Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Outline: Factors Influencing Muscle Action
Uploaded by
Theodor MoldoveanuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Outline: Factors Influencing Muscle Action
Uploaded by
Theodor MoldoveanuCopyright:
Available Formats
Outline
revise functional anatomy of:
– tibialis posterior and anterior
– triceps surae
– peroneals
– digital musculature
manual muscle testing
– grading system
Muscles: testing and Function video (program
5) by Florence Kendall
– BUND AV Reserve 617.58075
– Reappraisal of most important muscles to test
Lecture & Video
Factors influencing muscle action
Outline
Need to be able to clinically perform position of tendinous insertion relative to
manual muscle testing of the joint axis
aforementioned muscles lever arm
– Assumed knowledge for 3rd year clinics variation in joint axis position (eg: medially
– Clinic tutorial soon deviated STJ axis)
position of adjacent joint (ie: AJ DF or PF
affects muscle action at STJ)
Factors influencing muscle action
Subtalar joint moment arms
Tibialis posterior -19.2 Factors
Flexor hallucis longus
Triceps surae
-7.8
-5.3
influencing
Tibialis anterior -3.8 muscle action
Peroneus brevis 20.5
Peroneus longus 21.8
from Klein et al (1996) Clinical Biomechanics 29: 21-30.
Tibialis anterior
Tibialis anterior
origin: proximal 2/3 of function
anteriolateral surface of tibia – decelerates pronation and plantarflexion from HC
and interosseus membrane
– toe clearance during swing phase
insertion: dorsal aspect of
base of first ray pathology
actions: – weak: foot drop, XS pronation
– contracture: supinated foot
– dorsiflexes AJ
– supinates long. axis MTJ
– supinates STJ
Tibialis posterior Tibialis posterior
origin: posterior,
proximal tibia function
insertion: pl. surf. of – decelerates STJ pronation from HC
all tarsal bones – supinates STJ during propulsion
except the talus
actions: pathology
– stabilizes midfoot – weak: XS pronation > pes planus
– major supinator / – contracture: supinated foot
anti-pronator
Triceps surae Triceps surae
consists of actions:
gastrocnemius and
– plantarflexes AJ
soleus
– supinates a supinated STJ, pronates a
origin: gastrocs: above
pronated STJ
femoral condyles,
soleus: soleal line of function
tibia and fibula – active from FFL to TO for propulsion
insertion: achilles pathology
tendon into posterior
– contracture: muscular equinus
aspect of calcaneus
Peroneals Peroneals
origin: lateral aspect of fibula
insertion:longus - base of first ray, brevis -
styloid process of 5th met.
actions:
– PL: stabilises forefoot, plantarflexes first
ray, pronates STJ
– PB: pronates STJ and OA MTJ
Peroneals Digital musculature
long flexors /
function extensors insert
– stabilize forefoot prior to heel lift into distal phalanx
pathology and produce
motion at DIPJ
– weak: overpowering of supinators > supination
deformity short flexors /
– contracture: pes planus extensors insert
into intermediate
phalanx and
produce motion at
PIPJ
Digital Musculature Digital Musculature
interossei: dorsal and plantar layer, originate
from met. shafts and insert into proximal
phalanges
– act to stabilise proximal phalanges in transverse
and sagittal planes
lumbricals: originate from medial side of FDL
tendon slips, insert into base of proximal
phalanx
– plantarflex proximal phalanx and straighten pull of
FDL
Manual muscle testing Clinical applications...
