnergyDocument1 pageProblem 3.41: Chapter Ill - Conservation of Mass and EnergyLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Iii - Conservation of Mass and Energy: Fl. FLDocument1 pageIii - Conservation of Mass and Energy: Fl. FLLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part94 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part94 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part67 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part67 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Problem 3.55: Chapter Iii - Conservation of Mass and EnergyDocument1 pageProblem 3.55: Chapter Iii - Conservation of Mass and EnergyLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- M (H M (H M (H M (H: Chapter Ill - Conservation of Mass and EnergyDocument1 pageM (H M (H M (H M (H: Chapter Ill - Conservation of Mass and EnergyLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part55 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part55 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part68 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part68 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part73 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part73 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part93 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part93 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Mass and Energy: Isc.MDocument1 pageConservation of Mass and Energy: Isc.MLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.13: Chapter Iv - Properties of Pure SubstancesDocument1 pageProblem 4.13: Chapter Iv - Properties of Pure SubstancesLiz ArfinNo ratings yet
- Thermo Solutions - Part102 PDFDocument1 pageThermo Solutions - Part102 PDFLiz ArfinNo ratings yet