Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Protein Folding Virtual Activity 1
Uploaded by
api-521773978Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Protein Folding Virtual Activity 1
Uploaded by
api-521773978Copyright:
Available Formats
Protein Folding Virtual Activity
Learning Objective:
Explain how a change in the subunits of a polymer may lead to changes in structure or
function of the macromolecule. (protein)
Website: https://learn.concord.org/resources/787/protein-folding
(You will have to create a free account.)
Setup:
● Make sure 3-letter codes are checked.
● Click on the hydrophobicity section and click on Charge and Hydrophobicity.
● Click on solvent type as Water.
● Generate a random protein
● Push play (at bottom)
Directions:
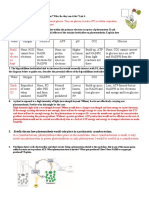
Use Amino Acid Chart at the end of the handout to answer questions 1-4.
1. What properties do the brown amino acids exhibit?
The brown amino acids are all exhibiting nonpolar hydrophobic properties.
2. What properties do the purple amino acids exhibit?
The purple amino acids are exhibiting positive charges.
3. What properties do the green amino acids exhibit?
The green amino acids are exhibiting polar hydrophilic properties
4. What properties do the pink amino acids exhibit?
The pink amino acids are exhibiting negative charges
Use the simulation to answer the following questions.
5. Where do most of the brown amino acids congregate? Why?
Most of the brown amino acids congregate in the center away from the water because
they are nonpolar and do not like water.
6. Where do the green amino acids tend to be exhibited? Why?
The green amino acids are generally on the outside of the protein because they are
hydrophilic and polar and are attracted to water.
7. Why do purple and pink amino acids attract each other?
The pink and purple amino acids are attracted somewhat to the water but also to
themselves because the pink are negative and the purple are positive and opposites
attract. Also, since the water has partial charges, they are attracted to the water.
Change in settings:
● Click on Generate random protein
● Click on All hydrophobic
● Push Play
TAKE A SCREEN SHOT
8. What happened? Why do you think this occurred?
The amino acids are crowded together to the center. That is because the amino acids
are hydrophobic and afraid of water, so they immediately moved to the center to get
away from the water.
Change in settings:
● Change water to oil
9. What happened? Why do you think this occurred?
The amino acids spread out and stopped being attracted to each other. This happened
because the oil is nonpolar like the amino acids and the amino acids are no longer
afraid of the water solvent, causing the amino acids to spread out in the oil.
TAKE A SCREEN SHOT
Change in settings:
● Click Generate Random Protein.
● Click All Hydrophilic
● Click Water
● Push Play
TAKE A SCREEN SHOT
10. What happens? Why do you think this occurred?
The amino acids spread out again, although some are still attracted to each other. That
is because the amino acids are polar and attracted to water, so they want to get close to
the water, thus spreading out.
11. Why do some still cluster?
Some still cluster because there are also charged amino acids in the hydrophilic amino
acid, since charged amino acids are attracted to the partially charged water. Some
cluster because the charged amino acids are attracted to each other due to their full
charges.
Further Thinking:
12. What causes amino acids to fold in different patterns to form different looking
structures?
The bonds and properties of the amino acids cause the different patterns that form
different structures.
Research:
12. What would happen if you changed ONE amino acid in the primary chain?
Depending on what the amino acid was changed to, there might have a serious effect,
little effect, or no effect.
13. How would this affect its shape?
If there is no effect, nothing will change. If there is little effect, something minor changed
in the shape(that might go on later to do serious damage). If there is a serious effect,
the shape would be completely different and create a different function for the different
structure.
14. What type of bond occurs between two cysteines? What is its purpose?
Disulfide bonds occur between two cysteines. It’s purpose is to stabilize the 3-D
Structure
15. What type of bonds occurs between the amino acids?
Amino acids form peptide bonds, which are covalent bonds between the amine group
and carboxyl groups of different amino acids.
16. What type of bonds occurs between neighboring amino acids in a secondary
structure in creating alpha helices and beta pleats?
Hydrogen bonds occur between amino acids in a secondary structure in creating alpha
helices and beta pleats.
17. What type of bonds occurs in tertiary and quaternary structures to cause a
“globular” look?
Some bonds that can occur in tertiary and quaternary structures are Van der waals
bonds, ionic bonds, and covalent bonds depending on the R side group.