very useful, under-emphasised clinical – post-surgical
technique within podiatry shortening
Tendon tenotomy (eg: HAV)
clinical applications:
– to determine muscles affected by – post-traumatic weakness
neuromuscular conditions such as CP, eg: peroneal weakness post inversion
polio, CVA ankle sprain
– congenital shortening of muscle groups – tibialis posterior dysfunction
◊ ◊ ◊ Basic principles ◊ ◊ ◊ Grading system (as per Kendall)
test position Normal ++++
– one-joint muscles: end ROM position Good +++
– two-joint muscles: half-way through ROM Fair ++
stabilise proximal structures Poor +
apply resistance: Zero 0
– gradually, to let patient ‘get set and hold’, then
uniformly apply resistance Normal:can overcome > resistance than ‘good’
– directly opposite to line of action of the muscle Good: against slight resistance & gravity
always look for ‘assistance’ from other Fair: can raise part against gravity, full ROM
muscles Poor: partial ROM against gravity
Zero: no contraction felt
Summary Video
Need to remember: Lower Extremity Muscles
origin and insertion of lower limb muscles – BUND AV Reserve Video
effect of contraction at AJ, STJ, MTJ, MPJs – 617.585
effects of contracture and weakness – BRN 810506
– agonists and antagonists
grading system
Always revise anatomy
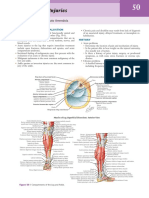
Tibialis Anterior Tibialis Posterior
Pt: supine/sitting Pt: supine with extremity in
Fixn: examiner stabilises foot lateral rotation
just above AJ Fixn: examiner stabilises leg
Test: DF of AJ and inversion above the AJ
of the foot, without extension Test: inversion of the foot with
of hallux PF of the AJ
Pressure: against dorso- Pressure: against the medio-
medial side of the foot, in the plantar surface of the foot, in
direction of PF of the AJ and the direction of DF of the AJ
eversion of the foot and eversion of the foot
Peroneals 30 second brief testing
Pt: supine with extremity
medially rotated
Fixn: examiner stabilises foot
above AJ
QuickTime™ and a
Test: eversion of the foot with Video decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
PF of the AJ
Pressure: against the lateral
border and sole of the foot in
the direction inversion of the
foot and DF of the AJ. To
more specifically test PL,
attempt to DF the 1st ray
You might also like
- ELBOWDocument7 pagesELBOWPhoebe DemegilloNo ratings yet
- Functional Movement Presentation-Jostone4Document43 pagesFunctional Movement Presentation-Jostone4paulNo ratings yet
- Muscle Chart Body MapDocument4 pagesMuscle Chart Body MapmaspogiakosayoNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Application SolutionsDocument3 pagesShoulder Application SolutionsDNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of Foot and AnkleDocument34 pagesBiomechanics of Foot and AnkleKanwal KhanNo ratings yet
- Length Tension Testing Book 1, Lower Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy TechniquesFrom EverandLength Tension Testing Book 1, Lower Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy TechniquesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Gait Analysis: Prerequisite of Normal GaitDocument4 pagesGait Analysis: Prerequisite of Normal GaitKieran Levi100% (1)
- Length Tension Testing Book 2, Upper Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy TechniquesFrom EverandLength Tension Testing Book 2, Upper Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy TechniquesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Total Hip Arthroplasty - Medical and Biomedical Engineering and Science Concepts-Springer (2022)Document271 pagesTotal Hip Arthroplasty - Medical and Biomedical Engineering and Science Concepts-Springer (2022)drbane123100% (3)
- Theme 3. Lumbopelvic Motor Control, Instability and PainDocument9 pagesTheme 3. Lumbopelvic Motor Control, Instability and PainThéo BattalianNo ratings yet
- Anterior and Medial Aspects of The Thigh andDocument23 pagesAnterior and Medial Aspects of The Thigh andHarshilNo ratings yet
- IASTM and Stretching Plantar FasciitisDocument11 pagesIASTM and Stretching Plantar FasciitisNicolás Ayelef ParraguezNo ratings yet
- Ijspt-Biomechanics and Pathomechanics of The Patellofemoral JointDocument11 pagesIjspt-Biomechanics and Pathomechanics of The Patellofemoral JointDevi MigiekaNo ratings yet
- Fascia and Fascia Lines PDFDocument7 pagesFascia and Fascia Lines PDFBeta LisboaNo ratings yet
- Hip Application SolutionsDocument3 pagesHip Application SolutionsDNo ratings yet
