Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table 1 Calculated Bolt Sizes: 2.4.8 Recommendations For Anchor Bolt and Foundation Design
Uploaded by
anwarali1975Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Table 1 Calculated Bolt Sizes: 2.4.8 Recommendations For Anchor Bolt and Foundation Design
Uploaded by
anwarali1975Copyright:
Available Formats
14
TABLE 1 Calculated bolt sizes
Tension Fy Fut 2001 Spec. Proposed Method
in Bolt (ksi) (ksi) Min. Bolt Min. Bolt Min. Bolt Min. Bolt Dia. Min. Bolt
(kips) Dia. Based Dia. Dia. Based Based on Bearing Dia. Based
on Steel Based on on Bearing of Hex Head or Nut on Bearing
Strength Steel Area with (in) of Hooked
(in) Strength Hardened Bolt (in)
(in) Washer (in)
3 36 58 1/2” 1/2” 1/2” 1/2” 5/8”
10 36 58 7/8” 3/4” 3/4” 3/4” 1-1/8”
20 36 58 1-1/4” 1” 1” 1-1/8” 1-5/8”
30 36 58 1-1/2” 1-1/4” 1-1/4” 1-3/8” 2”
40 36 58 1-3/4” 1-3/8” 1-3/8” 1-1/2” -
50 36 58 2” 1-1/2” 1-1/2” 1-3/4” Heavy Hex -
60 36 58 2” 1-3/4” 1-3/4” 1-3/4” Heavy Hex -
5 55 75 1/2” 3/8” 3/8” 1/2” 7/8”
10 55 75 3/4” 5/8” 5/8” 3/4” 1-1/8”
20 55 75 1” 7/8” 7/8” 1-1/8” 1-5/8”
30 55 75 1-1/4” 1-1/8” 1-1/8” 1-3/8” 2”
40 55 75 1-3/8” 1-1/4” 1-1/4” 1-1/2” -
50 55 75 1-1/2” 1-3/8” 1-3/8” 1-3/4” Heavy Hex -
60 55 75 1-3/4” 1-1/2” 1-1/2” 1-3/4” Heavy Hex -
70 55 75 1-3/4” 1-3/4” 1-3/4” 2” Heavy Hex -
80 55 75 2” 1-3/4” 1-3/4” - -
90 55 75 2” 2” 2” - -
10 105 125 1/2” 1/2” 1/2” 3/4” 1-1/8”
20 105 125 3/4” 3/4” 3/4” 1-1/8” 1-5/8”
30 105 125 7/8” 7/8” 1” 1-3/8” 2”
40 105 125 1” 1” 1-1/8” 1-1/2” -
50 105 125 1-1/8” 1-1/8” 1-1/4” 1-3/4” Heavy Hex -
60 105 125 1-1/4” 1-1/4” 1-3/8” 1-3/4” Heavy Hex -
70 105 125 1-3/8” 1-1/4” 1-3/8” 2” Heavy Hex -
80 105 125 1-3/8” 1-3/8” 1-1/2” - -
90 105 125 1-1/2” 1-1/2” 1-3/4” - -
100 105 125 1-3/4” 1-1/2” 1-3/4” - -
110 105 125 1-3/4” 1-3/4” 2” - -
120 105 125 1-3/4” 1-3/4” 2” - -
130 105 125 1-3/4” 1-3/4” - - -
140 105 125 2” 1-3/4” - - -
150 105 125 2” 2” - - -
160 105 125 2” 2” - - -
170 105 125 2” 2” - - -
prevent failure and that the hook or head area is large enough anchor bolts 66 inches long should be used. This is somewhat
to prevent concrete crushing. Therefore, it is assumed that, as longer than the average value for anchor bolts reported by state
a worst case, a crack develops just below the head or hook of transportation agencies, but much less than the maximum
the bolt and propagates through the foundation at a 35-degree value. The development length was calculated using conserv-
angle, which is consistent with the assumed ACI failure cone. ative, default values for all parameters. A more rigorous cal-
This failure plane intersects the foundation-reinforcing steel, culation using the new provisions of ACI 318 Code (14, 16)
which provides the rest of the anchorage load path. would probably result in a shorter required bolt length.
