Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Major Gases in Atmosphere and Gas Laws
Uploaded by
Mi Cha Cou Ui0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views5 pagesThis document contains questions and explanations about gas laws and properties of gases. It begins by asking about the major gases in the atmosphere (nitrogen, oxygen, argon) and the greenhouse effect. It then discusses kinetic molecular theory and its assumptions to describe gas behavior. Several gas laws are covered, including Boyle's law relating pressure and volume at constant temperature, Charles' law relating volume and temperature at constant pressure, Gay-Lussac's law relating pressure and temperature at constant volume, and combined gas law. Concepts like partial pressures, molar volume, Henry's law of gas solubility, and density of gases are also addressed.
Original Description:
Original Title
gc 1 st
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains questions and explanations about gas laws and properties of gases. It begins by asking about the major gases in the atmosphere (nitrogen, oxygen, argon) and the greenhouse effect. It then discusses kinetic molecular theory and its assumptions to describe gas behavior. Several gas laws are covered, including Boyle's law relating pressure and volume at constant temperature, Charles' law relating volume and temperature at constant pressure, Gay-Lussac's law relating pressure and temperature at constant volume, and combined gas law. Concepts like partial pressures, molar volume, Henry's law of gas solubility, and density of gases are also addressed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views5 pagesMajor Gases in Atmosphere and Gas Laws
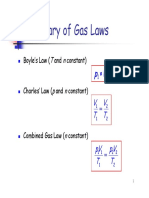
Uploaded by
Mi Cha Cou UiThis document contains questions and explanations about gas laws and properties of gases. It begins by asking about the major gases in the atmosphere (nitrogen, oxygen, argon) and the greenhouse effect. It then discusses kinetic molecular theory and its assumptions to describe gas behavior. Several gas laws are covered, including Boyle's law relating pressure and volume at constant temperature, Charles' law relating volume and temperature at constant pressure, Gay-Lussac's law relating pressure and temperature at constant volume, and combined gas law. Concepts like partial pressures, molar volume, Henry's law of gas solubility, and density of gases are also addressed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
1. What are the major gases in our 11.
How could you prove that air takes up
atmosphere? space and has mass?
Nitrogen, oxygen, argon Think about your Air-Extraordinaire Lab
2. What is the greenhouse effect and when answering this question.
what gases contribute? 12. Under what conditions do gases expand?
The greenhouse effect is the trapping of Gases expand to fit their container; gases
solar energy by gases in our atmosphere, also expand when heated
namely carbon dioxide and water vapor. 13. What is diffusion?
Gas molecules moving from areas of high
3. Explain how greenhouse gases relate
concentration to low concentration.
to burning hydrocarbons. 4. Measuring Gases and STP
The combustion of hydrocarbons creates
...
water vapor and carbon dioxide, both of
14. What four quantities are needed to
which are greenhouse gases.
accurately describe a gas?
2. The Kinetic-Molecular Theory and Real
Pressure, volume, amount of gas (moles),
Gases
temperature
...
15. Define pressure.
4. Define kinetic-molecular theory.
Number of collisions between gas
This theory describes the behavior of matter
molecules and the sides of the container
in terms of particles in motion: all matter is
16. The SI unit for pressure is
made of tiny particles that are constantly in
_____________________.
motion.
Pascals or kilopascals
5. Restate the six assumption of the kinetic-
17. How does changing the area of contact
molecular theory of gases in YOUR words.
affect the amount of pressure exerted by an
Particles in an ideal gas...
object?
-Are relatively far apart
Increasing area decreases pressure (inverse
-Are very tiny (almost no volume or mass)
relationship).
-Have elastic collisions,
18. A device used to measure atmospheric
-Are in constant, random, straight-line
pressure is called a __________________.
motion,
barometer
-Don't attract or repel each other,
19. An instrument used to measure the
-Have an average KE directly related to
pressure of an enclosed gas is called a
Kelvin temperature
__________________.
6. What is the difference between elastic
manometer
and non-elastic collisions?
20. List the three common units of pressure
An elastic collision is one in which no KE is
and their relationship to 1 atmosphere (atm).
lost; in non-elastic collisions, KE is lost.
1 atm = 101.325 kPa (kilopascal) = 760 mm
7. What is the difference between an ideal
Hg = 760 torr = 14.7 psi
and real gas?
