Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Marik Covid Protocol Summary
Uploaded by
elasticemperorOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Marik Covid Protocol Summary
Uploaded by
elasticemperorCopyright:
Available Formats
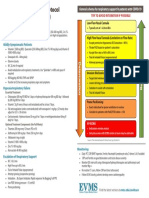
Critical Care COVID-19 Management Protocol General schema for respiratory support in patients with COVID-19
(updated 7-09-2020) TRY TO AVOID INTUBATION IF POSSIBLE
Low-Flow Nasal Cannula
Prophylaxis
■ Typically set at 1-6 Liters/Min
While there is very limited data (and none specific for COVID-19), the following “cocktail” may
have a role in the prevention/mitigation of COVID-19 disease.
High Flow Nasal Cannula
■ Vitamin C 500 mg BID and Quercetin 250-500 mg BID
■ Accept permissive hypoxemia (O2 Saturation > 86%)
■ Zinc 75-100 mg/day
■ Titrate FiO2 based on patient’s saturation
■ Melatonin (slow release): Begin with 0.3mg and increase as tolerated to 2 mg ■ Accept flow rates of 60 to 80 L/min
at night ■ Trial of inhaled Flolan (epoprostenol)
■ Vitamin D3 1000-4000 u/day ■ Attempt proning (cooperative proning)
■ Optional: Famotidine 20-40mg/day
Deterioration
Mildly Symptomatic patients (at home): Invasive Mechanical Ventilation
Recovery
■ Vitamin C 500mg BID and Quercetin 250-500 mg BID ■ Target tidal volumes of ~6 cc/kg
■ Zinc 75-100 mg/day ■ Lowest driving pressure and PEEP
■ Sedation to avoid self-extubation
■ Melatonin 6-12 mg at night (the optimal dose is unknown)
■ Trial of inhaled Flolan
■ Vitamin D3 2000-4000 u/day
■ Optional: Ivermectin 150-200ug/kg (single dose) Prone Positioning
■ Optional: ASA 81/325mg/day ■ Exact indication for prone ventilation is unclear
■ Optional: Famotidine 20-40mg/day ■ Consider in patients with PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 150
In symptomatic patients, monitoring with home pulse oximetry is recommended.
Ambulatory desaturation below 94% should prompt hospital admission SALVAGE THERAPIES
Mildly Symptomatic patients (on floor): ■ High dose corticosteroids; 120 -250 mg methylprednisolone q 6-8 hourly
■ Plasma exchange
■ Vitamin C 500 mg PO q 6 hourly and Quercetin 250-500 mg BID (if available)
■ “Half-dose” rTPA
■ Zinc 75-100 mg/day ■ Siltuximab and Tocilizumab (IL-6 inhibitors)
■ Melatonin 6-12 mg at night (the optimal dose is unknown) ■ ?? ECMO < 60 yrs. and no severe comorbidities/organ failure
■ Vitamin D3 2000-4000 u/day
■ Enoxaparin 60 mg daily ■ Optional: Ivermectin 150-200 ug/kg (single dose)
■ Famotidine 40mg daily (20mg in renal impairment) ■ N/C 2L /min if required (max 4 L/min; consider early t/f to ICU for escalation of care).
■ Methylprednisolone 40 mg q 12 hourly; increase to 80 mg q 12 if poor response ■ T/f EARLY to the ICU for increasing respiratory signs/symptoms and arterial
■ Optional: Remdesivir 200mg D1 then 100mg daily for 9 days. desaturations.
continued on next page
Find the latest version at evms.edu/covidcare
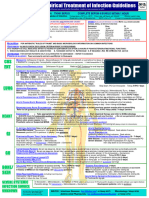
Critical Care COVID-19 Management Protocol
(updated 6-17-2020)
Respiratory symptoms (SOB; hypoxia- requiring N/C ≥ 4 L min:
admit to ICU): 15. Escalation of respiratory support; See General Schema for Respiratory
Support in Patients with COVID-19.
Essential Treatment (dampening the STORM)
Salvage Treatments
1. Methylprednisolone 80 mg loading dose then 40 mg q 12 hourly for at
least 7 days and until transferred out of ICU. In patients with poor response,
■ Plasma exchange. Should be considered in patients with progressive
increase to 80 mg q 12 hourly. oxygenation failure despite corticosteroid therapy. Patients may require
up to 5 exchanges.
2. Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) 3g IV q 6 hourly for at least 7 days and/or until
transferred out of ICU. Note caution with POC glucose testing.
■ High dose corticosteroids; 120 mg methylprednisolone q 6-8 hourly
3. Full anticoagulation: Unless contraindicated we suggest FULL
■ Siltuximab and Tocilizumab (IL-6 inhibitors)
anticoagulation (on admission to the ICU) with enoxaparin, i.e 1 mg kg s/c ■ Convalescent serum; the role and timing of convalescent serum are
q 12 hourly (dose adjust with Cr Cl < 30mls/min). Heparin is suggested with uncertain.
CrCl < 15 ml/min. Treatment of Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS)
Note: Early termination of ascorbic acid and corticosteroids will likely result in a ■ A sub-group of patients will develop MAS. A ferritin > 4400 ng/ml
rebound effect.
is considered diagnostic of MAS. Other diagnostic features include
Additional Treatment Components (the Full Monty) increasing AST/ALT and increasing CRP.
4. Melatonin 6-12 mg at night (the optimal dose is unknown). ■ Methylprednisolone 120 mg q 6-8 hourly for at least 3 days, then wean
5. Famotidine 40mg daily (20mg in renal impairment) according to Ferritin, CRP, AST/ALT. Ferritin should decrease by at least
6. Vitamin D 2000-4000 u/day 15% before weaning corticosteroids.
7. Thiamine 200mg IV q 12 hourly Monitoring:
8. Simvastatin 80 mg/day (caution drug-drug interactions) or Atorvastatin ■ On admission: PCT, CRP, IL-6, BNP, Troponins, Ferritin, Neutrophil-
80mg/day Lymphocyte ratio, D-dimer and Mg.
9. Magnesium: 2 g stat IV. Keep Mg between 2.0 and 2.4 mmol/l. Prevent ■ Daily: CRP, Ferritin, D-Dimer and PCT. CRP and Ferritin track disease
hypomagnesemia (which increases the cytokine storm and prolongs Qtc). severity closely (although ferritin tends to lag behind CRP).
10. Optional: Azithromycin 500 mg day 1 then 250 mg for 4 days ■ Thromboelastogram (TEG) in patients with high D-dimer and repeated as
indicated.
11. Optional: Remdesivir, 200 mg IV loading dose D1, followed by 100mg day IV
for 9 days ■ In patients receiving IV vitamin C, the Accu-Chek™ POC glucose monitor
will result in spuriously high blood glucose values. Therefore, a laboratory
12. Broad-spectrum antibiotics if superadded bacterial pneumonia is suspected
glucose is recommended to confirm the blood glucose levels
based on procalcitonin levels and resp. culture (no bronchoscopy).