In order to develop this mechanism, the required anchor
bolt length is equal to the development length of the rein-
forcing bar, plus the clearance to the top of the foundation 2.4.8 Recommendations for Anchor Bolt and
(ctop), plus the spacing between the bar and the anchor (sanchor). Foundation Design
This last requirement conservatively assumes a 45-degree
failure plane. For headed anchor bolts, the benefit of using higher-
For example, assume a foundation is reinforced with Num- strength steels is limited. Required bolt diameter is reduced,
ber 8 reinforcing bars, and 3,000-psi concrete is used. The but the head diameter cannot be reduced because it is gov-
required development length for these reinforcing bars is 55 erned by concrete bearing stress. Furthermore, lower-yield
inches. If the top clearance is 2 inches and the spacing between steels are more ductile. Because of the upper limit of 125,000
the anchors and longitudinal reinforcement is 9 inches, then psi on Fut in Equation 1, using steel with yield strength
You might also like
- Bird Tracks & Sign: A Guide to North American SpeciesFrom EverandBird Tracks & Sign: A Guide to North American SpeciesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CU AL Ampacity Chart FinalDocument1 pageCU AL Ampacity Chart FinalRobertoHerediaJacoboNo ratings yet
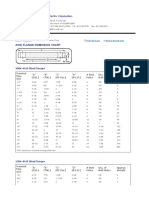
- TexasFlange - Bolt and Stud Dimensions ASME B16.5Document2 pagesTexasFlange - Bolt and Stud Dimensions ASME B16.5cristinelbNo ratings yet
- ASME Flange Bolting Take OffDocument3 pagesASME Flange Bolting Take Offshankar sharmaNo ratings yet
- Bolts DimensionsDocument59 pagesBolts Dimensionsaravind100% (1)
- Minerae00024 53Document1 pageMinerae00024 53soayNo ratings yet
- Bolt Torquing Value (FT-LBS) For Spiral Wound Gasket Bolt Torquing Value (FT-LBS) For Spiral Wound GasketDocument2 pagesBolt Torquing Value (FT-LBS) For Spiral Wound Gasket Bolt Torquing Value (FT-LBS) For Spiral Wound GasketDhameemAnsariNo ratings yet
- Preinstallation VerificationDocument5 pagesPreinstallation VerificationbalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Fishing Tools For 8 and Half HoleDocument1 pageFishing Tools For 8 and Half HolehamidNo ratings yet
- Bolt & Gasket Sets - Spec Sheet: Non-Asbestos Red RubberDocument3 pagesBolt & Gasket Sets - Spec Sheet: Non-Asbestos Red RubberPatel MehulNo ratings yet
- Wolouf CatalogueDocument3 pagesWolouf CatalogueJawad AbusamhaNo ratings yet
- 002 Steel StructuralDocument16 pages002 Steel Structuraljalv.mendoza25No ratings yet
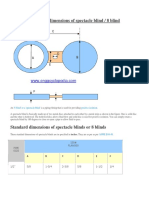
- Standard dimensions of spectacle blinds under 40 charsDocument10 pagesStandard dimensions of spectacle blinds under 40 charsSubrata MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Flange bolt size and spanner size chartDocument6 pagesFlange bolt size and spanner size chartŠhiññ ŠóhäïNo ratings yet
- Drillstar Roller ReamerDocument2 pagesDrillstar Roller ReamerLOURIDOMICHELLENo ratings yet
- Astm A325 & A490 Bolts & NutsDocument6 pagesAstm A325 & A490 Bolts & NutsagusfitriyadiNo ratings yet
- Flange APIDocument29 pagesFlange APIputujuliandikaNo ratings yet
- DIN 3015 Clamp Guide for Pipes & HosesDocument32 pagesDIN 3015 Clamp Guide for Pipes & Hosesxuanphuong2710No ratings yet
- Measurements/ Specifications: Torque Wrench Selection GuideDocument5 pagesMeasurements/ Specifications: Torque Wrench Selection GuideSylvester RakgateNo ratings yet
- Bolt Stud Dimensions For FlangesDocument1 pageBolt Stud Dimensions For FlangesMULAYAM SINGH YADAVNo ratings yet
- L Series BrochureWebDocument16 pagesL Series BrochureWebmadhavikNo ratings yet
- Wire Rope CapacitiesDocument1 pageWire Rope CapacitiesJose DiazNo ratings yet
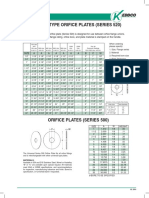