21. What does STP stand for? What are the
Ideal gases act EXACTLY as the KMT
values?
describes the behavior of gases; real gases
Standard temp & pressure; 101.3 kPa and
deviate from this, theory in some way.
273 K
8. What conditions lead to the least ideal
22. When studying gases what unit should
behavior? Why?
you always use for temperature?
High pressures and low temps Polar
, Kelvin
molecules - b/c they are attracted to each
5. Boyle's Law
other, Large nonpolar molecules - b/c they
...
have more mass and volume
23. State Boyle's law to account for
3. Properties of Gases
pressure-volume changes in a gas.
...
At a constant temp and for a constant
9. What is compressibility?
amount of gas, as the volume increases,
The ability to reduce the volume of the gas
pressure of the gas will decrease; and as
10. Why are gases easier to compress than
volume decreases, pressure will increase.
solids or liquids?
24. Is this a direct or indirect relationship?
More empty space between the particles
Indirect (or inverse)
25. A mass of air occupies a volume of 5.7L ...
at a pressure of 0.52 atm. What is the new 35. State the combined gas law.
pressure if the same mass of air at the same P1V1/T1 = P2V2/2
temperature is transferred to a 2.0L 36. What is the volume at STP of a sample
container? of CO2 that has a volume of 75.0 mL at
(0.52 atm) (5.7 L) = P2(2.0 L) P2 = 1.5 atm 30.0°C and 680 mmHg?
26. The pressure on 2.5 L of N2O changes (680 mmHg)(75.0 mL) = (760 mmHg)V2
from 105 kPa to 40.5 kPa. If temperature V2 = 60. mL 303 K 273 K
does not change 9. Dalton's Law of Pressure
what will the new volume be?, (105 kPa) ...
(2.5 L) = (40.5 kPa) V2 V2 = 6.5 L 37. State Dalton's law of partial pressures.
6. Charles' Law The total pressure of a mixture of gasses is
... the sum of the partial pressures exerted by
27. State Charles' law to account for each of the gasses in the mixture
temperature-volume changes in a gas. 38. Determine the total pressure of a gas
At a constant pressure and for a constant mixture that contains CO
amount of gas, as the temperature increases, Ne, and He if the partial pressures of the
volume of the gas will increase; and as gases are PCO = 1.53 atm,, PNe = 0.82 atm,
temperature decreases, volume will and PHe = 0.34., Ptotal = PCO + PNe + PHe
decrease. Ptotal = 1.53 atm + 0.82 atm + 0.34 atm
28. Is this a direct or indirect relationship? Ptotal = 2.69 atm
Direct 10. Avogadro's Law and Mole-Mass-
29. Why is it important to convert the Volume relationship
temperature from Celsius to Kelvin? ...
Kelvin is the absolute temperature, with 0 39. What is Avogadro's hypothesis/law?
Kelvin measuring the temp. at which all Equal volumes of different gases contain the
molecular motion stops. same number of molecules, if they are at the
30. A volume of 20.0 L of O2 is warmed same temp and pressure.
from -30.0°C to 85.0°C. What is the new 40. Is this a direct or indirect relationship?
volume Direct
if the pressure is constant?, 20.0 L = V2 V2 41. What is the molar volume for any gas at
= 29.5 L, 243 K 358 K STP?
31. If a sample of gas occupies 6.8 L at 1 mol = 22.4 L
325oC 11. Henry's Law
what will its volume be at 25oC if the ...
pressure does not change?, 6.8 L = V2 V2 = 42. What is Henry's law?
3.4 L 598 K 298 K At a given temperature, the solubility of a
7. Gay-Lussac Law gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the
... pressure of the gas above the liquid.
32. State Gay-Lussac's law to account for 43. Is this a direct or indirect relationship?
temperature-pressure changes in a gas. Direct
At a constant volume and for a constant 44. The solubility of CO2 in a can of soda is
amount of gas, as the temperature increases, measured at about 0.11 g/L and the pressure
pressure of the gas will increase; and as over the solution is measured at about 276
temperature decreases, pressure will kPa. When the can is opened the pressure
decrease. drops to 100 kPa. What will the new
33. Is this a direct or indirect relationship? solubility be
Direct in g/L?, sol1 = sol2 0.11 g/L = sol2 sol2 =
34. A rigid (constant volume) container 0.04 g/L P1 P2 276 kPa 100 kPa
holds a gas at a pressure of 0.55 atm at a 12. Density of Gases
temperature of -100.0°C. What will the ...