You might also like
- Biomolecules MCQ-1Document4 pagesBiomolecules MCQ-1BikashNo ratings yet
- Biochem Med ChaptersDocument19 pagesBiochem Med Chaptersschxzerrydawn100% (1)
- Chapter 16 PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 16 PDFnabeelkhanNo ratings yet
- Food TestsDocument25 pagesFood TestsPeter Hong Leong Cheah100% (5)
- Solutions to analytical chemistry problemsDocument2 pagesSolutions to analytical chemistry problems한공주50% (2)
- Population Ecology GraphsDocument4 pagesPopulation Ecology GraphsBinal DaliaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - CAPE BioDocument15 pagesSyllabus - CAPE BioTravis SatnarineNo ratings yet
- Solubility Questions and AnswersDocument2 pagesSolubility Questions and AnswersBrittany100% (2)
- MacromoleculesDocument46 pagesMacromoleculesLady Ayessa AllonNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Chapter 2 by Rey CapangpanganDocument13 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Chapter 2 by Rey CapangpanganDrakeNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules Revision NotesDocument49 pagesBiological Molecules Revision NotesAyaz Nasih88% (8)
- Expt.4 Isolation of Casein From Milk and Analysis of Amino AcidsDocument10 pagesExpt.4 Isolation of Casein From Milk and Analysis of Amino Acidsbenina biancaNo ratings yet
- Biuret Test Detects Proteins Through Peptide BondsDocument6 pagesBiuret Test Detects Proteins Through Peptide BondsAaliyah Santillan100% (1)
- Formal Report-Proteins and Amino AcidsDocument10 pagesFormal Report-Proteins and Amino AcidsQuenieMarielIlar100% (1)
- Winogradsky Column Microbial Ecology ExperimentDocument15 pagesWinogradsky Column Microbial Ecology ExperimentTricia BarotNo ratings yet
- CHE311 Analytical Chemistry Quizzes CollectionDocument161 pagesCHE311 Analytical Chemistry Quizzes CollectionRenee KimNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Elution Order from Cation Exchange ColumnDocument8 pagesAmino Acid Elution Order from Cation Exchange ColumnDela Cruz, Amirah Anne D.No ratings yet
- Chemical Composition of Cells RevealedDocument5 pagesChemical Composition of Cells RevealedJustin Riel63% (8)
- 7 SolubilityDocument5 pages7 SolubilityJoeco Abay-abayNo ratings yet
- Identification and Structures of Selected AlgaeDocument15 pagesIdentification and Structures of Selected AlgaeValentinoDullSatin100% (1)
- Effect of PH On The Activity of Potato CatalaseDocument1 pageEffect of PH On The Activity of Potato CatalaseNathuAndrews50% (2)
- Lab Report Osmosis in A PotatoDocument3 pagesLab Report Osmosis in A Potatoapi-34769855750% (4)
- Vitamin CDocument4 pagesVitamin CHema JothyNo ratings yet
- Tilapia Dissection and Guide: Lab Questions #1: Tilapia Belong To What Class of Bony Fish?Document9 pagesTilapia Dissection and Guide: Lab Questions #1: Tilapia Belong To What Class of Bony Fish?Alain Salvador100% (1)
- Enzymes Lab Report - Activty 8Document6 pagesEnzymes Lab Report - Activty 8JengNo ratings yet
- CHM 3103 Lab # 3.1 ReportDocument5 pagesCHM 3103 Lab # 3.1 ReportRaja GokhulNo ratings yet
- Glucose OxidaseDocument42 pagesGlucose OxidaseShauqah Mawaddah0% (1)
- Final Report Chem - Acids, Bases, & SaltsDocument7 pagesFinal Report Chem - Acids, Bases, & SaltsCharmaine Uri0% (1)
- Semester-II Paper-VI: Computer Aided Drug Designing (CADD) : Practicals Pertaining To Above TopicsDocument12 pagesSemester-II Paper-VI: Computer Aided Drug Designing (CADD) : Practicals Pertaining To Above Topicschandan kumarNo ratings yet
- My Copyprotein Folding Virtual ActivityDocument7 pagesMy Copyprotein Folding Virtual Activityapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Experiment 6 - Enzymes (EDITED 2nd Sem 2019-2020)Document4 pagesExperiment 6 - Enzymes (EDITED 2nd Sem 2019-2020)Samantha Ysabelle AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- ProteinDocument16 pagesProteinRosnadia RosliNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of ProteinsDocument5 pagesIsolation and Characterization of ProteinsMiguel Sabillena100% (1)
- In Calibrating A 10Document4 pagesIn Calibrating A 10GrenlyKerehNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Color Reactions of AlbuminDocument6 pagesQualitative Color Reactions of AlbuminJennifer HerediaNo ratings yet
- Dihybrid ProblemDocument5 pagesDihybrid ProblemJohn Keir Pedregosa PasquinNo ratings yet
- Conclusions and Recommendations4Document1 pageConclusions and Recommendations4Lara Melissa Orense50% (2)
- Protein structure and denaturation experimentDocument11 pagesProtein structure and denaturation experimentJamielle Fuentes EliseoNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid & ProteinDocument9 pagesAmino Acid & ProteinMaryGraceVelascoFuentesNo ratings yet