- Reference For Orifice SelectionDocument1 pageReference For Orifice Selectiondeepak_313No ratings yet
- Equipment Catelogue2Document21 pagesEquipment Catelogue2Mateo AlvaNo ratings yet
- ASME - ANSI B16.5 - Flanges and Bolt Dimensions Class 150 To 2500Document7 pagesASME - ANSI B16.5 - Flanges and Bolt Dimensions Class 150 To 2500Amer FiqriNo ratings yet
- Hand Shut-Off Valve GuideDocument16 pagesHand Shut-Off Valve Guidequoc sach NguyenNo ratings yet
- Kant-Twist Clamps: Specifications SheetDocument3 pagesKant-Twist Clamps: Specifications SheetOmegacoolNo ratings yet
- Washers - Standard Flat WasherDocument1 pageWashers - Standard Flat WasherMohammed KhalidNo ratings yet
- Broch ArmacellProductSelector - en.US.2023 9Document1 pageBroch ArmacellProductSelector - en.US.2023 9Nadeer Mon PNo ratings yet
- Wireline Operations - Slickline ToolsDocument2 pagesWireline Operations - Slickline ToolsMohsin PvNo ratings yet
- Mss SP 97 DimensionsDocument9 pagesMss SP 97 DimensionsMichał KlebanNo ratings yet
- Steel Hex Nuts SAE Grade 2: Finished FullDocument1 pageSteel Hex Nuts SAE Grade 2: Finished FullWahyu Candra WardanaNo ratings yet
- Formulas, Facts and Figures PDFDocument13 pagesFormulas, Facts and Figures PDFश्रीराज् कथलियिल्No ratings yet
- Set Screw Couplings: SteelDocument1 pageSet Screw Couplings: SteelsoayNo ratings yet
- Jig and Screw Selection Chart for Mating Workpieces 1/2" to 1-1/2Document1 pageJig and Screw Selection Chart for Mating Workpieces 1/2" to 1-1/2Nakkhirin NakkhongkhamNo ratings yet
- PCE WL Releasable OvershotDocument2 pagesPCE WL Releasable OvershotFabio ParceroNo ratings yet
- RD RecommendedhangerspacingglasspipedataDocument1 pageRD RecommendedhangerspacingglasspipedatakyongngNo ratings yet
- Current Api Thread Standards: Size IN MM O.D. Pipe Tubing & CasingDocument5 pagesCurrent Api Thread Standards: Size IN MM O.D. Pipe Tubing & CasingJohan LinggaNo ratings yet
- BOLTS-FASTENERDocument20 pagesBOLTS-FASTENERUpadrasta HarishNo ratings yet
- List Bolt, Gasket, Valve Size U-337Document70 pagesList Bolt, Gasket, Valve Size U-337daniNo ratings yet
- Stud & Bolt Dimensions ANSI 150 FlangesDocument1 pageStud & Bolt Dimensions ANSI 150 FlangesFachrul HidayatNo ratings yet
- Test Plug BrochureDocument4 pagesTest Plug BrochuresitaNo ratings yet
- Stem Bar PDFDocument2 pagesStem Bar PDFJose ZarateNo ratings yet
- Victor Tip Charts: Acetylene Cutting Tip ChartDocument3 pagesVictor Tip Charts: Acetylene Cutting Tip ChartahmedNo ratings yet
- Hand Expansion Valves GuideDocument12 pagesHand Expansion Valves GuideАлександр ЩербаковNo ratings yet
- (Inches) (Inches) (Inches) (Inches) (Inches) : Nominal Pipe Size NPS Class 150Document10 pages(Inches) (Inches) (Inches) (Inches) (Inches) : Nominal Pipe Size NPS Class 150Brilliant Adi SjahranieNo ratings yet
- ANSI B16 Flange Dimensions GuideDocument17 pagesANSI B16 Flange Dimensions GuideDjoko Dwi IrwantoNo ratings yet
- WSTyler Digital IWW Handbook V34-1Document46 pagesWSTyler Digital IWW Handbook V34-1MNo ratings yet
- Department of Transportation Federal Aviation AdministrationDocument6 pagesDepartment of Transportation Federal Aviation Administrationjacques SUIRENo ratings yet
- Bolts InformationDocument12 pagesBolts InformationsathyakumaryjNo ratings yet
- ANSI Flange DimensionDocument8 pagesANSI Flange DimensionGalaco EngineeringNo ratings yet
- 1221 Standard Pipe NipplesDocument1 page1221 Standard Pipe NipplesmvinuNo ratings yet
- Dimension Flange AsmeDocument10 pagesDimension Flange AsmeHanif SaidonNo ratings yet
- Model 58-93R Tubing Power Tong ManualDocument44 pagesModel 58-93R Tubing Power Tong ManualFrank MoralesNo ratings yet
