Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Why Are Information Systems Vulnerable To Destruction, Error, and Abuse ?
Uploaded by
Urvashi Sharma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 views4 pagesDigital data and computer systems are vulnerable to destruction, errors, and abuse from both internal and external threats. Hackers can launch denial-of-service attacks or penetrate networks to disrupt systems, while computer viruses and worms can disable systems and websites. A lack of proper security and controls can compromise confidential information and legal compliance, potentially resulting in lost productivity, sales, and legal liability for organizations.
Original Description:
Original Title
answar_chaptir_7 (2).docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDigital data and computer systems are vulnerable to destruction, errors, and abuse from both internal and external threats. Hackers can launch denial-of-service attacks or penetrate networks to disrupt systems, while computer viruses and worms can disable systems and websites. A lack of proper security and controls can compromise confidential information and legal compliance, potentially resulting in lost productivity, sales, and legal liability for organizations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 views4 pagesWhy Are Information Systems Vulnerable To Destruction, Error, and Abuse ?
Uploaded by
Urvashi SharmaDigital data and computer systems are vulnerable to destruction, errors, and abuse from both internal and external threats. Hackers can launch denial-of-service attacks or penetrate networks to disrupt systems, while computer viruses and worms can disable systems and websites. A lack of proper security and controls can compromise confidential information and legal compliance, potentially resulting in lost productivity, sales, and legal liability for organizations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
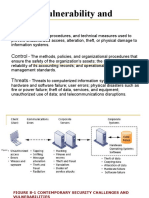
Why are information systems vulnerable
?to destruction, error, and abuse
Digital data are vulnerable to destruction, misuse, error, fraud,
and hardware or software failures. The Internet is designed to
be an open system and makes internal corporate systems more
vulnerable to actions from outsiders. Hackers can unleash
denial-of-service (DoS) attacks or penetrate corporate
networks, causing serious system disruptions. Wi-Fi networks
can easily be penetrated by intruders using sniffer programs to
obtain an address to access the resources of the network.
Computer viruses and worms can disable systems and Web
sites. The dispersed nature of cloud computing makes it
difficult to track unauthorized activity or to apply controls from
afar. Software presents problems because software bugs may
be impossible to eliminate and because software vulnerabilities
can be exploited by hackers and malicious software. End users
.often introduce errors
What is the business value of security and
?control
Lack of sound security and control can cause firms relying on
computer systems for their core business functions to lose sales
and productivity. Information assets, such as confidential
employee records, trade secrets, or business plans, lose much
of their value if they are revealed to outsiders or if they expose
the firm to legal liability. New laws, such as HIPAA, the
Sarbanes-Oxley Act, and the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, require
companies to practice stringent electronic records
management and adhere to strict standards for security,
privacy, and control. Legal actions requiring electronic evidence
and computer forensics also require firms to pay more
.attention to security and electronic records management
What are the components of an
organizational framework for security and
?control
Firms need to establish a good set of both general and
application controls for their information systems. A risk
assessment evaluates information assets, identifies control
points and control weaknesses, and determines the most cost-
effective set of controls. Firms must also develop a coherent
corporate security policy and plans for continuing business
operations in the event of disaster or disruption. The security
policy includes policies for acceptable use and authorization.