Post ICU management
13. Maintain EUVOLEMIA
a. Enoxaparin 40-60 mg s/c daily c. Vitamin C 500 mg PO BID
14. Early norepinephrine for hypotension.
b. Methylprednisone 40 mg day, d. Melatonin 3-6 mg at night
then wean slowly
Find the latest version at evms.edu/covidcare Developed and updated by Paul Marik, MD, Chief of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, VA
You might also like
- Marik Covid Protocol Summary PDFDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol Summary PDFJody VivasNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol SummaryInternos YopalNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol Summaryshubham rathodNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol SummaryCamille05No ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol SummaryDocument2 pagesMarik Covid Protocol SummaryCaterina PrepelitaNo ratings yet
- Marik Covid Protocol Summary PDFDocument1 pageMarik Covid Protocol Summary PDFCiuvat Dumitru ValentinNo ratings yet
- FRONT LINE COVID-19 CRITICAL CARE ALLIANCE HOSPITAL TREATMENT PROTOCOLDocument2 pagesFRONT LINE COVID-19 CRITICAL CARE ALLIANCE HOSPITAL TREATMENT PROTOCOLBhanu Kumar100% (1)
- Hospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Document4 pagesHospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Adrian BoboceaNo ratings yet
- CCF IpDocument1 pageCCF IpBryan FjbNo ratings yet
- Hospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Document2 pagesHospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Nandor KissNo ratings yet
- FRONT LINE COVID-19 CRITICAL CARE ALLIANCE PROTOCOLSDocument2 pagesFRONT LINE COVID-19 CRITICAL CARE ALLIANCE PROTOCOLSCornel ComanNo ratings yet
- Farma StrokeDocument37 pagesFarma StrokeDAHLIANo ratings yet
- FLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDocument3 pagesFLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDavid GrayNo ratings yet
- FLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDocument3 pagesFLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHJhonn BlackNo ratings yet
- FLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHDocument3 pagesFLCCC Alliance MATHplus Protocol ENGLISHfernandohNo ratings yet
- COVID MX BsmmuDocument2 pagesCOVID MX BsmmuNuhiat NahreenNo ratings yet
- CNS: Ent:: Review Antibiotic Therapy Daily - Can You: Stop? Switch? Simplify? or State Duration?Document1 pageCNS: Ent:: Review Antibiotic Therapy Daily - Can You: Stop? Switch? Simplify? or State Duration?Fitri RachmadaniNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord CompressionDocument4 pagesSpinal Cord Compressionian3yeung-2No ratings yet
- MX Protocol Book FinalDocument42 pagesMX Protocol Book FinalPawan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Amiodarone Mechanism, Uses, Dosing & MonitoringDocument10 pagesAmiodarone Mechanism, Uses, Dosing & MonitoringsarahhhNo ratings yet
- Revised COVID 19 SARS-COV2 Treatment Protocol - FinalDocument6 pagesRevised COVID 19 SARS-COV2 Treatment Protocol - FinalupsahuNo ratings yet
- STEMI NotesDocument8 pagesSTEMI NotesIzzul HafiyNo ratings yet
- VTE-Prophylaxis-Protocol - MOHDocument13 pagesVTE-Prophylaxis-Protocol - MOHreham ONo ratings yet
- Antibiotic hospital manDocument1 pageAntibiotic hospital manarshiya.manasekiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Cases Pharmacology PDFDocument7 pagesClinical Cases Pharmacology PDFAnkur HazraNo ratings yet
- NICU Drugs GuideDocument49 pagesNICU Drugs GuideArhanNo ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms Adult 2010Document12 pagesACLS Algorithms Adult 2010anon_336736395No ratings yet
- Lab 11 AntianginalDocument4 pagesLab 11 AntianginalanaNo ratings yet
- Anti-Anginal DrugsDocument39 pagesAnti-Anginal Drugspoonam rana100% (1)
- ANTI-ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS Veterinary PharmacologyDocument5 pagesANTI-ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS Veterinary PharmacologyljramosNo ratings yet
- Medical TherapyDocument6 pagesMedical Therapyvinay reddyNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulation strategies for COVID-19 patients at BMCDocument1 pageAnticoagulation strategies for COVID-19 patients at BMCAvinash KumbharNo ratings yet