- ASME Bronze Flange Sizes and Specs for 150 and 300 lb ClassesDocument6 pagesASME Bronze Flange Sizes and Specs for 150 and 300 lb ClassesKarim ShamsNo ratings yet
- ASME and ANSI B16.5 Flanges and Bolt Dimensions Class 150 To 2500Document8 pagesASME and ANSI B16.5 Flanges and Bolt Dimensions Class 150 To 2500Swaminathan ThayumanavanNo ratings yet
- ASME and ANSI B16.5 Flanges and Bolt Dimensions Class 150 To 2500Document8 pagesASME and ANSI B16.5 Flanges and Bolt Dimensions Class 150 To 2500elias2505No ratings yet
- Drag Coefficient Table for Bend Radius MethodsDocument1 pageDrag Coefficient Table for Bend Radius Methodsanwarali1975No ratings yet
- NCRP - Sign 31Document1 pageNCRP - Sign 31anwarali1975No ratings yet
- NCRP - Sign 28Document1 pageNCRP - Sign 28anwarali1975No ratings yet
- NCRP - Sign 33Document1 pageNCRP - Sign 33anwarali1975No ratings yet
- NCRP - Sign 32Document1 pageNCRP - Sign 32anwarali1975No ratings yet
- NCRP - Sign 30Document1 pageNCRP - Sign 30anwarali1975No ratings yet
- Drag Coefficient Transition Equations for Multisided Pole SectionsDocument1 pageDrag Coefficient Transition Equations for Multisided Pole Sectionsanwarali1975No ratings yet
- NCRP - Sign 25Document1 pageNCRP - Sign 25anwarali1975No ratings yet
- Development Length of Anchor Bolt in A Drilled ShaftDocument1 pageDevelopment Length of Anchor Bolt in A Drilled Shaftanwarali1975No ratings yet
- Specifications Allows Waiving of Subsurface Exploration If: 2.5.2 Drilled Shaft FoundationDocument1 pageSpecifications Allows Waiving of Subsurface Exploration If: 2.5.2 Drilled Shaft Foundationanwarali1975No ratings yet
- NCRP - Sign 19Document1 pageNCRP - Sign 19anwarali1975No ratings yet
- 2.5 Foundations: Bridge Design Specifications (7) and A Number of Other PubliDocument1 page2.5 Foundations: Bridge Design Specifications (7) and A Number of Other Publianwarali1975No ratings yet
- NCRP - Sign 27Document1 pageNCRP - Sign 27anwarali1975No ratings yet
- Foundation selection criteria for transportation structuresDocument1 pageFoundation selection criteria for transportation structuresanwarali1975No ratings yet
- NCRP - Sign 16Document1 pageNCRP - Sign 16anwarali1975No ratings yet
- Table 3 Foundation Dimension For Washington DOT (33) : Typical Lead Section of Steel Screw-In FoundationDocument1 pageTable 3 Foundation Dimension For Washington DOT (33) : Typical Lead Section of Steel Screw-In Foundationanwarali1975No ratings yet
- Allow hooked anchor bolts due to cheaper costDocument1 pageAllow hooked anchor bolts due to cheaper costanwarali1975No ratings yet
- NCRP - Sign 15Document1 pageNCRP - Sign 15anwarali1975No ratings yet
- NCRP - Sign 12Document1 pageNCRP - Sign 12anwarali1975No ratings yet
- NCRP - Sign 18Document1 pageNCRP - Sign 18anwarali1975No ratings yet
- 9) - An Example That Demonstrates The Effect of Gusset PlatesDocument1 page9) - An Example That Demonstrates The Effect of Gusset Platesanwarali1975No ratings yet
- Research Findings: 2.1.1 State DOT Survey and ResultsDocument1 pageResearch Findings: 2.1.1 State DOT Survey and Resultsanwarali1975No ratings yet
- Recommendations for improving support structure specificationsDocument1 pageRecommendations for improving support structure specificationsanwarali1975No ratings yet
- NCRP - Sign 7Document1 pageNCRP - Sign 7anwarali1975No ratings yet
- Introduction and Research Approach: 1.1 BackgroundDocument1 pageIntroduction and Research Approach: 1.1 Backgroundanwarali1975No ratings yet
- NCRP - Sign 6Document1 pageNCRP - Sign 6anwarali1975No ratings yet
- Research Findings: 2.1.1 State DOT Survey and ResultsDocument1 pageResearch Findings: 2.1.1 State DOT Survey and Resultsanwarali1975No ratings yet
- NCRP - Sign 5Document1 pageNCRP - Sign 5anwarali1975No ratings yet
- NCRP - Sign 4Document2 pagesNCRP - Sign 4anwarali1975No ratings yet