Comprehensive and systematic MIS auditing helps
organizations determine the effectiveness of security and
.controls for their information systems
What are the most important tools and
technologies for safeguarding information
?resources
Firewalls prevent unauthorized users from accessing a private
network when it is linked to the Internet. Intrusion detection
systems monitor private networks from suspicious network
traffic and attempts to access corporate systems. Passwords,
tokens, smart cards, and biometric authentication are used to
authenticate system users. Antivirus software checks computer
systems for infections by viruses and worms and often
eliminates the malicious software, while antispyware software
combats intrusive and harmful spyware programs. Encryption,
the coding and scrambling of messages, is a widely used
technology for securing electronic transmissions over
unprotected networks. Digital certificates combined with public
key encryption provide further protection of electronic
transactions by authenticating a user’s identity. Companies can
use fault-tolerant computer systems or create high-availability
computing environments to make sure that their information
systems are always available. Use of software metrics and
rigorous software testing help improve software quality and
.reliability
You might also like
- 0 - Security and Control in Information System 12-13Document26 pages0 - Security and Control in Information System 12-13Amneet KaurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SummaryDocument2 pagesChapter 8 SummaryGraciella AudreyNo ratings yet
- SIM Summary CH8 - 14 Edition SIM Summary CH8 - 14 EditionDocument9 pagesSIM Summary CH8 - 14 Edition SIM Summary CH8 - 14 EditionRidhi BNo ratings yet
- Summary Chapter 8 Securing Informatin SystemDocument6 pagesSummary Chapter 8 Securing Informatin SystemTasha NurafifahNo ratings yet
- Your System's Sweetspots: CEO's Advice on Basic Cyber Security: CEO's Advice on Computer ScienceFrom EverandYour System's Sweetspots: CEO's Advice on Basic Cyber Security: CEO's Advice on Computer ScienceNo ratings yet
- System Vulnerability and Abuse: SecurityDocument23 pagesSystem Vulnerability and Abuse: Securityv2winsNo ratings yet
- CYBER SECURITY HANDBOOK Part-1: Hacking the Hackers: Unraveling the World of CybersecurityFrom EverandCYBER SECURITY HANDBOOK Part-1: Hacking the Hackers: Unraveling the World of CybersecurityNo ratings yet
- CYBER SECURITY HANDBOOK Part-2: Lock, Stock, and Cyber: A Comprehensive Security HandbookFrom EverandCYBER SECURITY HANDBOOK Part-2: Lock, Stock, and Cyber: A Comprehensive Security HandbookNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Network SecurityDocument45 pagesLecture 5 Network SecurityWilfried MonkamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Cybersecurity and Risk Management TechnologyDocument30 pagesChapter 5. Cybersecurity and Risk Management Technologyarmando.lykajovel.dllNo ratings yet
- Monitoring and Surveillance Agents: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandMonitoring and Surveillance Agents: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- CYBERDocument13 pagesCYBERHassan SesayNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document26 pagesUnit 4Parth SuruNo ratings yet
- CH-5 IotDocument22 pagesCH-5 IotpreetiNo ratings yet
- Security: Challenges/Threats To Is SecurityDocument16 pagesSecurity: Challenges/Threats To Is SecuritysarvemNo ratings yet
- System Information and Technology Weekly Assignment: Chapter 8 Summary Securing Information Systems (Aileen Irmina P. 19/440371/EK/22297)Document3 pagesSystem Information and Technology Weekly Assignment: Chapter 8 Summary Securing Information Systems (Aileen Irmina P. 19/440371/EK/22297)Aileen Irmina PutriNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 Presentation2 COMPUTER LITERACYDocument10 pagesWEEK 4 Presentation2 COMPUTER LITERACYjesseadic1953No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - 1 MIS - Ethical Issues and PrivacyDocument56 pagesChapter 3 - 1 MIS - Ethical Issues and PrivacyAKSHAY KumarNo ratings yet