- Nitrates andDocument61 pagesNitrates andMrunalini DandamudiNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation TDDocument6 pagesAtrial Fibrillation TDapi-594366475No ratings yet
- COVID-19 Protocol by EVMSDocument13 pagesCOVID-19 Protocol by EVMSKrishnamurthi CG100% (1)
- EVMS Critical Care COVID-19 ProtocolDocument17 pagesEVMS Critical Care COVID-19 ProtocolInternos YopalNo ratings yet
- Medication Administration PolicyDocument76 pagesMedication Administration PolicyJully GaciasNo ratings yet
- Treatment Protocol Covid-19Document4 pagesTreatment Protocol Covid-19Shiv singhNo ratings yet
- Mild Moderate Severe Clinical Criteria: Covid ProtocolDocument4 pagesMild Moderate Severe Clinical Criteria: Covid ProtocolSiaNo ratings yet
- Acls Algorithms 2012Document12 pagesAcls Algorithms 2012kivuNo ratings yet
- LBL DoneDocument6 pagesLBL DoneShoaib KhatikNo ratings yet
- Drugs in PregnancyDocument40 pagesDrugs in PregnancyhkkanhaNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Urgency EmergencyDocument5 pagesHypertensive Urgency Emergencydamondouglas100% (3)
- Master Drug ChartDocument22 pagesMaster Drug ChartMahadhir AkmalNo ratings yet
- CMSCN R IgevDocument2 pagesCMSCN R Igevdiana8827534No ratings yet
- Drugs Study Neh Jai2xDocument10 pagesDrugs Study Neh Jai2xjai2xNo ratings yet
- Icu Adult and PaedsDocument2 pagesIcu Adult and PaedsPrashin RocharamNo ratings yet
- Drugs requiring loading dosesDocument1 pageDrugs requiring loading dosesandirio7486No ratings yet
- Suspected COVID-19 Cases Management in Triage HospitalsDocument6 pagesSuspected COVID-19 Cases Management in Triage HospitalsMuhamed RamadanNo ratings yet
- WB Covid Protocol Book 25.09 .20 (1)Document49 pagesWB Covid Protocol Book 25.09 .20 (1)El MirageNo ratings yet
- Consortium ProtocolDocument16 pagesConsortium Protocolthe kingfishNo ratings yet
- Medad TeamDocument18 pagesMedad TeamAxmed MaxamedNo ratings yet
- Routine Anesthesia Set UpDocument4 pagesRoutine Anesthesia Set UpSteve Johnstone100% (2)
- EVMS Critical Care COVID-19 Protocol PDFDocument18 pagesEVMS Critical Care COVID-19 Protocol PDFGreyWolf1776No ratings yet
- Pediatric Dosage CalculationsDocument5 pagesPediatric Dosage CalculationsLovely Anjenell MacalingaNo ratings yet
- Finding A Good Essay QuestionDocument1 pageFinding A Good Essay QuestionelasticemperorNo ratings yet
- Live Within Your Window of ToleranceDocument19 pagesLive Within Your Window of Toleranceelasticemperor0% (1)
- Call For Papers 2019-2020 PDFDocument5 pagesCall For Papers 2019-2020 PDFelasticemperorNo ratings yet
- Planning Toolkit for Gendered Violence PreventionDocument14 pagesPlanning Toolkit for Gendered Violence PreventionelasticemperorNo ratings yet
- The 22 Convention Make Women Great Again™ PDFDocument1 pageThe 22 Convention Make Women Great Again™ PDFelasticemperorNo ratings yet
- FREEZEABLE MEALS UNDER 40 CHARACTERSDocument20 pagesFREEZEABLE MEALS UNDER 40 CHARACTERSelasticemperorNo ratings yet
- Exeter Learning Environment: Getting Started WithDocument32 pagesExeter Learning Environment: Getting Started WithelasticemperorNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus - Fight for Socialist Alternative and Workers' RightsDocument2 pagesCoronavirus - Fight for Socialist Alternative and Workers' RightselasticemperorNo ratings yet
- small axe journal explores caribbean thoughtDocument16 pagessmall axe journal explores caribbean thoughtelasticemperorNo ratings yet
- Pay As Little As: Savings ProgramDocument1 pagePay As Little As: Savings ProgramelasticemperorNo ratings yet
- 2020 Strike Handbook For UCU ActivistsDocument32 pages2020 Strike Handbook For UCU ActivistselasticemperorNo ratings yet
- FREEZEABLE MEALS UNDER 40 CHARACTERSDocument20 pagesFREEZEABLE MEALS UNDER 40 CHARACTERSelasticemperorNo ratings yet
- Mari Fitness Home Guide PDFDocument30 pagesMari Fitness Home Guide PDFviva100% (1)
- Live Within Your Window of ToleranceDocument19 pagesLive Within Your Window of Toleranceelasticemperor0% (1)
- Yoga London Pose NotesDocument19 pagesYoga London Pose NoteselasticemperorNo ratings yet