pressure be when the temperature is 45. What is the formula for density?
increased to 200.0°C? d=m/v
0.55 atm 473 K P2 = 1.5 atm 373 K 46. One liter of a gas at STP has a mass of
8. Combined Gas Law 5.75g. What is the density?
5.75g/1L = d = 5.75 g/L = .00575g/mL Neon will have a higher rate of effusion
47. Calculate the density of Cl2 at STP. since it has a lower molar mass than argon.
What would it be at 27°C and 1 atm?
d at STP = mol mass d = 70.90 g/mol d =
3.17 g/L 22.4 L/mol 22.4 L/mol
To find density at non-STP conditions
(27°C and 1 atm)
you must determine what the volume of the
same amount of gas would be before
calculating density. Since 1 atm is STP, you
only need to worry about how the changing
temp will affect the volume (Charles's
Law)., 22.4 L = V2 V2 = 24.6 L 273 K
300.K d = 70.90 g/mol d= 2.88 g/L 24.6
L/mol
48. The molar mass of a gas is 20 g/mol.
Calculate the density at STP.
d = 20 g/mol d = 0.9 g/L 22.4 L/mol
13. Gas Stoichiometry
...
Write a balanced equation for the reaction
of aluminum with hydrochloric acid.
Answer the following:
...
49. How many moles of aluminum are
required to produce 5 mol hydrogen gas?
2 Al + 6 HCl ! 2 AlCl3 + 3 H2(g) 2 5 mol
H2 2 mol Al = 3 mol Al 3 mol H2
Pressure definition
50. How many liters of hydrogen gas can be
produced from 3 mol Al? =force per unit area
3 mol Al 3 mol H2 22.4 L H2 = 100 L H2 2 Common units for pressure
mol Al 1 mol H2 pressure = force/area
51. When 45.7 g of aluminum are burned in Derived unit for pressure
the presence of oxygen at 2.13 atm and 1 Pascal = Newtons per sq meters
45°C Why is mercury more suitable to
how many liters of O2 are used?___Al + use in a thermometer than water?
___O2 → __Al2O3, _4__Al + _3__O2 → Density....
__2_Al2O3 47.5g Al 1 mol Al 3 mol O2 Explain how a unit of length (mm
22.4 L O2 318 K 1 atm = 15.5 L O2 26.98 g Hg) can be used as unit of pressure.
Al 4 mol Al 1 mol O2 273 K 2.13 atm
760 mm Hg in a column = one
14. Diffusion and Graham's Law of Effusion
... atmosphere (p. 176)
52. What types of gas molecules typically State Boyle's Law and the
diffuse and effuse faster? conditions under which the law is
Ones with a low molar mass applicable. Include the units.
53. What is the difference between effusion The pressure of a fixed amount of gas at
and diffusion? a constant temperature is inversely
Diffusion: Spreading of gas molecules proportional to the volume of the gas:
throughout a container until evenly P1V1 = k = P2V2 .
distributed. Effusion: Passing of gas State Charles' & Gay-Lussac's
molecules through a tiny opening in a Law, the conditions under which it
container
is applicable, and the units.
54. Compare the rates of effusion of neon
and argon. The volume of a fixed amount of gas
maintained at a constant pressure is
directly proportional to the absolute The density of a gaseous organic
temperature of the gas: V1/T1 = k = compound is 3.38 g/L at 40 degrees
V2/T2 . Celsius and 1.97 atm. What is its
State Avogadro's Law, the molar mass?
conditions under which it is =44.1 g/mol
applicable, and the units. State Dalton's law of partial
-At a constant pressure and temperature, pressures.
the volume of a gas is directly The total pressure of a mixture of gases
proportional to the number of moles of is just the sum of the pressures that each
the gas present: k = RT/P gas would exert if it were present alone.
Manometer Total Pressure = P1 + P2 + P3 ....
--Device used to measure the pressure of Mole Fraction
gases other than the atmosphere. A dimensionless quantity that expresses
The Ideal Gas Equation the ration of the number of moles of one
PV = nRT at conditions 0 degrees C compound to the number of moles of all
(273.15 K) and 1 atm of pressure. compounds present.
1 mole of gas occupies .... volume? A sample of natural gas contains
=22.414 L at STP 8.24 moles of methane (CH4), 0.421
STP mole of ethane (C2H6), and 0.116
-Standard Temp & Pressure: 0 degrees C mole of propane (C3H8). If the total
and 1 atm pressure of the gases is 1.37 atm,
R in the ideal gas law what are the partial pressures of the
Proportionality Constant = 0.082057 gases?