- Ankle Joint and Ligament AnatomyDocument5 pagesAnkle Joint and Ligament AnatomyHafizah HoshniNo ratings yet
- USGDocument337 pagesUSGambar mustika100% (2)
- WWW Energygatesqigong UsDocument10 pagesWWW Energygatesqigong UsspiraldaoNo ratings yet
- ICF-Ankle Trimalleolar FractureDocument18 pagesICF-Ankle Trimalleolar FracturedvenumohanNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of The Painful Ankle Foot Part 1Document25 pagesDiagnosis and Management of The Painful Ankle Foot Part 1Kamila PeñaililloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Function, and Rehabilitation of The Popliteus Musculotendinous ComplexDocument16 pagesAnatomy, Function, and Rehabilitation of The Popliteus Musculotendinous ComplexJacinta SeguraNo ratings yet
- Jumper's Knee: Joseph M. David, MS, Pt1Document5 pagesJumper's Knee: Joseph M. David, MS, Pt1Hanako HanabiNo ratings yet
- The Patho-Mechanics of LBPDocument32 pagesThe Patho-Mechanics of LBPydpNo ratings yet
- 10.popliteus Musculotendinous ComplexDocument15 pages10.popliteus Musculotendinous Complex黃郁庭No ratings yet
- Jospt 1999 29 2 93Document13 pagesJospt 1999 29 2 93Eray YüceelNo ratings yet
- UseofMulliganSNAGs PDFDocument1 pageUseofMulliganSNAGs PDFMestereaga AlinNo ratings yet
- Special TestsDocument5 pagesSpecial TestsVienGameNo ratings yet
- Effect of Sensorimotor Insoles On Lower Limbs Muscles Activity in People With Flexible FlatfootDocument13 pagesEffect of Sensorimotor Insoles On Lower Limbs Muscles Activity in People With Flexible FlatfootOndřej LaštovičkaNo ratings yet
- Muscle Test Summary - 230613 - 232607Document14 pagesMuscle Test Summary - 230613 - 232607عثمان عابدينNo ratings yet
- Running Gait Analysis and Biomechanics.2Document2 pagesRunning Gait Analysis and Biomechanics.23i4.mastersNo ratings yet
- Ankle and Foot Injuries in Sports MedicineDocument107 pagesAnkle and Foot Injuries in Sports MedicinebaoNo ratings yet
- Cruris FractureDocument9 pagesCruris FractureNindya KiranaNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Management of Plantar FasciitisDocument40 pagesEvidence Based Management of Plantar FasciitisMohamed ElMeligieNo ratings yet
- Knee Pain H and P PDFDocument6 pagesKnee Pain H and P PDFKKNo ratings yet
- 3-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging EvaluationDocument9 pages3-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging EvaluationAtlas FizyoterapiNo ratings yet
- Plantar ReflexDocument5 pagesPlantar ReflexrazakmdpaedNo ratings yet
- Muscles: If You Want To Know If Your Brain Is Flabby, Feel Your LegsDocument23 pagesMuscles: If You Want To Know If Your Brain Is Flabby, Feel Your LegsTovar GermanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 5-6Document10 pagesAnatomy 5-6Gladys Mae S. BañesNo ratings yet
- 41-Article Text-59-1-10-20190211Document3 pages41-Article Text-59-1-10-20190211Faishol Reza AdiyaksaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Flatfoot Model The Contribution of Dynamic LoadingDocument6 pagesExperimental Flatfoot Model The Contribution of Dynamic LoadingGeorge FernandoNo ratings yet
- 5 Biomechanics of The Vertebral Column 2Document40 pages5 Biomechanics of The Vertebral Column 2Daniel PereiraNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb OrthosisDocument47 pagesUpper Limb OrthosisPraneethaNo ratings yet
- Lateral - Ankle Reconstruction ProtocolDocument5 pagesLateral - Ankle Reconstruction ProtocolNovaria PuspitaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Biomechanics of The HipDocument8 pages2016 Biomechanics of The HipilanNo ratings yet
- PT3 ROM-GonioDocument3 pagesPT3 ROM-Gonioim. EliasNo ratings yet
- Makalah Pleno Blok 5 Skenario 4Document12 pagesMakalah Pleno Blok 5 Skenario 4Anisa Aulia ReffidaNo ratings yet
- Exercise Technique: The Long-Lever Posterior-Tilt PlankDocument2 pagesExercise Technique: The Long-Lever Posterior-Tilt Plankdejvidveb1988No ratings yet
- A Functional Approach To The Treatment of TFCC Problems KroonDocument16 pagesA Functional Approach To The Treatment of TFCC Problems KroonLaineyNo ratings yet
- Ankle and Leg Injuries: John E. Femino and Annunziato AmendolaDocument9 pagesAnkle and Leg Injuries: John E. Femino and Annunziato Amendolanayab kanwalNo ratings yet
- Jospt 1995 21 5 277Document6 pagesJospt 1995 21 5 277GERARDO TORRES RUIZNo ratings yet
- 1-5-22 OMM Repro Considerations MasterDocument67 pages1-5-22 OMM Repro Considerations MasterTanner HancockNo ratings yet
- Ankle Evaluation FormDocument7 pagesAnkle Evaluation FormselcukhalitNo ratings yet