- Iodine Test: Polysaccharides Color Reaction With IodineDocument2 pagesIodine Test: Polysaccharides Color Reaction With IodineAlexandra TarucNo ratings yet
- Written Report - Osmosis in Red Blood CellsDocument6 pagesWritten Report - Osmosis in Red Blood CellsmortbresnanNo ratings yet
- Potato Osmosis OMPDocument12 pagesPotato Osmosis OMPCalvin Hon100% (2)
- Qualitative Analysis of Carbohydrates: Materials RequiredDocument4 pagesQualitative Analysis of Carbohydrates: Materials RequiredCivil JeganNo ratings yet
- Post-Lab Ex 4Document3 pagesPost-Lab Ex 4Daniel Seth AndalNo ratings yet
- Colloids Experiment No. 2Document5 pagesColloids Experiment No. 2Chris K. Ramirez100% (1)
- Analytical ChemistryDocument26 pagesAnalytical ChemistryJohannesNo ratings yet
- Identify Common Anions (39Document7 pagesIdentify Common Anions (39addislibroNo ratings yet
- Covalent and Ionic Properties LabDocument6 pagesCovalent and Ionic Properties LabMadi WellsNo ratings yet
- 2 Water The Solvent For Biochemical ReactionsDocument68 pages2 Water The Solvent For Biochemical ReactionsSiej Go100% (1)
- Strawberry DNA Extraction LabDocument5 pagesStrawberry DNA Extraction Labjackhume4No ratings yet
- CBB4032 2Document38 pagesCBB4032 2db9021090100% (1)
- Lab-Synthesis and Analysis of AlumDocument2 pagesLab-Synthesis and Analysis of Alumhels245No ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument43 pagesReviewerTiffany LiuNo ratings yet
- Test For Aliphatic Hydrocarbons: Inorganic & Organic Chemistry (Laboratory)Document1 pageTest For Aliphatic Hydrocarbons: Inorganic & Organic Chemistry (Laboratory)Nowair Tuan100% (1)
- Polysaccharides: Types and FunctionsDocument21 pagesPolysaccharides: Types and FunctionsCemal SarwarNo ratings yet
- Identifying MacromoleculesDocument21 pagesIdentifying MacromoleculesMarkJasperCalabanoNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry CalculationsDocument7 pagesStoichiometry CalculationsDora Naj100% (1)
- Lab Properties of Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument4 pagesLab Properties of Ionic and Covalent Compoundsapi-4515686250% (1)
- Osmosis Lab ReportDocument5 pagesOsmosis Lab Reportapi-281921983No ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Laboratory Activity Sheet For Physical and Chemical Properties of ProteinsDocument5 pagesExperiment 2 - Laboratory Activity Sheet For Physical and Chemical Properties of ProteinsDelosreyes ChildrenNo ratings yet
- Biology Report (Experiment 1)Document2 pagesBiology Report (Experiment 1)djash9267% (3)
- Formal Report: Stability of ProteinsDocument7 pagesFormal Report: Stability of ProteinsQueenie Tenedero100% (2)
- Biology Lab - Biuret TestDocument7 pagesBiology Lab - Biuret TestZoe Bradshaw0% (1)
- Protein Folding Virtual ActivityDocument3 pagesProtein Folding Virtual Activityapi-524061079No ratings yet
- Protein Folding Virtual Activity 1Document5 pagesProtein Folding Virtual Activity 1api-522789883No ratings yet
- DC Week 5 PolypeptideDocument56 pagesDC Week 5 PolypeptideHifsa batoolNo ratings yet
- Immune System Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesImmune System Review Questionsapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Reviewing Mitosis Discussion QuestionsDocument3 pagesReviewing Mitosis Discussion Questionsapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Feedback MechanismDocument4 pagesFeedback Mechanismapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Model Two Show 1 Signaling PathwaysDocument1 pageModel Two Show 1 Signaling Pathwaysapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Overview Chapter 11 QuestionsDocument1 pageOverview Chapter 11 Questionsapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Inihibitors ReviewDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis Inihibitors Reviewapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 HWDocument5 pagesChapter 8 HWapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosphorylation Inhibition ActivityDocument3 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation Inhibition Activityapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Organism Energetics ReviewDocument2 pagesOrganism Energetics Reviewapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Cell Transport HWDocument3 pagesChapter 7 Cell Transport HWapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Respiration Diagram NewDocument3 pagesRespiration Diagram Newapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis ModelingDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis Modelingapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Autotrophs and Hetertrophs Making Macromolecules HWDocument4 pagesAutotrophs and Hetertrophs Making Macromolecules HWapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory Systemapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Water Potential Word Problems 2Document3 pagesWater Potential Word Problems 2api-521773978No ratings yet