L atm / K mol CH4: 1.29 atm, C2H6: 0.0657 atm, and
What is the volume (in liters) C3H8: 0.0181 atm.
occupied by 49.8 g of Hal at STP? What does SCUBA stand for?
=30.6 L Self-Contained Underwater Breathing
Calculate the volume in liters Apparatus
occupied by 2.12 moles of nitric SCUBA diving involves the direct
oxide (NO) at 6.54 atm and 76 application of which gas law?
degrees C. Dalton's partial pressures. (p. 200)
=9.29 L Kinetic molecular theory of gases
A sample of oxygen gas initially at Four assumptions: separated molecules,
0.97 atm is cooled from 21 degrees constant motion, neither attracted nor
C to -68 degrees C at a constant repulsed by each other, and KE
volume. What is its final pressure in proportional to the temp in K. (p. 203)
atm? Graham's Law of Diffusion
=0.68 atm Under the same conditions of T and P,
A gas initially at 4.0 L, 1.2 atm, and rates of diffusion for gases are inversely
66 degrees Celsius undergoes a proportional to the square roots of their
change so that its final volume and molar masses.
temp are 1.7 L and 42 degrees Effusion
Celsius. What is its final pressure? The process whereby a gas under
Assume the number of moles pressure escapes from one compartment
remains unchanged. of a container to another by passing
=2.6 atm through a small opening.
What is the density in g/L of van der Waals equation
uranium hexafluoride (UF6) at 779 Explains deviation for ideal behavior --
mmHg and 62 degrees Celsius? i.e., real gas behavior at the molecular
13.1 g/L level.
You might also like
- Week 7-8Document35 pagesWeek 7-8Muhammad Ubaid Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersFrom EverandPhysical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chap5 GasesDocument35 pagesChap5 GasesNur Afiqah Mohd ZakiNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Explained: Boyle's, Charles', and MoreDocument16 pagesGas Laws Explained: Boyle's, Charles', and MorepankajNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Technology 5Document52 pagesChemistry For Technology 5menishaNo ratings yet
- Anchor Guide GasesDocument6 pagesAnchor Guide GasesDaniel ZhangNo ratings yet
- GAS LAWS EXPLAINEDDocument19 pagesGAS LAWS EXPLAINEDralphNo ratings yet
- Gas Revsion NotesDocument9 pagesGas Revsion NotesbrosreaperNo ratings yet
- G10-Q4-WEEK1FINALDocument11 pagesG10-Q4-WEEK1FINALANALYN DEL CASTILLONo ratings yet
- Kelvin Temperature Scale and Gas Laws SummaryDocument10 pagesKelvin Temperature Scale and Gas Laws SummarySuperFly SmithNo ratings yet
- 5.states of Matter AK 2018-19Document12 pages5.states of Matter AK 2018-19XXXNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Module 1Document7 pagesUnit 4 Module 1Antonette FrankeNo ratings yet
- KMT and Boyles LawDocument67 pagesKMT and Boyles Lawpandoralistik1No ratings yet
- Understanding Gases and Gas LawsDocument43 pagesUnderstanding Gases and Gas LawsKathleen Kate MonsalveNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 - Module 2 Behavior of GasesDocument27 pagesQuarter 4 - Module 2 Behavior of GasesdepmodulefindderNo ratings yet
- Gas Law NotesDocument6 pagesGas Law NotesLloydDagsilNo ratings yet
- Gas_Law_Pt_1Document31 pagesGas_Law_Pt_1Berlin Wendy ReginaldeNo ratings yet
- General Physics1 Q2 W8 Module8 ThermodynamicsDocument23 pagesGeneral Physics1 Q2 W8 Module8 ThermodynamicsRegine Ann ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Differences between gas, liquid, and solid molecules explainedDocument26 pagesDifferences between gas, liquid, and solid molecules explainedJoshua PhillippsNo ratings yet
- 40 Chemistry1702951908Document62 pages40 Chemistry1702951908ilegbedionkNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 1Document10 pagesQ4 Week 1Claudie MabiniNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Subjective TypeDocument8 pagesStates of Matter Subjective TypePrajesh BiswasNo ratings yet
- 4 - State of Matter IDocument41 pages4 - State of Matter IHenry ChongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Gases Properties of Gases: Atmospheric Pressure or Barometric Pressure?Document15 pagesChapter 5 - Gases Properties of Gases: Atmospheric Pressure or Barometric Pressure?Hera EstoseNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Theory NotesDocument20 pagesKinetic Molecular Theory NotesPiolo JazulNo ratings yet