- CEH: Certified Ethical Hacker v11 : Exam Cram Notes - First Edition - 2021From EverandCEH: Certified Ethical Hacker v11 : Exam Cram Notes - First Edition - 2021No ratings yet
- Cyber Security: PeopleDocument2 pagesCyber Security: PeopleKashif RehmanNo ratings yet
- NetworksecurityDocument3 pagesNetworksecurityRaymond RamirezNo ratings yet
- 7 Types of Information Security IncidentsDocument9 pages7 Types of Information Security IncidentsebrahimranamaNo ratings yet
- Need For E-Security: by Prof T.R. VaidyanathanDocument39 pagesNeed For E-Security: by Prof T.R. VaidyanathanPrabhat KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 MisDocument11 pagesUnit-5 MisDr. MURALI KRISHNA VELAVETINo ratings yet
- Incident Response Plan For Fictional Company - Delta Force Solutions IncDocument6 pagesIncident Response Plan For Fictional Company - Delta Force Solutions Incthazni kassimNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1MD.foysalNo ratings yet
- Why Is Computer Security Important?Document9 pagesWhy Is Computer Security Important?nuhamin desalegnNo ratings yet
- Unit FirstDocument17 pagesUnit FirstTamannaNo ratings yet
- Ecommerce: EsecurityDocument20 pagesEcommerce: EsecurityJoseph ContehNo ratings yet
- Ethical and Security IssuesDocument6 pagesEthical and Security IssuesPaulina BossNo ratings yet
- HW 8th CasesDocument14 pagesHW 8th CasesQumoriNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security: (Prof. Ashok K. Bhateja, IIT Delhi)Document10 pagesCyber Security: (Prof. Ashok K. Bhateja, IIT Delhi)Jatin GoyalNo ratings yet
- Securing Information Systems: COM 2KA3Document34 pagesSecuring Information Systems: COM 2KA3RyanNo ratings yet
- What Is Network SecurityDocument28 pagesWhat Is Network SecurityTamannaNo ratings yet
- Information Assurance and CybersecurityDocument18 pagesInformation Assurance and Cybersecurityzahra zahidNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Management Information SystemDocument17 pages2.2 Management Information Systemnatashashaikh93No ratings yet
- Group 6: CybersecurityDocument4 pagesGroup 6: CybersecurityCherlie Mae DumaluanNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 CyberSecurityDocument22 pagesUnit-1 CyberSecurityAditya PandeyNo ratings yet
- Reflection Chap 07Document3 pagesReflection Chap 07Fizza JunaidNo ratings yet
- Internet Security Journal - Internet Security Principles by Obedience Munashe KuguyoDocument9 pagesInternet Security Journal - Internet Security Principles by Obedience Munashe KuguyoObedience Munashe Kuguyo100% (15)
- Tugas 8 - Defananda Arya Fadaldala - 2006576552Document10 pagesTugas 8 - Defananda Arya Fadaldala - 2006576552Defan AryaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cyber SecurityDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Cyber SecurityKunal MhatreNo ratings yet
- Network Security PolicyDocument3 pagesNetwork Security PolicyHaniNo ratings yet
- Information Security: BY: Dr. Shailja TripathiDocument55 pagesInformation Security: BY: Dr. Shailja Tripathisaket kumarNo ratings yet
- MIS-Unit 5Document48 pagesMIS-Unit 5ghimirebob1998No ratings yet
- It ReportDocument20 pagesIt Reportcristine rose celestialNo ratings yet
- ورقه عمل عن الامن الاسيبرانيDocument14 pagesورقه عمل عن الامن الاسيبرانيMohammed NassfNo ratings yet
- Basic of CyberSecurityDocument4 pagesBasic of CyberSecurityshuvo43432No ratings yet
- Big Data Visualization PowerPoint Templates (Autosaved)Document80 pagesBig Data Visualization PowerPoint Templates (Autosaved)Malek SbNo ratings yet
- Big Data Visualization PowerPoint TemplatesDocument94 pagesBig Data Visualization PowerPoint TemplatesMalek SbNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument14 pagesDocumentMlondi DlaminiNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Interview Questions For Freshers: 1. What Is The Main Objective of Cyber Security?Document24 pagesCyber Security Interview Questions For Freshers: 1. What Is The Main Objective of Cyber Security?Gilgamesh berserkerNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity Fundamentals - Module 10Document5 pagesCybersecurity Fundamentals - Module 10joelyrics9No ratings yet