- Analysis and Simulation of Mini Pyrolysis Reactor For Conversion ofDocument5 pagesAnalysis and Simulation of Mini Pyrolysis Reactor For Conversion ofDidit Setyo PamujiNo ratings yet
- Plastiment P 121 R Pds enDocument2 pagesPlastiment P 121 R Pds enArdy YulisetiantoNo ratings yet
- Johnson Industrial Screens PDFDocument20 pagesJohnson Industrial Screens PDFjaime palenzuela rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Is 1367 13 1983Document7 pagesIs 1367 13 1983Dharmendra TomarNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Under Uniaxial LoadingDocument8 pagesMechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Under Uniaxial LoadingCristián JiménezNo ratings yet
- Pemex PoroFlexDocument34 pagesPemex PoroFlexvictorNo ratings yet
- Part 18 - Prestressed ConcreteDocument8 pagesPart 18 - Prestressed Concretetkram1981No ratings yet
- Lead Free Series 35 Quick-Connect Valves Specification SheetDocument4 pagesLead Free Series 35 Quick-Connect Valves Specification SheetWattsNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To ChemistryDocument10 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To ChemistryJhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- Antigen-Antibody Interactions: The Basis of Immune RecognitionDocument3 pagesAntigen-Antibody Interactions: The Basis of Immune RecognitionTinku MeherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9. Non-Ferrous Materials: Copper and Copper AlloysDocument4 pagesChapter 9. Non-Ferrous Materials: Copper and Copper AlloysOmkar EllendulaNo ratings yet
- ZP11 MCE3 AUS DTC排故手册 20180419 PDFDocument723 pagesZP11 MCE3 AUS DTC排故手册 20180419 PDFtallerr.360No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Drilling Fluids TechnologyDocument134 pagesFundamentals of Drilling Fluids TechnologySaleem Abubakar UsmanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer TextbookDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer Textbookapi-3800348100% (1)
- Seismic Rehabilitation of Damaged Reinforced Concrete Frames Using Combined Metallic Yielding Passive DevicesDocument16 pagesSeismic Rehabilitation of Damaged Reinforced Concrete Frames Using Combined Metallic Yielding Passive DevicesLuis Vilca AsenciosNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study of A Passive Thermal Management PDFDocument8 pagesExperimental Study of A Passive Thermal Management PDFHiba MhiriNo ratings yet
- Wedge Belts Veco 200 Dynam System: ST - API - ISO 4184 - DIN 7753 - BS 3790Document2 pagesWedge Belts Veco 200 Dynam System: ST - API - ISO 4184 - DIN 7753 - BS 3790Alexandre GelsiNo ratings yet
- CH 1 (Sample)Document3 pagesCH 1 (Sample)bkhidirNo ratings yet
- F 2111 - 01 - RjixmtetmdeDocument4 pagesF 2111 - 01 - Rjixmtetmdemohan chand mulpuriNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Chemical EquationsDocument18 pagesChemical Reactions and Chemical EquationsproodootNo ratings yet
- Astm D2257 PDFDocument5 pagesAstm D2257 PDF郭哲宏No ratings yet
- IS 14458 - 5 Cement Stone WallDocument9 pagesIS 14458 - 5 Cement Stone WallAnju Karki100% (2)
- DPT ProcedureDocument3 pagesDPT ProcedureAmit HasanNo ratings yet
- Chemical CharacterisationDocument66 pagesChemical Characterisationvenkatakrishna chalapaathiNo ratings yet
- Standards For Corrosion RatesDocument2 pagesStandards For Corrosion RatesHai LeNo ratings yet
- Celanese EVA Product BrochureDocument8 pagesCelanese EVA Product BrochureMayrarelCadpeNo ratings yet
- Lincoln ER 80SGDocument2 pagesLincoln ER 80SGabhishekme03No ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellen0% (1)
- Seminar On MramDocument28 pagesSeminar On MramShibojyoti BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- SCC StudyDocument201 pagesSCC StudyUmair Sarwar100% (1)