- Science Gas LawDocument27 pagesScience Gas LawAl Jean DelgadoNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Modelling A Gas - NewDocument58 pages3.2 Modelling A Gas - NewUlung Gondo Kusumo KhoeNo ratings yet
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET-CHEM 1 q1 Week 4Document8 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET-CHEM 1 q1 Week 4Jhude JosephNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Gas Laws Cut VersionDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Gas Laws Cut VersionbusyfireflyNo ratings yet
- CH Gas Laws NotesDocument6 pagesCH Gas Laws Notesapi-293306937No ratings yet
- Gases, Liquids, and Solids 7.1 Kinetic Molecular Theory of MatterDocument11 pagesGases, Liquids, and Solids 7.1 Kinetic Molecular Theory of MatterVanessa JabagatNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Unit 10: The Gas LawsDocument58 pagesChemistry: Unit 10: The Gas LawsDhea Angela A. CapuyanNo ratings yet
- Bicol University - The Gaseous State of Matter: Gas Laws & Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument32 pagesBicol University - The Gaseous State of Matter: Gas Laws & Kinetic Molecular TheoryAngelo Bon BalmesNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws LecDocument43 pagesGas Laws LecJune Francis AngNo ratings yet
- Gases CODocument26 pagesGases COLyndy PantaoNo ratings yet
- Gases and The Gas Laws PDFDocument2 pagesGases and The Gas Laws PDFMohammed Asif NNo ratings yet
- Properties of Gases: University of Zakho Collage of Education General Science DepartmentDocument16 pagesProperties of Gases: University of Zakho Collage of Education General Science DepartmentNihad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Module 7 General Physics 1 q2Document11 pagesModule 7 General Physics 1 q2Freya SalorNo ratings yet
- Summary of Gas Laws: P V P VDocument25 pagesSummary of Gas Laws: P V P VGabriel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Summary of Gas Laws: P V P VDocument25 pagesSummary of Gas Laws: P V P VFunny videosNo ratings yet
- Science 10: Melcs - Based Learning Activity SheetDocument4 pagesScience 10: Melcs - Based Learning Activity SheetTrisha Aizel BioNo ratings yet
- Basic Gas Law Notes 2017Document14 pagesBasic Gas Law Notes 2017Sreeja TipirneniNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument14 pagesGas LawsShahid DarNo ratings yet
- Learning+mtrl+6+gen Chem+2Document10 pagesLearning+mtrl+6+gen Chem+2cappuccino muffinNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Assignment AnswersDocument0 pagesUnit 3 Assignment AnswersRosanna LombresNo ratings yet
- Properties of gasDocument12 pagesProperties of gasRaghaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Gas LawsDocument10 pagesUnderstanding Gas LawsHazel AlconNo ratings yet
- EAS 1600 Fall 2018 Lab 03: The Ideal Gas Law + Heat TransferDocument22 pagesEAS 1600 Fall 2018 Lab 03: The Ideal Gas Law + Heat TransfersamNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws ExplainedDocument14 pagesGas Laws ExplainedJoela Faith Ming GongNo ratings yet
- IDEAL GAS LAWS AND EQUATIONSDocument6 pagesIDEAL GAS LAWS AND EQUATIONSRica ChavezNo ratings yet
- CHM 111 - States of MatterDocument81 pagesCHM 111 - States of MatterBABATIMILEYIN OLLANo ratings yet
- Learning Module: 1 MatterDocument8 pagesLearning Module: 1 MatterErika Magat CustodioNo ratings yet
- Gases and The Atmosphere: Robert Boyle 1627-1691. Jacques Charles 1746-1823. J. Charles 1783Document34 pagesGases and The Atmosphere: Robert Boyle 1627-1691. Jacques Charles 1746-1823. J. Charles 1783ade dosmariaNo ratings yet
- Gases and The Atmosphere: Robert Boyle 1627-1691. Jacques Charles 1746-1823. J. Charles 1783Document34 pagesGases and The Atmosphere: Robert Boyle 1627-1691. Jacques Charles 1746-1823. J. Charles 1783ade dosmariaNo ratings yet
- GasesDocument36 pagesGasesMarcus MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- Ideal and Real Gases: Properties and Reservoir TypesDocument15 pagesIdeal and Real Gases: Properties and Reservoir Typesعلي حميد زغير صحنNo ratings yet
- Combined Avogadros and Ideal Gas LawsDocument25 pagesCombined Avogadros and Ideal Gas Lawslevi0417No ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 3 of FSC Part IDocument69 pagesChemistry Chapter 3 of FSC Part IMuhammad HamzaNo ratings yet
- Test Ch.10: Multiple ChoiceDocument6 pagesTest Ch.10: Multiple ChoiceMj LeeNo ratings yet