- Informations Management Unit 4Document10 pagesInformations Management Unit 4MukulNo ratings yet
- Lesson-2 1Document12 pagesLesson-2 1Bagongon, Jacob Yrrje C.No ratings yet
- Lecture CH 2 Sec 110Document46 pagesLecture CH 2 Sec 110Gary BaxleyNo ratings yet
- Full Malware Scan & Removal Guide To Clean Heavy Infected Computers - Wintips - Org - Windows Tips & How-TosDocument22 pagesFull Malware Scan & Removal Guide To Clean Heavy Infected Computers - Wintips - Org - Windows Tips & How-Toskomang arimbawaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 07Document11 pagesQuiz 07sullivan583No ratings yet
- Black BookDocument17 pagesBlack BookAastha AlshettyeNo ratings yet
- Revised UNIT 4 Records and Information ManagementDocument38 pagesRevised UNIT 4 Records and Information ManagementMelissia EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Living in The IT ERA PrelimsDocument4 pagesLiving in The IT ERA PrelimsMiks Solon43% (7)
- Lesson 1: Introduction To Ict: ICT - Information and CommunicationDocument60 pagesLesson 1: Introduction To Ict: ICT - Information and CommunicationLouis Gerard PadayaoNo ratings yet
- COM PROG - JAVA NC III Module 6 GRADE10 4Document32 pagesCOM PROG - JAVA NC III Module 6 GRADE10 4Ronnel Singson100% (1)
- Unit 11 Computer Networks Assignment 2 2Document28 pagesUnit 11 Computer Networks Assignment 2 2api-591240453No ratings yet
- McAfee Training EPo Training-Session 2Document23 pagesMcAfee Training EPo Training-Session 2SDeepan100% (1)
- Bab 4 Programs and Apps Productivity, Graphics, Security and Other ToolsDocument42 pagesBab 4 Programs and Apps Productivity, Graphics, Security and Other ToolsLaras Indah MaulidiiaNo ratings yet
- W To Remove Palevo From Your ComputerDocument11 pagesW To Remove Palevo From Your ComputerMartaSekulicNo ratings yet
- Agri 3 TPDocument46 pagesAgri 3 TPAICCAT INCNo ratings yet
- Itt320 Project ProposalDocument25 pagesItt320 Project ProposalNurul Farah Syuhada Binti ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Pixeles Bca & Mca (Ignou) : ClassesDocument15 pagesPixeles Bca & Mca (Ignou) : ClassesslayrNo ratings yet
- P1 Nursing InfoDocument18 pagesP1 Nursing InfoMargarita Limon Balunes100% (1)
- Device Protection With Microsoft Endpoint Manager and Microsoft Defender For Endpoint - Module 06 - Endpoint Protection Alerts and ReportingDocument22 pagesDevice Protection With Microsoft Endpoint Manager and Microsoft Defender For Endpoint - Module 06 - Endpoint Protection Alerts and ReportingLuke WhitemanNo ratings yet
- f1603667736 Home Networking Do-It-Yourself For DummiesDocument443 pagesf1603667736 Home Networking Do-It-Yourself For DummiesOoi Ah Guan89% (9)
- Networking, Cloud Computing, Protocol, Risk and ControlsDocument32 pagesNetworking, Cloud Computing, Protocol, Risk and ControlsNaija DefenceNo ratings yet
- Forticlient Admin 505Document129 pagesForticlient Admin 505bizmarkyNo ratings yet
- CCPS Module - 1Document77 pagesCCPS Module - 1sofia janitNo ratings yet
- Afp Ccustoms and TraditionsDocument20 pagesAfp Ccustoms and TraditionsIan Barcena IINo ratings yet
- ZEN 2012 SP2 - Installation GuideDocument42 pagesZEN 2012 SP2 - Installation Guideandrew glidleNo ratings yet
- Kaspersky Internet Security: Application Version: 14.0Document85 pagesKaspersky Internet Security: Application Version: 14.0Mauricio UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Iso-Iec 13335-1 Concepts and Models For IT SecurityDocument28 pagesIso-Iec 13335-1 Concepts and Models For IT SecurityTechaphon NitiNo ratings yet
- Cse Virus and Anti Viruses Report SeminarDocument32 pagesCse Virus and Anti Viruses Report SeminarKapilesh JalkoteNo ratings yet
- Principia ManualDocument13 pagesPrincipia ManualaabsmotosNo ratings yet
- Q&a - DFT20083 Sbitp Revision (T1-4)Document12 pagesQ&a - DFT20083 Sbitp Revision (T1-4)vijayavjvictoriaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document10 pagesAssignment 5api-694098467No ratings yet
- Class 10 Computer NotesDocument38 pagesClass 10 Computer NotesShreya KatwalNo ratings yet