- Makalah Pleno Blok 5 Skenario 4Document11 pagesMakalah Pleno Blok 5 Skenario 4Anisa Aulia ReffidaNo ratings yet
- Rectus Femoris in Gait CycleDocument5 pagesRectus Femoris in Gait CycleanjelikaNo ratings yet
- LAB12 MUSCLowerDocument4 pagesLAB12 MUSCLowerBechris BambiNo ratings yet
- Knee AnatomyDocument15 pagesKnee Anatomysamiamehboob786No ratings yet
- Jospt 1995 21 5 277Document10 pagesJospt 1995 21 5 277GerardoNo ratings yet
- Biomechanic of Foot PDFDocument8 pagesBiomechanic of Foot PDFMichealowen BabygoalNo ratings yet
- Biomechanic of FootDocument8 pagesBiomechanic of FootMichealowen BabygoalNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledFahim Abarar KhanNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Long Versus Short Pectoralis Minor Resting Length On Scapular Kinematics in Healthy IndividualsDocument12 pagesThe Effect of Long Versus Short Pectoralis Minor Resting Length On Scapular Kinematics in Healthy IndividualsAmit DhawanNo ratings yet
- Noi Neurodynamics Handbook Peroneal NerveDocument8 pagesNoi Neurodynamics Handbook Peroneal NerveGizem BulutNo ratings yet
- Ankle Instab Presentation and ManagementDocument7 pagesAnkle Instab Presentation and Managementfahmiatul lailiNo ratings yet
- Patellofemoral Arthralgia Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD)Document4 pagesPatellofemoral Arthralgia Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD)Carlos GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Principles of Manual Medicine for Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction: Arthrokinematic Approach-Hakata MethodFrom EverandPrinciples of Manual Medicine for Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction: Arthrokinematic Approach-Hakata MethodShigehiko KatadaNo ratings yet
- Technique of Internal Fixation of Fractures 1st 1965Document280 pagesTechnique of Internal Fixation of Fractures 1st 1965nguyen namNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Unit Test Lumhs 2007Document2 pagesAnatomy Unit Test Lumhs 2007Dr-Irfan HabibNo ratings yet
- Pawan MuktasanaDocument3 pagesPawan MuktasanaArun Kumar UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- 2009 GlosarioDocument10 pages2009 GlosarioVíctor Muñoz LópezNo ratings yet
- Manual Muscle Test Handout by DR Chaman LalDocument6 pagesManual Muscle Test Handout by DR Chaman LalChaman Lal KarotiaNo ratings yet
- What Is Osteogenesis ImperfectaDocument2 pagesWhat Is Osteogenesis ImperfectaVajiha TahirNo ratings yet
- CPT Session 1 - GMFADocument23 pagesCPT Session 1 - GMFAAgrashek TiwariNo ratings yet
- Pinky - Plantar FasciitisDocument34 pagesPinky - Plantar FasciitisRavindra choudharyNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W1Document6 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W1Shiela RoaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Congenital AnomaliesDocument40 pagesPediatric Congenital AnomaliesHzm MusNo ratings yet
- Flexor & Extensor RetinaculumDocument13 pagesFlexor & Extensor RetinaculumInsyirah Johari100% (1)
- Biomechanics of The Human SpineDocument5 pagesBiomechanics of The Human SpineLusian VissNo ratings yet
- BPT 2nd Practical Manual SampleDocument112 pagesBPT 2nd Practical Manual Samplezikra annNo ratings yet
- DeepSquat Review Barbell Daily 3-27-15Document11 pagesDeepSquat Review Barbell Daily 3-27-15adituzlaNo ratings yet
- Body Condition Score Chart Dogs - 0Document1 pageBody Condition Score Chart Dogs - 0dacaNo ratings yet
- Colgan 2016Document6 pagesColgan 2016Wahyu InsanNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle StructureDocument38 pagesSkeletal Muscle Structuretoyy100% (1)
- Approach To Arthritis PatientDocument20 pagesApproach To Arthritis Patientapi-3716867No ratings yet
- Chapter-20 Locomotion and Movement: Is The Voluntary Movement of An Individual From One Place ToDocument8 pagesChapter-20 Locomotion and Movement: Is The Voluntary Movement of An Individual From One Place ToLishaNo ratings yet
- Phy2 13560 PDFDocument6 pagesPhy2 13560 PDFMalcolmNo ratings yet
- Iso Stick GuideDocument4 pagesIso Stick GuideanthNo ratings yet
- Juvenile Osteology ReportDocument2 pagesJuvenile Osteology ReportKamren MoradiNo ratings yet
- Anaphy - Rabe - ReviewerDocument19 pagesAnaphy - Rabe - ReviewerAyessa Marie BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Froments and Jeanne SignDocument1 pageFroments and Jeanne SignjauNo ratings yet
- Faq PRP CebuDocument2 pagesFaq PRP CebuAllanSalardaAdemNo ratings yet