- BIMx LogDocument1 pageBIMx LogMi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- Archdes Form &spaceDocument1 pageArchdes Form &spaceMi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- Photo Essay 3Document1 pagePhoto Essay 3Mi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- Engine LogDocument1 pageEngine LogMi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- Types of SurveyingDocument3 pagesTypes of SurveyingMi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- InstallDocument1 pageInstallbryamNo ratings yet
- DAUBA, Mica T. Bs Arch 2BDocument1 pageDAUBA, Mica T. Bs Arch 2BMi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution QDocument2 pagesWater Pollution QMi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- Development of Surveying InstrumentDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Surveying InstrumentMi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- SCHEDARCH1Document1 pageSCHEDARCH1Mi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- Tour Du Mont BlancDocument1 pageTour Du Mont BlancMi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- APA Style ResearchDocument4 pagesAPA Style ResearchMi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- The anatomy of the respiratory systemDocument2 pagesThe anatomy of the respiratory systemMi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- RPH Ass.Document3 pagesRPH Ass.Mi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- Water PollutionDocument3 pagesWater PollutionMi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution QDocument2 pagesWater Pollution QMi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- The anatomy of the respiratory systemDocument2 pagesThe anatomy of the respiratory systemMi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- 1996-Review of Contra Rotating Axial CompressorDocument10 pages1996-Review of Contra Rotating Axial CompressorLakshya KumarNo ratings yet
- Products and Technologies For All Your Application Needs, Today and TomorrowDocument579 pagesProducts and Technologies For All Your Application Needs, Today and TomorrowMarcioNo ratings yet
- NIRMAL PRODUCTS FOR PROCESS AND NATURAL GAS INDUSTRIESDocument8 pagesNIRMAL PRODUCTS FOR PROCESS AND NATURAL GAS INDUSTRIESConcept -CEPLNo ratings yet
- PRS09 TC V PDFDocument4 pagesPRS09 TC V PDFengp3077No ratings yet
- Industrial Refrigeration Control Valves: Catalog CC-11c/USDocument52 pagesIndustrial Refrigeration Control Valves: Catalog CC-11c/USzhyhhNo ratings yet
- B&G Sizing Cooling Tower Pumps and Piping TEH-275Document12 pagesB&G Sizing Cooling Tower Pumps and Piping TEH-275ChowKC03100% (3)
- T843603001X0F1Document43 pagesT843603001X0F1deva017No ratings yet
- Contoh Penawaran HargaDocument2 pagesContoh Penawaran HargaKurniawan FebryNo ratings yet
- Charles LawDocument9 pagesCharles LawShabina KhalidNo ratings yet
- Millennium Scroll SCD340AC01Document1 pageMillennium Scroll SCD340AC01Igor Reinberger TakahashiNo ratings yet
- Propulsion Systems ExplainedDocument40 pagesPropulsion Systems ExplainedShabeer830No ratings yet
- Pneurobotic ArmDocument15 pagesPneurobotic ArmYogi BhimaniNo ratings yet
- FAST-Mask PDF 2007 Issue 2Document2 pagesFAST-Mask PDF 2007 Issue 2pnsanatNo ratings yet
- Naval ships technical manual chapter on gasoline and JP-5 fuel systemsDocument160 pagesNaval ships technical manual chapter on gasoline and JP-5 fuel systemsDaveNo ratings yet
- Control Valve Specification SheetDocument1 pageControl Valve Specification SheetJuan Krloz CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Steam-Distillation ExperimentDocument3 pagesSteam-Distillation Experimentrachit rayNo ratings yet
- Vendor DataDocument6 pagesVendor DatasubudhiprasannaNo ratings yet
- Liquids and SolidsDocument68 pagesLiquids and SolidsPaul AniceteNo ratings yet
- High Pressure BoilersDocument3 pagesHigh Pressure BoilersRajendrakumar B VariaNo ratings yet
- Injection Well ProblemsDocument12 pagesInjection Well Problemsdriller2250% (2)
- CHE243 Thermodynamics Pressure DifferenceDocument2 pagesCHE243 Thermodynamics Pressure DifferenceChips AhoyNo ratings yet
- Fractional Distillation Lab ReportThe provided title is too long at 40 characters. Here is a concise, SEO-optimized title for the document:TITLE Lab Report: Fractional Distillation ExperimentDocument31 pagesFractional Distillation Lab ReportThe provided title is too long at 40 characters. Here is a concise, SEO-optimized title for the document:TITLE Lab Report: Fractional Distillation ExperimentAdekoya IfeoluwaNo ratings yet