- Planning Toolkit for Gendered Violence PreventionDocument14 pagesPlanning Toolkit for Gendered Violence PreventionelasticemperorNo ratings yet
- Coding deCoding class insightsDocument18 pagesCoding deCoding class insightsShalabh Vikram SahuNo ratings yet
- Customer Status Update Report 27th January 2015 ColourDocument20 pagesCustomer Status Update Report 27th January 2015 ColourmaryNo ratings yet
- Sap GlossaryDocument324 pagesSap GlossaryNikos TataliasNo ratings yet
- 04powertrain 1010Document8 pages04powertrain 1010francis_15inNo ratings yet
- The DriversDocument277 pagesThe DriversADENIKE JOHNSONNo ratings yet
- CIE Master 2022 (New Master Programme) ENDocument171 pagesCIE Master 2022 (New Master Programme) ENZar MaghustNo ratings yet
- Loveology: God. Love. Marriage. Sex. and The Never-Ending Story of Male and Female. by John Mark Comer, SamplerDocument32 pagesLoveology: God. Love. Marriage. Sex. and The Never-Ending Story of Male and Female. by John Mark Comer, SamplerZondervan40% (5)
- Budha Dal Aarti Aarta FULLDocument1 pageBudha Dal Aarti Aarta FULLVishal Singh100% (1)
- Important Characteristics of an Ideal InductorDocument4 pagesImportant Characteristics of an Ideal Inductorsreekantha reddyNo ratings yet
- Colossians 1Document1 pageColossians 1aries john mendrezNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Awareness and PFA Training ReportDocument4 pagesMental Health Awareness and PFA Training ReportSHEILA MAE PERTIMOS100% (14)
- NES 362 Type and Production Testing of Mechanical Equipment Category 3Document36 pagesNES 362 Type and Production Testing of Mechanical Equipment Category 3JEORJENo ratings yet
- Early strength predicts long-term performance of asphalt cold mixesDocument7 pagesEarly strength predicts long-term performance of asphalt cold mixesMonu GhadwalNo ratings yet
- Palm Kernel Reinforced Composites for Brake Pad ApplicationsDocument18 pagesPalm Kernel Reinforced Composites for Brake Pad ApplicationsSachin SukumaranNo ratings yet
- Solar/Wind/Diesel Hybrid Energy System With Battery Storage For Rural ElectrificationDocument15 pagesSolar/Wind/Diesel Hybrid Energy System With Battery Storage For Rural ElectrificationWelde AynaleNo ratings yet
- Siemens: Building A Structure To Drive Performance and Responsibility - CaseDocument6 pagesSiemens: Building A Structure To Drive Performance and Responsibility - CaseBitopan SonowalNo ratings yet
- Logistic Growth Rate Functions Blumberg1968Document3 pagesLogistic Growth Rate Functions Blumberg1968Jonnathan RamirezNo ratings yet
- Galloway 1989 Genetic Stratigraphic Sequence Basin Analysis IDocument18 pagesGalloway 1989 Genetic Stratigraphic Sequence Basin Analysis IMitreNo ratings yet
- Energy Performance of Hot, DryDocument128 pagesEnergy Performance of Hot, DrySrinu ReddyNo ratings yet
- Macalloy Corporate Brochure September 2018 LR PDFDocument12 pagesMacalloy Corporate Brochure September 2018 LR PDFsampathkumarNo ratings yet
- PHL Ad 17 01 Operationalguidance 2017 Eng Ops Manual Adolescent Health Development ProgramDocument111 pagesPHL Ad 17 01 Operationalguidance 2017 Eng Ops Manual Adolescent Health Development ProgramJoanne G Haw GetidaNo ratings yet
- Mystic Mystique Face Reading-IIDocument10 pagesMystic Mystique Face Reading-IIVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Acc Gr11 May 2009 PaperDocument13 pagesAcc Gr11 May 2009 PaperSam ChristieNo ratings yet
- Akali NihangsDocument19 pagesAkali NihangsAngad YuvrajNo ratings yet
- 2Tafseer2019Sep4 17 24oc1 8 29nov5 262020jan7 21F11 18 25Document96 pages2Tafseer2019Sep4 17 24oc1 8 29nov5 262020jan7 21F11 18 25Aroob YaseenNo ratings yet
- JuliadatascienceDocument214 pagesJuliadatascienceFulvio JoséNo ratings yet
- Philippine School Action Plan for Scouting ProgramDocument1 pagePhilippine School Action Plan for Scouting ProgramLaira Joy Salvador - ViernesNo ratings yet
- Cbs BookDocument294 pagesCbs Bookadmiralninja100% (1)
- Mechanics of Solids by Sadhu Singhpdf Ebook and Ma PDFDocument1 pageMechanics of Solids by Sadhu Singhpdf Ebook and Ma PDFNeeraj Janghu0% (2)
- Physics Universe ModelsDocument14 pagesPhysics Universe ModelsTracy zorca50% (2)