- Cell Modeling 2Document3 pagesCell Modeling 2api-521773978No ratings yet
- Chapter 36 Water Potential HWDocument4 pagesChapter 36 Water Potential HWapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Nutrition Label Ap ProjectDocument5 pagesNutrition Label Ap Projectapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Ws 1Document3 pagesCell Organelle Ws 1api-521773978No ratings yet
- HW Proteins Enzymes 1Document2 pagesHW Proteins Enzymes 1api-521773978No ratings yet
- Why Are Cells So Small Virtual Lab 1Document2 pagesWhy Are Cells So Small Virtual Lab 1api-521773978No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 HW Review Introductory ChemistryDocument2 pagesChapter 2 HW Review Introductory Chemistryapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Updated Chapter 5 Macromlecules HW 1Document4 pagesUpdated Chapter 5 Macromlecules HW 1api-521773978No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Propteries of Water HWDocument2 pagesChapter 3 Propteries of Water HWapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Do Grasshoppers Sweat Note SheetDocument3 pagesDo Grasshoppers Sweat Note Sheetapi-521773978100% (4)
- BSC Biochemistry Syllabus CBCSDocument20 pagesBSC Biochemistry Syllabus CBCSRama Krishna SaiNo ratings yet
- Protein MaterialDocument61 pagesProtein MaterialAlyssa NesianandaNo ratings yet
- Crystallization and Drying of BromelainDocument120 pagesCrystallization and Drying of BromelainRavikant DevakateNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 14 Biomolecules PDFDocument19 pagesChemistry 14 Biomolecules PDFinfinilifeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 - Synthetic and Natural Organic PolymersDocument14 pagesChapter 25 - Synthetic and Natural Organic Polymersmaniz442100% (1)
- RNA Extraction: OverviewDocument3 pagesRNA Extraction: OverviewArturo BasantezNo ratings yet
- Al-Falah Group of Schools and Colleges Jhumra City CHP (2,3,4,5) Mcqs Time: 120 MintsDocument12 pagesAl-Falah Group of Schools and Colleges Jhumra City CHP (2,3,4,5) Mcqs Time: 120 MintsAhsan RazaNo ratings yet
- Major Biomolecules Types and FunctionsDocument4 pagesMajor Biomolecules Types and FunctionsDuaneNo ratings yet
- Information Theory in Molecular Biology: Christoph AdamiDocument30 pagesInformation Theory in Molecular Biology: Christoph AdamiNONAME69No ratings yet
- Protein-Nucleic Acid InteractionsDocument23 pagesProtein-Nucleic Acid InteractionsHelenNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Microbiology With Diseases Taxonomy 4th Edition BaumanDocument26 pagesTest Bank For Microbiology With Diseases Taxonomy 4th Edition Baumana790342823No ratings yet
- Answer Questions04Document5 pagesAnswer Questions04yo-cheng100% (1)
- Multiple-choice Questions on Organic Chemistry ConceptsDocument37 pagesMultiple-choice Questions on Organic Chemistry ConceptsTheo CaldasNo ratings yet
- Protein Isolation From Whole BloodDocument8 pagesProtein Isolation From Whole BloodShadia HeyariNo ratings yet
- A Fresh Look at The Ramachandran Plot and The Occurrence of Standard Structures in ProteinsDocument25 pagesA Fresh Look at The Ramachandran Plot and The Occurrence of Standard Structures in ProteinsWendy torresNo ratings yet
- The 20 Common Amino Acids That Build ProteinsDocument50 pagesThe 20 Common Amino Acids That Build ProteinsGurdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatics: Protein Structure Prediction: Chandrayani N.Rokde DR - Manali KshirsagarDocument5 pagesBioinformatics: Protein Structure Prediction: Chandrayani N.Rokde DR - Manali Kshirsagarpooja kuttyNo ratings yet
- Homology ModelingDocument22 pagesHomology ModelingBasab GhoshNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids, Proteins, and EnzymesDocument62 pagesAmino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymesendale gebregzabherNo ratings yet
- BSc Biochemistry Syllabus Covers Nutrition, Metabolism, EnzymesDocument32 pagesBSc Biochemistry Syllabus Covers Nutrition, Metabolism, EnzymesParthi ParthibanNo ratings yet
- 07 Nucleic Acids Test PDFDocument8 pages07 Nucleic Acids Test PDFUkjun JungNo ratings yet
- Free Study Materials for Competitive ExamsDocument12 pagesFree Study Materials for Competitive ExamsM. Amebari NongsiejNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesShilpaNo ratings yet
- Caiet BM MG Eng PDFDocument188 pagesCaiet BM MG Eng PDFИрина АндреевнаNo ratings yet