- AE6011 Aero Engine MaintenanceDocument2 pagesAE6011 Aero Engine MaintenanceanandNo ratings yet
- Global Warming DebateDocument2 pagesGlobal Warming DebateAry WulanNo ratings yet
- Study Flow Boiling's PhasesDocument9 pagesStudy Flow Boiling's PhasesSamsung Note 9No ratings yet
- A1 4Document6 pagesA1 4Mohit PassiNo ratings yet
- Dual Fuel SystemDocument2 pagesDual Fuel Systemchdeepak96No ratings yet
- Reservoir Engineering Lecture Notes: G.C.EnyiDocument39 pagesReservoir Engineering Lecture Notes: G.C.EnyiRaimundoNo ratings yet
- ARO FlowDocument86 pagesARO FlowAnonymous z4Fe39jNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pumps TRGDocument35 pagesCentrifugal Pumps TRGsudhakarrajam2002No ratings yet
- Machinery Lubrication Technician (MLT) I and II Certification Exam GuideFrom EverandMachinery Lubrication Technician (MLT) I and II Certification Exam GuideRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataFrom EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Machine Learning and Data Science in the Oil and Gas Industry: Best Practices, Tools, and Case StudiesFrom EverandMachine Learning and Data Science in the Oil and Gas Industry: Best Practices, Tools, and Case StudiesPatrick BangertRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Practical Wellbore Hydraulics and Hole Cleaning: Unlock Faster, more Efficient, and Trouble-Free Drilling OperationsFrom EverandPractical Wellbore Hydraulics and Hole Cleaning: Unlock Faster, more Efficient, and Trouble-Free Drilling OperationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Gas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsFrom EverandGas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsFrom EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Industrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualFrom EverandIndustrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- Hydraulic Fracturing in Unconventional Reservoirs: Theories, Operations, and Economic AnalysisFrom EverandHydraulic Fracturing in Unconventional Reservoirs: Theories, Operations, and Economic AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Asset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresFrom EverandAsset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Integrity: Management and Risk EvaluationFrom EverandPipeline Integrity: Management and Risk EvaluationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Oil and Gas Pipelines and Piping Systems: Design, Construction, Management, and InspectionFrom EverandOil and Gas Pipelines and Piping Systems: Design, Construction, Management, and InspectionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (16)
- Biostratigraphic and Geological Significance of Planktonic ForaminiferaFrom EverandBiostratigraphic and Geological Significance of Planktonic ForaminiferaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Practical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationFrom EverandPractical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Essentials of Coating, Painting, and Lining for the Oil, Gas and Petrochemical IndustriesFrom EverandEssentials of Coating, Painting, and Lining for the Oil, Gas and Petrochemical IndustriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Asphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors: Theoretical and Practical ProspectsFrom EverandAsphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors: Theoretical and Practical ProspectsNo ratings yet
- A Practical Guide to Piping and Valves for the Oil and Gas IndustryFrom EverandA Practical Guide to Piping and Valves for the Oil and Gas IndustryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Risk Management in the Oil and Gas Industry: Offshore and Onshore Concepts and Case StudiesFrom EverandRisk Management in the Oil and Gas Industry: Offshore and Onshore Concepts and Case StudiesNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion: How Corporations and Governments Addicted the World to Oil and Subverted the AlternativesFrom EverandInternal Combustion: How Corporations and Governments Addicted the World to Oil and Subverted the AlternativesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Prevention of Valve Fugitive Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryFrom EverandPrevention of Valve Fugitive Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryNo ratings yet